BIO Plants 4 - Seed Plants & Gymnosperms
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
3 innovations of seed plants
wood, seeds, pollen
era has tallest trees
now (holocene) but they are carniferous that evolved cretaceous era
tree simple vs strict definition
plant with single stem, branching canopy, can reach large heights thanks to specialized cells
has wood and increases in girth (trunk thickens)
Gilboa Tree
first tree like plant
mid devonian → late … 8m → 20m
dont have true wood - just xylem stands that with spoungy tissue around
paleobotanical discovery
First Carboniferous Era Forest
ancient fern, clubhorse, and giant horsetail forests (50m tall) that dominated wetlands that covered pangea
shallow roots and plants would fall over and get compressed peat→ coal
**coal not renewable resource
Wood
Vascular Cambium: ring of cells beneath bark that produces xylem and phloem
dead xylem cells accumulate
woods is made up of lignified xylem
**all allow for growth wide and height
Emerald Ash Borer
invasive beatle whos larvae eat phloem and outer xylem…trees dont store nutrience and starve to death 1-2 years later
Archaeopteris
fossils found - extinct genus of fern like trees - show the evolutionary transition from ancient trees to modern gymnosperms
similar conifer wood
trunks 30m with reinforced branch joints
fern like leaves
reproduce via heterspory (2 types of spores)
Distinct Life Cycle Charecteristics from Fern Life Cycle **might delete
no longer dependent on water for mating
pollination
diploid life stage doing dispersal
gametophytes not free living - germinate on female tissue
reduced gametophyte stage
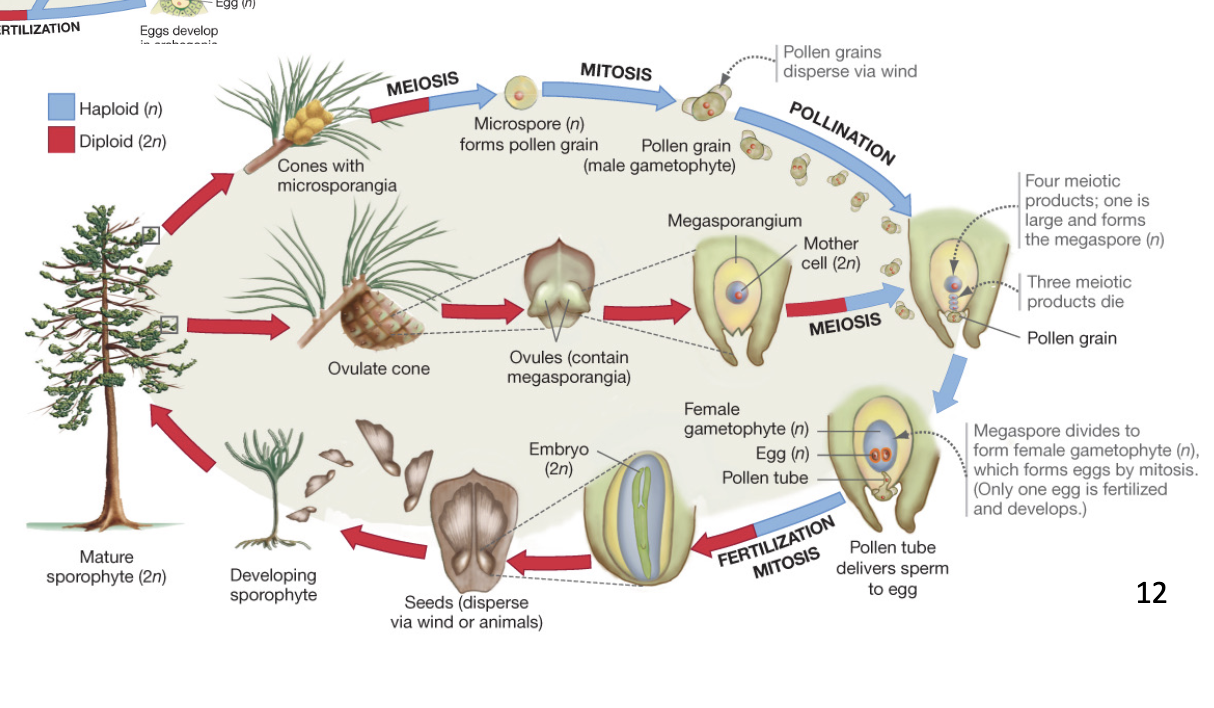
Heterospory description
key innovation of gymnosperms
2 sizes of spores with different sexes
megaspores (F) → become seeds
microspores (M) → become pollin
lead to evolution of seeds and pollin
Evolution megagamyetophyte to seeds
changes happening simultaneously…
becomes 1 megaspore per sporeangium (instead of MANY)
megaspore retained in sporangium while it germinates
integument - megaspore becomes surrounded by protective outer layer
ovule - megasporagium enclosed in integument - not exposed to air and can colonize drier evironment
integument
protective tissue that surround sporangium - protection from environmental conditions…will eventually develop into seed coat
ovule
megasporaguim that is completely closed expect for micopile in integument
consequences of need of male gametophyte to burrow to access female gametophyte (megaspore)
plants can recognize own pollen and then prevent inbreeding (egg fertilizing own pollen)
seed
a fertilized ovule
heterospory as an important evolutionary step
lead to evolution of seeds pollen, Protection of the Female Gametophyte, nourishment of embryo from parent plant - enhancing survial rates
evolution of microgametytophyte to pollen
microspores evolve into pollen grains or male gametophyte
these are 2-3 cells covered in coat of sporopellenin (makes pollen desication resistant) and can travel through environment without water
germinates when lands on right spot of female tissue and becomes pollen tube and then pollen swims through
allowed for efficient reproduction in dry habitats
**male gametes no longer has to travel through environment … pollen is only released when pollen tube formed
modern gymnosperm ‘naked seed’ charecteristics
seed plants without flowers or ovaries
their seeds are solitary (rare) or develop in/on scales/leaves
ovules are open to the air to be directly pollinated (by pollen that does travel through air)
age of gymnosperms
mesozoic
cycads specifically dominated and many herbivore dinos ate them
extant gymnosperms
cycads, ginkos, conifers
Cycads
mostly tropical
100 species
slow growing and live long
large cone at apex of trunk
have seperate female and male plants
motile sperm with 40000 tails

ginkgos
first appeared 270 mya, didn’t diversify a lot
1 extant species, most closely related to cycads
visibly related to prehistoric fossils
seperate female and male plants
motlie sperm
males are resistant to pollution
conifers ‘cone bearers’
most diverse extant gymnosperms - 630 species
woody, cone bearing
dominate boreal forest (largest boreal environment
tallest and oldest non-conal living organism
pine dryness specialization
hot and cold
thin waxy densly packed needles reduce wind
pine cold specialization
thick bark, cone shelter seedsp
pine snow adaptation
cone shaped, down facing, flexible branches
urban heat island effect
dark material that absorb heat
canyons created by tall buildings that trap heat
**montreal is 10C hotter that surrounding land
cooling effect
trees have largest cooling effect
bc of shade, evaporative cooling (like sweat)
2ND: temp difference under canopy creates breeze that cools significantly