Honors Anatomy - Ch.13 Respiratory System
1/279
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
280 Terms
Stig Severinsen
What is the name of the man that holds the world record for holding his breath?
Purify, humidify, warm incoming air
Main functions of the respiratory system (hint: PHW)
Conducting region
This is the region from the nasal cavity to the bronchioles
Conducting region
Where does purification, humidifying, and warming of incoming air occur?
Gas exchange
This exchange between the blood and external environment occurs in the alveoli of the lungs
Respiratory region
This region is also known as the alveoli of the lungs
Nares
Another name for the external nostrils
Olfactory receptors
Receptors that relay information from odorant molecules to your brain
Located in the mucosa on the superior surface
Moistens air, traps incoming foreign particles
What is the function of mucosa? (hint: MT)
Goblet cells
Cells found in the mucous membranes of the respiratory and intestinal tracts that produce and secrete mucus
Nasal conchae
Curved, bony structures protruding from the lateral walls of the nasal cavity
Increase surface area, increase air turbulence within the nasal cavity
Functions of the nasal conchae (hint: II)
Palate
The nasal cavity is separated from the oral cavity by the ___
Sinuses
Cavities within bones surrounding the nasal cavity
Frontal, sphenoid, ethmoid, maxillary
What are the four paranasal sinuses?
Lighten the skull, aid in speech production, produce mucus
What are the functions of the paranasal sinuses? (hint: LAP)
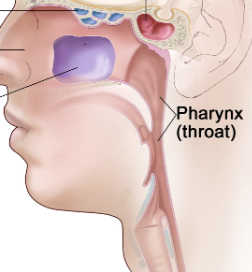
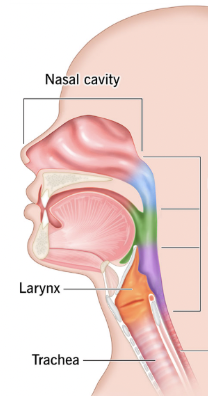
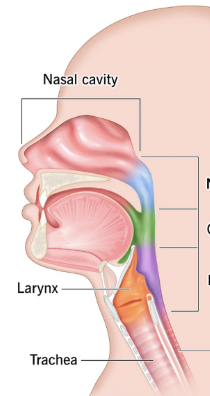
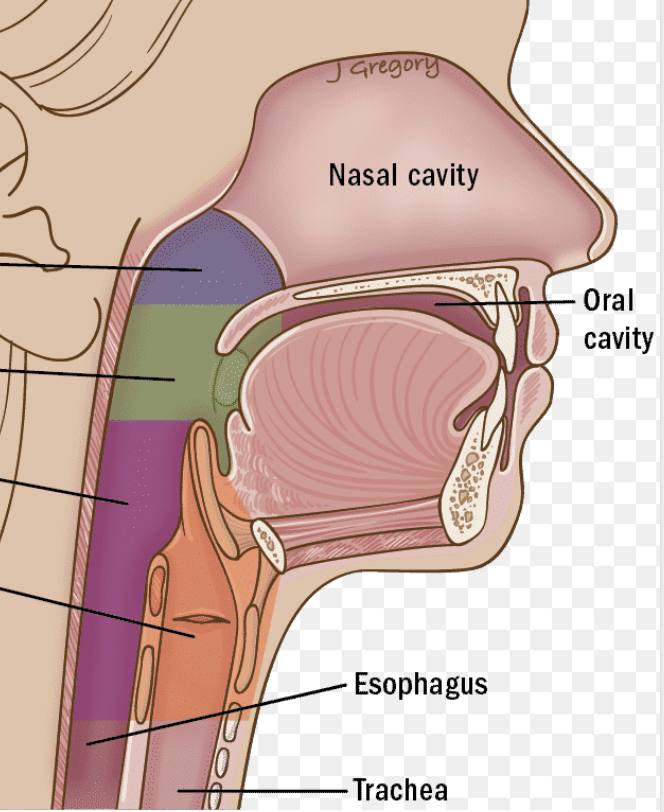
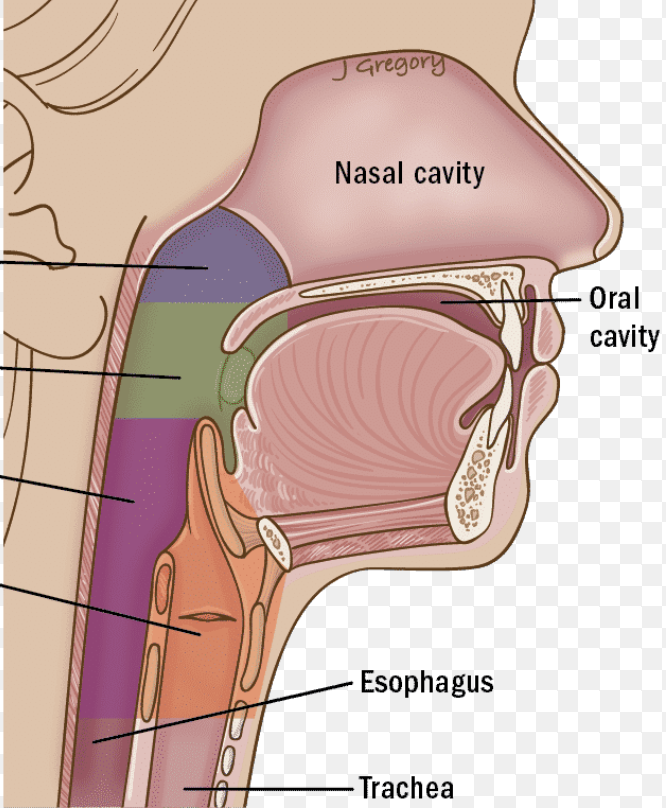
Pharynx/throat
Muscular passage from nasal cavity to larynx
Nasopharynx, oropharynx, laryngopharynx
What are the three regions of the pharynx?
Pharynx/throat
Frontal sinus
Green
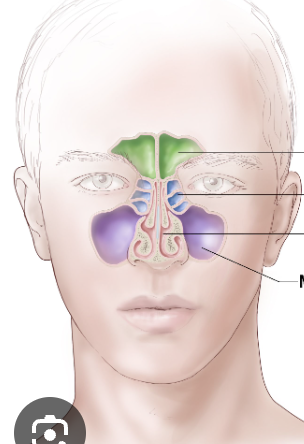
Ethmoid sinus
Blue
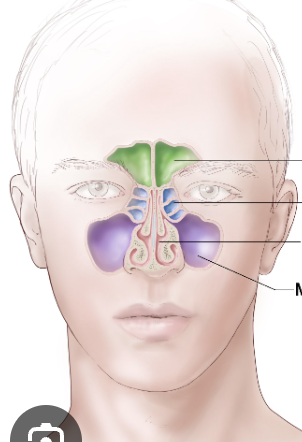
Maxillary sinus
Purple
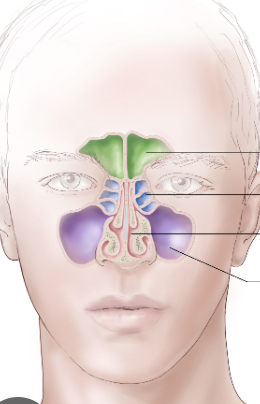
Sphenoid sinus
Red
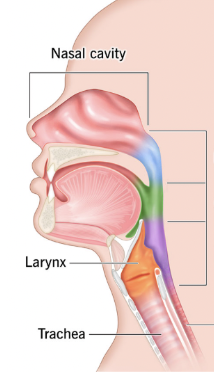
Nasopharynx
Superior region behind nasal cavity (blue)
Nasopharynx
Blue
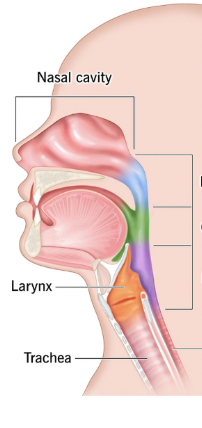
Oropharynx
Middle region behind mouth (green)
Oropharynx
Green
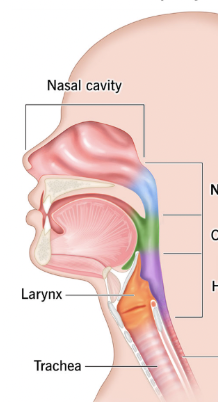
Laryngopharynx
Inferior region attached to larynx (purple)
Laryngopharynx
Purple
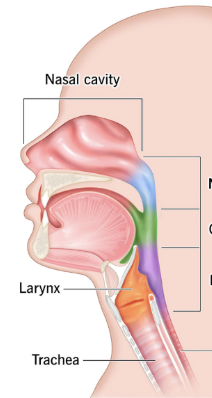
Oropharynx, laryngopharynx
The ___ and ___ are common passageways for air and food
Pharyngotympanic tubes
Tubes that open into the nasopharynx
Pharyngeal, palatine, lingual
What are the three tonsils of the pharynx?
Pharyngeal tonsil (adenoid)
Tonsil that is located in the nasopharynx (similar to lymph nodes to help fight infections)
Red
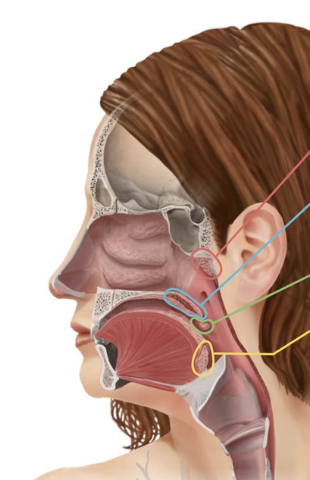
Pharyngeal tonsil
Red
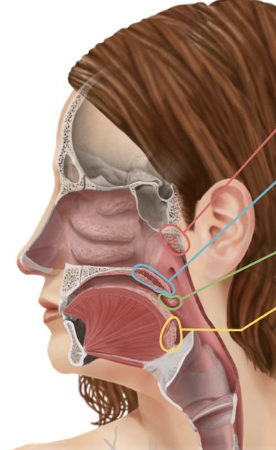
Palatine tonsils
Green
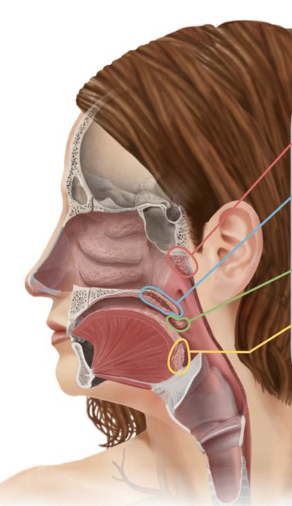
Lingual tonsil
Yellow
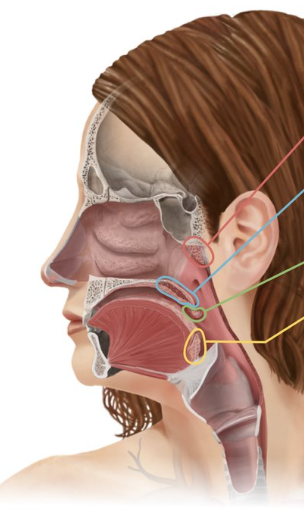
Lingual tonsil
Tonsils that are found at the base of the tongue
Yellow
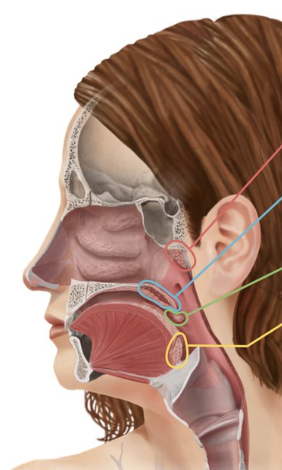
Palatine tonsils
Tonsils that are located in the oropharynx
Green
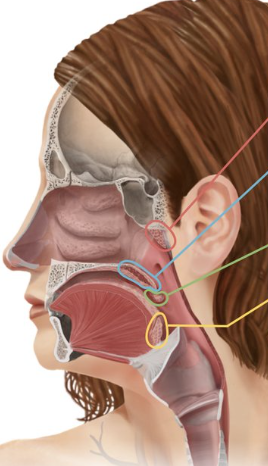
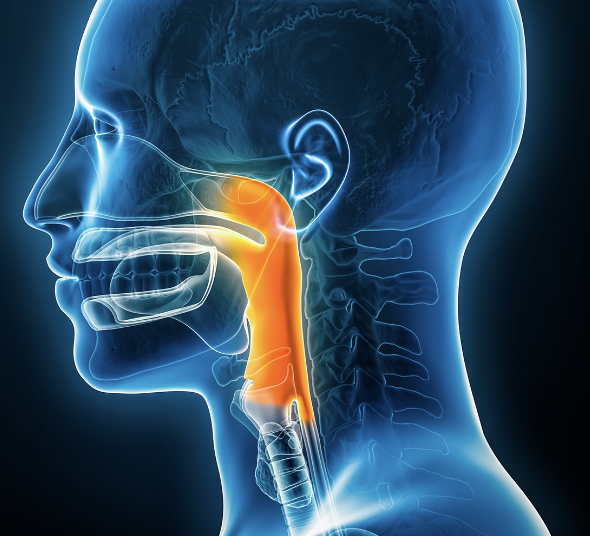
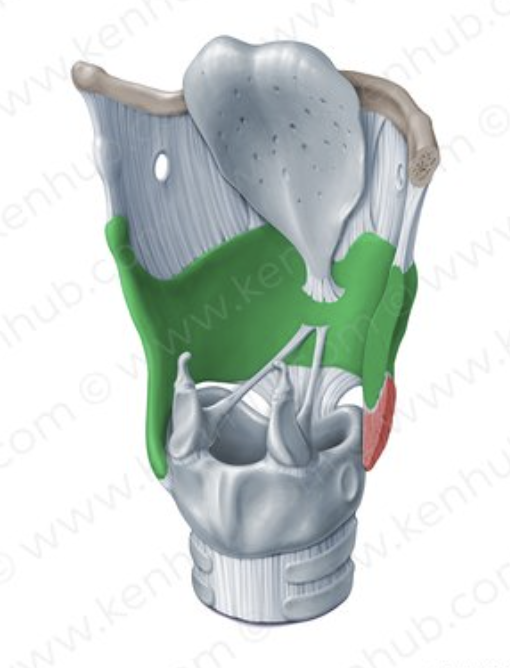
Larynx/voice box
Structure that routes air and food into proper channels
Plays a role in speech, swallowing, breathing, coughing, & vomiting (original role was to protect lungs)
Made of eight rigid hyaline cartilages and a spoon-shaped flap of elastic cartilage (epiglottis)
Orange
Larynx/voice box
Orange
Speech, swallowing, breathing, coughing, vomiting
What does the larynx play a role in? (hint: SSBCV)
Epiglottis
Spoon-shaped flap of elastic cartilage
Protects the superior opening of the larynx
Routes food to the posteriorly situated esophagus and routes air toward the trachea
When swallowing, rises and forms a lid over the opening of the larynx
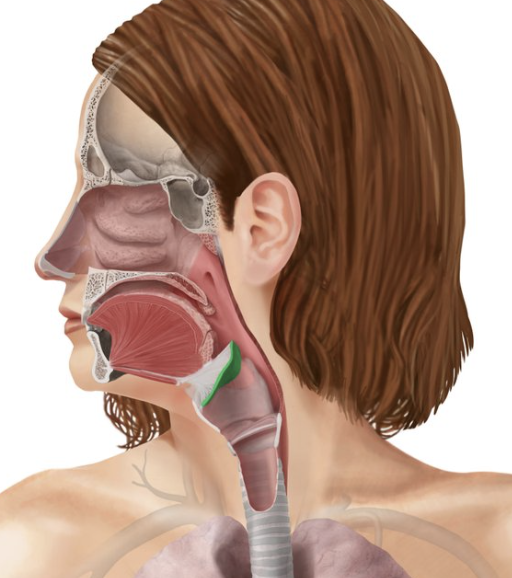
Epiglottis
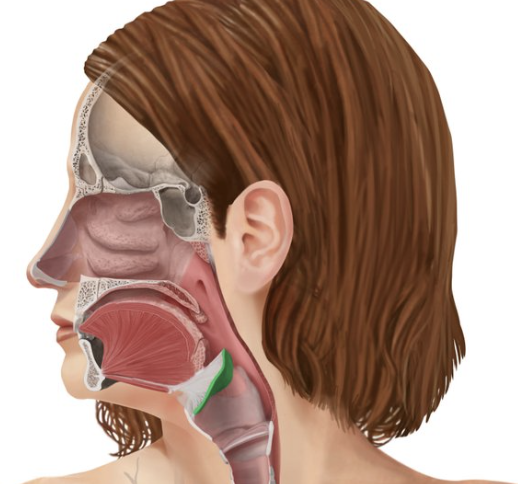
Thyroid cartilage
Largest of the hyaline cartilages of the larynx
Protrudes anteriorly (Adam’s apple)
Laryngeal prominence
Another name for the Adam’s apple
Testosterone
Why is the laryngeal prominence larger in males than in females?
Chondrolaryngoplast/tracheal or laryngeal shave
Surgical procedure in which the thyroid cartilage is reduced in size by shaving down the cartilage through an incision in the throat, generally to aid those who are uncomfortable with the girth of their Adam’s apple
Vocal folds
True vocal cords
Vibrate with expelled air
Grey-ish section
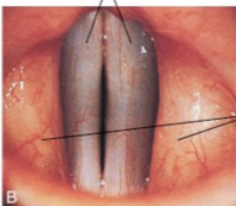
Glottis
The part of the larynx consisting of the vocal cords and the slit-like pathway between them
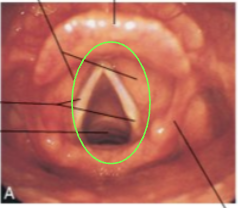
Pitch
Rate of vibration, size and tension on cords
Volume
Amount of air passing through vocal folds
Tobacco, vitamin deficiency, alcohol, HPV infections, acid reflux, asbestos exposure
Risk factors of laryngeal cancer (hint: TVAHAA)
Sore throat, change of voice, hoarseness, pain, cough, breathing problems, weight loss, bleeding
Symptoms of laryngeal cancer (hint: SCHPCBWB)
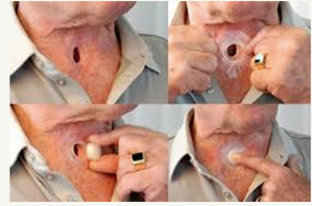
Laryngectomy
Surgical removal of the larynx
Trachea/windpipe
4-inch-long tube that connects larynx with bronchi
Walls are reinforced with C-shaped hyaline cartilage, which keeps it patent
Lined with ciliated mucosa
C-shaped hyaline cartilage
What are the walls of the trachea reinforced with?
Ciliated mucosa
What is the trachea lined with?
Trachea/windpipe
Primary bronchi
Formed by division of the trachea
Each bronchus enters the lung at the hilum (medial depression)
Right bronchus is wider, shorter, and straighter than left
Bronchi subdivide into smaller and smaller branches
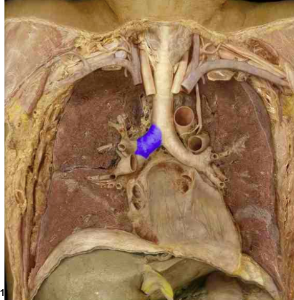
Hilum
Medial depression at which each bronchus enters the lungs
Mediastinum
Central portion of the thoracic cavity that the heart inhabits
Near the clavicle
Where is the apex of the lungs located?
Diaphragm
What does the base of the lungs rest on?
Fissures
Each lung is divided into lobes by ___
5, 3, 2
How many lobes does a human lung have? How many are from the right lung? How many are from the left lung?
7, 4, 3
How many lobes does a pig lung have? How many are from the right lung? How many are from the left lung?
6, 4, 2
How many lobes does a dog lung have? How many are from the right lung? How many are from the left lung?
Serosa
Covers the outer surface of the lungs
Visceral pleura
Serous layer that covers the lung surface
Parietal pleura
Serous layer that lines the walls of the thoracic cavity
Pleural fluid
Fills the area between layers to allow gliding and decrease friction during breathing
Pleural cavity
Cavity found between the serous layers of the lungs
Horizontal fissure
Which fissure divides the right superior and middle lobes?
Oblique fissure
Which fissure divides the right middle and inferior lobes?
Oblique fissure
Which fissure divides the left superior and inferior lobes?
Primary bronchi → secondary bronchi → tertiary bronchi → bronchioles → terminal bronchioles → respiratory bronchioles
Bronchial tree divisions from largest to smallest (use →)
Bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveolar sacs, alveolus
Respiratory zone structures (hint: BAAA)
Alveolus
Air sacs with alveolar pores (singular)
Alveolar sacs
Cluster of alveoli
Alveoli
Air sacs with alveolar pores (plural)
Respiratory membrane
Creates an air-blood barrier (on one side of the membrane is air, and on the other side is blood flowing past)
Formed by alveolar and capillary walls
Alveolar pores
Connect neighboring air sacs
Pulmonary capillaries
Cover external surfaces of alveoli and exchange gases between the alveoli and the blood
Type I
Type of alveolar cell involved in gas exchange
Type II
Type of alveolar cell that produces surfactant
Alveolar macrophages
“Dust cells” that add protection by picking up bacteria, carbon particles, and other debris
Surfactant
A lipid molecule that coats gas-exposed alveolar surfaces
Tidal volume (TV)
Amount of air that you move in and out of your lungs while breathing normally
500mL
How much air does normal breathing typically move with each breath? (TV)
Size, sex, age, physical condition
Which factors affect respiratory capacity? (hint: SSAP)
Inspiratory capacity (IC)
Amount of air drawn into lungs after a normal respiration cycle
3000mL
What is the typically amount of air drawn into the lungs after a normal respiration cycle? (IC)
Inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)
Amount of air that can be taken in forcibly over the tidal volume
3100mL
What is the typical amount of air that can be taken in forcibly over the tidal volume? (IRV)
Expiratory reserve volume (ERV)
Amount of air that can be forcibly exhaled after a tidal expiration
1200mL
What is the typical amount of air that can be forcibly exhaled after a tidal expiration? (ERV)
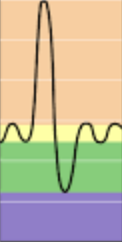
Tidal volume (TV)
Yellow
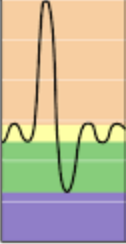
Inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)
Orange
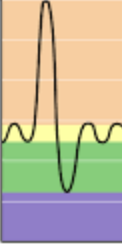
Expiratory reserve volume (ERV)
Green
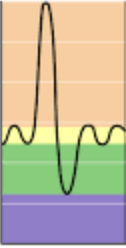
Residual volume (RV)
Purple