mod 4- arthritis and finger deformities
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
osteoarthritis
which kind of arthritis is also known as degenerative joint disease (DJD)?
OA
arthritis characterized by erosion of articular cartilage and a decrease in synovial fluid
DIP, PIP, CMC joints of UE (small joints most affected)
what joints does OA primarily affect?
RA
arthritis characterized by inflammatory changes of the joints, tendons, and their sheaths
RA
arthritis that involves the immune system attacking joints
RA
arthritis that is a chronic disease
inflammation, loss of flexibility, contractures
ways that soft tissue is affected by OA
osteophytes, loss of joint congruity
ways that bone tissue is affected by OA
RA
which arthritis presents with noticeable fatigue?
instability, subluxation, dislocation, inflammation
common joint issues of RA
16
age under which juvenile arthritis is diagnosed
loss of motion in prox. and distal radioulnar joints, flexion contracture, collateral ligament laxity, bursitis
effects of arthritis on the elbow joint
> 4 mm space between humerus and ulna
what is the “drop sign”
radial deviation of wrist, ulnar deviation of fingers, finger deformities
effects of arthritis on the hand
RA
are hand deformities more common in OA or RA?
palmar subluxation, ulnar deviation of extensor and and sometimes flexor tendons
effects of arthritis on the MCP joints
synovitis causes collateral ligaments to shorten and the joint capsule to stretch
effects of arthritis on the proximal IP joints
lateral bands displace palmarly
how does arthritis cause a Boutonniere deformity?
lateral bands become stuck dorsally
how does arthritis cause a swan neck deformity?
extension, flexion, extension
the boutonniere deformity involves _____ of the MCP, _____ of the PIP, and _____ of the DIP
flexion, hyperextension, flexion
the swan neck deformity involves ____ of the MCP, _____ of the PIP, and _____ of the DIP
affected joints are CMC, MCP, IP
how is the thumb’s PIP joint affected by arthritis
depends on MCP and PIP joints
how to determine if DIP joint will be in flexion or hyperextension due to arthritis
decreases inflammation, prevents further deformity, rests and supports, improves function, aids in post-op rehab, immobilizies
indications for splinting? (name 3)
more force
result of smaller moment arm in UEO
more pressure
result of smaller surface area in UEO
shear
what kind of force needs to be considered for suspension in UEO? (shear, gravitational)
within 1 cm from apex of humeral epicondyle
distance of elbow orthosis joint from landmark to prevent it from migrating
resting hand splint
orthosis that positions the wrist and digits statically to align joints
10-20d extension, 5d ulnar deviation
wrist angle for resting hand splint
abducted, opposed
thumb position for resting hand splint
slight flexion
fingers position for resting hand splint
cock-up splint
other common name for wrist orthosis
ulnar deviation orthosis
orthosis that supports MCP joints and provides a radially directed force
ulnar deviation orthosis
what is this?

thumb spica splint
orthosis that provides support to the CMC and MCP joints for acute RA or OA in the thumb
thumb spica splint
what is this?
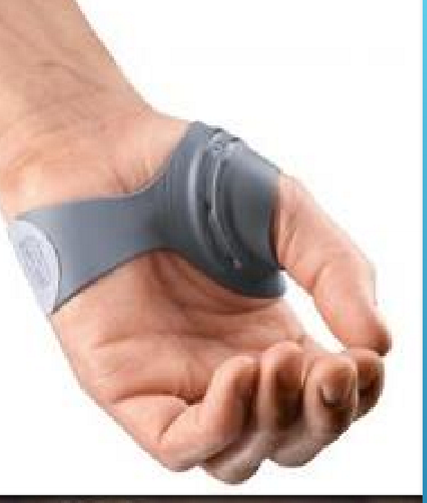
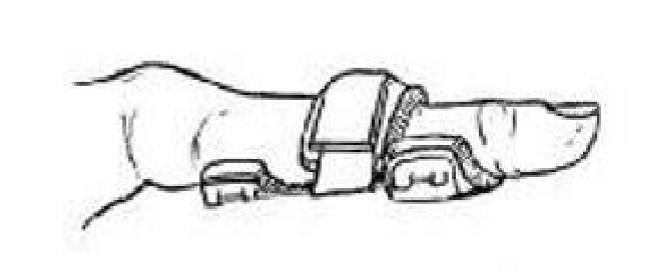
IP splint
what is this?
radial and ulnar styloid, MCP and IP joints, any bony prominences
landmarks for a WHO
ML at styloids and MCP joints, circumference at wrist and MCP, wrist to fingertip, wrist to elbow
measurements to take for a WHFO
CMC, MCP
what joints does a thumb spica provide support to?