Roman Architecture
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/86
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
1
New cards
GEOGRAPHICAL INFLUENCE
Rome has a commanding position in the Mediterranean sea which enabled to act as an intemediary in spreading art and civilization over Europe Western Asia and North Africa. There is marked geographical differences between Greek and the Romans with regards to national character, Romans were very close.
2
New cards
CONCRETE
GEOLOGICAL INFLUENCE the chief building material which renderer finest example of Roman Architecture. They also have ample supply of marbles, terracota, stone, bricks, sand, gravel & timber.
3
New cards
pozzolana
Concrete was made up of stone or brick rubble & a mortar of which the important ingredient was "_______"
4
New cards
CLIMATIC INFLUENCE
Rome was divided into three regions (North, Central and South Italy). Because of this variety of climatic conditions, there was a diversity of architectural features & treatment in the peninsula itself.
5
New cards
RELIGIOUS INFLUENCE
Religion became a part of the constitution of the state. They venerated more their emperors than their gods and because of this attitude, there were less temples for worship.
6
New cards
ARCHITECTURAL CHARACTER
a. Vastness & Magnificence, b. Ostentation & Ornateness
7
New cards
PERIODS OF DEVELOPMENT
Etruscan and Roman
8
New cards
ETRUSCAN
notable for the use of the true & radiating arch. They were the earliest civilization & great builders, invented the "tusacan capital" and their temples were oriented at the south.
9
New cards
ROMAN
adopted the columnar & trabeated style of the Greeks and developed the Arch, vault and dome of the Etruscans.
10
New cards
DIFFERENT TYPES OF VAULTS DEVELOPMENT BY THE ROMANS
1\.) Semi-circular / wagon headed / Barrel vault
2\.) Cross Vault
3\.) Hemispherical Dome
2\.) Cross Vault
3\.) Hemispherical Dome
11
New cards
FIVE TYPES OF ROMAN CONCRETE WALLS
Opus Quadratum, Opus Incertum, Opus Recticulatum, Opus Testaceum, Opus Mixtum
12
New cards
OPUS QUADRATUM
made up of rectangular blocks of stone with or without mortar joints but frequently secured with dowels and cramps.
13
New cards
OPUS INCERTUM
made up of small stones laid in a loose pattern roughly assembling the polygonal work.
14
New cards
OPUS RECTICULATUM
fine joints were in diagonal lines like the meshes of a net.
15
New cards
OPUS TESTACEUM
triangular bricks (plan) specially made for facing the walls.
16
New cards
OPUS MIXTUM
consisted of bands of "tufa" introduced at intervals in the ordinary brick facing or alteration of rectangular blocks with small squared stone blocks.
17
New cards
Composite and Tuscan
TWO COLUMNS DEVELOPED BY ROMANS
18
New cards

COMPOSITE ORDER
One of the five classical orders, popular especially since the beginning of the Renaissance but invented by the ancient Romans, in which the Corinthian order is modified by superimposing four diagonally set Ionic volutes on a bell of Corinthian acanthus leaves.
19
New cards
TUSCAN ORDER
a simplified Roman Doric characterized by an unfluted column and a plain base, capital, and entablature having no decoration other than moldings.
20
New cards
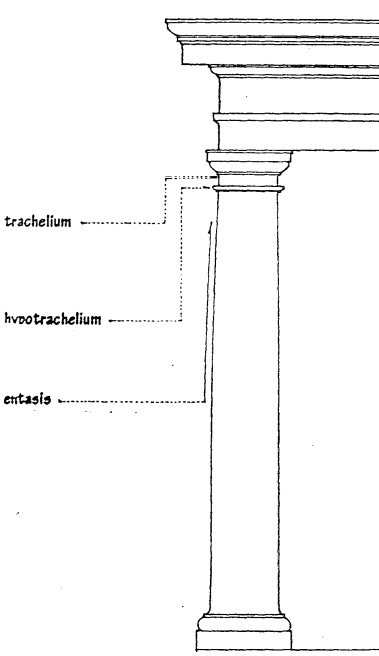
TRACHELIUM
that part of the necking between the hypotrachelium and the capital of a classical column.
21
New cards
HYPOTRACHELIUM
any member between the capital and the shaft of a classical column.
22
New cards
DRUM
any of several cylindrical stones laid one above the other to form a column or pier.
23
New cards
ROMAN BUILDING TYPES
forum, rectangular temples, circular &polygonal temples, basilicas, thermae, balneum, theaters/odeion, amphitheater, triumphal arches, town gatewats, pillars of victoryr monumental columns, palaces, roman houses, aquedects, bridges or pons, fountains
24
New cards
FORUM
open space used as a meeting place, market or rendezvous for political demonstrations.
25
New cards
eg FORUM OF TRAJAN
the largest Forum
26
New cards
eg FORUM ROMANUM
oldest and most important forum.
27
New cards
RECTANGULAR TEMPLES
used Pseudo-Peripteral Style, raised in a "podium" and oriented to the south.
28
New cards
CIRCULAR & POLYGONAL TEMPLES
derived fromt the temples of the Greeks & the Etruscans which became the prototype of the Christian baptistery
29
New cards
eg TEMPLE OF VESTA ROME
the most sacred shrine& source of Roman life and power.
30
New cards
eg THE PANTHEON ROME
most famous & perfect preservation of all ancient buildings in Rome.
31
New cards
BASILICAS
halls of justice or Assembly hall.
32
New cards
eg TRAJAN'S BASILICA
built by Apollodorus of Damascus.
33
New cards
eg BASILICA OF CONSTANTINE
also known as Basilica Maxentius or Basilica Nova.
34
New cards
THERMAE
a palatial public bath with three main parts
35
New cards
a. MAIN BUILDING
the central structure with chief apartments.
36
New cards
TEPIDARIUM
warm room
37
New cards
CALIDARIUM
hot room or with hot water bath
38
New cards
FRIGIDARIUM
cooling room
39
New cards
SUDARIUM
dry sweating room
40
New cards
APODYTERIA
dressing room
41
New cards
PALAESTRA
for physical exercise
42
New cards
UNCTUARIA/ UNTORIA
place for oils and perfumes
43
New cards
SPAERESTERIUM
game room
44
New cards
b. XYSTUS OR PUBLIC PARK WITH AVENUE OF TREES
a large open space with trees, statues & fountains, part of it was used as a stadium for foot racing and where athletic sports took place
45
New cards
c. OUTER RING OF APARTMENTS
LECTURE ROOMS, EXEDRAE, COLLONADE, LARGE RESERVOIR
46
New cards
eg THERMAE CARACALLA
with a capacity of 1,600 bathers
47
New cards
eg THERMAE OF DIOCLETIAN
largest capacity of 3000 bathers
48
New cards
BALNEUM
a private bath in Roman palaces and houses
49
New cards
TEPIDARIUM
warm room
50
New cards
CALIDARIUM
hot room or with hot water bath
51
New cards
FRIGIDARIUM
cooling room
52
New cards
eg HADRIAN VILLA
summer bath
53
New cards
THEATERS OR ODEION
Roman theaters were built up by means of concrete vaulting supporting tiers of seats, it was restricted to semi circle.
54
New cards
ORCHESTRA
a semicircular space in the front of the stage of an ancient roman theater, reserved for senators and other distinguished spectators.
55
New cards
AMPHITHEATER
used for gladiatorial combats, elliptical in plan.
56
New cards
eg COLOSSEUM
also known as "FLAVIAN AMPHITHEATER"
57
New cards
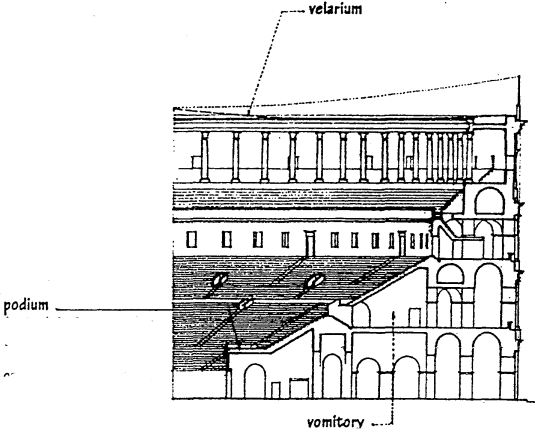
VELARIUM
a canvas awning drawn over an ancient Roman amphitheater to protect the audience from rain or sun.
58
New cards
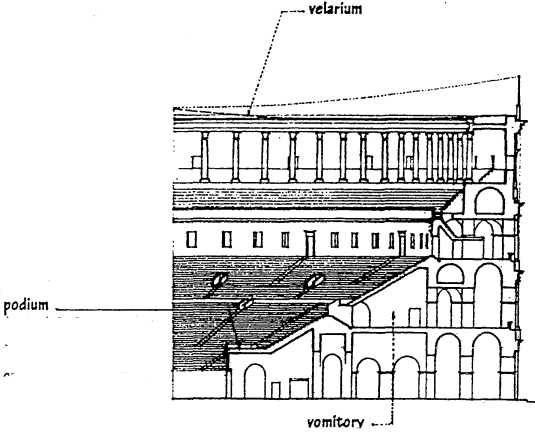
PODIUM
a raised platform encircling the arena of an ancient Roman amphitheater, having on it the seats of privileged spectators.
59
New cards
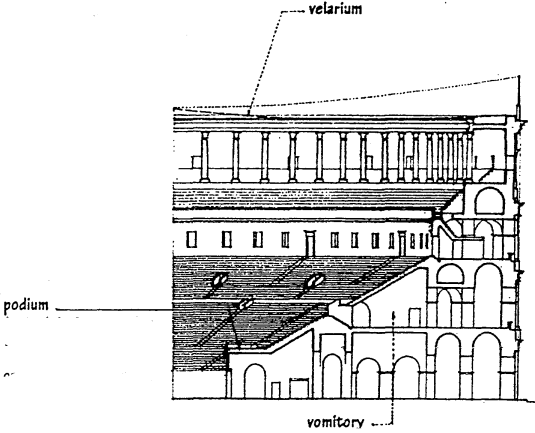
VORMITORY
a large opening, as in an ancient Roman amphitheater or stadium, permitting large numbers of people to enter or leave.
60
New cards
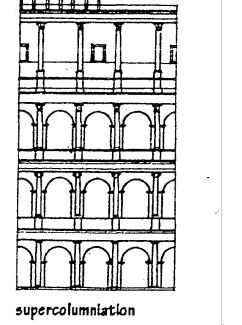
SUPERCOLUMNIATION
the placing of one order of columns above another, usually with the more elaborate orders at the top.
61
New cards
TRIUMPHAL ARCHES
erected to commemorate victorious campaign of emperors and generals
62
New cards
TOWN GATEWAYS AND ARCHWAYS
three main types
63
New cards
Three main types of gateways
a. As a protective wall & commemorative monument. b. As an ornamental portals & forum or market places c. Arch built at main street intersection which were collonated.
64
New cards
PILLARS OF VICTORYOR MONUMENTAL COLUMNS
were erected to record triumphs conquered by land of victorious Generals.
65
New cards
PALACES
use to house the Emperors.
66
New cards
AQUEDUCTS
use for water supply with smooth channels or "specus" lined with hard cement and carried on arches, in several tiers.
67
New cards
eg PALACE OF DIOCLETIAN
the largest roman palace and often called a "city in a house"covered a total of 8 acres.
68
New cards
ROMAN HOUSES
Three types of a Roman House
69
New cards
Three types of a Roman House
Domus, Villa/country house, Insula/ apartment block
70
New cards
DOMUS
center of family apartments.
71
New cards
PARTS OF DOMUS
prothyrum, atrium, tablinum, peristyle, cubicula, oecus, alae, kitchen and pantry
72
New cards
PROTHYRUM
entrance passage
73
New cards
ATRIUM
entrance court that is open to the sky.
74
New cards
TABLINUM
open living room
75
New cards
PERISTYLE
an inner collonated court with garden
76
New cards
CUBICULA
bedroom
77
New cards
OECUS
reception room
78
New cards
ALAE
recesses for conversation
79
New cards
KITCHEN & PANTRY
kitchen and pantry
80
New cards
B. VILLA OR COUNTRY HOUSE
a luxurious house with surrounding terraces and gardens, colonnades, palasestae, theaters, & thermae.
81
New cards
C. INSULA OR APARTMENT BLOCK
many storeyed tenement also called "Workmen's dwelling"
82
New cards
AQUEDUCTS
use for water supply with smooth channels or "specus" lined with hard cement and carried on arches, in several tiers.
83
New cards
BRIDGES OR "PONS"
simple, solid and practical construction designed to resist the rush of water.
84
New cards
FOUNTAINS
striking features of ancient & modern Rome.
85
New cards
Two Types of Roman Fountains
Lacus or Locus, Salientes
86
New cards
LACUS OR LOCUS
designed similar to a large basin of water.
87
New cards
SALIENTES
similar to a large basin of water with spouting jets.