IBC- quiz
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
What are the 3 types of bonds found in living things
Ionic- strongest
Covalent- Strong
Hydrogen- Weak
What are Ionic bonds
Occur when an atom transfers and electron to another atom
What are Ionic bonds made out of
They are made between metals and nonmetals
How to identify if its a ionic bond ( hint Electronegativity)
Electronegativity difference > 2.0
Are Ionic bonds souluble in water
Yes
Do they have either a high or low melting/boiling point
high melting / boiling point
Can they conduct electricity
Yes
What is a covalent bond
Sharing of electrons between nonmetals
What are covalent bonds made of
Gases, liquids or solids ( made of molecules)
How to determine a covalent bond in terms of electronegativity
Electronegativity difference < 2.0
DO covalent bonds have either a low/high melting / boiling point
low melting/boiling point
Can they conduct electricity
No
Are they souluble in water
No
What are Polar covalent bonds
Electrons unequally shared
What are polar covalent bonds electronegativity
electronegativity is >0.5<2
What is the partial charge of polar covalent bonds
Results in a charge separation in a bond- partial positive partial negative s- s+
What are nonpolar covalent bonds
Electrons share evenly in the bond
WHat is the difference in electronegativity and what types of molecules are they
No difference in electronegativity (delta EN) diatomic molecules H_2 ,N_2 ,O_2 or delta En is <0.5
What are molecules
Two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds
WHat are the 3 ways to represent molecules
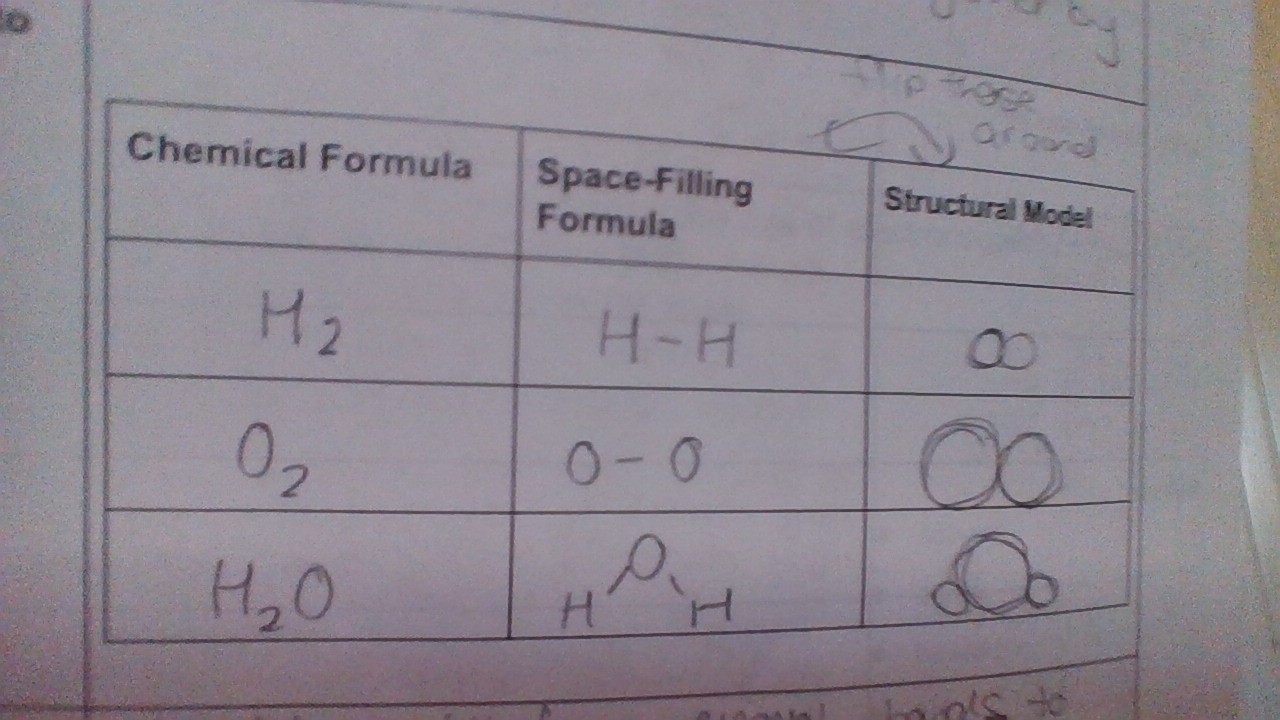

Multiple bonds
An atom will form enough bonds to fill its outer shell (octet)
What is an example of multiple bonds
Ex: carbon has 4 valence electrons . It will form 4 bonds to get a total of 8 electrons in its outer shell.
How many electron pairs can be shared
More than 1 electron pair can be shared at a time forming multiple bonds between atoms
Why are multiple bonds shorter than single bonds
Multiple bonds tend to he shorter than single bonds because the atoms are held more tightly together
Structure of water
Water is a polar covalent molecule . A polar covalent molecule forms between oxygen and hydrogen
What are the main properties of water and explain each of them
High melting boiling point
Ice less dense than liquid water
good solvent- polar molecules and ionic compounds
Cohesion/ adhesion
surface tension
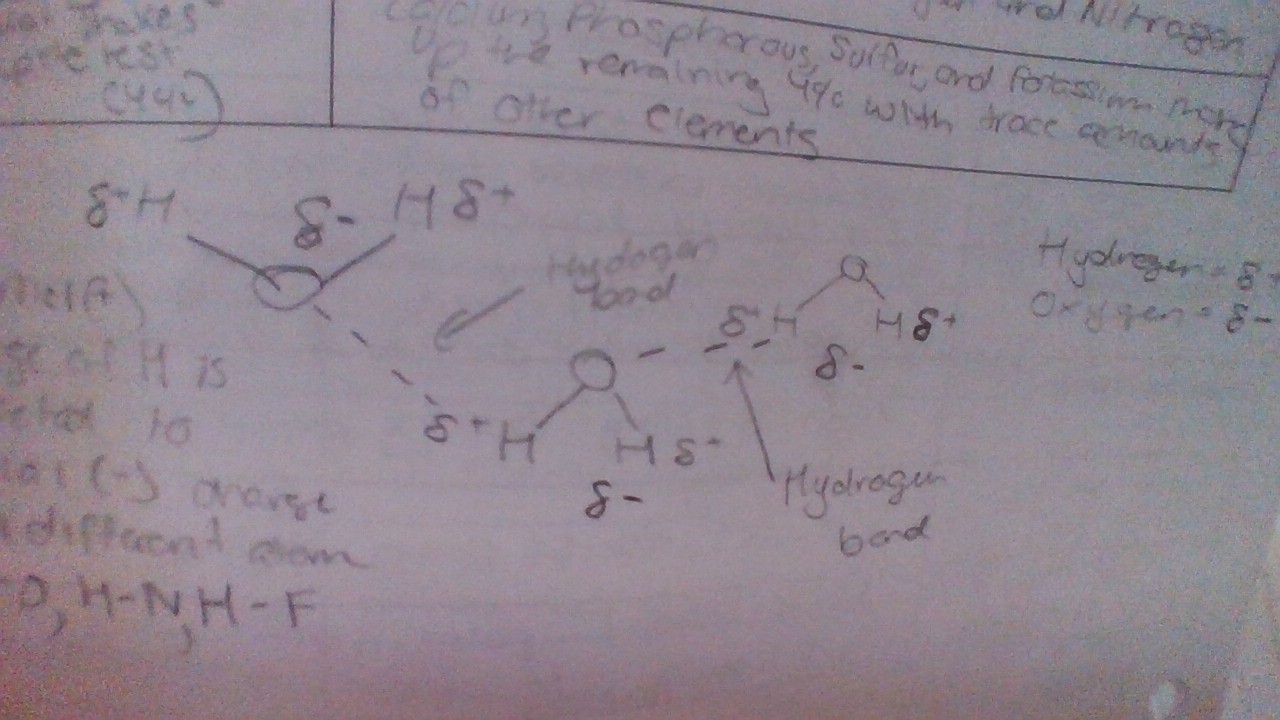
Hydrogen Bonds
are weak attractive forces between polar molecules, such as water, resulting from the attraction between the partially positive hydrogen atom and partially negative oxygen atom.
WHat are Acids Bases and PH
pH is the measure of the hydrogen ion (H+) concentration of a solution. Solutions with a high H+ concentration have a low pH (acid).
Solutions with a low H+ concentration have a high pH (base).
what is the PH scale
The pH scale is a logarithmic scale
Each pH unit is a tenfold
difference.
WHat is an example of a acid and a base
Ex. coffee is 100 times
more acidic than pure
water.
What are buffers
A buffer is a solution that resists changes in pH
by absorbing excess H+ ions (raise pH) or
by donating H+ (lower pH) ions.
what is the PH range most living organisms need to survive
Most organisms need to maintain a very narrow pH range, near neutral, to survive.
WHat are the elements of life
There are about 25 elements
that are essential to life
WHat are the 4 main elements of living things
96% of living matter is made
up of Oxygen, Carbon,
Hydrogen and Nitrogen.
What makes up the rest 4%
Calcium, Phosphorous, Sulfur,
and Potassium make up the
remaining 4% with trace
Amounts of other elements.
Draw a hydrogen bond

What is an ion?
A negatively or positively charged ion
Why would atoms form ionic bonds?
So that they can have a full octet shell and be stable (Have a noble gas configuration)
What are the two types of ions?
Cations and Anion
Which atoms tend to give away electrons and which atoms tend to take them?
Metals tend to give away electrons to form cations, while nonmetals tend to take electrons to form anions. Halogens and ALkali metals
What type of ions do different elements form?
Non Metal and nonmetal = Ionic bond
Nonmetal and metal = covalent bond
Polar (equally shared) and nonpolar (not equally shared) covalent
How can we represent an ionic bond? (Be able to draw how a lewis dot structure can help us figure out the chemical formula.)
An ionic bond can be represented through a Lewis dot structure by showing the transfer of electrons from a metal to a nonmetal, highlighting the formation of cations and anions.