Chp 12 - Distribution Channels
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
distribution channel
Institutions that transfer the ownership of goods and move goods from the point of production to the point of consumption
Part of overall supply chain
supply chain management
Refers to a set of approaches and techniques firms employ to efficiently and effectively integrate their suppliers, manufacturers, warehouses, stores, and transportation intermediaries into a seamless value chain in which merchandise is produced and distributed in the right quantities, to the right locations, and at the right time.
wholesalers
Those firms engaged in buying, taking title to, often storing, and physically handling goods in large quantities, and then reselling the goods (usually in smaller quantities) to retailers or industrial or business users
retailers
Sell products directly to consumers.
logistics management
The integration of two or more activities for the purpose of planning, implementing, and controlling the efficient flow of raw materials, in-process inventory, and finished goods from the point of origin to the point of consumption.
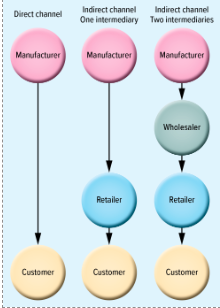
types of distribution
direct
indirect (one intermediary)
indirect (two intermediary)
push marketing strategy
ncrease demand by focusing on wholesalers, distributors, or salespeople, who push the product to consumers via distribution channels. Contests for sales ppl
pull marketing strategy
get consumers to pull the product into the supply chain by demanding that retailers carry it. Ads, Social Media, Store Displays
distribution intensity
The number of channel members to use at each level of the supply chain.
intensive
selective
exclusive
intensive
A strategy designed to get products into as many outlets as possible.
Ex. Walmart, Shoppers, LobLaws
selective
Lies between the intensive and exclusive distribution strategies; uses a few selected customers in a territory.
ex. lux brands
exclusive
Strategy of granting exclusive rights to sell to one or very few retail customers so no other customers can sell a particular brand.
ex. nespresso
distribution centre
A facility for the receipt, storage, and redistribution of goods to company stores or customers; may be operated by retailers, manufacturers, or distribution specialists.
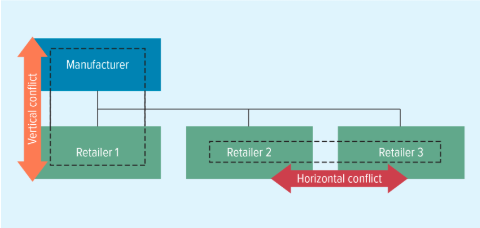
channel conflict
Results when supply chain members are not in agreement about their goals, roles, or rewards.
corporate vertical marketing system
A system in which the parent company has complete control and can dictate the priorities and objectives of the supply chain; it may own facilities such as manufacturing plants, warehouse facilities, retail outlets, and design studios.
vertical channel conflict
B/w Manufacturer + Retailer
(Black & Decker + Home Depot)
horizontal channel conflict
B/w Retailer 1 + Retailer 2
Nike sells to Footlocker + Walmart
contractual vertical marketing system
A system in which independent firms at different levels of the supply chain join together through contracts to obtain economies of scale and coordination and to reduce conflict.
franchising
A contractual agreement between a franchisor and a franchisee that allows the franchisee to operate a retail outlet, using a name and format developed and supported by the franchisor
strategic relationship
A supply chain relationship that the members are committed to maintaining long-term, investing in opportunities that are mutually beneficial; requires mutual trust, open communication, common goals, and credible commitments.
information flow
Flow 1 (Customer to Store)
Scans.. Universal Product Code- The b&w barcode on most merch.
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) tags - Tiny computer chips that auto transmit to special scanner all the info about a container’s contents or individual products.
Flow 2 (Store to Buyer)
POS system recc & transmits info
Flow 3 (Buyer to Manufacturer)
Customer info compiled for purchase decision
Flow 4 (Store to Manufacturer)
ALSO can be sales data fr store -> manu
Flow 5 (Store to Distribution Centre)
Store comms w center abt inventory/delivery
electronic data interchange (EDI)
The computer-to-computer exchange of business documents from a retailer to a vendor and back.
advanced shipping notice
An electronic document that the supplier sends the retailer in advance of a shipment to tell the retailer exactly what to expect in the shipment.
vendor-managed inventory (VMI)
An approach in which the manufacturer is responsible for replenishing inventory to meet retailers’ needs.
distribution centres
More accurate sales forecasts are possible when retailers combine forecast for many stores serviced by one distribution centre rather than rather than doing a forecast for each store.
Distribution centres enable the retailer to carry less merchandise in the individual stores
It is easier to avoid running or having too stock, having too stock in any particular store because merchandise is ordered from the distribution centre as needed
Retail store space in typically much expensive than is space at a distribution, and distribution centers are better equipped than stores to prepare merchandise for sale
mobile task management
An approach in which the manufacturer is responsible for replenishing inventory to meet retailers’ needs.
just in time inventory systems
inventory management systems designed to deliver less merchandise on a more frequent basis than traditional inventory systems; the firm gets the merchandise “just in time” for it to be used in the manufacture of another product; also known as quick-response (QR) systems in retailing.
quick response
An inventory management system used in retailing; merchandise is received just in time for sale when the customer wants it.