physical properties and changes of matter (TEAS 7)
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
density
the ratio of mass to volume
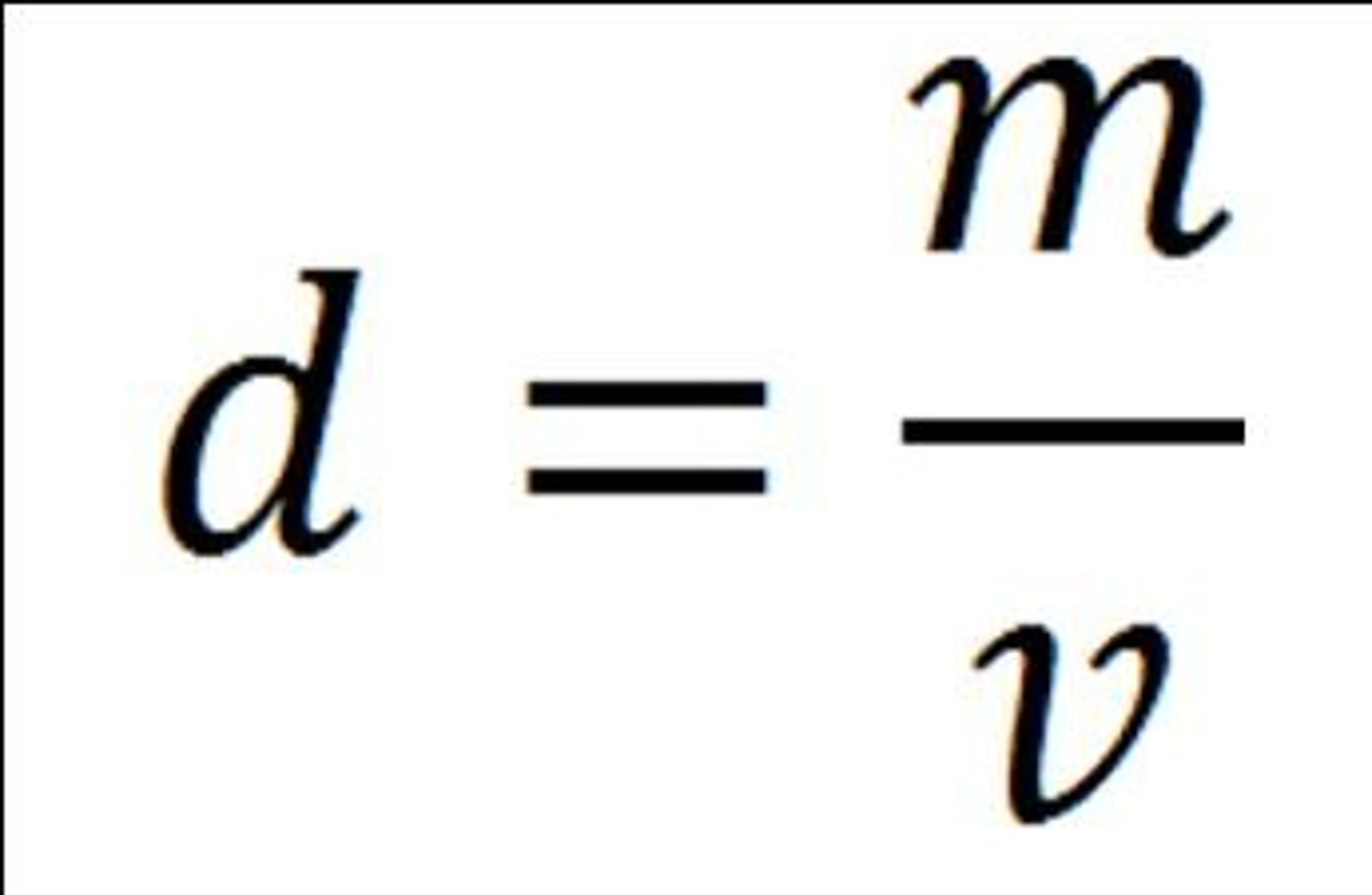
gram
metric unit of mass

physical properties of matter
refers to observed properties of the substances and those that can change the state without changing the identity of the substance.
ie: color, odor, shape and size, etc
example: boiling liquid water.

the steam (vapor) that is produced is a
gaseous state of water with the same molecular formula as liquid water.

the molecules in liquid water and vapor are both made up of
two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen- its identity has not changed.
the vapor can be condensed to form
liquid water again.

intensive properties such as density and boiling points
do not depend on the amount of matter present

extensive physical properties
Depend on the amount of matter present and include mass, length, and volume

mass is the
specific number of molecules

volume is the
amount of space taken up by that number of molecules
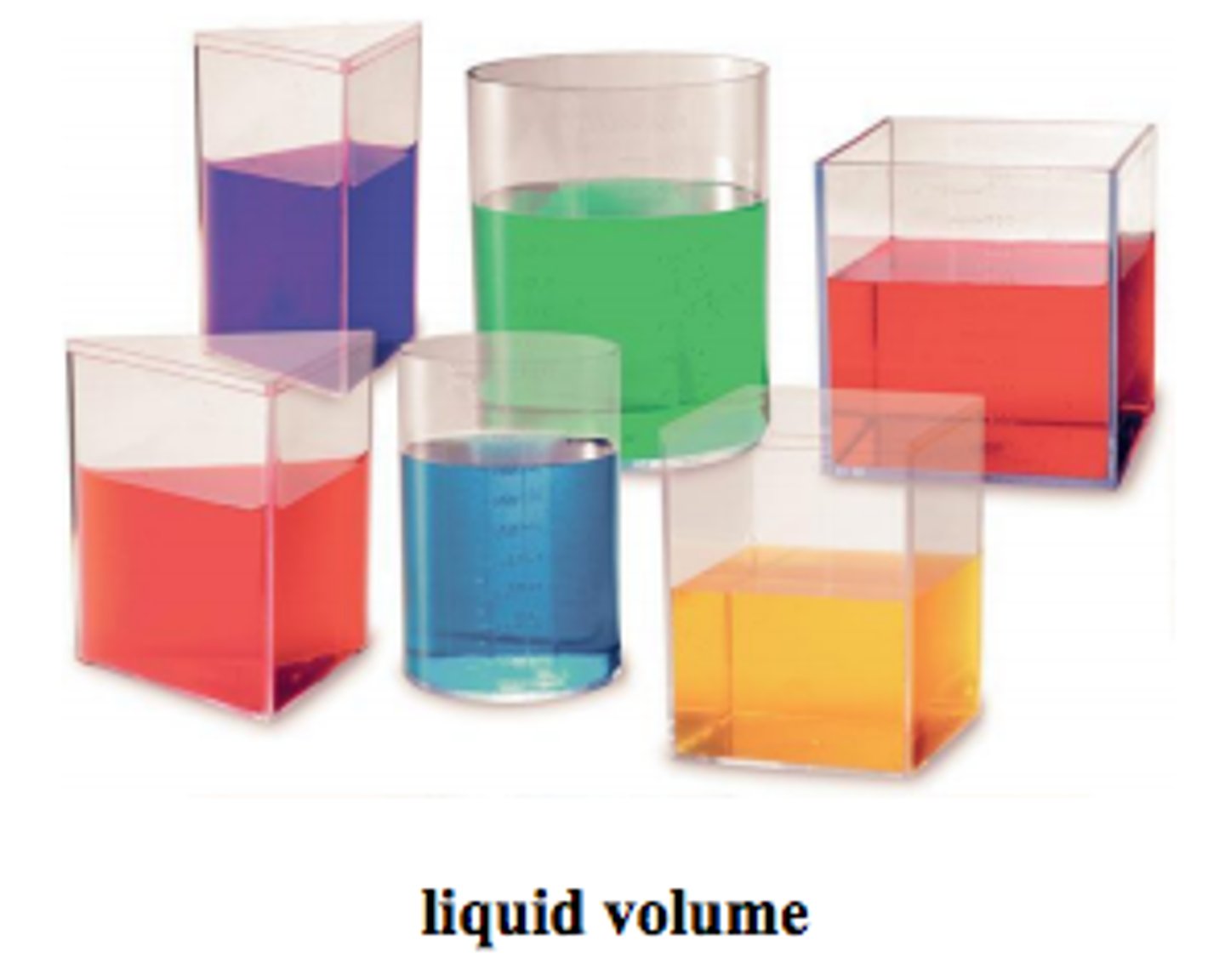

sample liquid of water has a density of
1 gram per cubic centimeter (1g/cm3) independent of the sample size.

denser substance will
sink
less dense substance will
float
ex: ice floats on liquid water because it is less dense.
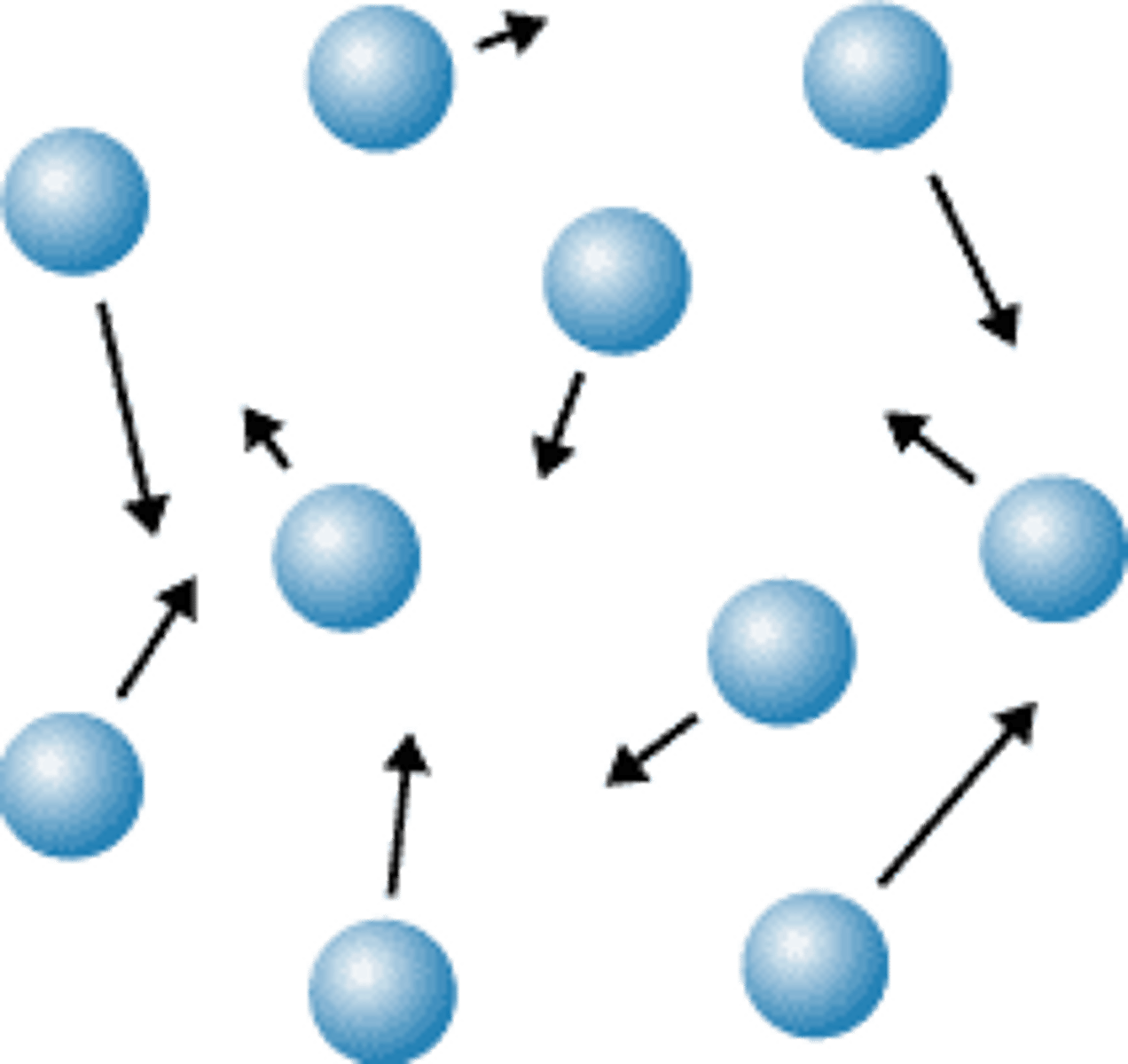
Kinetic Molecular Theory
a theory stating that the molecules that make up all matter are in constant motion, and the temperature of a substance is directly proportional to the average kinetic energy of its molecules.
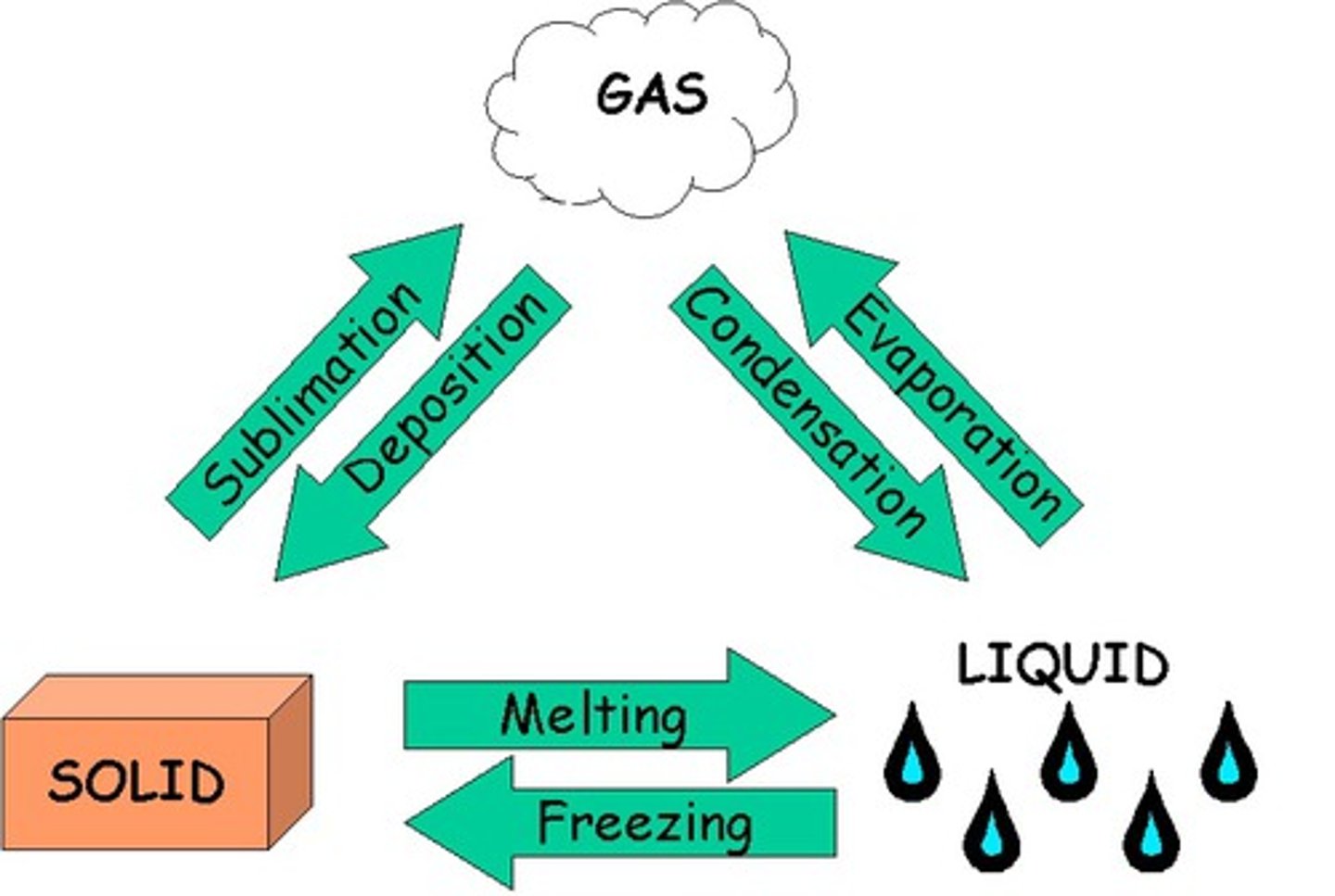
sublimation
the transition of a substance from solid to gas without passing through the liquid state.

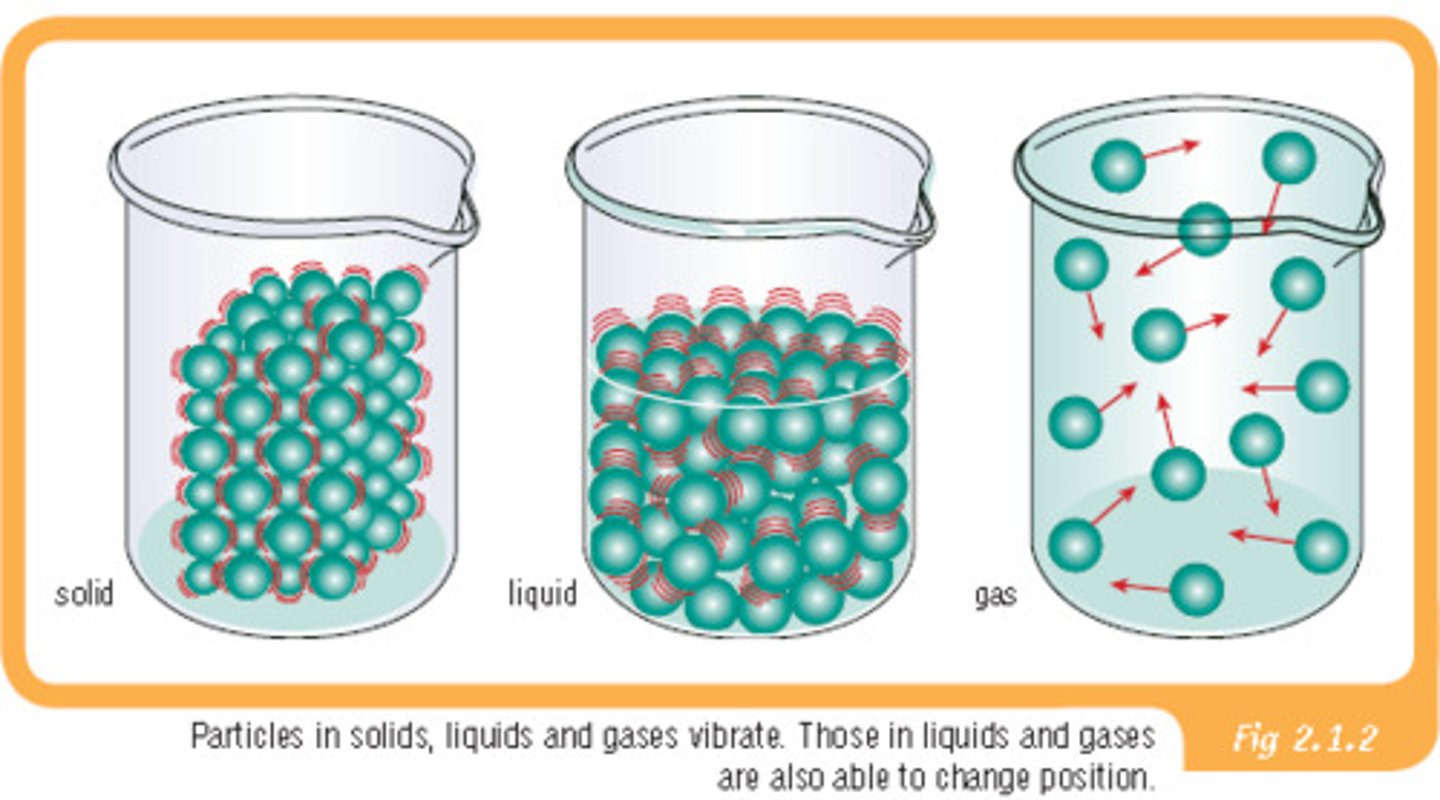
matter exist in four phases:
solid, liquid, gas, plasma
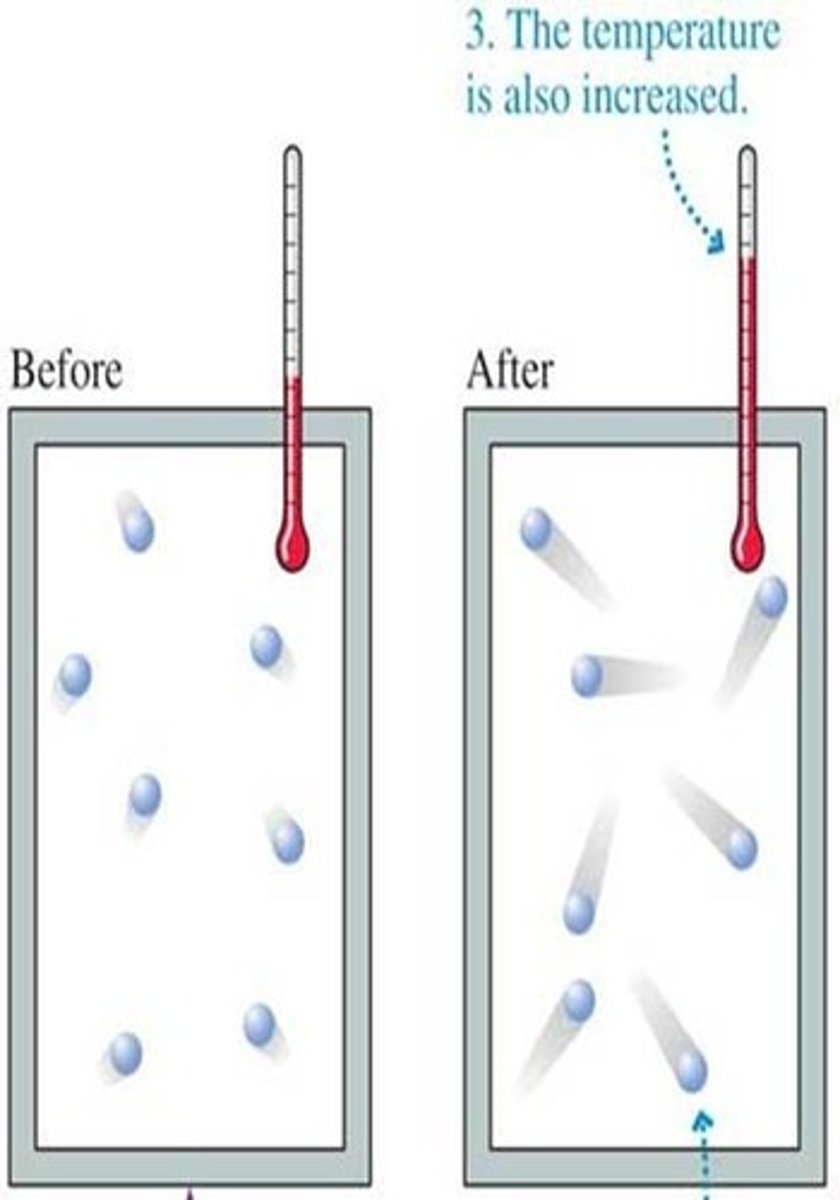
as temperature of a substance increases
The intermolecular forces that hold the molecules together are broken, causing the molecules to move away from each other.
the amount of heat required for a phase change
will not break the bonds within a molecule.

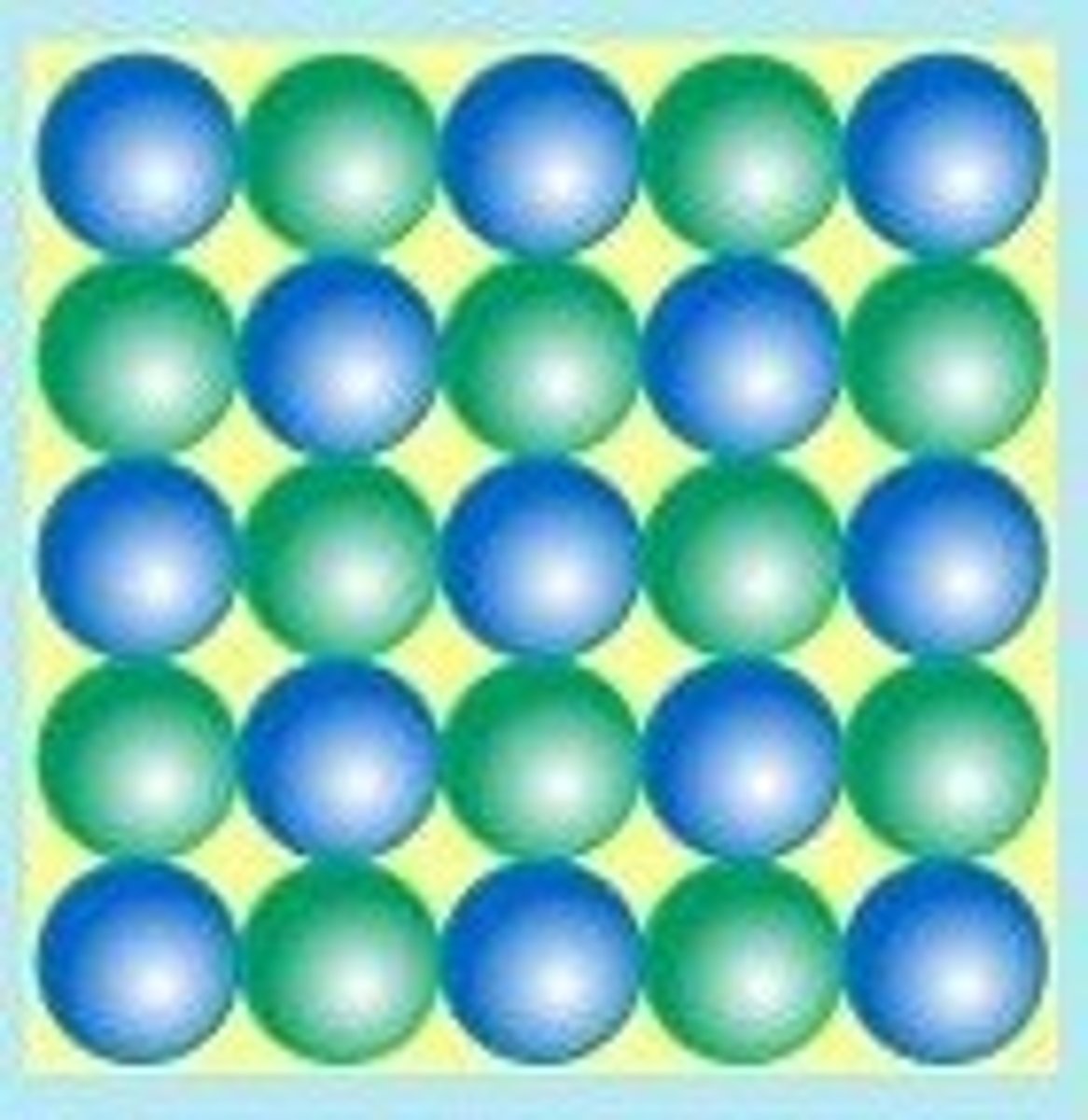
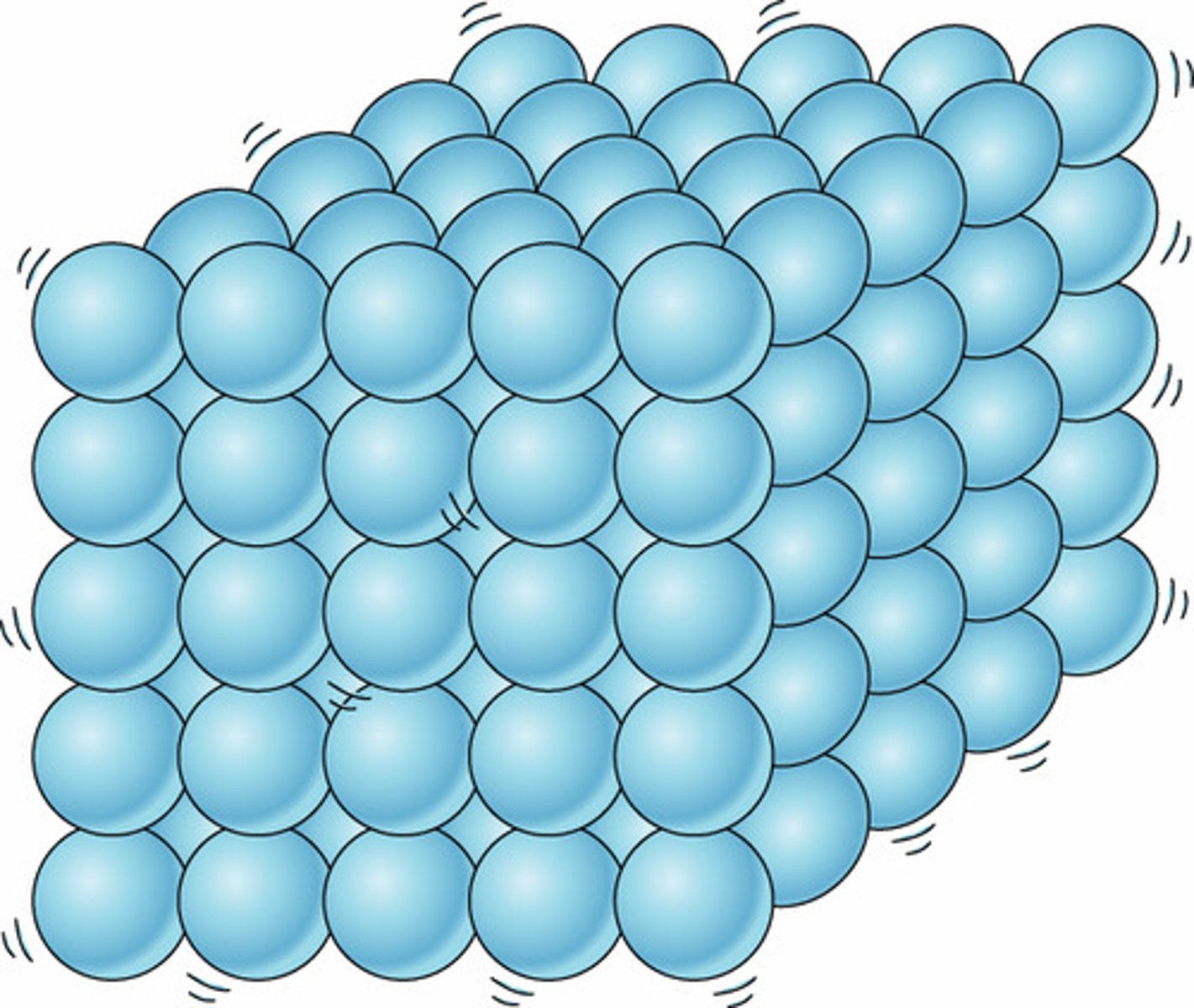
in solid, the molecules are
packed together tight, orderly pattern; there is vibrational motion but no translational motion experienced by the molecules.
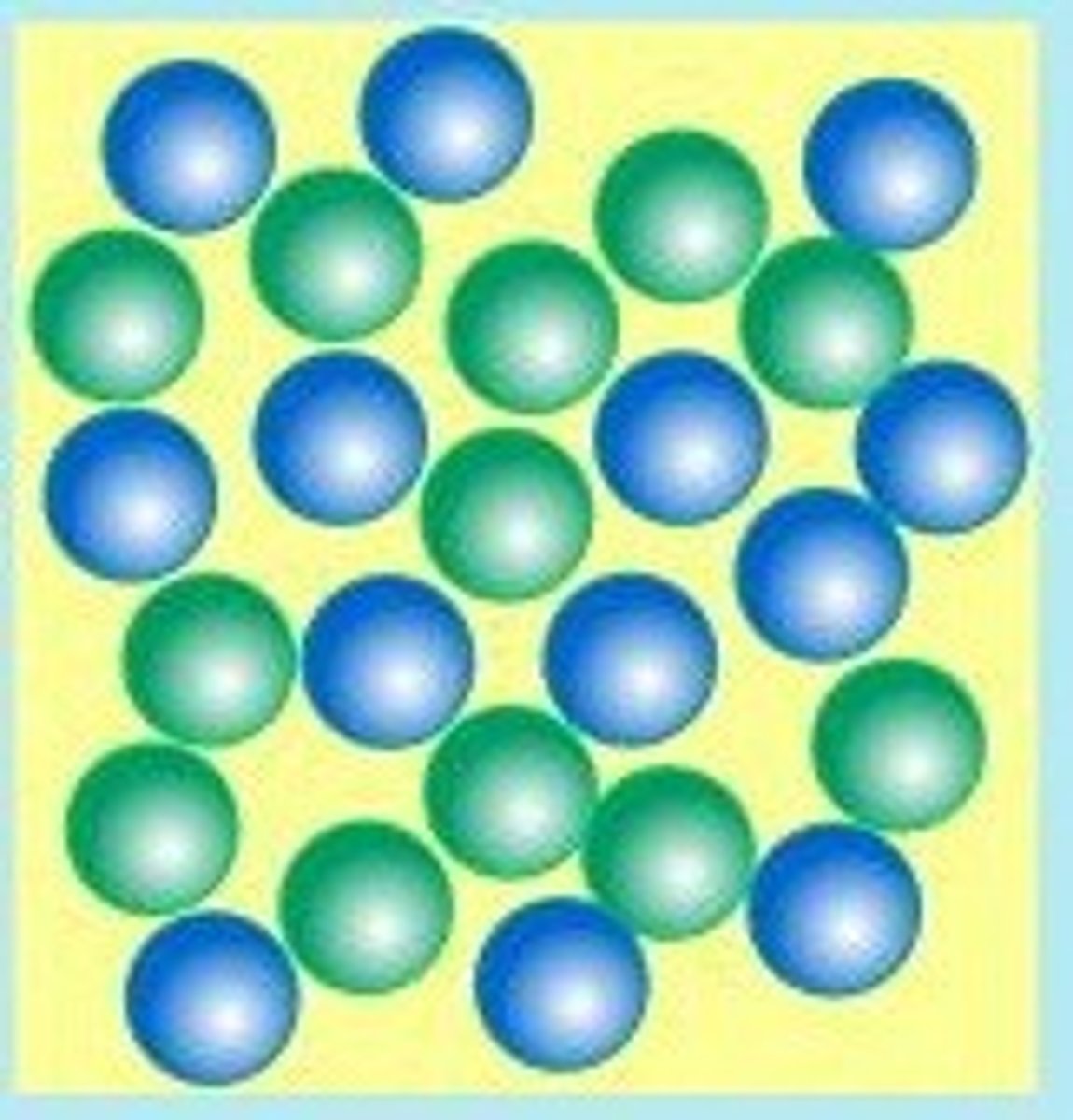
the molecules in liquids are
less ordered and exhibit both translational and vibrational motion
gas molecules are
Rapidly moving AND spread far apart
the phases of a substance depends on two conditions:
temperature and pressure.
increasing temperature has
a tendency to move the particles of matter apart
increasing pressure has
a tendency to pack them closer together
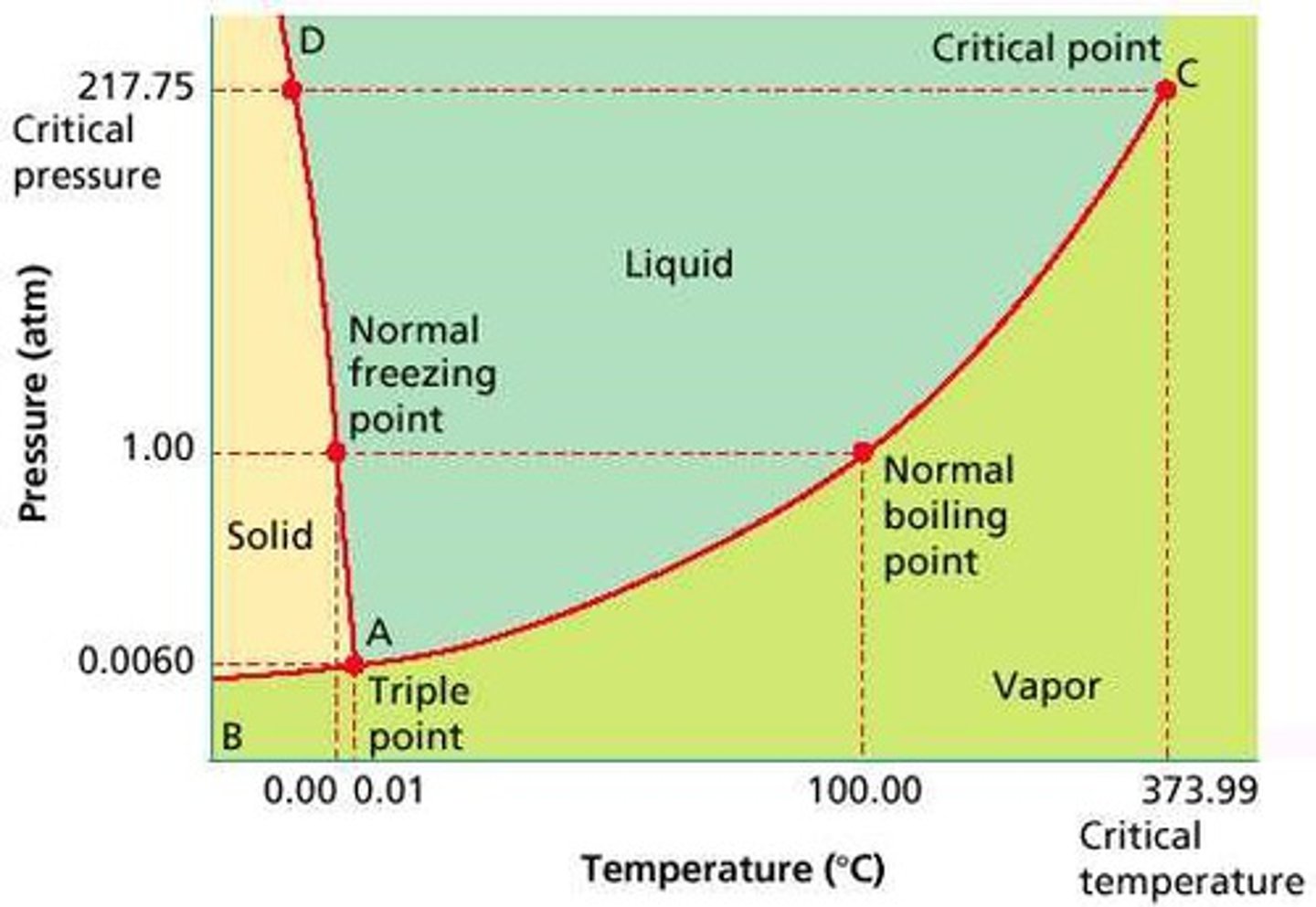
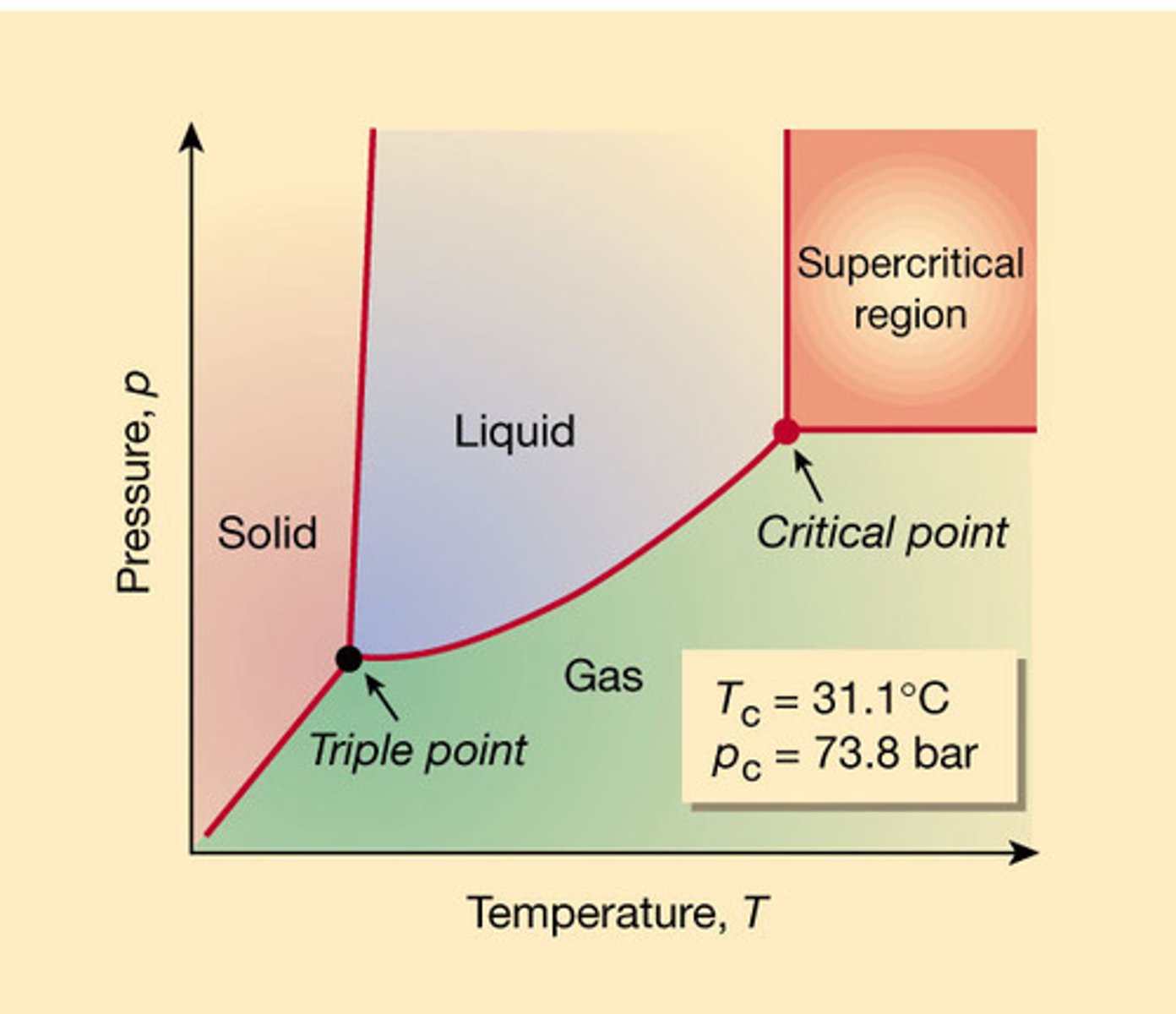
triple point on phase diagram
all three phases are in equilibrium and coexist; solid, liquid, and gas
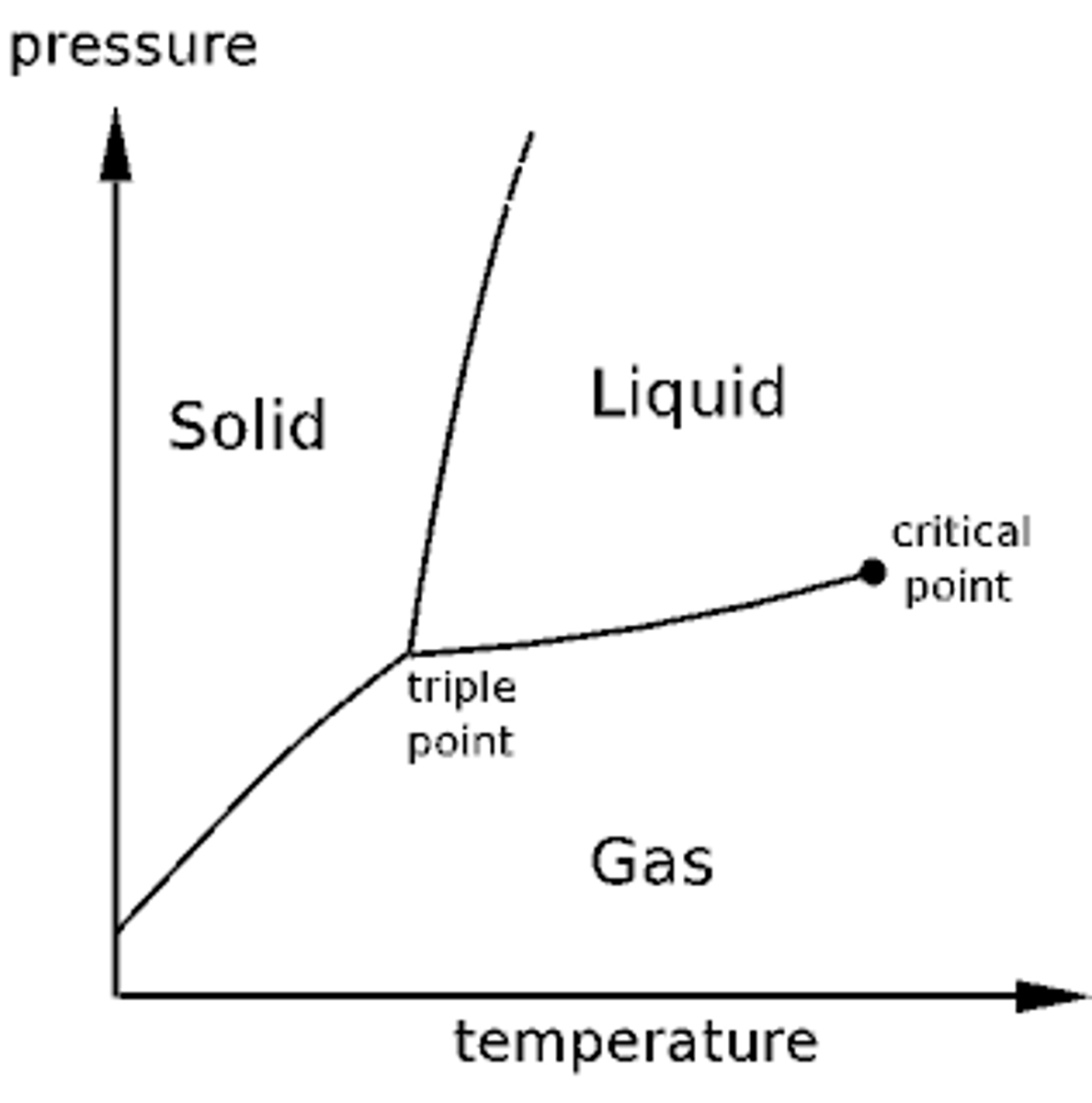
Critical point on phase diagram
liquid and gas coexist
solid matter has
definite volume and shape; it has a specific number of molecules (matter) and takes up a specific amount of space; non-compressible
liquid matter has
definite volume but no definite shape, meaning that it will conform to the shape of the container; non-compressible
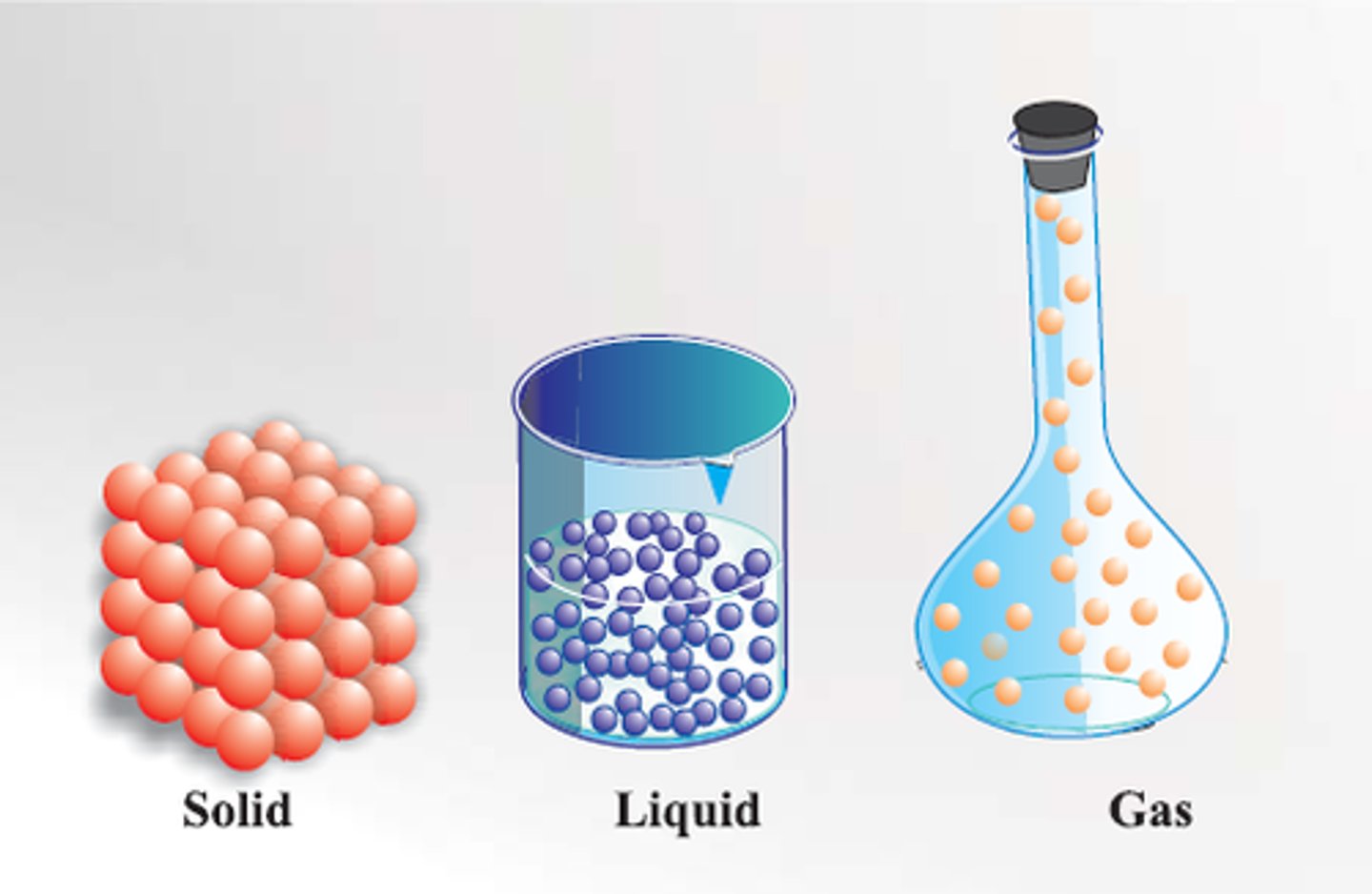
gas has
no definite shape or definite volume; they are highly compressible and subject to changes in volume.
a change from solid to liquid
is called melting; requires an addition of heat, which causes the molecules to become more energized.
-this increases vibrational and translational motion

change from liquid to gas
is called evaporation or boiling water; adding heat is required to change matter from liquid to gas

change gas to liquid
removing heat from matter is required to change gas to liquid; condensation or liquid to solid; freezing.

deposition
gas to solid; water vapor can directly become solid ice crystals causing the formation of frost on windows.