ARKY FINAL EXAM FLASHCARDS ( Textbook Chapters 7-8, 14, 16-18 and Lecture Slides from near east and on)
1/399
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
400 Terms
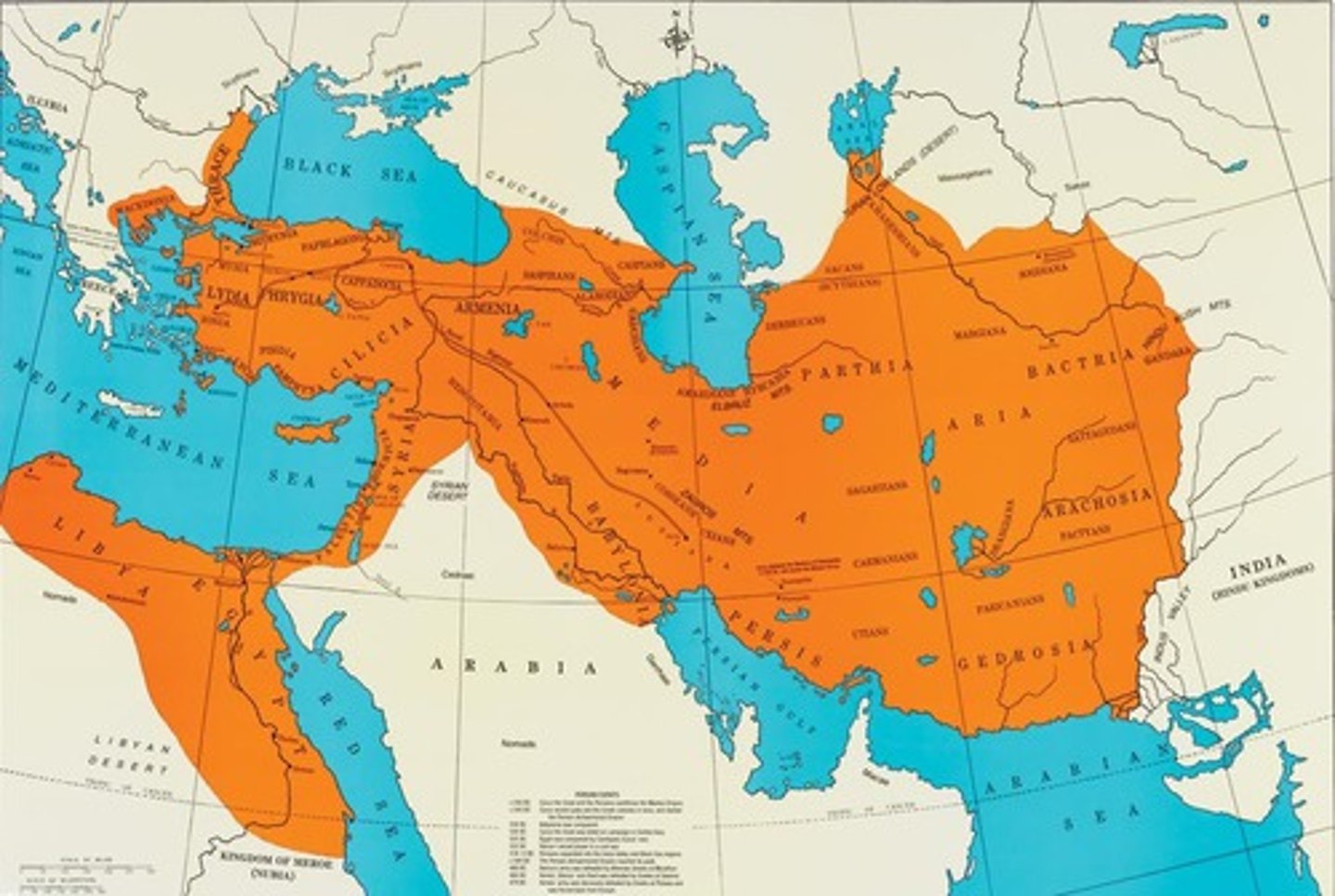
Ancient Near East regions
Mesopotamia, Anatolia, the Levant, and Iran.
Earliest major cultural centers before 2000 BCE
Ur and Uruk in southern Mesopotamia.
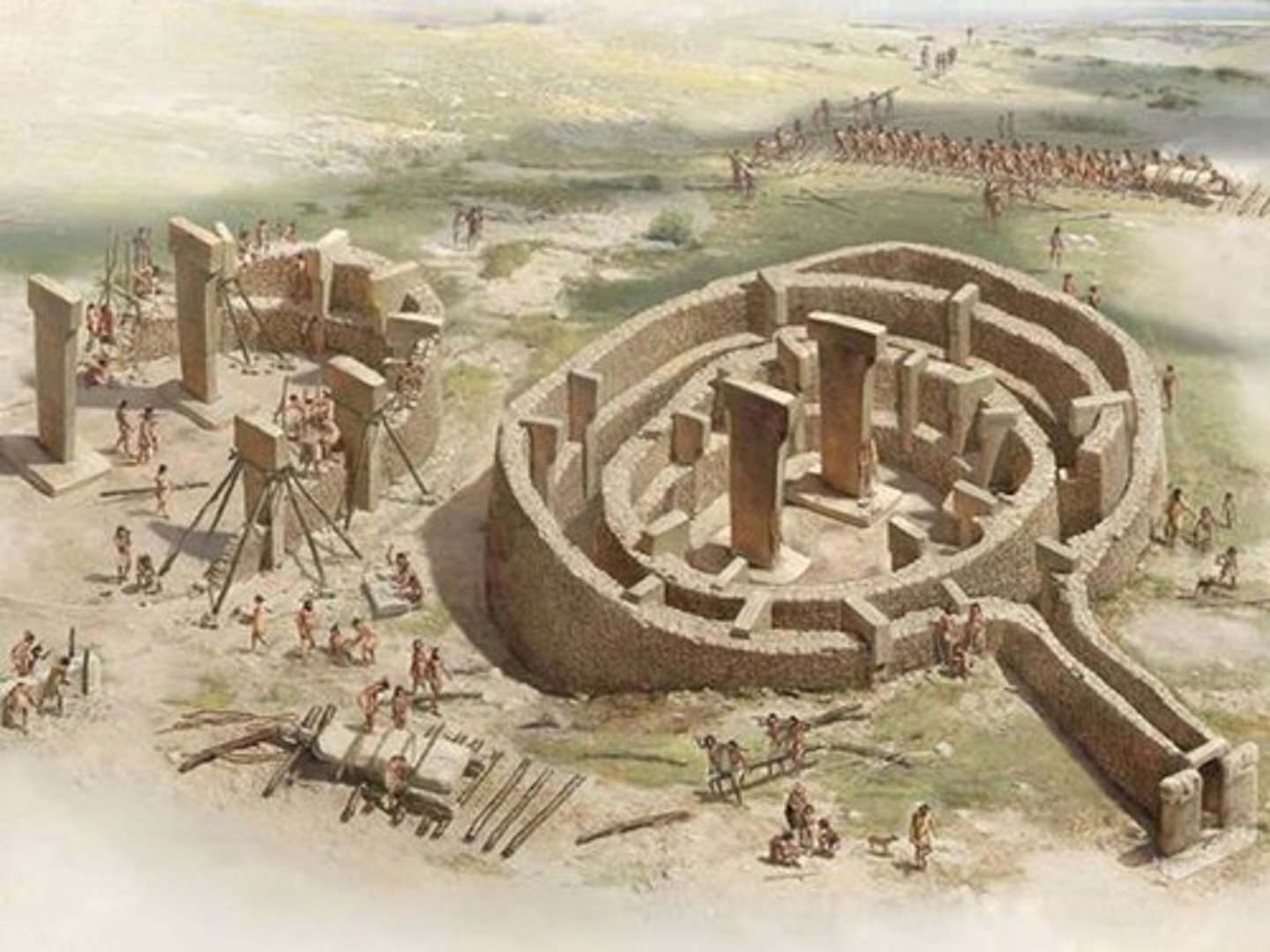
Göbekli Tepe (Anatolia)
Pre-pottery ritual site (9500-8000 BCE) with massive stone enclosures.

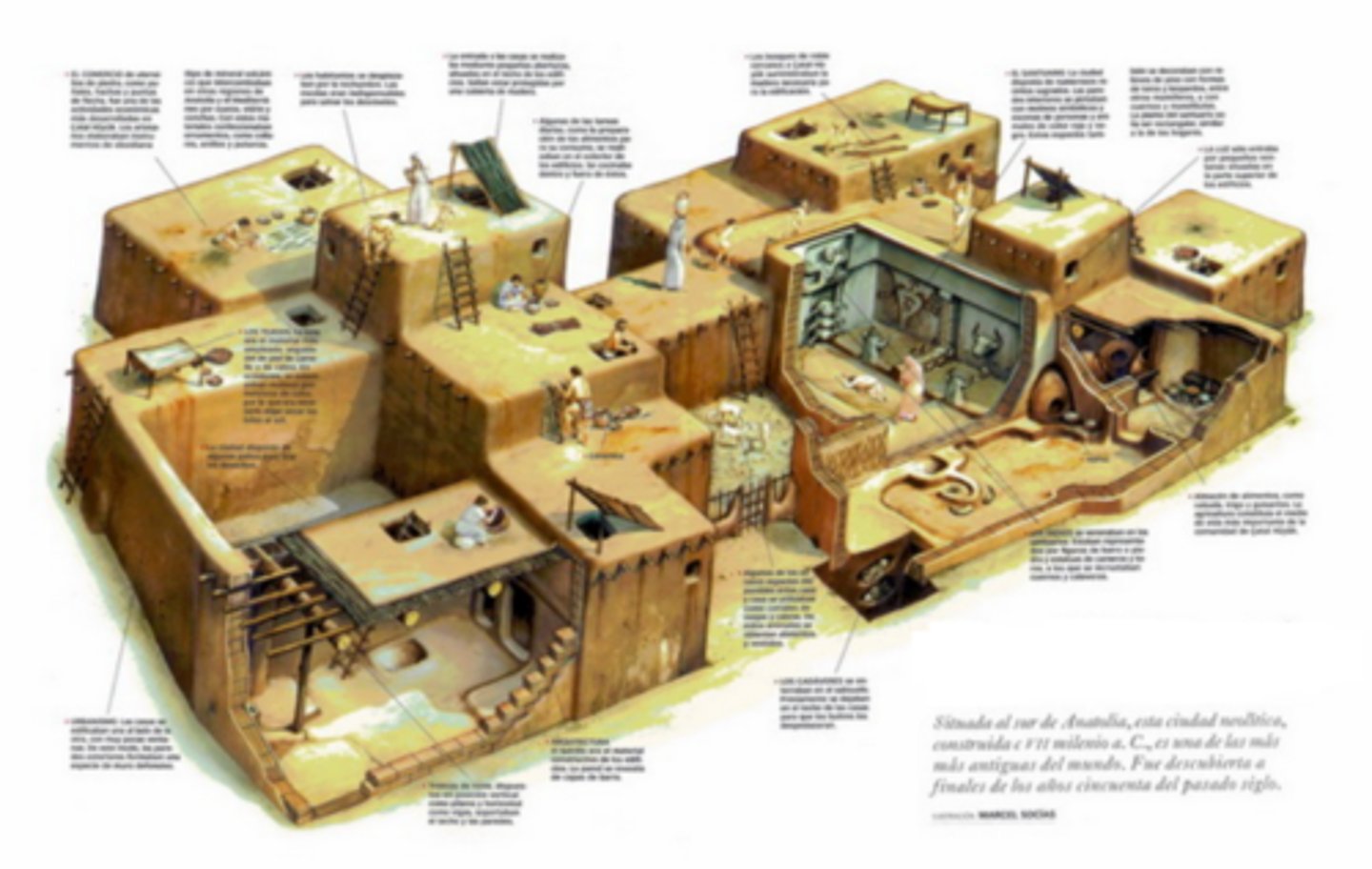
Çatalhöyük (Anatolia)
Dense Neolithic settlement (7500-6400 BCE) with wall-entry homes.
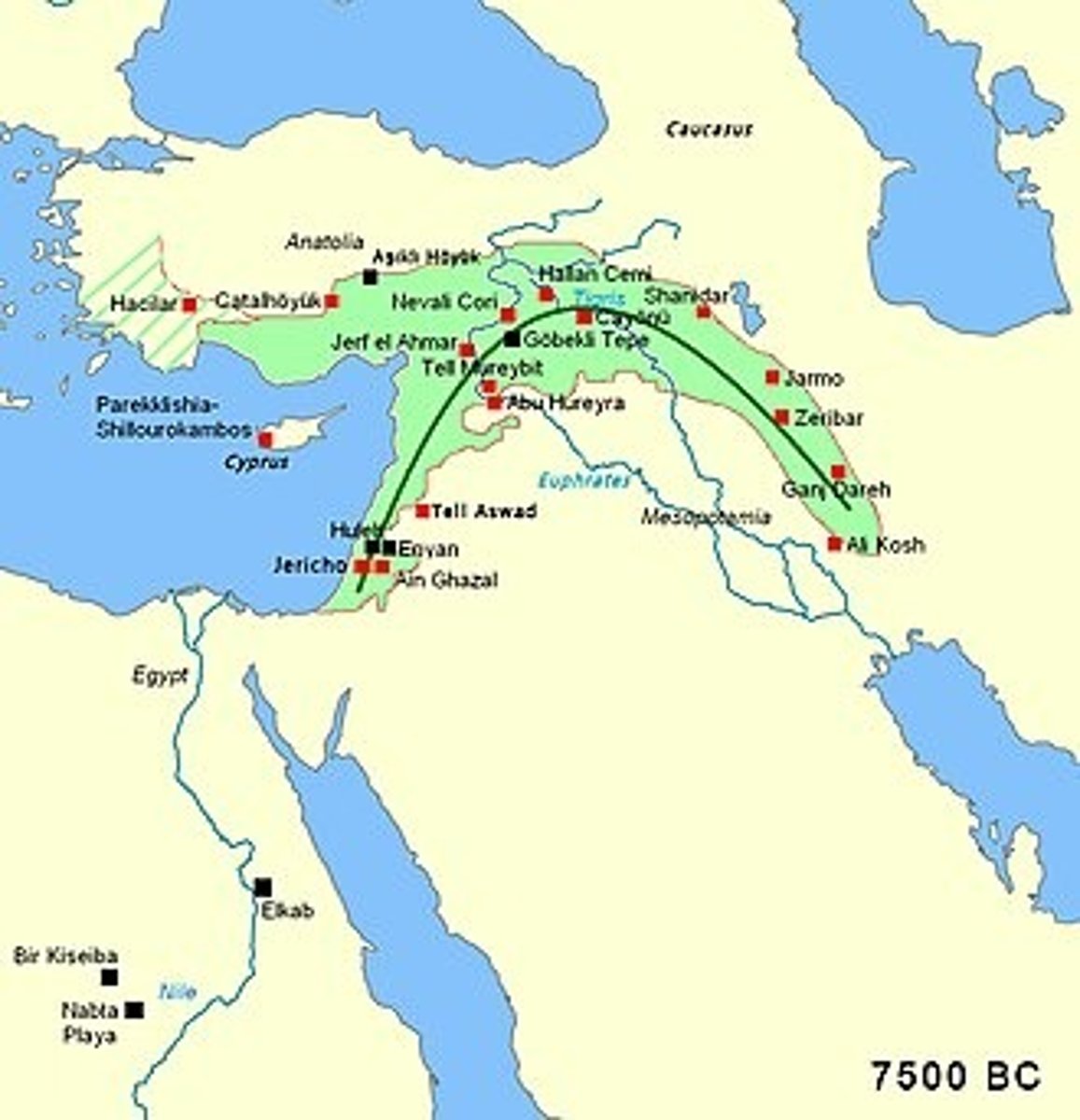
Earliest major Levantine Neolithic sites
Jericho, Tell Aswad, Ain Ghazal.
Definition of an empire
Large political entity ruling diverse societies under one ruler.

Two major traits of empires
Vast size and provincial autonomy with tribute.
Earliest empires of Near East
Akkadian; 3rd dynasty of Ur (Ur III); Elam.
Major 1st millennium BCE empires
Assyrians, Neo-Babylonians, Persians.
Political fragmentation of Mesopotamia after 2000 BCE
Collapse of Ur III, Amorite rise, Hurrian migrations.
Alaca Höyük (Anatolia)
A large Anatolian mound with rich Early Bronze Age royal tombs.
Date of Alaca Höyük Royal Graves
2350-2150 BCE.
Royal grave structure type
Shaft tombs sealed with wooden beams.
Goods found in Royal Graves of Alaca Höyük
Gold, electrum, bronze weapons, figurines, standards.
Earliest iron in Anatolia
Gold-handled meteoritic iron dagger at Alaca Höyük.
Purpose of Bronze Standards
Ritual symbols (solar disks, bulls, deer) mounted on poles/wagons.
Kanesh (Kültepe)
Assyrian merchant colony and major trade hub.
Karum (in Kanesh)
Assyrian trading quarter exempt from local taxes.
Dates of Assyrian trade at Kanesh
1900-1750 BCE.
Trade from Assur to Kanesh
Tin and textiles.
Trade from Kanesh to Assur
Silver.
Importance of Kanesh tablets
23,000+ cuneiform tablets documenting business and daily life.
What Kanesh tablets reveal
Marriage, loans, contracts, inheritance, merchant letters.
Earliest Indo-European language evidence
Hittite loanwords in Kanesh tablets.
Conqueror of Kanesh in 1820 BCE
Anitta of Kussara.
Significance of Anitta's conquest
Begins Hittite royal tradition; curses Kültepe.
Who were the Amorites
Semitic migrants from Syria who settled southern Mesopotamia.
Who were the Hurrians
People likely from the Caucasus who settled northern Mesopotamia.
Isin-Larsa Period
Struggle for power in Mesopotamia (2025-1763 BCE).
Founder of Isin dynasty
Ishbi-Erra.
Importance of Ishbi-Erra
Expelled Elamites; reestablished southern power.
Decline of Isin
Lost access to water after canals were rerouted.
Rise of Larsa
Controlled trade routes; strengthened by Larsan King Gungunum.
Key rivalries in Isin-Larsa
Isin vs Larsa competing for canal access and trade.
Mashkan-Shapir
Canal-based city and secondary capital of Larsa.
Mashkan-Shapir layout
5 districts, canals instead of streets, 2 harbors.
Industries in Mashkan-Shapir
Copper workshops, pottery, temples with animal statues.
Decline of Mashkan-Shapir
Early 2nd millennium collapse of Gulf trade.
Dilmun importance
Key trading hub between Mesopotamia and Indus Valley.
Dilmun peak prosperity
2300-1700 BCE.
Dilmun trade monopoly
Copper from Oman.
Cultural links of Dilmun
Dilmun seals found in Kanesh and Indus Valley.
Hammurabi dominance
Hammurabi (1792-1750 BCE).
Hammurabi unification method
Mixed diplomacy and warfare.
Hammurabi's conquests
Isin, Larsa, Mari, Eshnunna.
Hammurabi's centralization policy
Took estates from elites; strengthened royal control.
Hammurabi stele location
Susa (Iran).
Top scene on Hammurabi stele
Hammurabi receiving laws from Shamash, sun god.
Topics in Hammurabi's Code
Contracts, inheritance, wages, slavery, crime, medicine.
Social classes in Hammurabi's Code
Aristocrats, commoners, slaves.
Women's rights in Hammurabi's Code
Hold property, divorce abusive husbands if 'virtuous'.
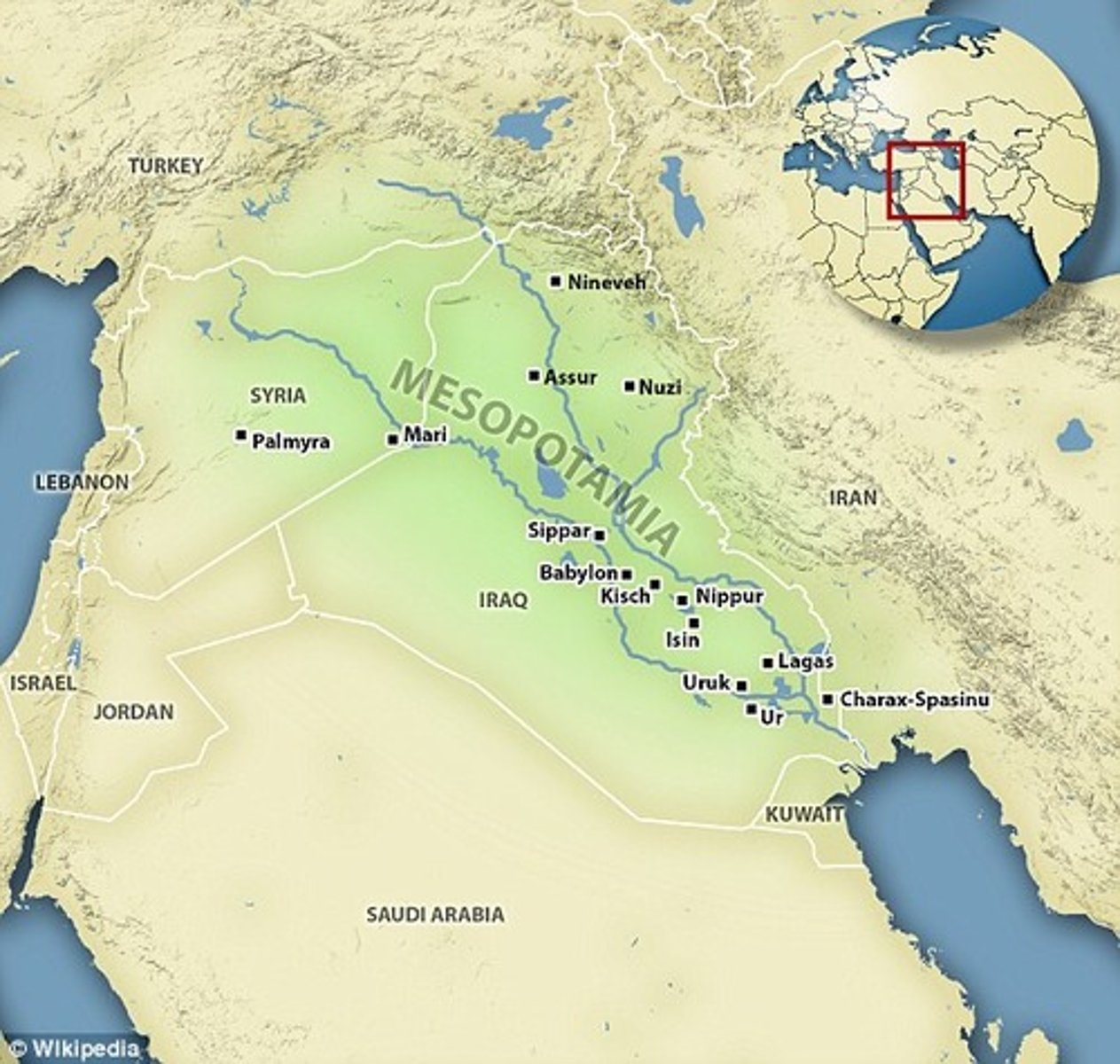
Mari
A powerful city-state on the Euphrates.
Preservation of Mari's archives
Destruction by Hammurabi.
Number of Mari tablets
20,000.
Revelations from Mari letters
Diplomacy, politics, marriage alliances, economy.
King of Mari
Zimri-Lim.
Iconic Mari fresco
Ishtar granting kingship to Zimri-Lim.
Hittite dynasty founder
Labarna (early king in Hittite history).
Hattusili I accomplishments
Conquered Hatti; made Hattusa capital.
Mursili I achievement
Sacked Babylon in 1595 BCE.
Hattusa significance
Capital with 10,000 clay tablets.
Hattusa archaeological importance
Massive fortifications, temples.
Mitanni culture
Hurrian-speaking; elite with Indo-Aryan names.
Mitanni dates
1500-1300 BCE.
Mitanni capital
Washukanni.
Powers competing around 1400 BCE
Egypt, Mitanni, Hittites.
Ahmose I major action
Drove out Hyksos; reclaimed Levant.
Thutmose I expansion
Reached Euphrates River.
Battle of Megiddo date
1457 BCE.
Battle of Megiddo winner
Thutmose III (Egypt).
Suppiluliuma I significance
Rebuilt Hittite Empire; defeated Mitanni.
Dakhamunzu letter
Egyptian queen asking for a Hittite prince.
Fate of the Hittite prince
Murdered en route to Egypt.
Amarna Letters date
1350-1332 BCE.
Language of Amarna letters
Akkadian.
Importance of Amarna letters
Reveal diplomacy and vassal politics.
Common themes in Amarna letters
Loyalty claims, betrayal, requests for troops.
Location of Qatna
Syria at crossroads of major routes.
Findings at Qatna
Rich royal tombs with jewelry and statues.
Destruction of Qatna
Hittites in 1340 BCE.
Who destroyed Qatna?
Hittites in 1340 BCE.
Uluburun date?
~1400 BCE.
Significance of shipwreck?
Evidence for international luxury trade.
Contents of Uluburun cargo?
Copper ingots, glass, ivory, ebony, gold jewelry.
Date of Hittite collapse?
Around 1200 BCE.
Causes of Hittite collapse?
Sea Peoples, famine, internal revolts.
What happened to Hattusa?
Abandoned and burned.
Neo-Hittite states?
Small Iron Age states in Syria/Anatolia.
Who were the Sea Peoples?
Aegean/Eastern Mediterranean raiders.
Egyptian king who fought them?
Ramesses III.
Impact of Sea Peoples?
Collapse of Hittites, destruction of coastal cities.
Philistines origin?
Likely Aegean; multiple origins confirmed.
Philistine settlement region?
Southern Levant coastal plain.
Philistine Pentapolis?
Gaza, Gath, Ekron, Ashkelon, Ashdod.
Philistine cultural traits?
Mycenaean pottery, Aegean rituals.
Philistine contributions to Levant?
Iron technology, new plants (opium poppy, cumin, sycamore).
Phoenician homeland?
Lebanon coast: Tyre, Sidon, Byblos.
Phoenician economic strengths?
Maritime trade, purple dye, ivory carving.
Tyrian purple source?
Murex snail.
Phoenician colonies?
Carthage, Cádiz, Mediterranean ports.