Lecture 2 - Roman Social History
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What are the basic periods of Roman history?
1. Archaic or 'regal' period (ca. 800 - ca. 509 BC) 2. Republican period (ca. 509 - 31 BC) 3. Imperial period or 'principate' (31 BC - AD 284) 4. Late antiquity or 'dominate' (AD 284 - ?)
What is the significance of Pliny the Younger's quote regarding equality in Roman society?
It emphasizes that despite the notion of equality, distinctions of rank (ordo) and status (dignitas) were crucial and must be preserved.
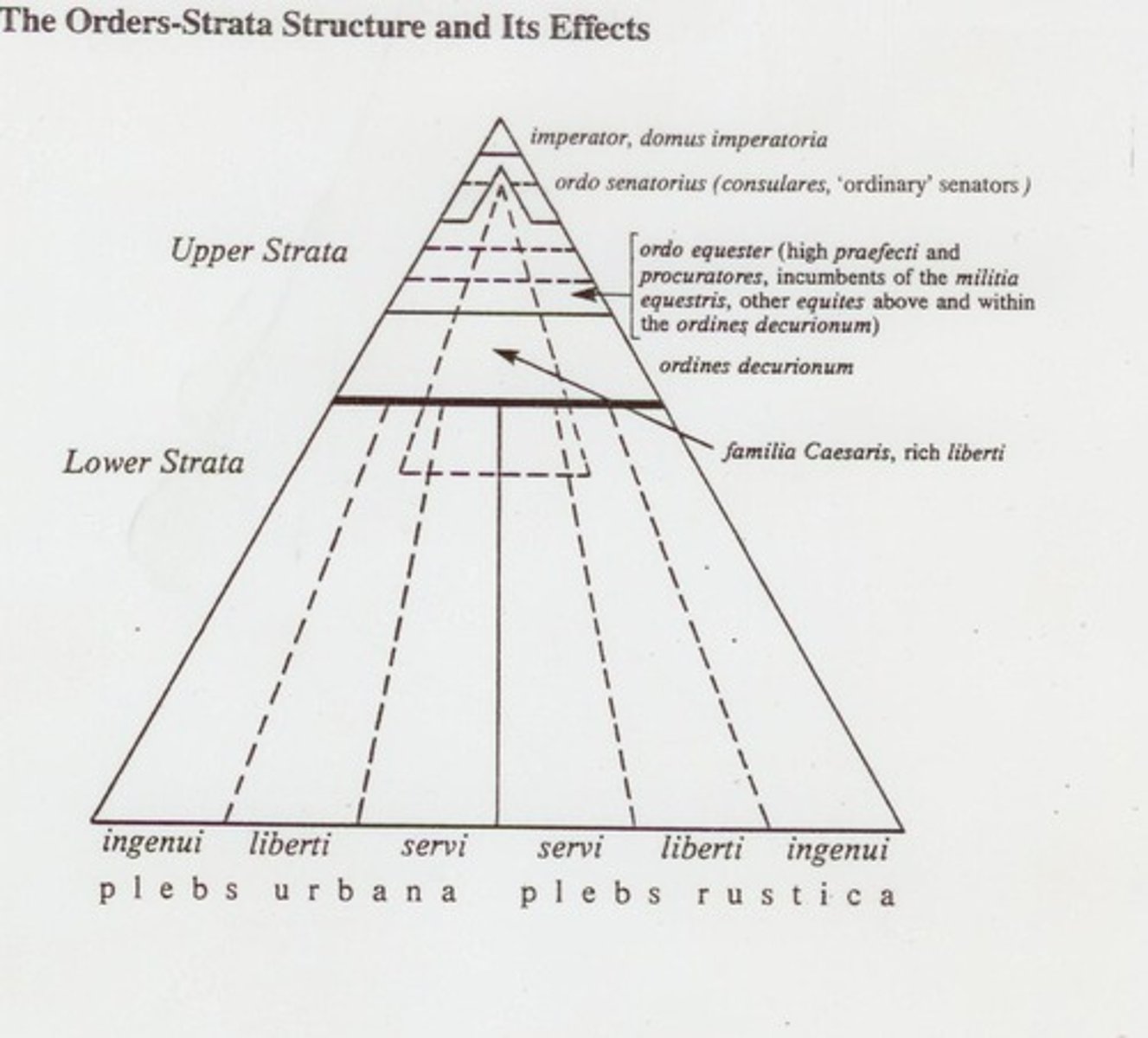
What are the primary divisions within Roman society?
1. Free & unfree 2. Citizen & non-citizen 3. Rich and Poor 4. Senator & non-senator (with gradations like eques, decurion, merchant, peasant) 5. Noble (honestiores) & ignoble (humiliores) 6. Patron and client 7. Friend and enemy 8. Soldier and civilian 9. Male and female.
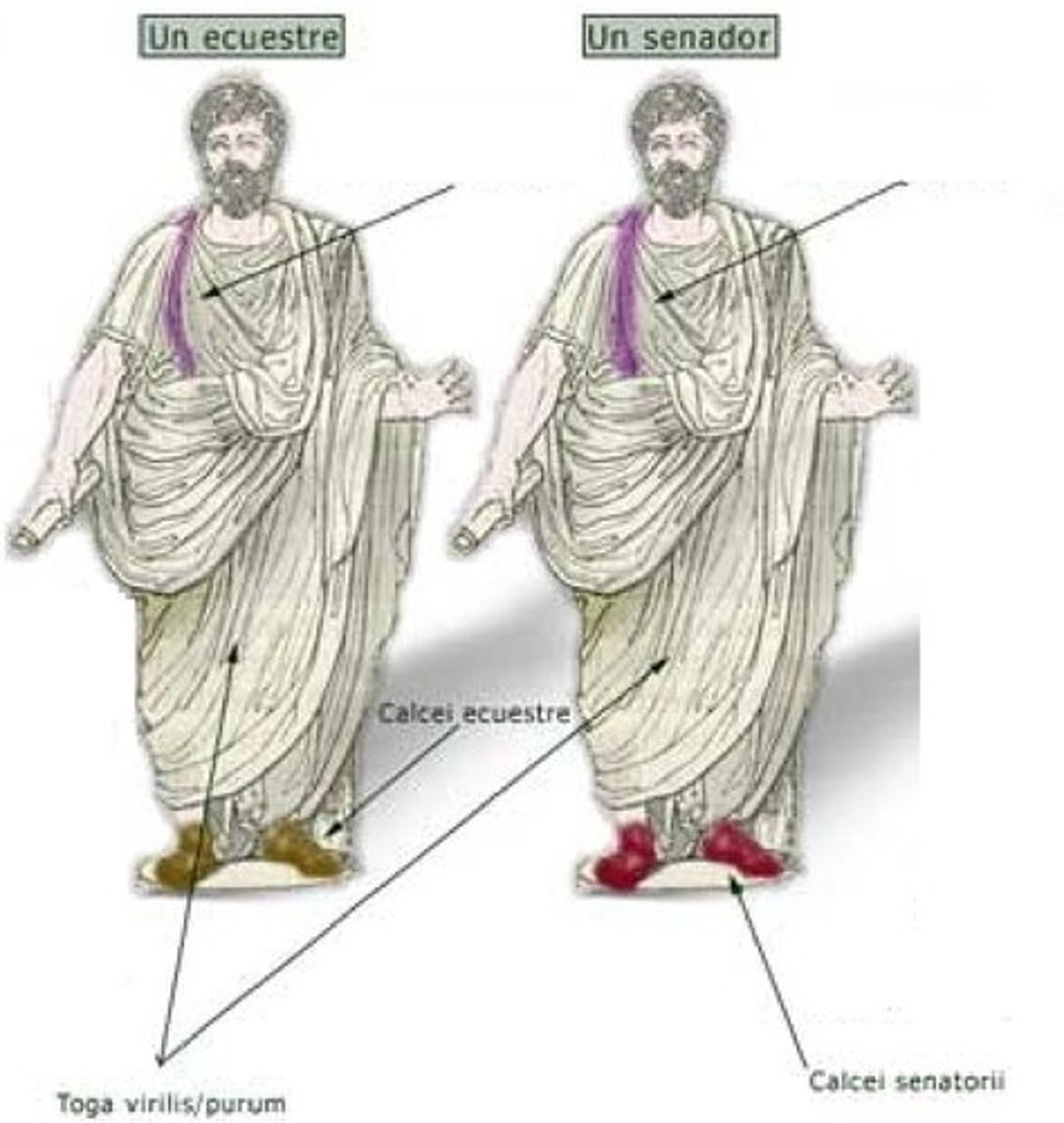
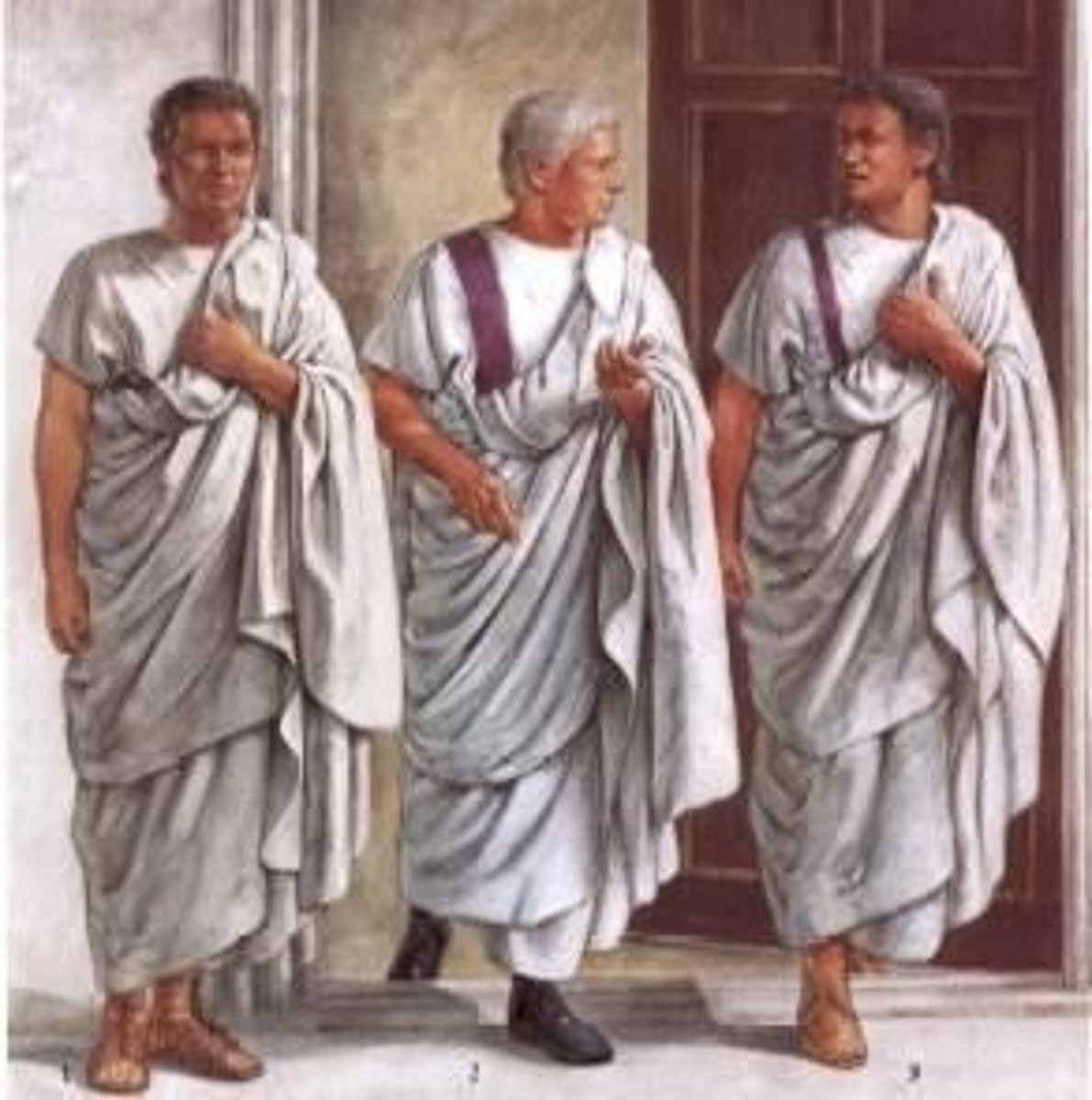
What is the term for the Roman social class of knights?
Equites (singular: eques) are the Roman social class of knights.
What does the term 'tria nomina' refer to in Roman citizenship?
Tria nomina refers to the three names a male Roman citizen typically had: praenomen, nomen, and cognomen.
Provide an example of the tria nomina for a Roman citizen.
Gaius Julius Caesar, Marcus Tullius Cicero, Publius Vergilius Maro.
How did adoption affect Roman names?
When adopted, a person would take their adoptive father's name, resulting in a new name that included the adoptive family name, e.g., Lucius Aemilius Paullus adopted by Publius Cornelius Scipio becomes Publius Cornelius Scipio Aemilianus.
What was the impact of the Constitutio Antoniniana in AD 212?
It granted citizenship to all free individuals in the Roman Empire, creating distinctions between honestiores (elites) and humiliores (lower classes).
What naming convention did citizen women typically follow in Rome?
Citizen women generally had one name or two, such as Tullia (daughter of Marcus Tullius Cicero).
What happens to a slave who is freed in terms of naming?
Freed slaves take their master's name(s) and keep their slave name as a cognomen, e.g., Tiro becomes Marcus Tullius Tiro.
What does 'M. l.' signify in Roman naming conventions?
M. l. indicates a freedman (libertus) of Marcus.
What is the significance of social mobility in Roman society?
Social mobility was limited, with a rigid hierarchy that created tensions and status dissonance.
What are the two main social classes in Roman society?
The two main social classes are the honestiores (elite) and humiliores (commoners).

What is the role of patron-client relationships in Roman society?
Patron-client relationships were crucial for social structure, where patrons provided protection and support to their clients in exchange for loyalty.
What is the difference between a senator and a non-senator in Roman society?
Senators were part of the elite ruling class, while non-senators included various social gradations such as equites, decurions, merchants, and peasants.
What are the materials required for week 2 tutorials?
Roman Social History sourcebook pp. 3-42 and Subject Handbook pp. 39-62 (+ pp. 15-16): Dinner at Trimalchio's.
When do the tutorials for this course take place?
Wednesday 4-5 in Babel 303 and Friday 2-3 in Babel 204.
What is the focus of Lecture 3 in this course?
Lecture 3 focuses on Slavery.
What pages of the sourcebook cover the topic of slavery?
Roman Social History sourcebook pp. 154-204.
What is the significance of social stratification in Roman history?
Social stratification defined the hierarchy and relationships among different classes, influencing political, economic, and social interactions.
What is the meaning of 'ordo' and 'dignitas' in the context of Roman society?
Ordo refers to order or class, while dignitas refers to status, both of which were essential in maintaining social hierarchy.