All Chemical Identification Stuff for Organic Chemistry 2
1/111
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Colorado Mesa Univserity - Richards OChem 2 Class
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
O-H in IR
3200-3600(strong and broad)
N-H
3200-3600(medium and broad, one for each NH)
O-H (RCO2H)
2500-3600 (strong and very broad)
C-H(sp)
3200-3300(strong)
C-H(sp2)
3000-3200(variable, depends on number of groups)
C-H(sp3)
2850-3000(variable, depends on number of groups)
O=C-H
2750 and 2850(two sharp peaks, may be masked)
C=-N
2220-2260(medium)
C=-C
2100-2260(medium, narrow)
C=C
1600-1700(medium, narrow)
C=C(Ar)
1500 and 1600(two narrow peaks)
C=O
1600-1800(very strong)
C-O
1050-1250(strong)
C-N
1020-1230(medium to strong)
Spectroscopy
study of the interaction of matter and electromagnetic radiaion(light)
Frecuency(v)
number of waves per unit time (number of waves per second, Hz)
Wavelengths
distance between wave crests
Wavenumber
number of waves per unit distance(# of waves per cm,cm-1)
Which type of vibrations are we most interested in in IR Spectroscopy?
Stretching vibrations
How does IR spectroscopy work?
A light source is shined at a sample, some of the light is absorbed by the sample and some light is TRANSMITTED through the sample to the detector. The light that is transmitted is what we’re seeing.
What can the amount of light be quantified as?
absorbance or percent transmittance
Where do you spend most of your time in an IR Spectrum?
above 1400 (anything lower is the fingerprint region, above is the functional group region)
The higher the peak in IR…
the higher the absorbance
What can you use IR Spectroscopy for?
determine functional groups present
What determines the wavenumber of absorbance?
atomic mass, bond strength
What determines bond strength?
type of bond (C=-C, C=C, C-C), hybridization, and resonance
What factors determine intensity of absorbtion?
Polarity (more polar more intense absorbance) and number of bonds (more bonds, more intense absorbance)
What determines the broadness of absorbance?
H-bonding
What is H-Bonding?
When an electronegative atom (O,N,F) steals the H’s from other atoms.
Why is the O-H bond so broad?
Because of hydrogen bonding which allows interactions with neighboring atoms. The oxygen hydrogen bond stretching vibrations vary in frequencies vs one sharp frequency.
The lighter the atoms…
the higher the wavenumber
The stronger the bond in IR…
the higher the wavenumber because stronger bonds require more energy to vibrate.
Methyl
15
Ethyl
29
Propyl
43
Butyl
57
Pentyl
71
Chlorine
35
Bromine
79
With each addition of a carbon chain how much do you add to the previous MS number? (Ex: ethyl 29 + ? = propyl)
14
What does the y-axis represent in a MS graph?
Abundance of fragments
What does the x-axis represent on a MS graph?
Molecular Weight(MW)
What is the molecular ion peak?
The highest molecular weight fragment that is the most significant(tells the molecular weight for the original compound)
What is the base peak?
Tallest peak (can be important, just depends)
What determines fragmentation abundance?
Stability and similar MW despite a different fragment piece.
What does an odd molecular ion peak mean?
Presence of Nitrogen
What does it mean if the M+2 peak has one that’s 1/3 the size of the M peak?
Potentially the presence of chlorine
What if the M+2 peak is the same size of the M peak?
Potential presence of Bromine
Phenyl
77
Formyl
29
Acetyl
43
Which fragment will be shown in the MS graph?
Positive ones
What happens when the beam hits an electron?
The electron gets knocked out of orbit and turns the atom positively charge.
What is the first step after injecting your sample in Mass Spectroscopy?
A neutral sample molecule gets shot with an electron beam and an electron will get ejected and turn the molecule positively charged.
What happens after a molecule is positively charged in Mass Spectroscopy.
Molecular Ion (radical cation) gets fragmented into smaller pieces and the positive fragments gets read in the instrument.
Ionization Energy
E it takes to lose an electron
Which electron will be removed?
Highest energy electron
What are the two types of fragmentation for Alkyl Chloride/Bromide and Ethers?
Heterolytic Fragmentation and alpha cleavage(homolytic fragmentation)
What is heterolytic fragmentation?
fragmentation of the X or O bond. (results in a peak we CAN see)
Draw the mechanism for a heterolytic fragmentation for CH3-CH(Cl)-CH3 and CH3CH2CH(CH3)-O-CH(CH3)-CH3.
INSERT PHOTO(2)
Draw the mechanism for an alpha cleavage for CH3-CH(Cl)-CH3 and CH3CH2CH(CH3)-O-CH(CH3)-CH3.
INSERT PHOTO(2)
What two types of fragmentation do Alcohols do?
Dehydration (heterolytic fragmentation) and alpha cleavage.
Draw a mechanism for dehydration of CH3CH2CH(H)CH2-CH(OH)-CH3
INSERT PHOTO
How much mass do you lose and which hydrogen is used for dehydration?
lose 18 and the 3rd hydrogen
Why are some fragments more abundent?
Increased stability, different fragments but same MW
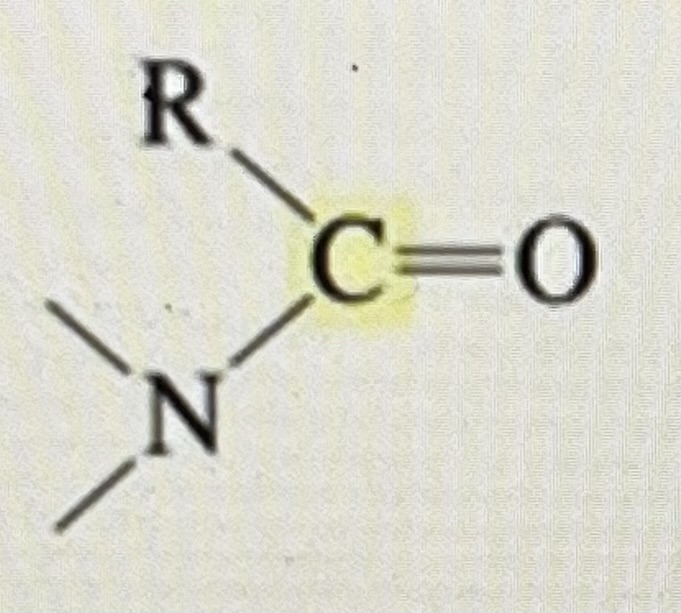
2* amide
165-175
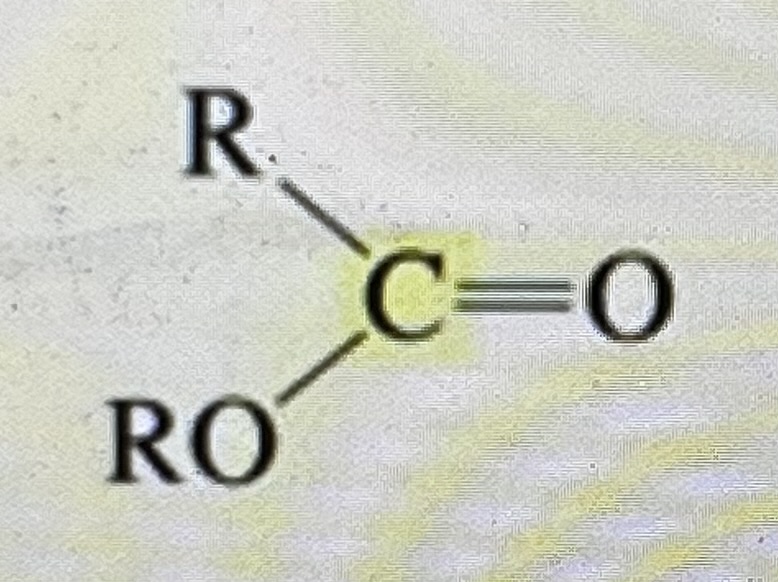
ester
165-175
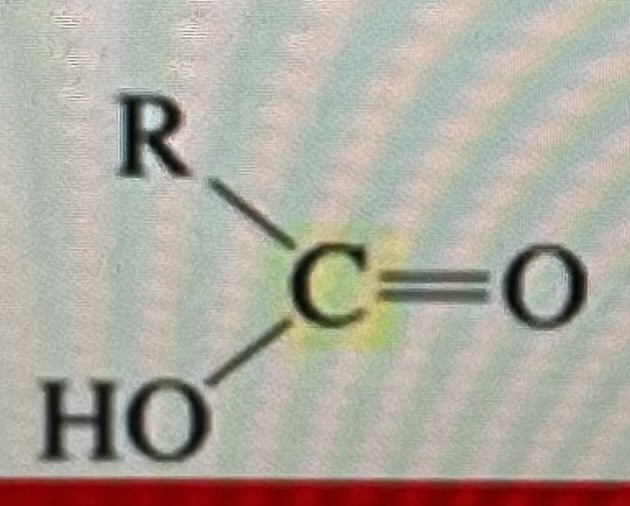
carboxylic acid
175-185
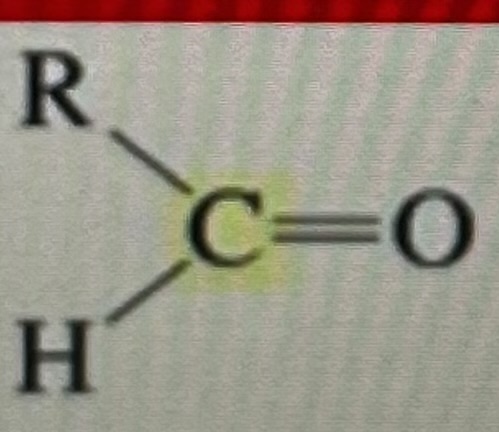
aldehyde
190-200
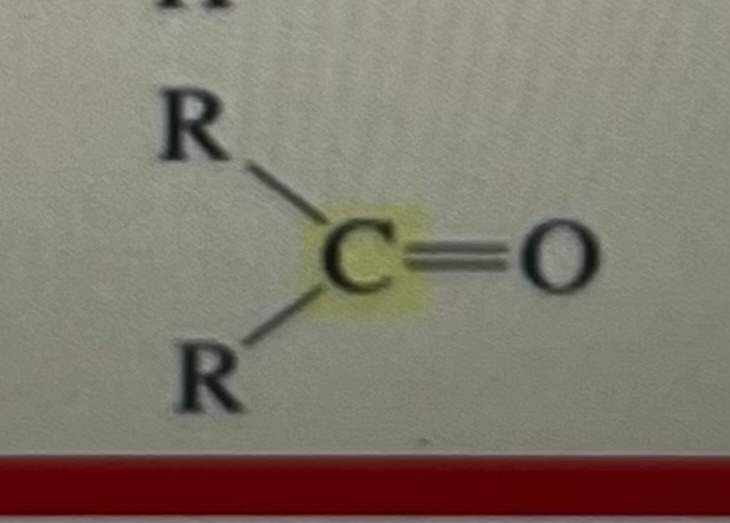
ketone
205-220
C=N
150-170
Ar-C
110-170
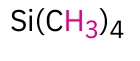
TMS(Reference)
0
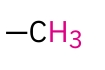
Primary Alkyl -CH3
0.7-1.3
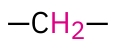
Secondary Alkyl -Ch2- in H NMR
1.2-1.6
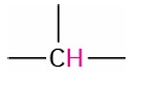
Tertiary Alkyl
1.4-1.8
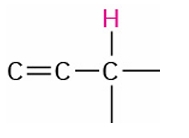
Allylic
1.6-2.2
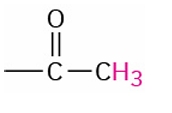
Methyl Ketone
2.0-2.4
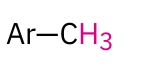
Aromatic Methyl
2.4-2.7
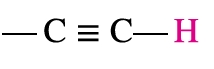
Alkyne
2.5-3.0
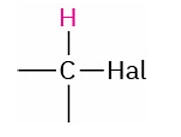
Alkyl Halide
2.5-4.0
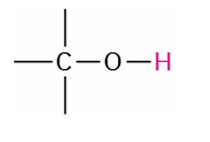
Alcohol
2.5-5.0
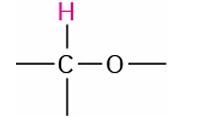
Alcohol, Ether
3.3-4.5
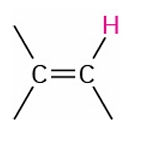
Vinylic
4.5-6.5
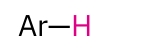
Aryl
6.5-8.0
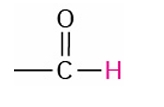
Aldehyde
9.7-10.0
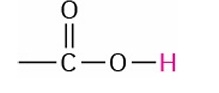
Carboxylic Acid
11.0-12.0
What does Nuclear Magnetic Resonance do?
It uses radio waves to interact w/ matter, its used to look at a nuclei that have a non-zero value for their quantum spin number.
What does Nuclear Magnetic Resonance show us?
Tells us about the carbon and hydrogen framework.
What is the spin state of a nucleus affected by?
An applied magnetic field
What happens when you remove a charge?
You create a magnetic fireld
What’s the orientation of a nucleus’s magnetic field without any applied magnetic field?
random
What are the two types of spin states?
Alpha(same direction) and Beta(anti-parallel)
What are the steps for Nuclear Magnetic Resonance?
Proton gets shot w/ MF and absorbs or releases radio waves .
What does the energy difference between the spin states depend on?
The strength of the magnetic field felt by the nuclei
What does the strength felt by the MF on the nuclei depend on?
Strength of the applied MF and the amount of shielding around the nucleus
What does a more electron rich environment mean?
More shielding
Nuclei in different electron environment absorb light at…
different energys (frequencies)
Upfield
goes to right
Downfield
goes to the left