structure and function (transport in plants)
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
what does the phloem do
from where to where
transports sucrose and amino acids made by the plant from photosynthesising leaves to non-photosynthesising regions in the roots and stem
movement of substances in the phloem is
up and down, either way
in diagrams, phloem is always on the _____ and the xylem is always on the ______
phloem is always on the outside and xylem is always on the inside
what does the xylem do
transports water and minerals from the roots to the stem and leaves via transpiration
xylem and phloem are arranged throughout plant in _______
xylem and phloem are arranged throughout plant in vascular bundles
structural features of xylem (2)
It is composed of dead cells which form hollow tubes
Xylem cells are strengthened by lignin and so are adapted for the transport of water in the transpiration stream
labelled xylem diagram
xylem/phloem cross section of a STEM
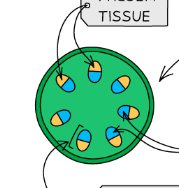
xylem/phloem + root _____ cells cross section of root
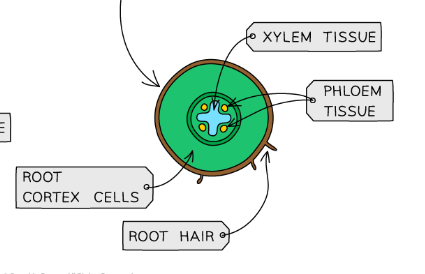
root hair cells grow _____ soil particles and ______ water and ________ from the soil
grow between soil particles and absorb water and minerals from the soil
how is water //mineral ions absorbed by root hair cells
Roots hair cells take up mineral ions from the soil by active transport
The water concentration of the cell cytoplasm is reduced due to the presence of mineral ions - cell is hypertonic (more solutes) to hypotonic, hypo → hyper
Water moves into the root hair cell by osmosis
root hair cells have a large ________ ________
large surface area → extended hair, more space for transport
define transpiration
the loss of water vapour from the parts of the plant that are above ground. e.g. leaves/stems
what is transpiration caused by, and where (2)
through evaporation of water at the surfaces of the spongy mesophyll cells
and diffusion of water vapour through the stomata
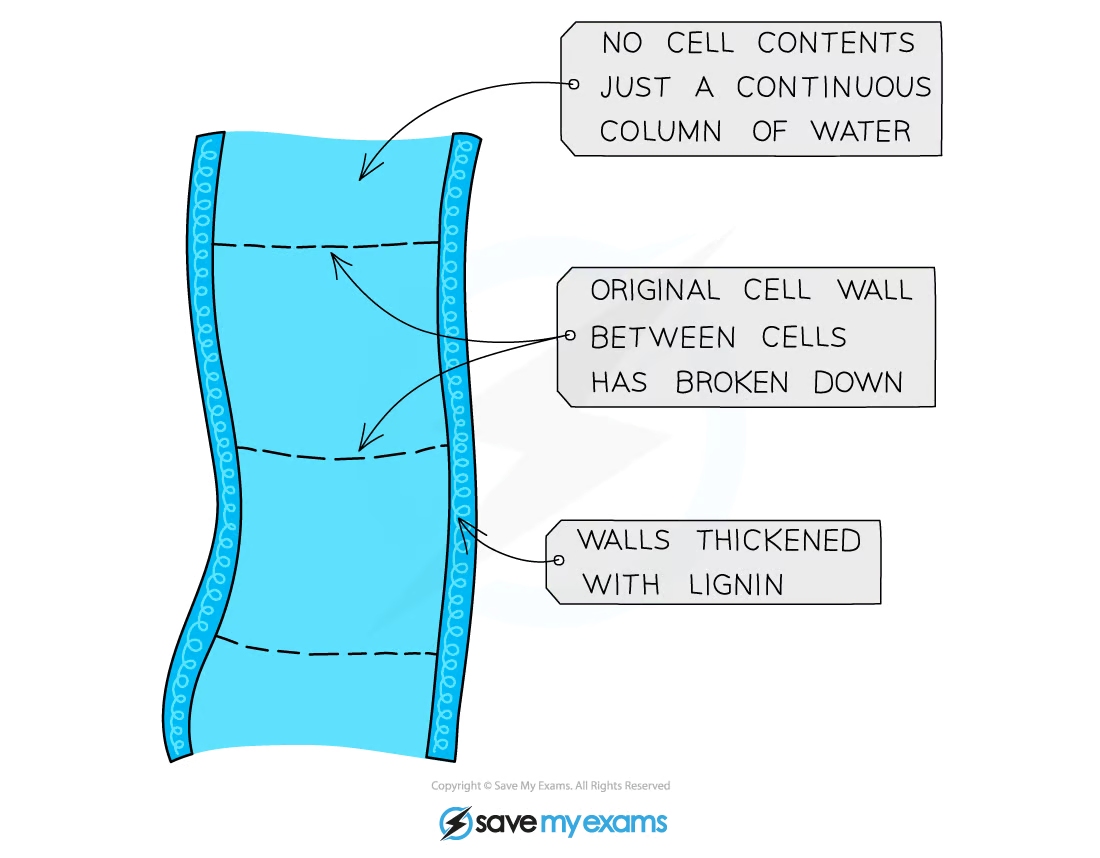
what is the transpiration stream, and what does it ‘look’ like
as water evaporates/diffuses out, water is drawn up from the rest of the plant through xylem to fill the empty space. this means more water is drawn up from roots
Due to cohesion, the water in the xylem creates a continuous unbroken column (each individual molecule ‘pulls’ on the one below it)
Transpiration produces tension or ‘pulls’ on the water in the xylem vessels
uses of water in plants (4) - so basically why transpiration is important
Turgidity: Water is stored in plant cells’ vacuoles to make them turgid, providing structural support.
Photosynthesis: Only 5% of water taken up by plants is used for photosynthesis, which is essential for making their own food.
Transport: Water transports mineral ions throughout the plant.
Cooling: Evaporation of water cools the leaves
why does transpiration cool the plant
the conversion of water (liquid) into water vapour (gas) as it leaves the cells and enters the airspace requires heat energy. The use of heat to convert water into water vapour helps to cool the plant down
If the rate of transpiration from the leaves increases, water molecules are pulled up the xylem vessels _______
If the rate of transpiration from the leaves increases, water molecules are pulled up the xylem vessels quicker
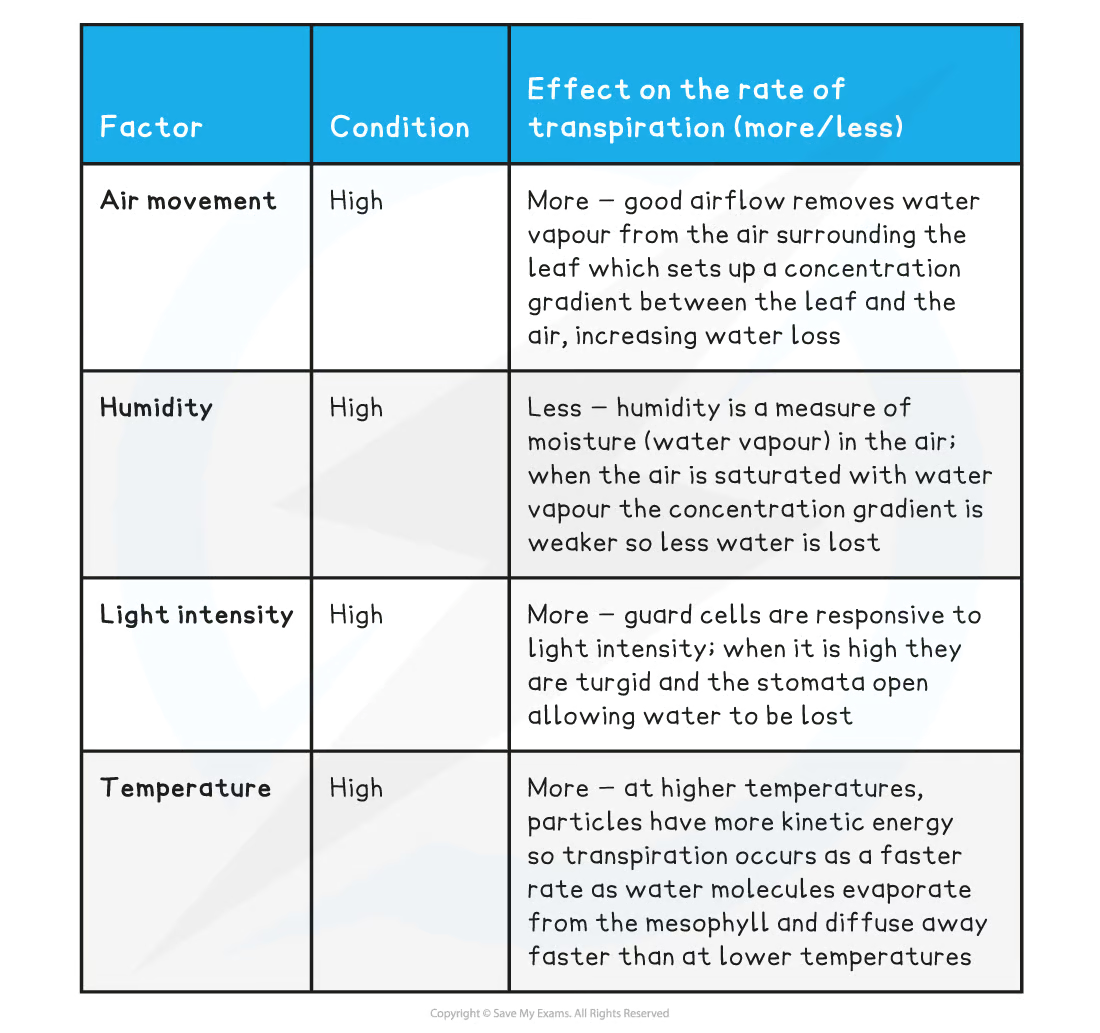
wind | high | |
humidity | high | |
light | high | |
temperature | high |
piece of equipment used to measure transpiration
potometer
how does a mass potometer work
measures a change in mass of a plant as a measure of the amount of water that has evaporated from the leaves and stem
how does a bubble potometer work
A bubble potometer measures the uptake of water by a stem as a measure of the amount of water that is being lost by evaporation consequently pulling water up through the stem to replace it
labelled bubble potometer diagram
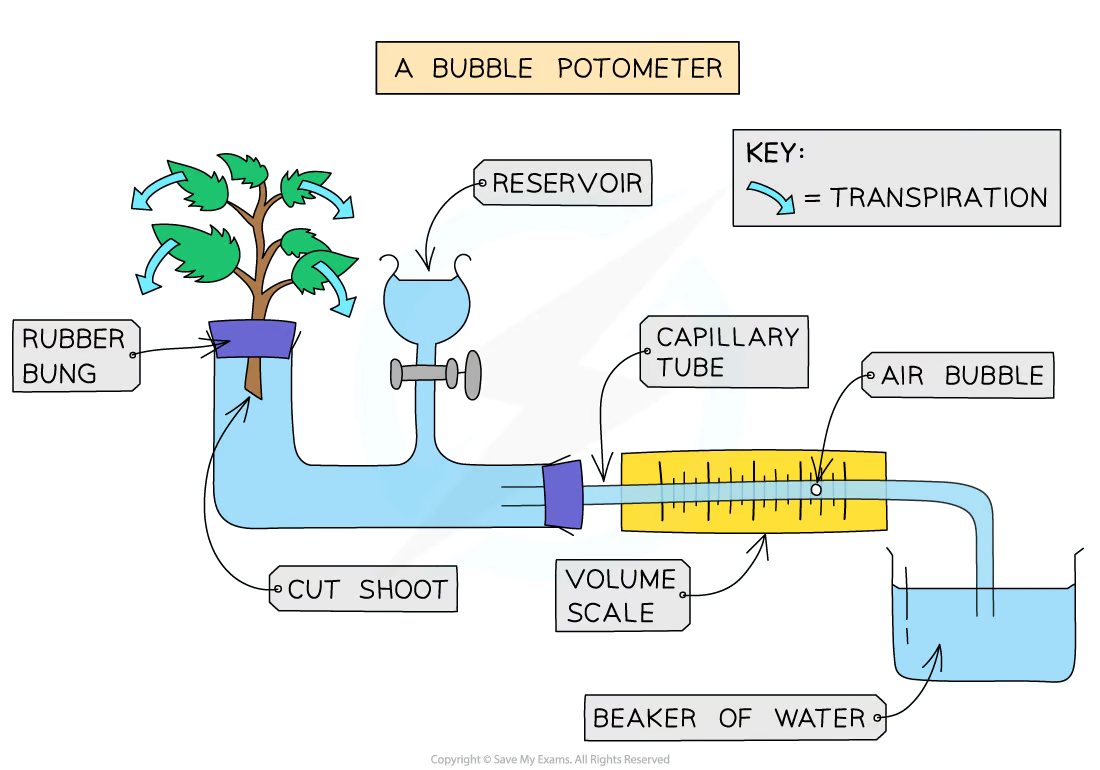
rate of transpiration (for bubble potometer) =
distance moved by bubble (m) / time (minutes)
transpiration method, and why for some steps
Cut a shoot underwater
To prevent air entering the xylem and place in tube
Set up the apparatus as shown in the diagram
make sure it is airtight, using Vaseline to seal any gaps
Dry the leaves of the shoot
Wet leaves will affect the results
Remove the capillary tube from the beaker of water to allow a single air bubble to form and place the tube back into the water
Set up a lamp 10cm from the leaf
Allow the plant to adapt to the new environment for 5 minutes
Record the starting location of the air bubble
Leave for 30 minutes
Record the end location of the air bubble
Change the light intensity
Reset the bubble by opening the tap below the reservoir
Repeat the experiment
Calculate the rate of transpiration by dividing the distance the bubble travelled by the time period
The further the bubble travels in the same time period, the greater the rate of transpiration
transpiration increases when light intensity is _____. this is because…
transpiration increases when light intensity is HIGH. This is becaues more stomata tend to be open in bright light in order to maximise photosynthesis
(The more stomata that are open, the more water can be lost by evaporation and diffusion through the stomatal pores)
transpiration potometer cormss
Change - change the intensity of the light
Organisms - same plant species, size, age, number of leaves
Repeat - repeat x3, take avgs
Measurement 1 - measure the distance travelled by the bubble (m)
Measurement 2 - ...in 30 minutes (to calculate the rate of transpiration)
Same - control the temperature, wind speed and humidity of the environment