Psych chapter 2
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Curiosity, open-mindedness, and skepticism
Scientific Attitudes
Case Study
in depth analysis on a specific event or person
Natural Observation
Observes behavior as it occurs naturally
Limitations of correlational studies
No caustation, cofounding variables, no temporal precedence, 3rd variable
Theory
a well substaintiated explanation of the natural world, based on a body of scientific evidence
Limitations for Natural oberservation
risk of subject/ observer bias
limitations for case study
lack of generalizability, time and resources
Research Question
clear, focused, and open-ended question that guides the research process. It identifies what the researcher aims to explore or understand.
Identify a question, gather information, conduct research, analyze data, build a body of knowledge
steps in the scienetific process
Limitations of expiremental research
over confidence in findings, cofounding variables
Hypothesis
A specific, testable prediction about the outcome of a study or experiment.
students could be any age, no specific time frame
What is wrong with this Hypothesis? Students who sleep continuously for 8 hours before an exam will score higher than those who sleep continuously for 4 hours
Independent variable amount of sleep dependent variable test scores
Identify the Independent Variable and the Dependent variable in the text: Students who sleep continuously for 8 hours before an exam will score higher than those who sleep continuously for 4 hours
Independent Variable
The variable that is manipulated by the researcher.
Dependent Variable
The variable that is measured and expected to change as a result of the independent variable.
Operational Definition
Defines a variable in terms of the specific procedures or measures used to assess it. for example studying academic sucess "a GPA of 3.5 or higher in a semester." is more specific
Subjective Measures
reporting your own thoughts, feelings, perceptions, sensations, behaviors. self report or proxy report
Behavior Measures
Directly observable behaviors, often using tools such as psychological or physiological tests.
Correlational method
A relationship between two variables; does not imply causation.
Positive Correlation
When one variable increases, the other variable also increases.
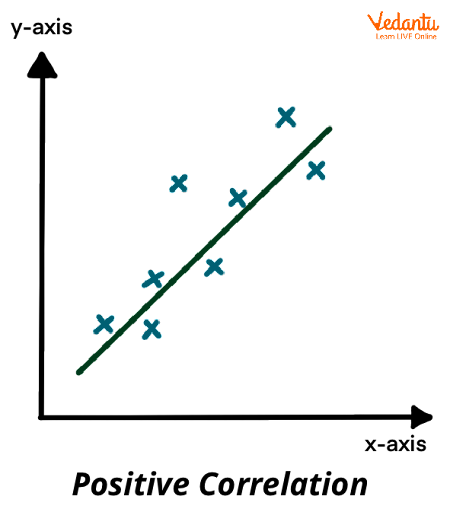

The taller you are the more you weigh
Postive correlation
Negative Correlation
When one variable increases, the other variable decreases.
Netflix watching increases, grade decreases
Negative correlation
Descriptive Research Method
observes and collects data, this method focuses on what is happening, not why. No cause-and-effect relationships are studied.
Experimental Research Method
researcher manipulates one or more variables to observe the effect on another variable while controlling other factors.
Validity
Refers to how well an expirement procedure actually tests what it is designed to test
Reliability
Refers to the ability to consistently produce a given result when measuring an expirement
Temporal Precedence
the ability to determine which variable happens first. If you can't tell the order, cause and effect can't be established.
Third Variable
An extra variable in a study that isn’t part of the main relationship being examined. It might influence the results, but not necessarily.
Random Sampling
A method of sampling from a population where every individual has an equal chance of selection; names are drawn at random
Representative Sample
A sample that accurately reflects the characteristics of the population; equal percentage of brown- and blonde-haired students in the sample as the population
Population
a set of individuals of intrest in a study
a sample
a set of individuals from a population. intended to represent the population
Nocebo
The negative version of placebo; feeling headaches after sugar pill because “headache” was said to be side effect
Social Desirability
The tendency to respond in a socially desirable manner; giving the answer you think someone wants to hear
Cofounding Variable
A specific third variable that affects both the independent and dependent variables, creating a false or misleading relationship between them.
Placebo Affect
people recieving a treatment show change in behavior because of their expectations not because the treatment itself
Expectancy effects
Subtle unintentional ways a researchers or participants expectation can influence the result of a study
Human research ethics
Consent for everything, Benefits outweigh risks, anonymous, no deception, they must be told purpose of study after, ethics team must be informed
Animal Research Ethics
Justifications must be made for the certain species, no unnecessary harm benefits outweigh the risks, 3 R’s replacement, reduction, refinement, very strict protocol overseen by veterinarians, and all protocals over seen by Ethics board
Limitation for Descriptive methods
Doesnt establish why something happens only that there is an occurance