coastal landforms and change
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
waves
main source of energy at the coastline
generated by wind
friction between wind and water surface
Fetch
The distance of open water the wind blows over
strength
how forceful the wind is
duration
how long the wind has been blowing
Constructive waves
lower wave height
strong swash and weak backwash
build up the beach
Destructive waves
higher height
weak swash and strong backwash
break down the beach
beach morphology in summer
Beach profiles are steeper in summer when there are fewer destructive waves
Beaches are formed from loose material
Waves alter the morphology (form/shape) of the beach
The morphology is also affected by the size and shape of the beach material
The type of wave in an area can vary depending on the time of year or coastal management
Beach morphology in winter
Storm berms may develop in winter when large destructive waves carry larger sediment further up the beach than normal
In winter beaches may also have a greater variation in pebble size as larger pebbles are deposited by the destructive waves and smaller pebbles are removed
Offshore ridges/bars are formed due to material being eroded from the beach by destructive waves and deposited offshore
erosional processes
abrasion
hydraulic action
corrosion
attrtion
abrasion
sediment and stones are picked up by the waves and wear away at the cliff/headland
hydraulic action
this is the shear force of the waves forcing air at high pressure into cracks in the cliff over time this weakens the rock and causes the joint to widen
corrosion
weak acids in seawater dissolve the rock particles
attrition
as rocks are moved around by the water they knock into each other gradually becoming smaller and rounder
factors affecting erosion
Wave type
Wave size
Lithology
wave type and size affecting erosion
Erosion tends to happen more during the winter due to a greater number of destructive waves
The size and type of waves affects the amount of hydraulic action and abrasion
lithology affecting erosion
Weaknesses in rocks erode more quickly
More resistant rocks erode more slowly
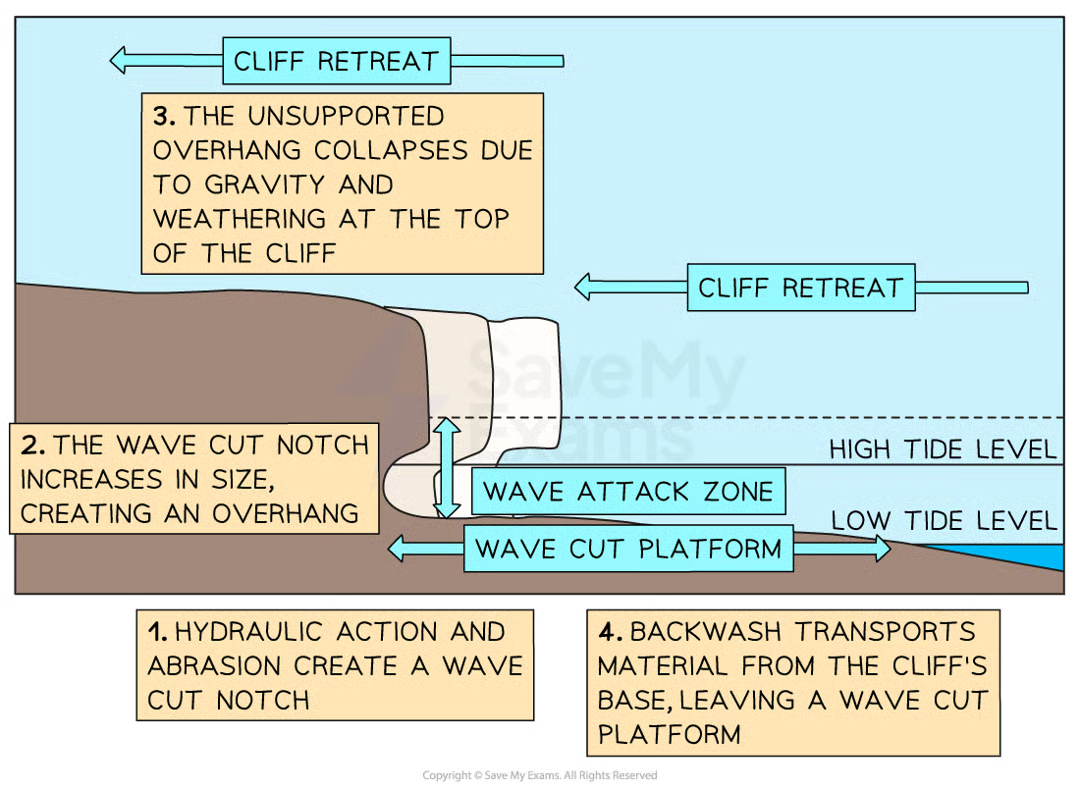
wave cut platforms
At high-energy coastlines, hydraulic action and abrasion can cause the formation of wave-cut platforms
Powerful destructive waves attack the base of the cliff at high tide
The hydraulic action and abrasion create a wave-cut notch which over time increases in size
This is called undercutting
Eventually, the overhang created by the undercutting collapses due to weathering and gravity
The cliff retreats, leaving a wave cut platform that is exposed at low tide
cave , arch, stack
Wave refraction concentrates wave energy onto the headland and can contribute to the formation of caves, arches, stack and stumps
Joints in the headland are susceptible to erosion by hydraulic action
Over time the joints widen forming a cave that is enlarged by hydraulic action and abrasion
Eventually, erosion cuts through the headland forming an arch
The roof of the cave will eventually collapse due to gravity and the lack of support
This leaves a stack that will over time be eroded by weathering, abrasion, and hydraulic action to form a stump