LABORATORY
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
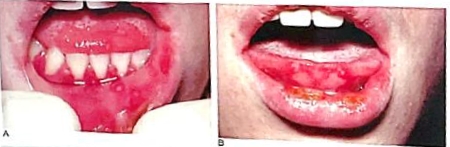
Identify the disease
Clinical feature
Histologic feature
Mode of transmission
Treatment
Primary herpetic gingivostomatitis
RARELY OCCURS BEFORE 6 MONTHS because of the presence of CIRCULATING ANTIBODIES in the infant DERIVED FROM THE MOTHER
Herpetic vesicle is an INTRAEPITHELIAL BLISTER filled with FLUID
transmission may occur by DROPLET INFECTION
ANTIBIOTIC THERAPY to prevent secondary infection
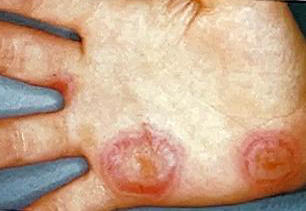
Identify the disease
Other name of the disease
Clinical feature
What is the associated syndrome
Erythema multiforme
Erythema multiforme exudativum
Occurs chiefly in YOUNG ADULTS, although it may develop at ANY AGE
Stevens-johnson syndrome
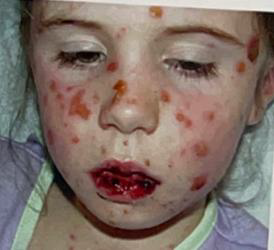
Identify the disease
Feature in the oral mucous membrane
Eye lesions feature
Genital lesions feature
Treatment
Prognosis
Stevens-johnson syndrome
Lesions may be EXTREMELY SEVERE and so painful that MASTICATION IS IMPOSSIBLE
Consist of PHOTOPHOBIA
Consist of non specific urethritis, balanitis or vaginal ulcers
No specific treatment
Seldom patient's life is ENDANGERED but chronic episodic recurrences may be DISCONCERTING
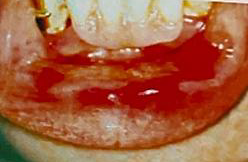
Identify the disease
Etiology
Clinical Features
Oral manifestation
Treatment
Stomatitis Venenata
DENTAL MATERIALS (vulcanite, acrylic, metal alloy bases)
If SECONDARY INFECTION occurs, the lesion may be SERIOUS
SECONDARY INFECTION is particularly common
DISCONTINUING ALL CONTACT with the offending material
Identify the disease
Other name
Clinical Features|
Oral manifestation
Treatment
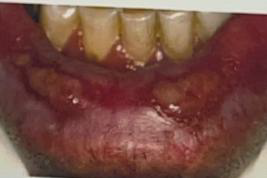
Stomatitis Medicamentosa
Drug allergy
Skin lesions
Common in gingiva, palate, lips, tongue
Antihistamine drugs
Identify the disease
Etiology
Clinical Features
4 types of pemphigus
Common features of the 4 types of pemphigus
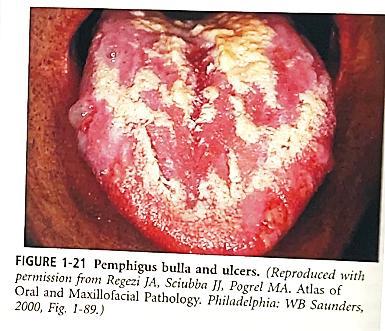
Pemphigus
Unknown since vesicles and bullae MAY ALSO DEVELOP IN MANY DISEASES
Any form of pemphigus may be accompanied by FEVER OR MALAISE
Pemphigus Vulgaris
Pemphigus Vegetans
Pemphigus Foliaceus
Pemphigus erythematosusThe INITIAL LESION of any type of pemphigus is always the VESICLE OR BULLA
Identify the disease
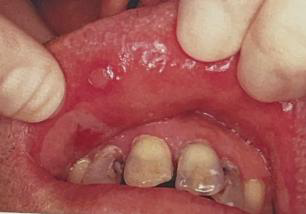
Course of pemphigus vulgaris is variable
Pemphigus Vulgaris
Terminating in death
Identify the disease
Clinical Feature
Course of pemphigus vulgaris is variable
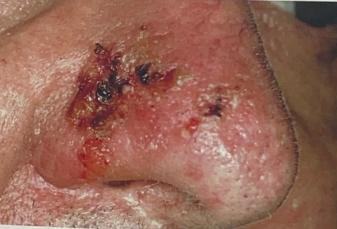
Pemphigus Vegetans
Occurs first on the NOSE, MOUTH, AXILLAE AND ANOGENITAL REGION
Terminating in death
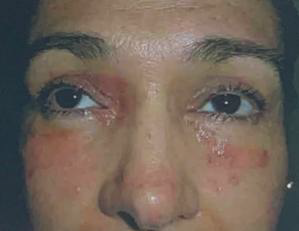
Identify the disease
Clinical feature
Pemphigus Foliaceus
Common in YOUNG ADULTS AND CHILDREN
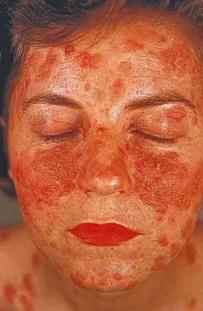
Identify the disease
Oral manifestation
Histologic feature
Differential diagnosis
Treatment
Products that can be used to relieve pain
Pemphigus erythematosus
Overwhelming STENCH
LOSS OF COHESIVENESS between epithelial cells
Erythema multiform
Corticosteroids
Rowagel
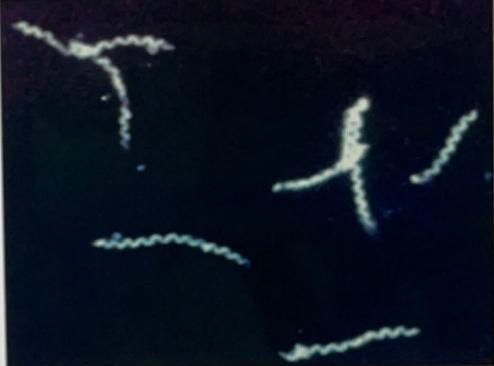
Identify the disease
Disease is caused by:
Oral manifestation
Syphilis
Treponema pallidum
Atrophic or interstitial glossitis is the most characteristic and important lesion of syphilis
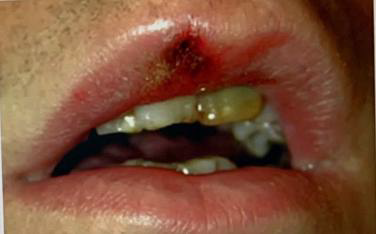
Identify the disease
Clinical feature
Primary stage of aquired syphilis
Lesion develops at the site of inoculation approximately three weeks after contact with the infection
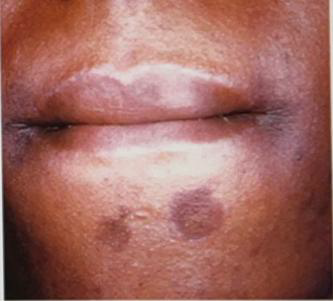
Identify the disease
Clinical feature
Secondary stage of aquired syphilis
Usually commencing about SIX WEEKS AFTER the primary lesion
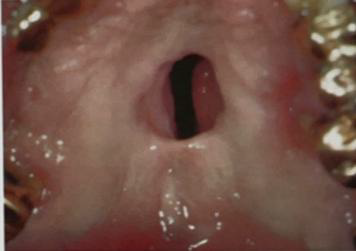
Identify the disease
Clinical feature
Tertiary stage of aquired syphilis
Late syphilis is not infectious
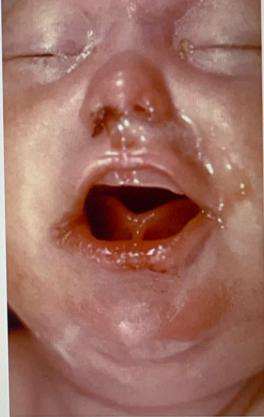
Identify the disease
Clinical feature
Histopathology
Differential diagnosis
Treatment
Congenital (prenatal) syphilis
HIGOUMENAKIS’S SIGN or IRREGULAR THICKENING of the sternoclavicular portion of the clavicle
PROLIFERATION of endothelial cells within small arteries and arterioles
SQUAMOUS CARCINOMA CELL
Dark field examination of SCRAPING or EXUDATE from active lesions
Penicillin
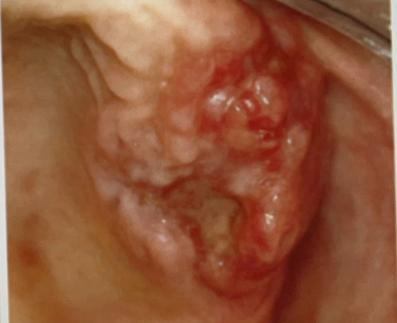
Identify the disease
One major form the disease
Etiology
Pathogenesis
Clinical feature
Oral manifestation
Forms of the disease
Histopathologic manifestation
Differential diagnosis
Definitive diagnosis
Treatment
Tuberculosis
MYCOBACTERIUM TUBERCULOSIS
AEROBIC (oxygenated)
The spread of M. tuberculosis is through small airborne droplets, which carry the organism through pulmonary air spaces
FEVER and CHILLS
Lesion occurring during the SECONDARY PULMONARY STAGE
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS
FOCI of CASEOUS NECROSIS surrounded by lymphocytes and occasional multinucleate giant cells
PRIMARY SYPHILIS
Microscopic examination
Prolonged multi drug therapy (isoniazid, rifampin, ethambutol)