Biology module 5 - topic 1 (reproduction)
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
Difference between sexual and asexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction just means combining genetic material from two parents. Asexual reproduction produces offspring genetically identical to the one parent.
define reproduction
one or more parent organisms producing offspring
Haploid
A cell that contains a single set of chromosomes. (e.g gametes aka sex cells)
how are haploid cells produced
meiosis (in germ cells)
zygote
fertilised egg (diploid)
how many chromosomes are in a zygote
46
external fertilisation (with example)
eggs combine with sperm OUTSIDE of female body
ex) spawning:
aquatic females release their eggs and males release their sperm in the same area at the same time, often triggered by environmental signals
what environmental signals may trigger spawning
water temperature, tides, length of daylight
what are the advantages of external fertilisation
1. faster, more abundant
2. parents do not expend energy for gestation and caring for younng
3. females can continue to reproduce without waiting for first young to develop
what are the disadvantages of external fertilisation
1. more gametes must be produced
2. no control of gametes once released
3. decreases chances of successful fertilisation (improved by synchronised release of gametes e.g spawning)
4. Gametes and zygotes are exposed to predation and disease immediately
internal fertilisation
male directly deposits sperm into female body during mating
types of animals that use internal fertilisation
1. Placental mammals - protect offspring in female body
2. Reptiles + Birds - protect offspring in shelled or tough membraned eggs
3. Marsupials - uterus --> womb --> pouch
advantages of internal fertilisation
1. Less gametes have to be produces
2. More likely to be successful as gametes are positioned close together in female reproductive tract
3. gametes/zygotes protected from predation/disease
4. Developing young are fed and protected from predation and disease
disadvantages of internal fertilisation
1. Usually slower with fewer offspring
2. Mating rituals and practice are more complex to get to point of copulation
3. Potential for spread of sexually transmitted diseases throughout population
4. Energetically costly, requires ongoing energy from female parent
4 types of asexual plant reproduction (vegetative propagation)
Tubers - potatoes
Runners - underground modified stems/roots e.g strawberries
Rhizomes - underground HORIZONTAl modified stems e.g grasses
Bulbs - underground production of tiny baby bulbs around root of bulb
How do tubers work
How do
what is apomixis
2 types of (seeded) sexual plant reproduction and their difference
1. Angiosperms: plants that produce flowers and bear their seeds in fruit (reproduce through flowers)
2. Gymnosperms: plants that reproduce through cones
what is ‘alternation of generations’ reproduction
plants that have lifecycle in which organism has multicellular haploid stage and multicellular diploid phase
what types of plants reproduce via ‘alternation of generations’ WITH EXAMPLES
seedless - e.g fern and mosses
gametophyte
multicellular haploid plant structure that produces haploid gametes
sporophyte
multicellular diploid plant structure that can produce haploid spores
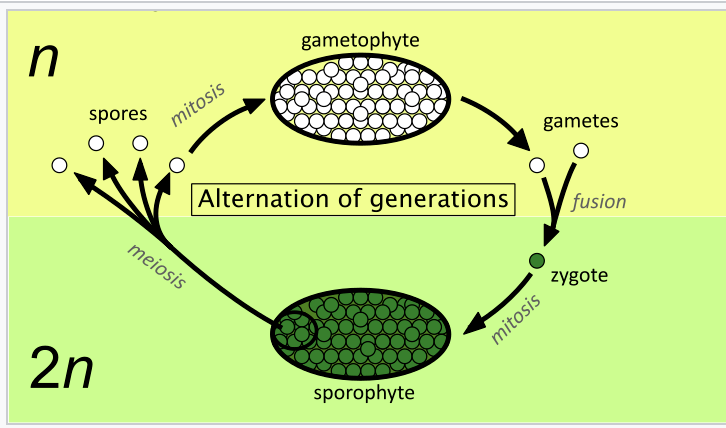
process of reproduction in ‘alternate generation’ planst
Gametophyte produces haploid gametes that fuse to form diploid zygote (SEXUAL REPRODUCTION)
Zygote grows by mitosis into diploid plant structure the sporophyte
Diploid sporophyte produces haploid spores by meiosis (ASEXUAL) which disperse and grow by mitosis into the gametophyte
what occurs in gymnosperm reproduction - cones examples
male cones (grow in lower branches) disperse a large number of pollen grains spread by wind relying on one to reach the right part of another individual of same species by chance
female cones grow in upper branches
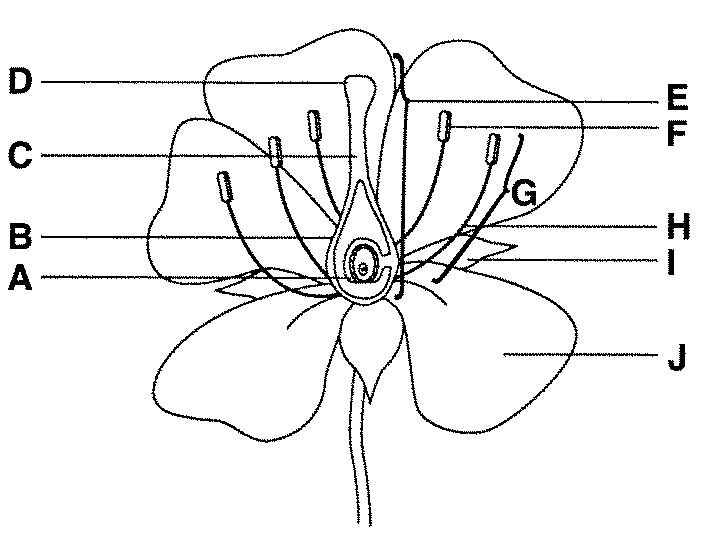
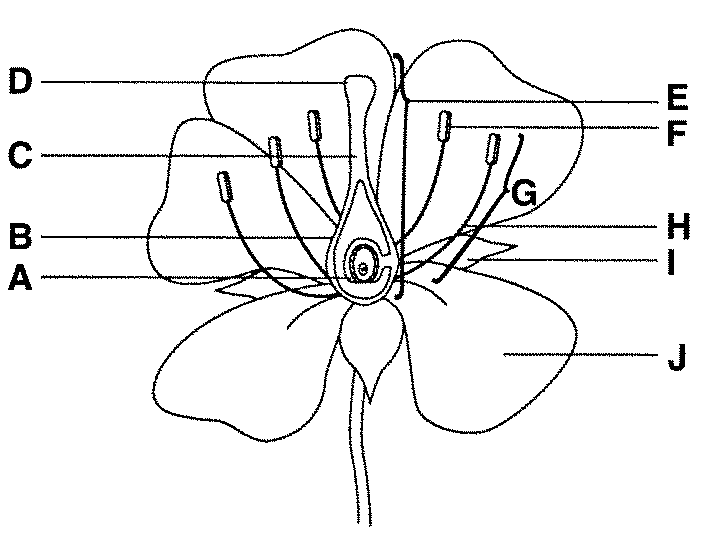
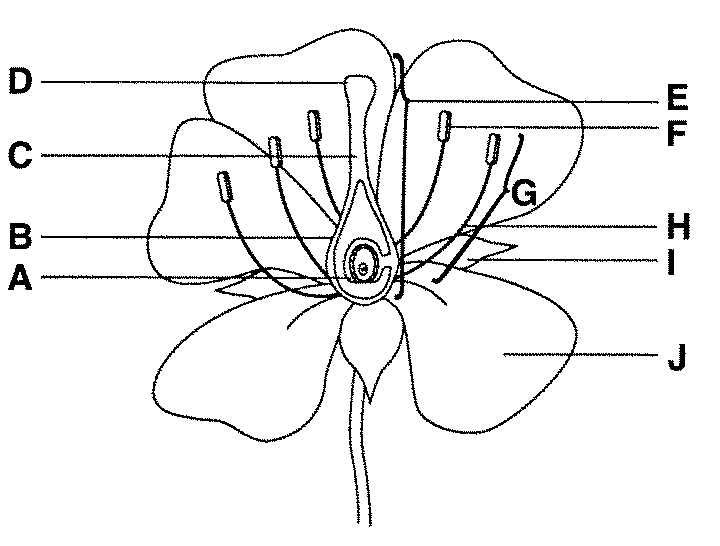
what is F function
anther male part of angiosperm that produces pollen - which contains sperm
what is H function
filament connects the anther to the base of the flower and supports it.
what is E
carpel/pistel — female section!
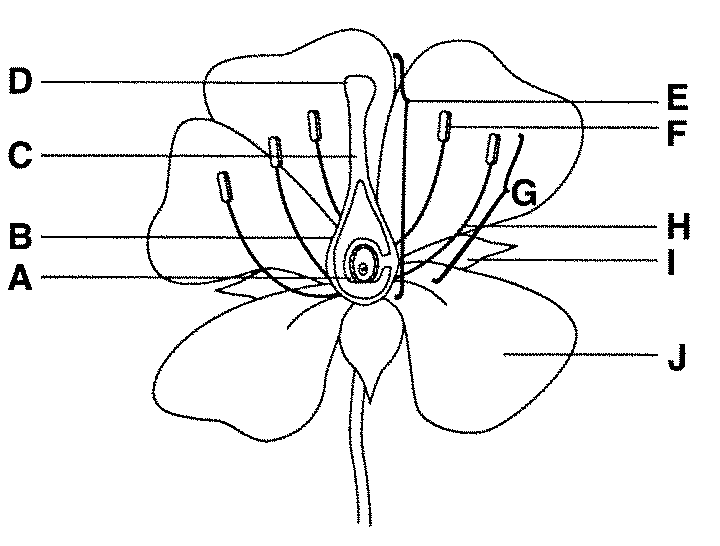
what is D and function
stigma, it is very sticky made to capture pollen
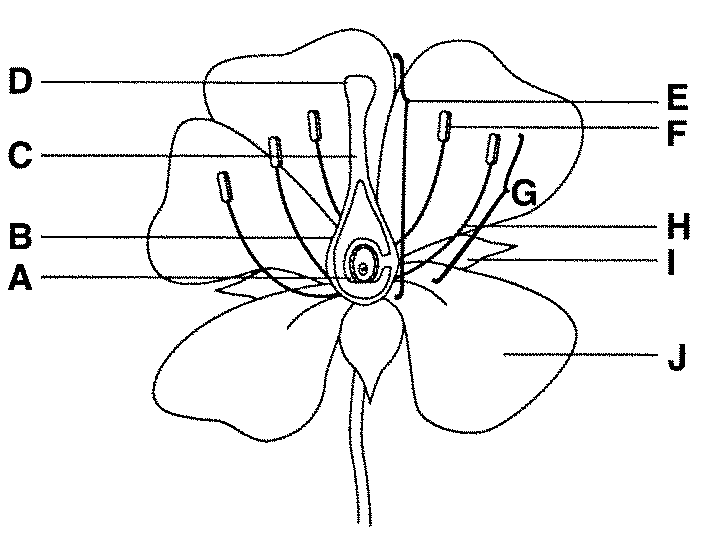
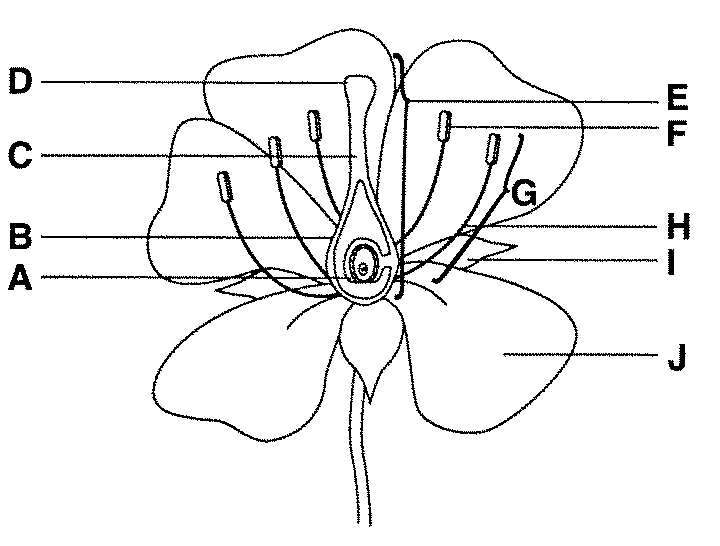
what is B and function
ovary, it grows to become fruit to protect the seeds
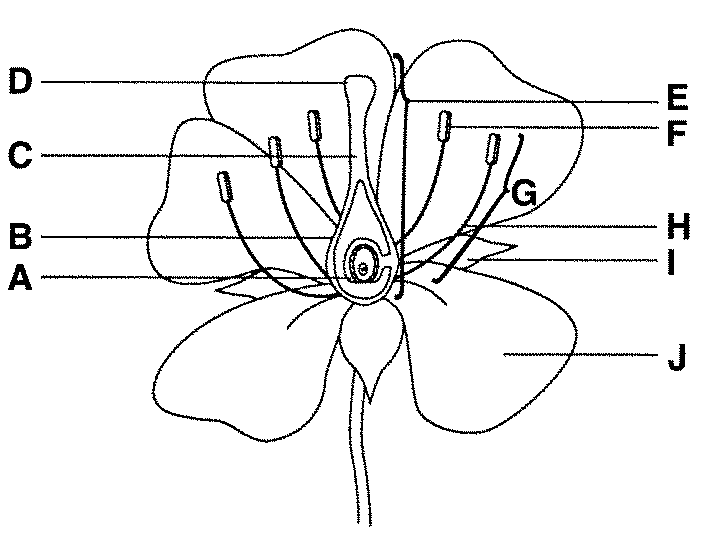
what is A and function
ovules are part of the ovary that is fertilised to become the seeds
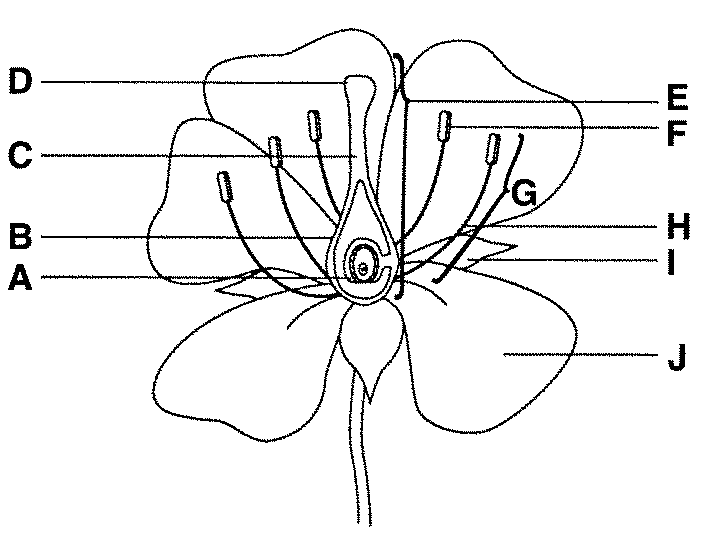
what is C and function
style - generates the pollen tube and blocks incompatible pollen from entering the ovaries
difference between self pollination and cross pollination
self pollination: transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma of the SAME plant
whilst cross pollination is the transfer of pollen between different plants, promoting genetic diversity.
between which plants does cross pollination occur
plants of the SAME SPECIES but different varieties —> can be diff species
characteristics of flowers that use wind pollination (+ explain why each part is useful)
plants with flowers grouped together and hang in tassels and blow in the wind easily, anthers are long and pollen is light + numerous
stigmas: are long and spread out to capture shedding pollen
what is the efficiency of wind pollination + examples that use it
not efficient, as large amounts of pollen must be produced and many Australian grasses use this
characteristics of flowers that bees pollinate
anthers: lower than stigma and often enclosed by petals to encourage access by bees, which helps in effective pollen transfer.
large pollen grains in small amounts that are very sitcky
fragrant, large + colourful
characteristics of flowers that birds pollinate
anthers are commonly lower that stigma, may be enclosed by petals
unscented, large + colourful, often in tubular shape
sticky or powdery pollen - small amout produced
ways that pollen is transferred
wind/water dispersal, bees/insects or birds
what is pollination
it is the transfer and fusion of gametes from anthers to stigma
what are the 2 components of a pollen grain
tube cell
generative cell
4 steps of Angiosperm reproduction
Pollination
Fertilisation
Seed dispersal
Germination
process of pollination
pollen transferred to stigma of a flower
pollen’s tube cell (formed from tube cell) creates a pollen tube from the stigma towards the ovary
pollen’s generative cell divides to form 2 sperm cells
process of fertilisation in plants
the 2 sperm cells enter one of the ovules within the plant’s ovary
Inside ovule, 1 sperm cell fertilises egg, the other sperm cell combines with polar nuclei to form endosperm (helps to provide nourishment for zygote)
After fertilisation, ovule becomes seed containing fertilised egg, and ovary becomes the fruit
2 methods of seed dispersal with examples
via dry fruits which have in built ‘explosive’ mechanism for dispersal by air,wind or water - often these plants are very light e.g banksia pods, gumnuts
vis flesh fruit which rely on insect/birds/mammals to ingest and transport seeds away from parent plant in their excretion
process of germination
starts once the seed has landed in suitable soil with sufficient water, oxygen + warmth
the fertilised egg in the seed develops into embryo which consists of:
radicle (root) to absorb water and soil nutrients
a plumule (stem) that develops green leaves for food production
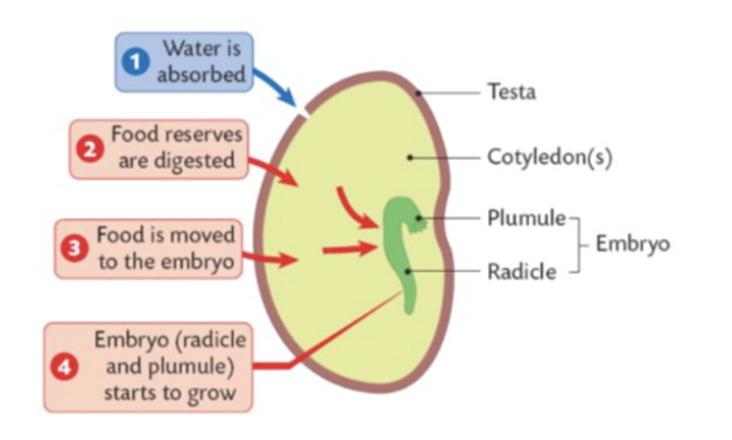
what are the 6 types of asexual reproduction - and what types of organism reproduces that way
Binary fission - bacteria, protists e.g amoebas
budding - animals + fungi
fragmentation - animals
spores - plants e.g mosses, ferns + some fungi
vegetative propagation - plants
apomixis/pathenogenesis - plants and animals
process of budding in 3 steps
adult cell gives rise to bus
DNA replication
Nucleus division occurs via mitosis, providing each cell with genetically identical nuceus
cytokinesis occurs once bud is almost as large as parent
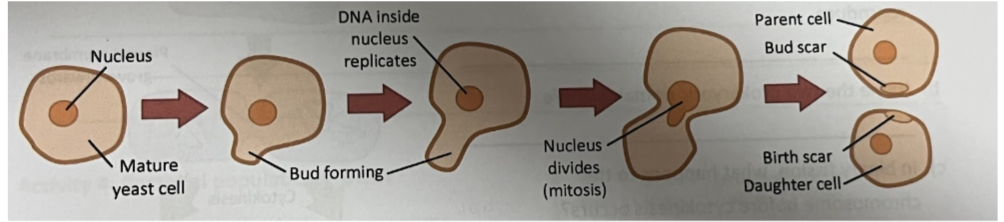
what type of organism reproduces via budding, with examples
fungi (yeast)
animals (eukaryotic) —> jellyfish, hydra, grooved brain coral
some plants too!
disadvantage of budding
if environment changes, entire species may rapidly decline due to identical offspring
what are spores + sporangia?
sporangia (sacs that prod. and store spores) prod large number of
spores - which are tiny unicellular reproductive cells that are very light for easy dispersal via wind
what organisms reproduce via spores?
mosses, ferns and fungi (moulds and mushrooms)
are fungi eukaryotic or prokaryotic
eukaryotic, and can be either multicellular or unicellular
why is fungi important to ecosystems
they help decomposition of organic matter - they secrete enzymes to break down environmental nutrients for absorption
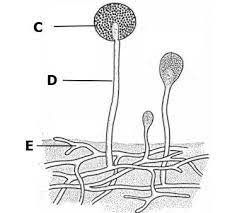
name and outline functions of the 3 main parts of a multicelluar fungi
hyphae - spreads through material on which fungi feeds
sporangium - storage of spores (can also release spores)
mushroom - ‘fruiting body’ releases spores into environment
what is interwoven mass of hyphae called
mycelium - visible to naked eye
how are spores produced
mitosis of haploid nuclei (of another spore)
what happens in sexual reproduction in fungi
two fungi temporarily fuse to create a diploid structure
process of binary fission
bacterial chromosome duplicates, beginning at origin of replication
After origin is duplicated, it moves to other end of cell and once entire chromosome is duplicated, cell begins to elongate
cytokinesis (plasma membrane growing inwards) splits cell into 2 identical cells
2 examples of organism that use binary fission for reproduction
prokaryotic unicellular - bacteria
eukaryotic unicellular - protists (e.g amoeba)
organelles inside eukaryotic cells - mitochondria
how do runners works
Runners are modified stems - that grow along the surface of the soil where, from each node on the stem produces leaves and roots that
prod new strawberries
continues the ‘runner’ stems across
what are the steps involved in sexual reproduction of mammals
ovulation
internal fertilisation
implantation
pregnancy
birth
3 types of mammals
monotremes egg laying
marsupial: pouched
Eutherians: placental
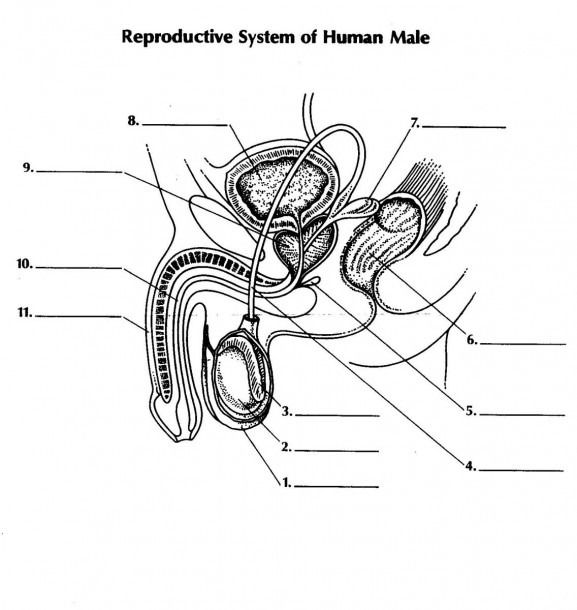
what is 1 and its function
scrotum - double walled pouch aids in regulating temperature of testes for optimal sperm production
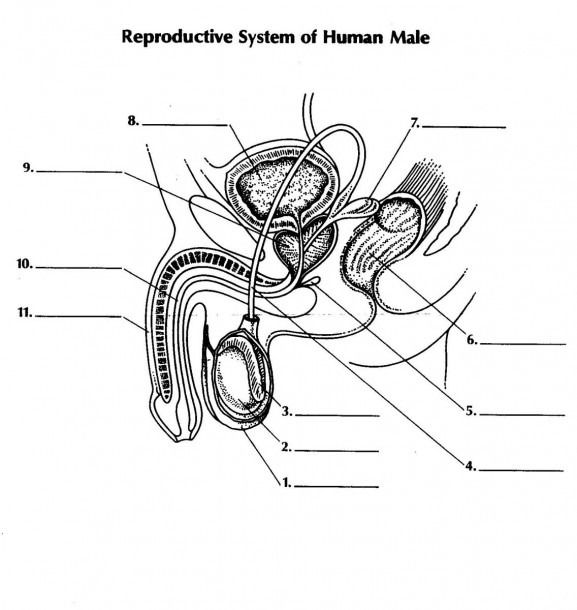
name 2 and its function
testicale (testes) - male gonads are responsible for prod. male gametes and secreting testosterone
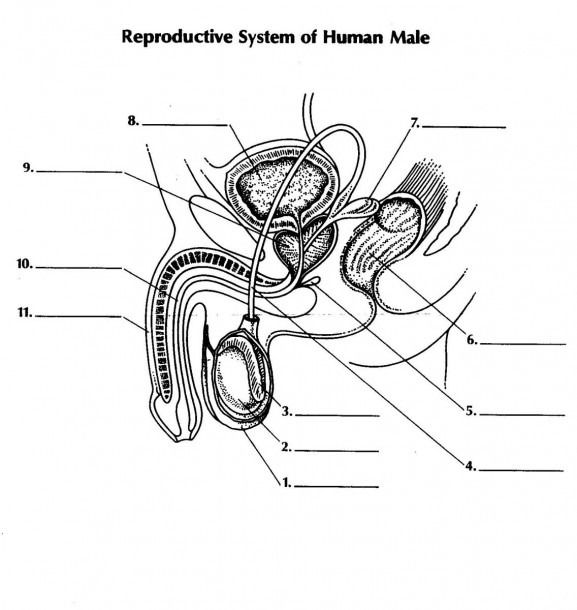
name 3 and its function
epididymus - coiled tube where sperm is stored temporarily while they mature
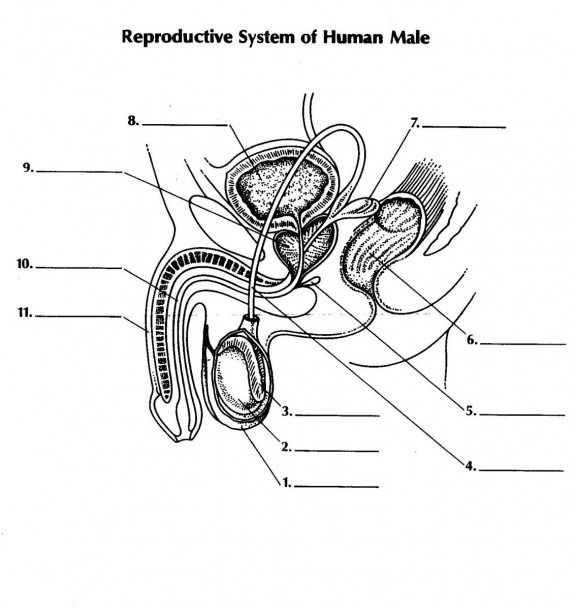
name 4 and its function
vas deferens - aka sperm duct a tubule that carries sperm from epididymus to the urethra
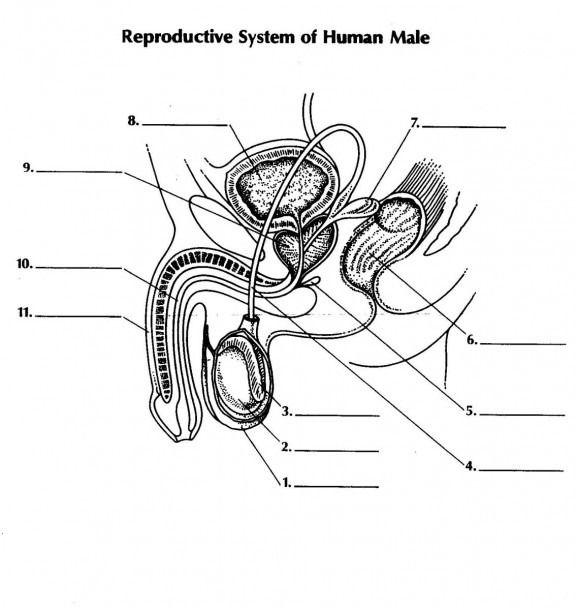
name 5 and its function
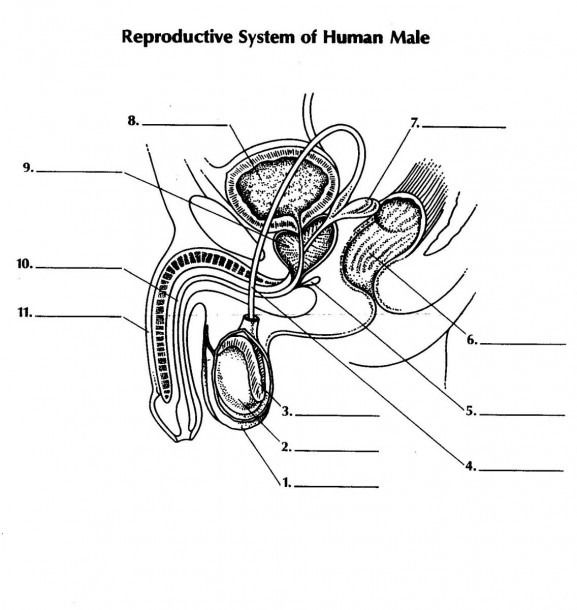
name 7 and its function
seminal vesicle: - secrete fluid to nourish aperm + allow sperm to swim
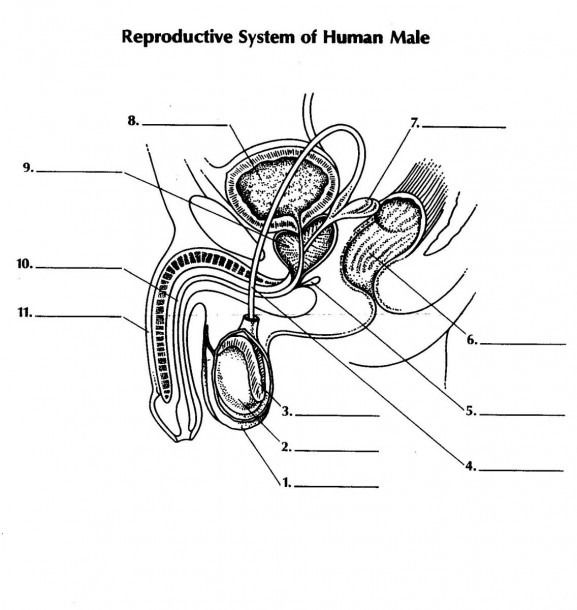
name 11 and its function
penis - used in intercourse to ejaculate semen containing sperm into female reproductive system
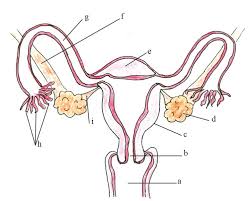
name a and its function
vagina - a canal with muscular walls through which baby is born,
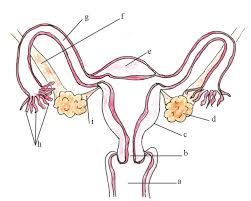
name b and its function
cervix - the lower part of the uterus, it is a narrow channel allowing sperm to enter the uterus and blood to leave during menstruation
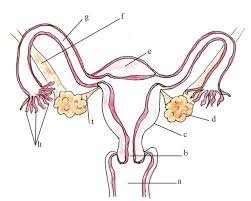
name d and its function
ovary - contains cells that divide to make female gametes
makes female reproductive hormones
ovulation occurs here
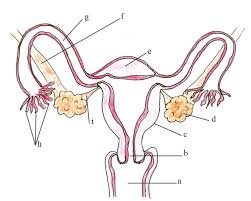
name g and its function
fallopian tube - transports the ovum to the site of fertilisation
fertilisation occurs here???
outline the 6 general steps of sexual reproduction from intercourse to birth
male + female have intercourse
Ejaculation causes semen from male to move ino female vagine
sperm cell travels through female reproductive tract —> through cervix —> into uterus —> into fallopian tube (oviduct)
single sperm cell fertilises available egg(s) (if it is fraternal twins) resulting in zygote(s)
zygote travels down fallopian tube into the uterus —> begins to grow through mitosis into blastocyst
blastocyst implant in endometrial wall of uterus to continue developing
embryo nourished by mother’s body via placenta —> grows to foetus —> baby
ovulation
when the egg (ovum) bursts out of the follicle in the middle of the cycle
difference between ovarian and menstrual cycle
ovarian cycle occurs in ovaries and prepares egg for fertilisation
menstural cycle occurs in uterus and prepares uterus wall to recieve fertilised egg
what occurs in the follicular phase of the ovarian cycle (in terms of hormones!!)
(day 1-14)
hypothalamus secretes GnRH which stimulates the pituatary gland to secrete Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) which travels from bloodstream to ovaries stimulating the growth/maturation of a follicle containing an egg
growth of follicle —> causes release of oestrogen stimulating endometrium ot thicken with blood vessels
hormonal situation during/causing ovulation
the follicle bursts to release the ovum
this is caused by a sudden peak in lutenising hormone secreted by pitutary gland, which is released as the egg matures
lutenising hormone also causes remnants of burst follicle to form corpeus luteum
what occurs in the luteal phase of ovarian cycle (hormones!)
day 15-21: remnants of burst follicle form the corpus luteum, which releases progesterone and oestrogen —> endometrium stabilises and thickens
Day 21-28: iff egg is not fertilised, corpus luteum disintegrates, decreasing progesterone + oestrogen triggering menstruation
another word for uterine lining
edometrium
another word for oviduct
fallopian tube
ovum
egg cell
what is a zygote
single cell result of fusion of gmetes
]
what 2 things must happen in order for successful fertilisation to occur?
sperm must be deposited into vagina within 24-72 hours after ovulation
sperm must travel through cervix —> uterus —> up fallopian tube —> to meet ovum
what happens immediately after fertilisation
once sperm enters egg, enzymes form to stop 2nd sperm from entering
after fertilisation, zygote remains in fallopian tube for about 72 hours developing rapidly via mitosis
what occurs in implantation (following fertilisation off egg in the oviduct, how does it develop?)
fertilised ovum (zygote) travels down to uterus for further cell division (also undergoing through mitosis in oviduct)
once fertilised cell arrives in uterus it is a blastocyst ready for implantation
upon implantation there is a spike in HCG and division continues gastrula —> embryo —> fetus
what are the 3 parts of a blastocyst and what do they become
inner cell mass —> embryo
outer cell mass —> initiates formation of placenta
trophoblast —> outer layer of blastocyst that secretes enzymes to break down some endometrial cells, allowing blastocyst to enter lining
purpose of HCG + how it is used in pregnancy testing
maintains corpus luteum (in ovary), allowing it to continue to secrete progesterone
as it is in such high concentration, it often is detectable in urine - so HCG is what is tested for in urine for pregnancy tests!
purpose of progesterone
stabilises uterine lining and thus ensures uterus lining remains receptive to embryo (continues feeding it)
difference between oestrogen and progesterone
estrogen builds up the uterine lining while progesterone stabilizes it to support implantation and pregnancy.
what happens in 1st trimester
HCG rises rapidly to maintain corpus luteum, which temporarily allows continued production of oestrogen and progesterone which help maintain uterus lining
high levels of progesterone during this time also enlarge uterus, form mucous plug to seal the cervix + aids breast growth
what happens in 2nd trimester
production of HCG declines and corpus luteum deteriorates
placenta takes over role of corpeus luteum, producing oestrogen and progesterone
what happens in 3rd trimester
increased oestrogen is released
oestrogen induces receptors to form on uterus wall that cna bind with hormone oxytocin - a hormone critical to triggering and maintaining labour
what hormones are involved in birth + how?
oxytocin (prod. by pitutary gland) —> causes muscular contractions of uterus, which push baby towards cervix and vaginal opening
as baby’s head pushes against the cervix, nerve pulses stimulate more production of oxytocin (positive feedback cycle)
adrenaline acts as pain relief + energy for baby to be pushed out
oxyocin also is released to help placenta to be expelled
after baby is born, prolactin + oxytocin help in breastfeeding
how are oxytocin and prolactin play diff roles in breastfeeding
prolactin —> stimulates milk prod
oxytocin —> stimulates release of milk from storage
what is assisted reproduction used for
allows favourable traits to be passed onto offspring —> higher quality food in agriculture
3 methods of assisted reproduction
selective breeding (artificial selection)
hybridisation
inbreeding
Artificial insemination
Artificial pollination
what is selective breeding + how does it work?
selective breeding: when farmers intentionally select and breed individual animals/plants with more desirable characteristics, with hopes that offspring will express such traits
how does it work: there must be a wide variation of genetic traits for selective breeding to occur, with new trains introduced through genetic mutation