Business U4AOS1
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Concept business change
¡Change: Any alteration in the internal or external environments
¡Business change: The alteration of behaviours, policies and practices of a business; resulting in a difference in the form or operation of a business over time.
Approaches to change
¡Proactive:
¡Initiating change rather than simply reacting to events
¡Change is planned
¡Reactive:
¡Waiting for a change to occur and then responding to it
¡Change is unplanned and takes place after the business has been affected by pressures from its environment
¡Successful managers are often proactive rather than reactive.
¡Poorly managed changes can lead to a loss in productivity, employee resistance and ultimately, unmet objectives.
types of changes
¡Changes can be radical (major alteration due to critical circumstances) or incremental (part of natural development-change to stay competitive).
KPI’s
¡Key performance indicators
¡A specific criteria as a way of measuring the success (efficiency, effectiveness and competitiveness), of a particular area of the business’s performance.
For KPI’S def, calculation and effect and why check paper
driving forces, internal driving forces
¡Driving forces are the forces affecting a situation that are pushing in a particular direction and are supporting the goal or proposed change.
Internal -The forces which the business has control over and are relevant to the internal environment
¡Owners and managers have influence on the business and will either provide the direction for the change or be involved in implementing the change ¡Supportive employees can lead to successful change
¡Employees are more likely to support the change if it is in line with their interests (i.e. high wages, good working conditions).
Pursuit of profit- ¡Opportunities to improve financial performance will often encourage a business to change.
Reduction of costs- ¡Costs and the pressure to reduce these can also lead to changes in a businesss.
External driving forces
external forces-¡Factors that exist outside of the business that encourage change to occur.
Competitors- ¡businesses always need to be ready to respond to any changes to ensure they do not lose customers or market share.
Legislation- ¡Businesses must be able to respond and change aspects of their operations in line with laws. (compulsory)
Globalistaion- ¡Businesses operating internationally need to find more efficient ways to operate in order to be internationally competitive
Tech- Advances in technology need to be accepted for a business to be competitive in the market.
innovation- ¡If a business fails to innovate then it is likely to be left behind. New ways of thinking and operating gives businesses a competitive edge.
Societal attitudes- ¡Pressure from society has forced businesses to implement change. For example, shift to online shopping, sustainability and CSR practices. Businesses need to keep up with societies values and trends.
Restraining forces
Work against any changes a manager or business is trying to implement
Managers- ¡Due to either poorly timed/unclear decisions, lack of skills and experience or indecisiveness, management may stop change from occurring.
Employees- Employees who do not feel part of the business or who do not feel appreciated will usually make change difficult to introduce
Time-¡Businesses may struggle to respond to change quickly if they have not planned or foreseen change.
Organisational interia- Management’s inactivity or lack of response to internal and external pressures when faced with proposed changes. ¡Resistance to change because businesses are stuck in ‘comfort zones’ and unable to react to internal and external pressures.
Legislation- Adjusting to a law that is unexpected, expensive or difficult to implement, can make it harder for the business to respond positively.
Financial consideration- ¡Lack of access to finance can restrict access to change for many small businesses.
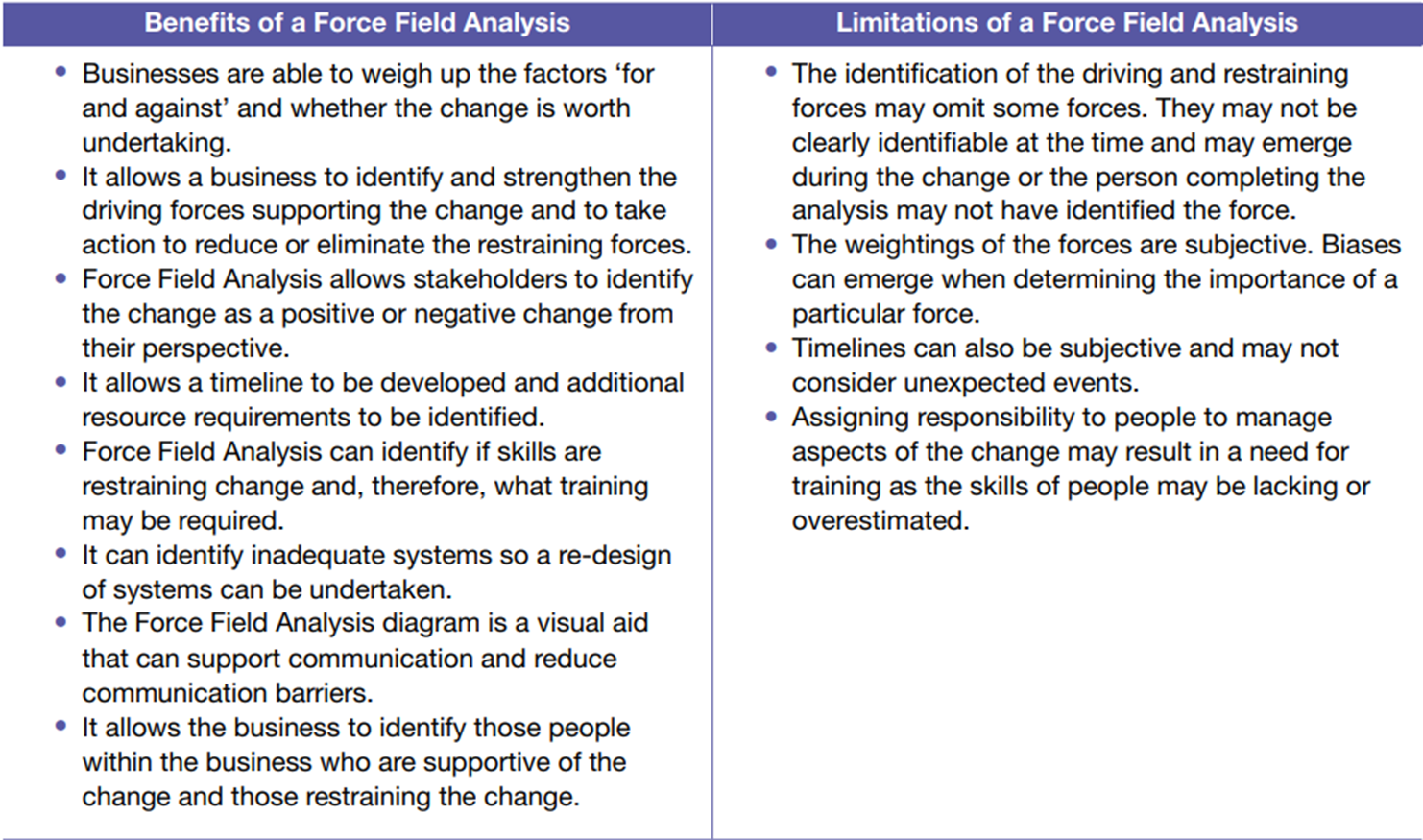
Key principles of force field analysis- Force field analysis
model describes how you can determine which forces drive and which resist a proposed change.
1.Identify the need for change
2.Identify driving forces and restraining forces
3.Assign scores to give a weighting to current forces: Determine the strength of each force by giving a score between 1 (weak) and 5 (strong) relative to the strength of the force.
4.Rank the top restraining forces to eliminate or strengthen them:
5.List actions required and implement a response
6.Evaluate the response
Strategic management by porter’s generic strategies
¡The objective of gaining a competitive advantage is to improve performance in those areas identified as KPIs.
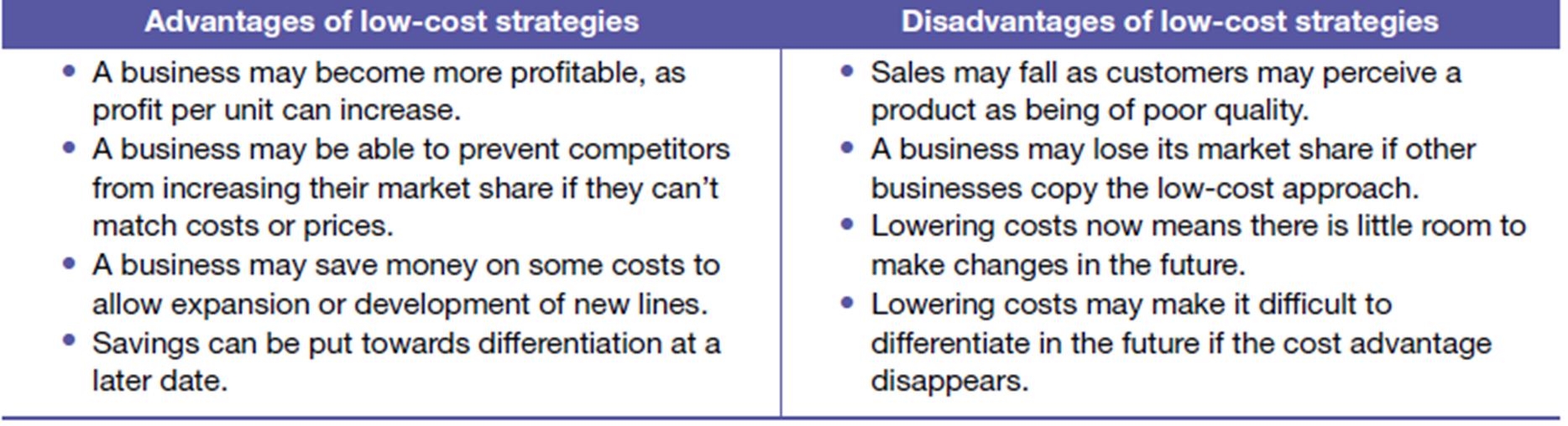
Porters lower cost strategy
¡gaining a competitive advantage through reducing or altering the costs of the business. ¡prices must be at or near the industry average.
Strategies to lower cost:
¡Reducing direct and indirect costs – by reducing wages, interest, supplies
¡Improving efficiency – minimising idle stock,, using resources more efficiently
¡Controlling areas of management responsibility – operations, HR, marketing etc.
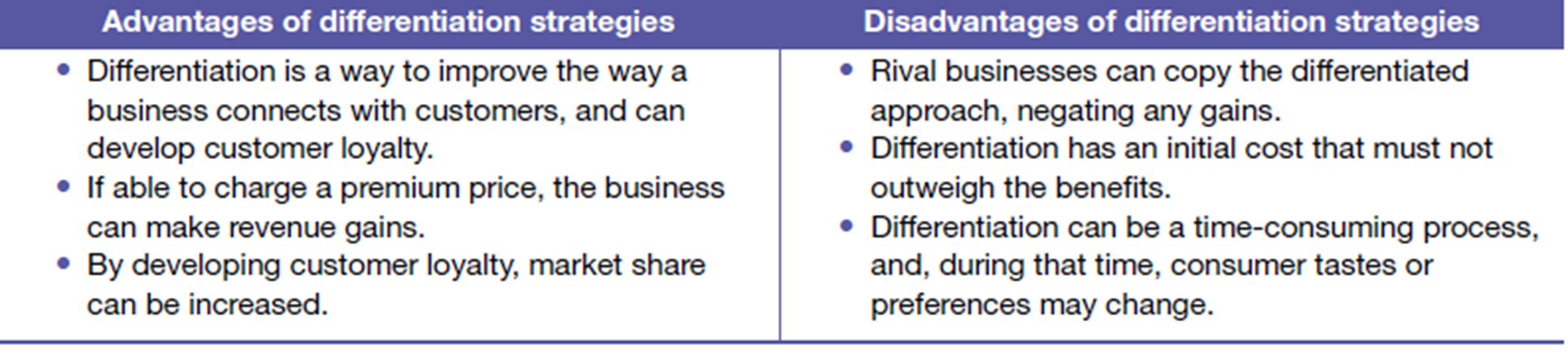
Porters differentiation strategy
an approach or method used to develop the uniqueness of the product or service and its attractiveness in order to attract and keep customers.
Strategies to differentiate:
¡High quality products – improving durability, customer service/support or extending warranties
¡Multiple branding – providing different/ more brands in the same market
¡Innovation/ Research & development – developing products with unique features
Similarities and differences between low cost and differentiation
