Unit 7
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Types of point defects
vacancies, interstitials, substitutional
Types of Line defects
dislocations
Types of area defects
interfaces (grain boundaries, phase boundaries, solid-liquid interfaces)
Vacancies
a type of point defect
vacant atomic sites in a structure
Self-interstitials
a type of point defect
“extra” host atoms position in interstitial positions between atoms
alloy
where impurity (solute) atoms are added to the host atoms to modify specific properties/characteristics of the materials

What type of impurity is this?
Substitutional solid solution
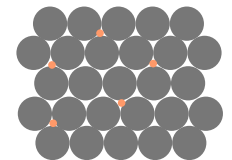
What type of impurity is this?
Interstitial solid solution
Solvent
host atom
Solute
impurity atom
Hume-Rothery Rules
Conditions for formation of substitutional solid solutions
1) difference in atomic radius < 15%
2) Proximity in periodic table (similar electronegativities)
3) Same crystal structure for pure metals
4) Valences: all else being equal, a metal will have a greater tendency to dissolve a metal of higher valence than one of lower valence
Estimate strength of a perfect material
Bonds typically break if stretched more than 10%. That is the stress is greater than E/10
Differences between ideal and actual strength for material types
metals: big difference
polymers: smallest difference
ceramics: biggest difference
Why are Polymers typically close to their ideal strength?
Polymer strands are almost perfect
Why are metals and ceramics typically not close to their ideal strength?
They are crystalline structures. Crystals are full of defects which decrease the strength of the material
Dislocations
caused by non-perfect alignment of crystallographic planes due to extra planes or shear planes
Edge dislocation
extra half plane
screw dislocation
if a region is slipped within a crystal
Moving dislocations
when a dislocation moves, only a line of bonds needs to be broken at one time. Significantly less force than breaking a whole plane of atoms
dislocations move when stresses are applied.
permanent (plastic) deformation results from dislocation motion
Slip planes
atoms like to slip along planes with the highest density of atoms (smallest jump to neighbor)
Where does slip occur?
on close packed planes in close packed directions
Glide or slip
dislocations move on the close packed plane in the close packed direction. Screw and edge dislocations move in different directions given the same applied force
Types of Interfaces in metallic systems
External (solid-vapor) surfaces, solid-liquid interface, phase boundaries, grain boundaries, twin boundaries
External (Solid-vapor) surfaces
interfaces where crystal structure ends. surface atom are not bonded to the maximum number of nearest neighbors. These atoms are at higher energy state than atoms at interior positions
Solid-liquid interfae
interfaces separating solid and liquid states of a material
plays key role during materials processing
Phase boundaries
an interface separating multiphase materials, in which a different phase exists on each side of the boundary
each of the constitute phases has its own distinctive physical and or chemical characteristics
Grain Boundaries
polycrystalline materials are composes of many crystals (called grains) that meet at internal interfaces, called grain boundaries
An interface that separate two grains (or crystals) of the same materials but having different orientations
Twin boundaries
a special type of grain boundary where there is a mirror lattice symmetry
atoms on one side of the boundary are located in mirror-image positions to those of the atoms on the other side
result from applies mechanicals stresses (mechanical twins) or during heating (annealing twins)
stacking faults
interfacial defect are found in FCC when there is interruption in the stacking sequence
In FCC the normal sequence is ABCABC becomes ABCABABC when there is a packing fault
Bulk defects
pores, cracks, and foreign inclusions
typically form during processing and fabrication