Heredity
1/114
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
115 Terms
paracrine signaling
cells communicate with other local cells in vicinity
growth factors
local regulation in animals that simulate target cells to grow and divide and simultaneously receive and report
synaptic signaling
in animal nervous system; electric signal along nerve cell triggers secretion of chemical signal carrying neurotransmitters eventually triggering response in target cell
hormones
both plants and animals use this for long-distance signaling (also called endocrine signaling)
types of local cell communication/signaling
cell-cell: gap junctions (animal cells) and plasmodesmata (plant cells)
paracrine, synaptic
Stages of cell signaling
reception, transduction and response
reception
target cells detection of signaling molecule from outside cell; signaling molecule (ligand) binds to receptor
transduction
step or series of steps that converts signal to bring cellular response
signal transduction pathway
sequence of changes in series of different molecules (relay molecules)
response
cellular activity that is triggered
ligand
molecule that specifically bonds to another molecule; usually changes shape of receptor, initiating interactions
G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR)
cell-surface transmembrane receptor that works with help of G-protein
G-protein
protein that binds to energy rich GTP
ligand-gated ion channel
membrane receptor with a region that can act as a “gate” for ions opening or closing due to induced fit
intracellular proteins
in cytoplasm on nucleosol target cells and must pass through plasma membrane. ex steroids
transcription factors
control what genes are transcribed into mRNA in particular cell and time
protein kinase
enzyme that transfers phosphate groups from ATP to a protein; compose most of relay molecules on signal transduction pathway
phosphorylation cascade
pathway of signal transduction pathway containing protein kinases where signals are transmitted by
protein phosphatases
enzymes that can rapidly remove phosphate groups from proteins- dephosphorylation; make protein kinases available for use
second messengers
small; nonprotein, water soluble molecules or ions that can spread throughout through diffusion
cyclic AMP (cAMP)
epinephrine binds to G-protein activating enzyme that converts ATP to cAMP; important in mitosis-
cell division
reproduction of cells; allows multicellular eukaryotes to develop from single cell and replace dead cells
cell cycle
life of a cell from the time it first formed during division of parent cell until own division into two daughter cells
genome
cells genetic information
chromosomes
structures of packaged DNA; structure maintained by proteins called histones; nuclei in humans contain 46 chromosomes
chromatin
entire complex of DNA and proteins of chromosomes
somatic cells
body cells except reproductive
gamete cells
reproductive cells; XX-female, XY-male
sister chromatids
2 in duplicated chromosomes; joined copies of original chromosome; cohesions connect chromatids along length by protein complexes- sister chromatid cohesion
centromere
region made up of repetitive sequences in the chromosomal DNA where chromatid is attached most closely to sister chromatid; mediated by proteins
mitosis
division of genetic material in nucleus into 2 genetically identical diploid cells; 5 phases
cytokinesis
follows mitosis; division of cytoplasm; cleavage starts process; outside, contractile ring of actin microfilaments interact wit myosin and contract, pinching cell into 2 cells
miotic phase (M phase)
part of cell cycle that includes mitosis and cytokinesis and usually shortest part of the cycle
Interphase
longer stage that alternates with M phase; divided into G1 phase, s phase and G2 phase
5 stages of mitosis
prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
prophase
chromatin fibers tightly coil; nucleoli disappear; each duplicated chromosome appears as 2 sister chromatids joined at centromeres, mitotic spindle begins to form centrosomes and microtubules; centrosomes move away from one another by lengthening microtubules
nucleoli
large structures in nucleus that are involved in synthesis of rRNA and ribosomes; disappear in prophase and reappear in telophase
prometaphase
nuclear envelope fragments; microtubules invade nuclear area; chromosomes become more condensed; kinetochores forms at each centromere of chromatid; microtubules attach to kinetochores; non-kinetochore microtubules lengthen cell with interactions
metaphase
longest stage; centrosomes at opposite ends of poles; chromosomes arrive at metaphase plate; kinetochores are attached to kinetochore microtubules of opposite plates.
anaphase
shortest stage; cohesion proteins are cleaves\d and each chromatid becomes independent chromosome; 2 new daughter chromosomes begin moving toward opposite ends as kinetochore microtubules shorten; cell elongates as non-kinetochore microtubules cohesion; both ends have equivalent and complete chromosomes
telophase
2 daughter cells in nuclei form in cell; nuclear envelopes arise from fragments of parent cells; nucleoli reappear; chromosomes become less condensed; microtubules are depolymerized
cleavage furrow
shallow groove in cell surface near old metaphase plate; oustide
cell plate
in plant cells, vesicles from Golgi move along microtubules to center where they release cell wall material so that cell plate enlarges until it fuses with plasma membrane
binary fission
prokaryotic reproduction in which cell grows to double its size and divides into two cells; DNA replicates and splits to opposite sides then cell divides.
growth factor
protein released by certain cells that stimulate other cells to divide
meiosis I and meiosis II
2 consecutive cell divisions resulting in 4 daughter cells with one set of parent cell chromosomes
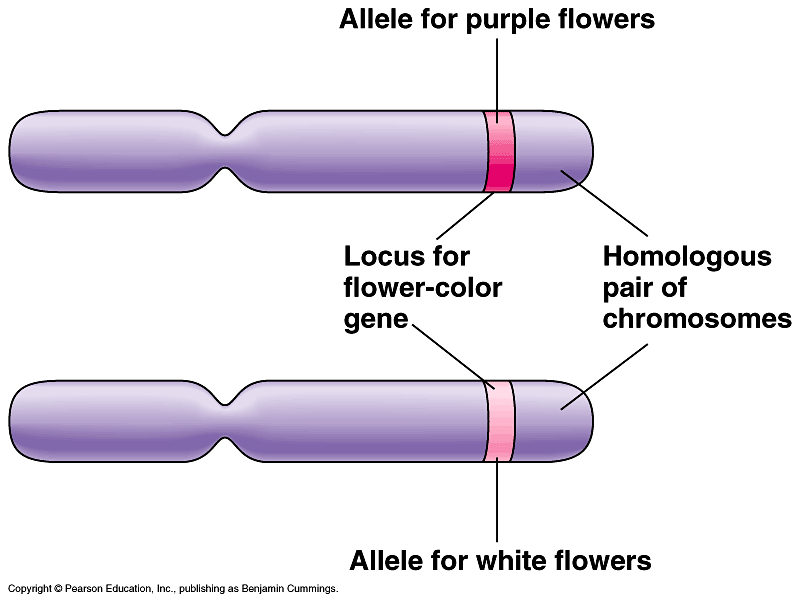
allele
different version of gene at corresponding loci; variations in gene nucleotide sequence
prophase 1
2 members of homologous chromosomes associate along length; synapsis and crossing over occurs, and duplicated homologs pair up and crossover
metaphase 1
pairs of homologous chromosomes align at metaphase plate
chiasma
location where crossing over and swapping of genes occur; holds together homologous chromosomes into a tetrad
recombinant chromosomes
individual chromosomes that carry genes from different parents; increases genetic variability; result of crossing over
independent assortment chromosomes
at metaphase 1, homologous pairs are situated at metaphase plate and each pair may randomly orient with either maternal or paternal homolog closer to given pole
character
heritable feature that varies among individuals
trait
each varient for a character
true breeding
breeding over many generations of self-pollination
hybridization
mating, or crossing of 2 true-breeding varieties
P generation
true-breeding parents, parental generation
F1 generation
hybrid offspring- first filial generation
F2 generation
allowing F1 hybrids to self-pollinate produces this -second filial generation
law of segregation
2 alleles for heritable character segregate during gamete formation and end up in different gametes
phenotype
appearance or observable trait and physiological
genotype
genetic makeup
testcross
breeding of an organism of unknown genotype with recessive homozygote; reveals genotype of organism
law of independent assortment
2 or more genes assort independently- each pair of alleles segregate independently of any other pair during gamete formation
multiplication rule
to determine probability of one event and other occurring, multiply probability of both events
addition rule
probability of any one of two or more mutually exclusive events will occur as calculated by adding individual properties
complete dominance
one allele shows up over another allele
incomplete dominance
neither allele is completely dominant; mix of phenotypes from parents; ex. pink flowers (from red/white)
codominance
2 alleles each affect phenotype in separate, distinguishable ways; ex. roan cow
Tay-Sach disease
inherited disorder in humans caused by recessive allele, brain cells in youth cannot metabolize lipids because of faulty enzyme and lipids accumulate, causing seizures, blindness, and degeneration of motor and mental performance; child dies within a few years
pleiotropy
genes that have multiple phenotypic effects; one gene affects lots of outcomes
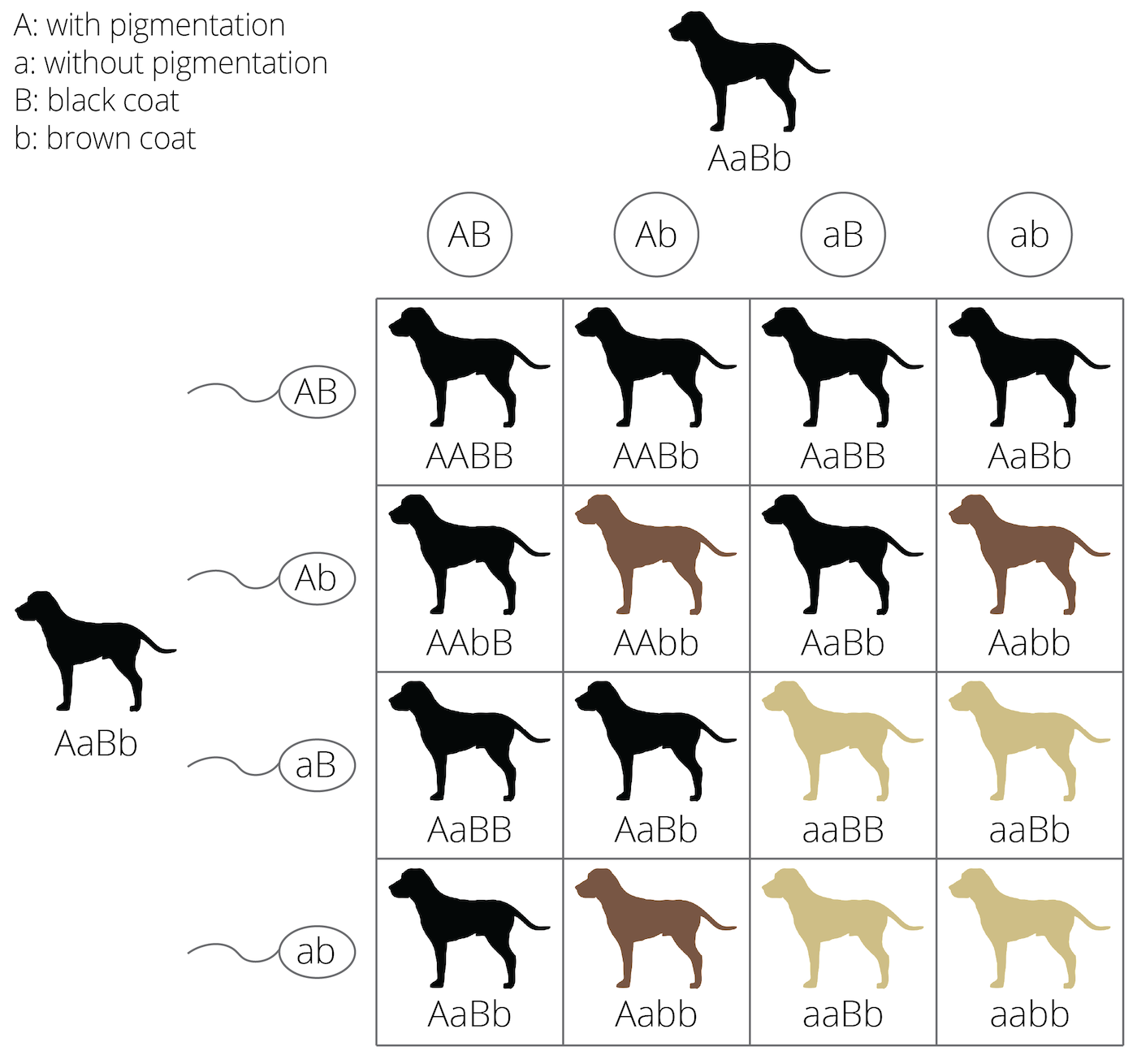
epistasis
one gene affects phenotype of another because 2 gene products interact; phenotypic expression of gene at one locus alters that of gene at second locus; ex. labs
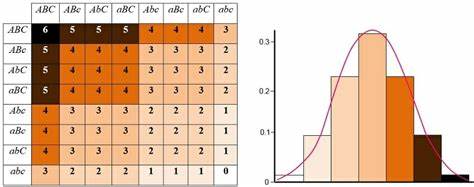
polygenic inheritance
additive effect of two or more genes on a single phenotypic character; many genes that affect one trait
multifactorial
many factors, both genetic and environmental that influence phenotypes
pedigree
family tree describing traits of parents and children across generations
carrier
seemingly phenotypically normal, heterozygotes that transmit recessive allele to offspring
cystic fibrosis
most common lethal genetic disease in U.S. due to recessive alleles; abnormally high concentrations of intracellular Cl, causing uptake of water making a mucus that builds up in the pancreas, digestive tract…; causes poor absorption of nutrients in intestines, chronic bronchitis, and recurrent bacterial infections
sickle cell disease
caused by substitution of single amino acid in hemoglobin protein of red blood cells; when O2 content of blood is low, hemoglobin molecules aggregate into long rods, detaching red blood cells into sickle shape; can clump and clog blood vessels leading to physical weakness, pain, organ damage, and stroke and paralysis
Huntington’s disease
degenerative disease of nervous system caused by lethal dominant allele without phenotypic effect until 35-40 years old
density-dependent inhibition
phenomenon in which crowded cells stop dividing
anchorage dependence
to divide, cells must be attached to something; signaled to cell cycle control system via plasma proteins
transformation
process that causes cells to behave like cancer cells and cause ability to divide indefinitely
benign tumor
tumor that moves to or survives at another site; usually can be removed
malignant tumor
cells who's genetic and cellular changes enable them to spread to new tissues and impair functions on one or more organs, cancerous tumor
metastasis
spread of cancer cells to locations distant from original site; requires chemotherapy
how does cancer develop?
cancer cells do not stop dividing when growth factors are depleted; they evade normal control that triggers apoptosis; forms tumor which is a clump of abnormal cells within normal tissues; it has a density sensing factor that cannot control growth in dense conditions; loses desmosomes
differences of mitosis and meiosis
mitosis: diploid and haploid cell division (somatic cells); DNA replicates during interphase, before mitosis; one division; 2 genetically identical diploid daughter cells to parent with equal number of chromosomes; asexual reproduction
meiosis; diploid cell division only (gametes); DNA replicates during interphase before meiosis I but not meiosis II; 2 divisions; synapsis occurs during prophase 1 with crossing over- chiasma holds pair of homologous chromosomes together with sister chromatid cohesion; 4 genetically different haploid daughter cells from parent and each other; sexual reproduction
chromosome theory of inheritance
Mendelian genes have specific loci along chromosomes, and it is the chromosomes that undergo segregations and independent assortment
wild type
phenotype for a character most commonly observed in natural populations; denoted as superscript
mutant phenotype
traits alternative to wild type and are dure to alleles assumed to have originated as mutations in wild type allele
sex-linked gene
gene associated on either sex chromosome
X-linked genes
most genes; genes that X chromosome contains
Duchenne muscular dystrophy
progressive weakening of muscles and loss of coordination; life expectancy is around 20; absence of key muscle protein which is on X chromosome locus
hemophilia
X-linked recessive disorder; absence of 1 or more proteins required for blood clotting; excessive bleeding from injury due to slow forming blood clot; treatable with protein injections
Barr body
inactive X in each cell of female condensed into compact object; only one X chromosome can be activated, so those with 2 X chromosomes only express one because the other is inactivated

nondisjunction
members of pair of homologous chromosomes do not move apart properly during meiosis I of sister chromatids fail to separate in meiosis II
aneuploidy
condition when either of aberrant gametes unites with normal one at fertilization and zygote has abnormal number of particular chromosomes
monosomic- aneuploid zygote with missing chromosome
trisomic- aneuploid with triple chromosome
polyploidy
organisms with more that 2 complete chromosome sets in all somatic cells
deletion
when chromosomal fragments is lost; missing certain genes
duplication
broken fragment that is reattached as extra segment to sister/Non sister chromatid