SNAB TOPIC 3-Voice of the Genome
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
3.1 Know that all living organisms are made of cells, sharing some common
features.
All living things are made of cells and share some common features:
In multicellular organisms:
Cells-->Tissues-->organs-->systems, each specified for a particular function(s)
3.2 Nucleus
Double membrane (nuclear envelope) with nuclear pores
Contains DNA, wrapped around histone proteins
Contains a nucleolus
3.2 80s ribosomes
Composed of two subunits
Site of protein synthesis
3.2 Lysosomes
Vesicles containing digestive enzymes
Bound by a single membrane
3.2 Mitochondria
Oval shaped, bound by a double membrane
Inner membrane folds, forming cristae
Contains enzyme for aerobic respiration
3.2 Golgi apparatus
Series of fluid filled, flattened and curved sacs
Vesicles surrounding edges
Modifies and packages proteins and lipids
Produces lysosomes
3.2 Smooth ER
System of membrane bound sacs
Produces and processes lipids
3.2 Centrioles
Perpendicular cylinders of microtubules
Involved in cell division
3.2 Rough ER
Series of flattened sacs, enclosed by a membrane
Ribosomes attached to the surface
Folds and processes proteins made on the ribosomes
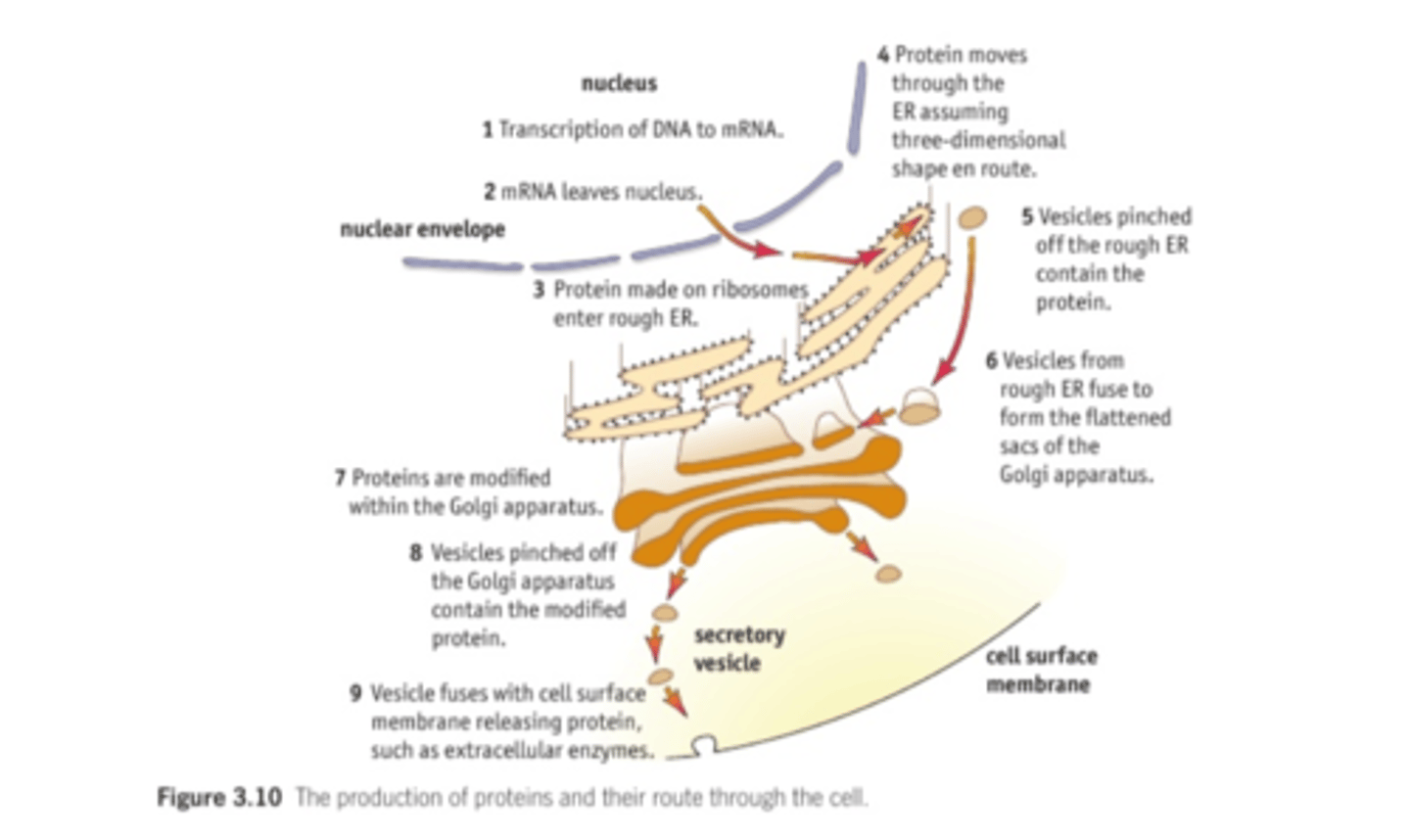
3.3 Understand the role of the rough endoplasmic reticulum (rER) and the Golgi apparatus in protein transport within cells, including their role in the formation of extracellular enzymes.
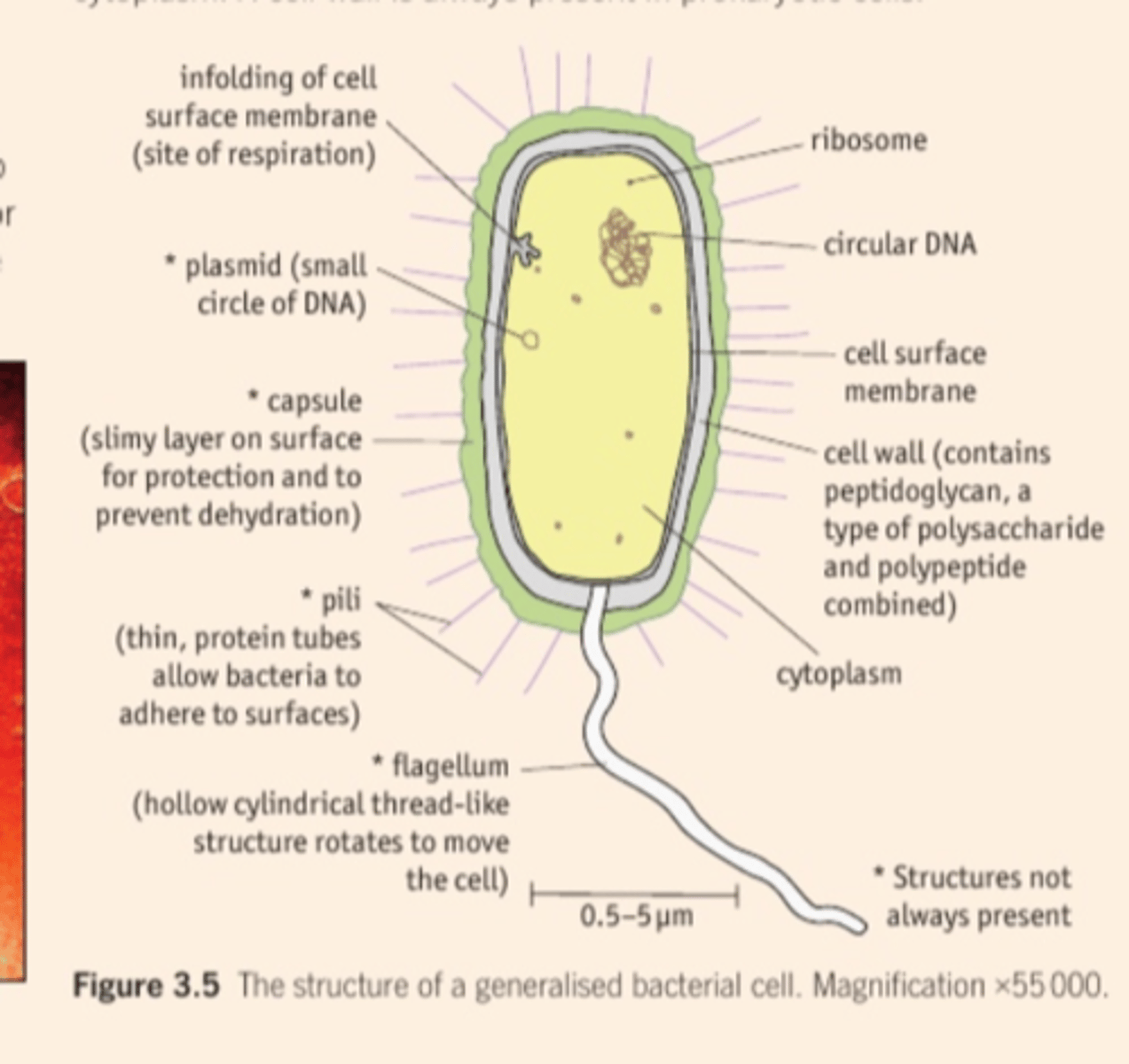
3.4 Know the ultrastructure of prokaryotic cells, including cell wall, capsule, plasmid, flagellum, pili, ribosomes, mesosomes and circular DNA.
3.5 Be able to recognise the organelles in 3.2 from electron microscope (EM) images.
Circle with blob= nucleus
Small bubbles= vesicles
Oval/circle with pattern= mitochondria
Long, flattened darker lines near nucleus= ER
3.6 Understand how mammalian gametes are specialised for their functions (including the acrosome in sperm and the zona pellucida in the egg).
Ovum:
-Zona pellucida, protective jelly like coating, prevents polyspermy
-Haploid nucleus
-Cortical granules, releasing enzymes that harden the zona pellucida
-Follicle cells form a protective coating around the egg.
Sperm cell
-Many mitochondria to make energy for flagellum
-Acrosomes contain digestive enzymes that break down the zona pellucida
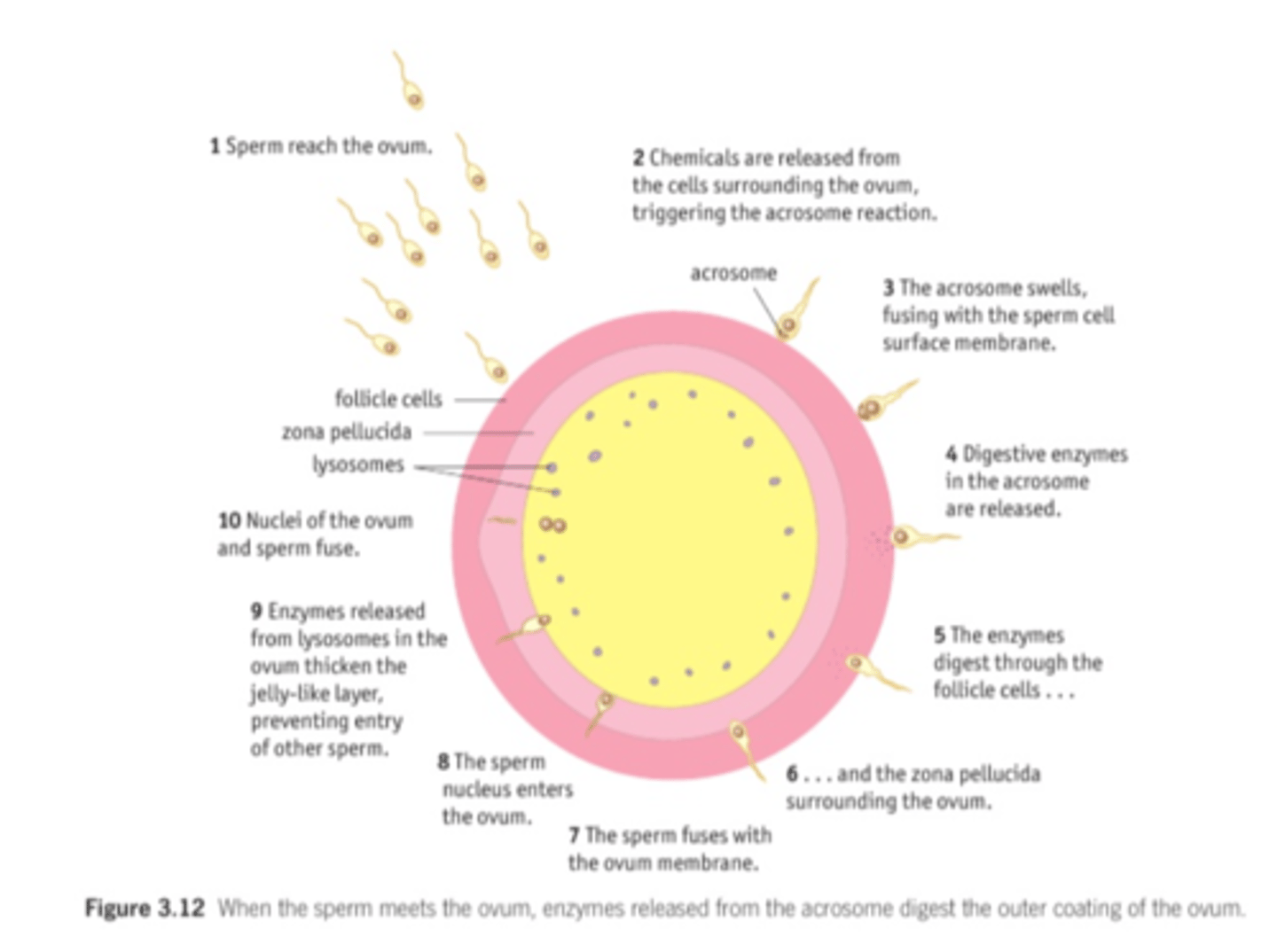
3.7 Know the process of fertilisation in mammals, including the acrosome reaction, the cortical reaction and the fusion of nuclei.
3.8 i) Know that a locus (plural = loci) is the location of genes on a chromosome.
a locus is the location of genes on a chromosome.
3.8 ii) Understand the linkage of genes on a chromosome and sex linkage.
Alleles on the same chromosomes= autosomally linked
-> The closer the loci of the alleles, the more likely they are inherited together (they are less likely to be separated during DNA exchange during meiosis)
Some genes are sex-linked because they only occur on the X-chromosome and not on the Y chromosome.
This means some genetic disorders are more likely to occur in men, as they only need one recessive allele to express characteristics.
3.9 Understand the role of meiosis in ensuring genetic variation through the production of non-identical gametes as a consequence of independent assortment of chromosomes and crossing over of alleles between chromatids (details of the stages of meiosis are not required).
Crossing over
Exchange of sections of DNA between homologous chromosomes
(homologous= a pair of two chromosomes)
Independent assortment
Different pairs of alleles separate from each other separately. Like shuffling a deck
( random combinations of ways that maternal and paternal chromosomes can be arranged in daughter cells of meiosis.)
3.10 Understand the role of mitosis and the cell cycle in producing identical daughter cells for growth and asexual reproduction.
Cell cycle:
Mitosis : prophase (condense), metaphase lined up), anaphase (pulled apart), telophase (nuclear envelopes reforming)
Cytokinesis: cytoplasm divides, membrane splits off a new genetically identical cell
Interphase:
G1-Growth of cell and DNA replication
S- chromosomes are replicated and begin to condense
G2- organelles replicate
CORE PRACTICAL 5:
Prepare and stain a root tip squash to observe the stages of mitosis.
Equipment
•Root tip
•Sharp knife
•Acetic alcohol
•HCl acid
•Ice cold distilled water
•Water bath at 60̊C
•Test tube
•Microscope, slides
•Mounted needle
•Toluidine blue stain
Method
1)Cut small piece of root tip
2) The root tip needs to be macerated
•Place test tube of HCl in water bath, leave to heat
•Place root tip in alcohol for 10 mins
•Remove tip, place in ice cold water for a few mins.
•Place tip in heated HCl for a few mins.
•Repeat this
3) Break the tip with the mounted needle
4) Prepare slide, add dye (blot out excess dye) view at 100x - 400x magnification.
5) Count number of cells in one frame. Count the number of cells with visible chromosomes, in the same frame.
Calculation
Calculate the mitotic index:
Mitotic index=
Number of cells with chromosomes/Total number of cells
3.11 i) Understand what is meant by the terms 'stem cell, pluripotency and
totipotency'.
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells that can divide into new stem cells or develop into specialised cells
Pluripotent:
Can give rise to many types of specialised cells but not placental cells
Totipotent
Can give rise to all types of specialised cells
3.11 ii) Be able to discuss the way society uses scientific knowledge to make
decisions about the use of stem cells in medical therapies.
They can replace damaged tissue such as nerve tissue in spinal cord injuries.
Some believe it is unethical as embryos are killed in the process
There is a risk of infection when cells are transplanted.
They could become cancerous.
They could be rejected.
3.12 Understand how cells become specialised through differential gene expression, producing active mRNA leading to synthesis of proteins, which in turn control cell processes or determine cell structure in animals and plants, including the lac operon.
Differential gene expression
Stimulus acts on unspecialised cells
Activator/repressor molecules bind to promoter regions
Some genes are switched on.
RNA polymerase can attach to active genes- Active genes are transcribed and translation occurs.
The protein that is made can change the structure and function of the cell
The cell can become specialised
Lac operon
When lactose is present, the repressor molecule is unable to bind to the promoter/operator region.
RNA polymerase can attach to DNA.
B-galactosidase enzyme is made, can now break down lactose.
3.13 Understand how the cells of multicellular organisms are organised into tissues, tissues into organs and organs into systems.
Cells of multicellular organisms are organised into tissues, tissues into organs and organs into systems.
3.14 i) Understand how phenotype is the result of an interaction between genotype and the environment.
Phenotype is the result of an interaction between genotype and the environment.
3.14 ii) Know how epigenetic changes, including DNA methylation and histone modification, can modify the activation of certain genes.
i made a small mistake (cant edit it) DNA methylation can both promote and prevent transcription
DNA methylation
Methyl group attaches to DNA, prevents transcription
Histone modification
Affects how tightly DNA is wrapped around histone proteins.
Tighter wrap=less available for transcription
Histone acetylation promotes transcription by making the DNA more accessible
3.14 iii) Understand how epigenetic changes can be passed on following cell division.
Epigenetic changes are copied with the DNA before mitosis/meiosis and are passed down to daughter cell(s)
3.15 Understand how some phenotypes are affected by multiple alleles for the same gene at many loci (polygenic inheritance) as well as the environment and how this can give rise to phenotypes that show continuous variation.
Combination of genotype and environment l
lung cancer: genetic predisposition + smoking increases risk
height: polygenic characteristic, but can be limited due to environmental factors like deficiencies.
Continuous variation
animal hair colour:
Some animals get darker fur at lower/higher temperatures
Discrete variation