Complex Waves & Wave Interactions - 9/8
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
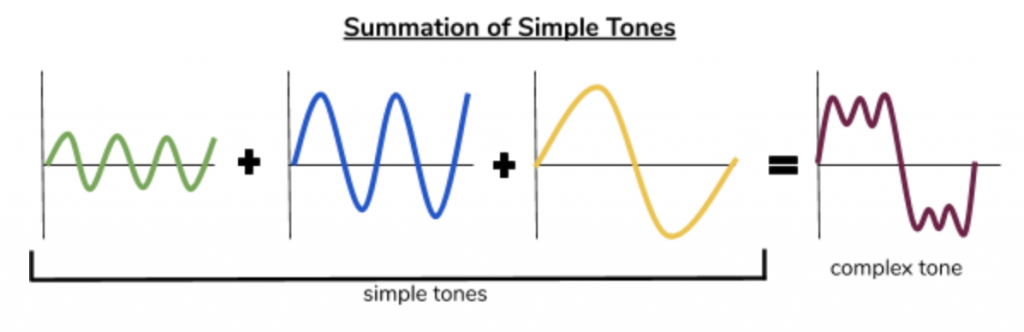
what is the difference between a simple and complex sound?
simple = 1 frequency = sine wave
complex = multiple frequencies
what is the difference between a periodic and aperiodic sound?
periodic has a repeating pattern, aperiodic does not
what are the two types of sound durations?
continuous = long
transient = short (eg. a gunshot)
the lowest frequency of a complex periodic sound is referred to as the ______
fundamental frequency, also known as f0
what are harmonics?
the frequencies that follow the fundamental frequency (f0) in whole number multiples of the f0
what makes us able to recognize someone’s voice?
their fundamental frequency (f0)
fundamental frequency is considered the _____ harmonic
first
if the f0 is 100 Hz, what are its harmonics?
200 Hz, 300 Hz, 400 Hz….
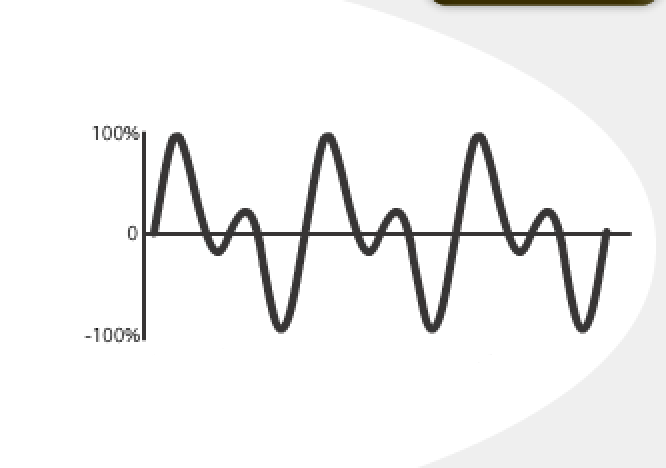
what is this an example of?
a complex periodic wave
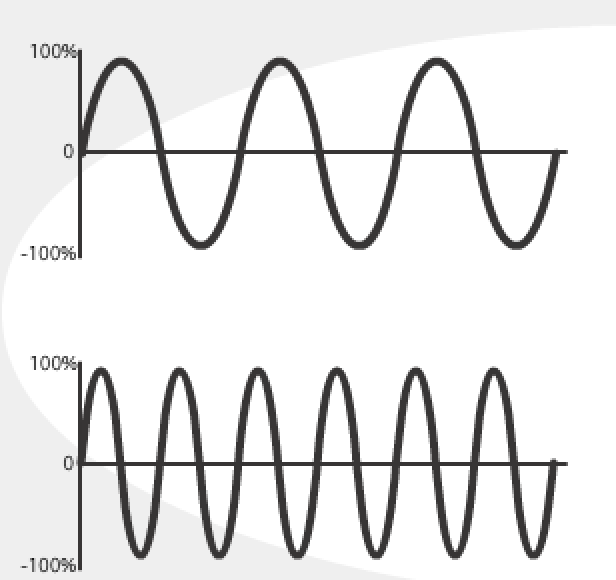
what are these examples of?
sine waves
what is fourier analysis?
a process that decomposes complex waves to determine amplitudes, frequencies, and phases of the sinusoidal components = a spectrum
what is fourier synthesis?
a process of reconstructing a complex waveform by adding together simple sine waves of different frequencies and amplitudes
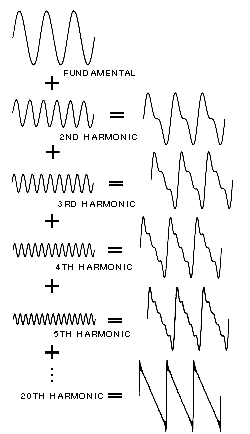
what is this image an example of?
fourier synthesis
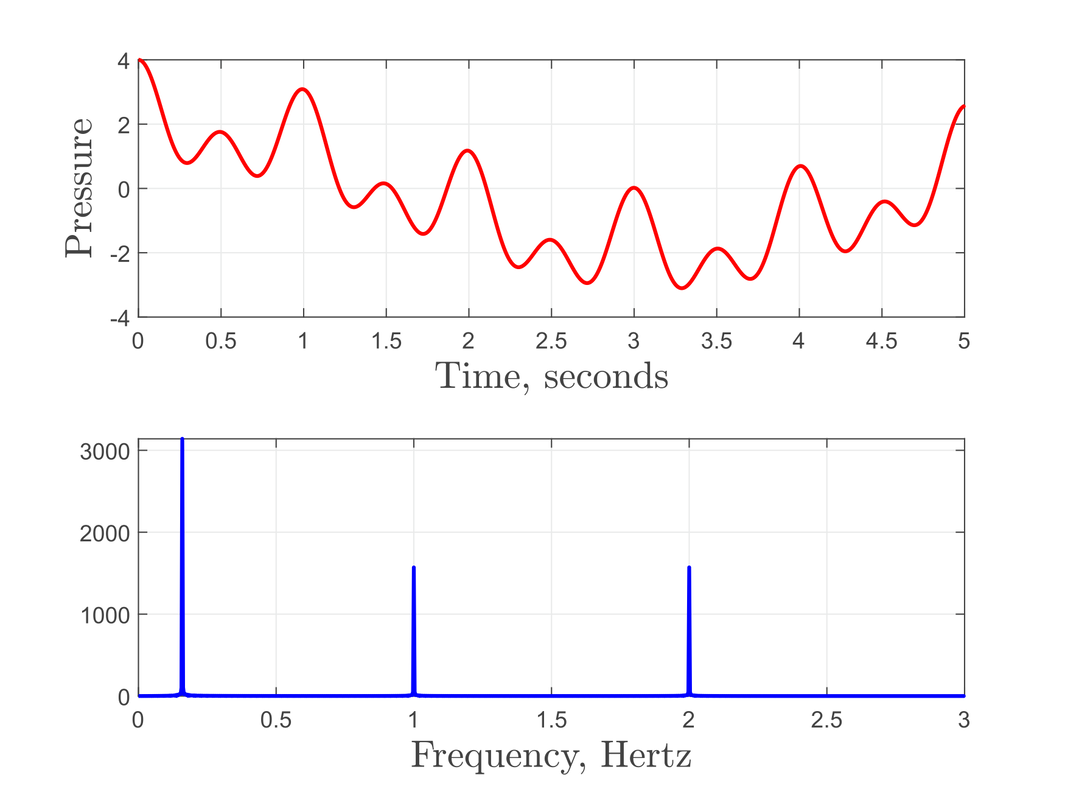
what is this image an example of?
fourier analysis
what are the four types of complex periodic sound waves?
sawtooth wave, square wave, triangular wave, pulse wave
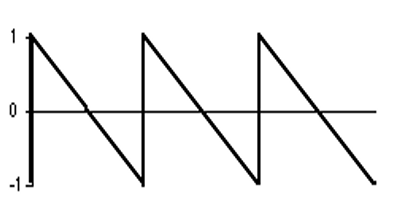
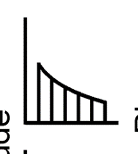
does a sawtooth wave have energy at odd or even harmonics? how does the amplitude of each harmonic decrease on the spectrum?
a sawtooth wave has energy at all harmonics.
amplitude of each harmonic decreases by the inverse of the harmonic number
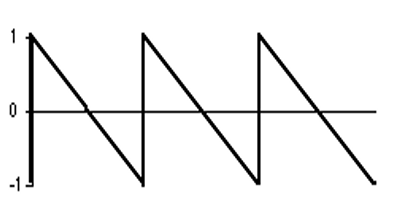
what is this image an example of? does it have energy at odd or even harmonics?
a sawtooth wave. has energy at ALL harmonics
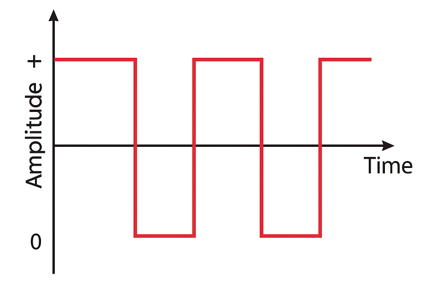
does a square wave have energy at odd or even harmonics? how does its spectral slope decrease? how does the amplitude of each harmonic decrease on the spectrum?
a square wave only has energy at ODD harmonics.
its spectral slope decreases by 6dB per octave.
amplitude of each harmonic decreases by the inverse of the harmonic number
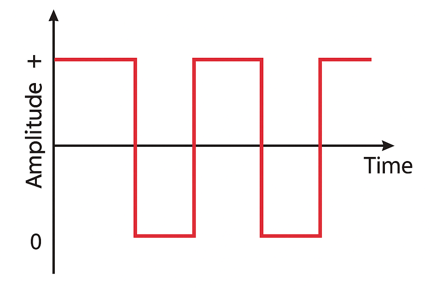
what is this image an example of? does it have energy at odd or even harmonics?
square wave. only has energy at ODD harmonics
what does going up an octave do to the frequency?
going up an octave doubles the frequency. 250 Hz → 500 Hz → 1000 Hz → 2000 Hz
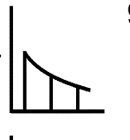
does a triangular wave have energy present at odd or even harmonics? how does its spectral slope decrease? how does the amplitude of each harmonic decrease on the spectrum?
a triangular wave only has energy present at ODD harmonics.
its spectral slope decreases by 12dB per octave.
the amplitude of each harmonic decreases as the reciprocal of the square of the harmonic number
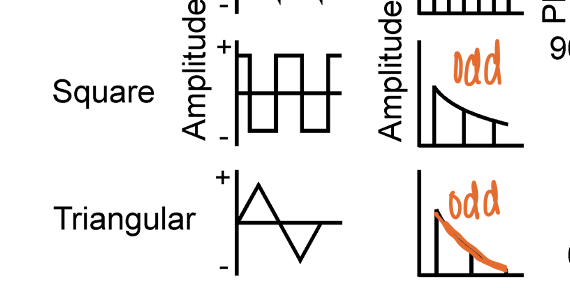
what distinguishes a triangular wave from a square wave?
slope of spectral envelope is steeper for triangular waves than square waves
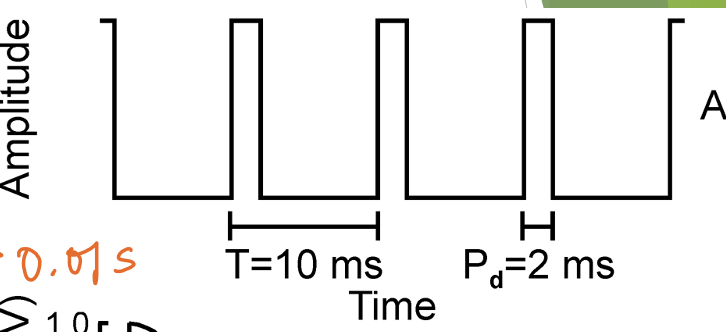
describe a pulse wave. what kind of wave is a pulse wave derived from? does it have energy at odd or even harmonics?
a wave where the second part of every cycle is silent
derived from square wave
each pulse in the wave has a duration (Pd).
has energy at ALL harmonics
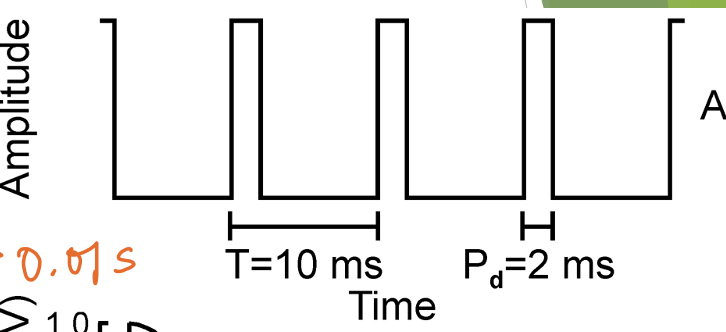
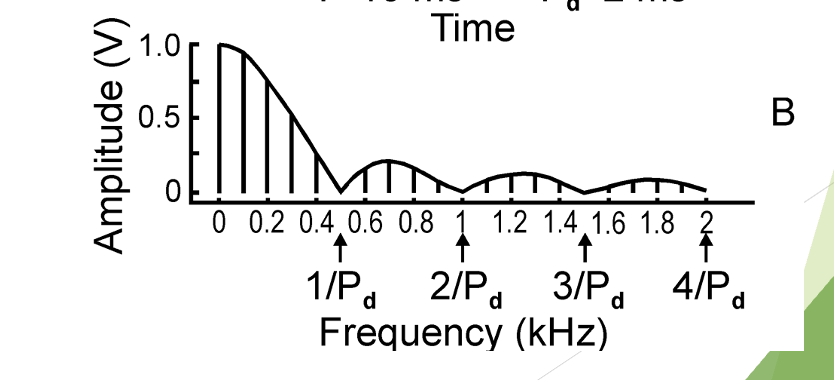
what is this image an example of? how long is the period of the entire cycle? how long is the pulse (Pd)?
it’s a pulse wave. T = 10 ms, pulse duration (Pd) = 2 ms
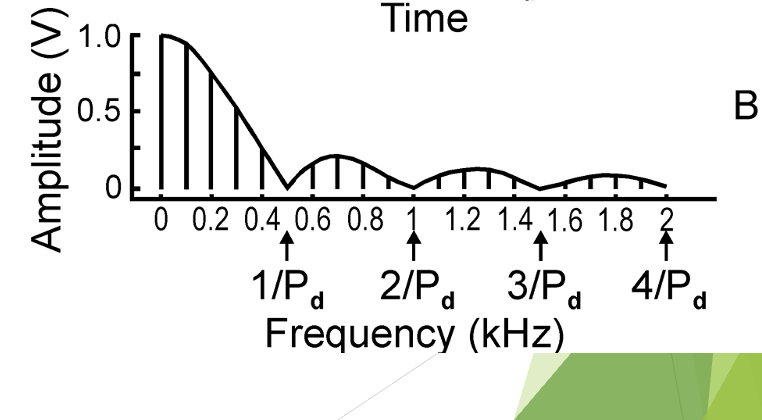
an amplitude spectrum of a pulse wave shows hills and valleys. the valleys are known as what? what is the pattern of the “valleys”?
valleys = nulls
nulls occur at integer multiples of the reciprocal of Pd.
Pattern: if Pd is 2, the first null be 1/2, the second null will be 2/2, the third null will be 3/2
how do you find pulse repetition frequency (PRF) for a pulse wave?
1/T = PRF
how many seconds is 10 ms?
0.01 s
if the period of a pulse wave = 10 ms, what is the PRF?
PRF = 1/T. T = 10 ms = 0.01 s. PRF = 1/0.01 s. PRF = 100 Hz.
what two kinds of complex periodic waves have energy at ALL harmonics?
sawtooth and pulse waves
what two kinds of complex waves have energy at only ODD harmonics?
square and triangular waves
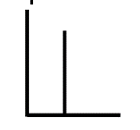
what kind of wave does this spectrum represent?
a sine wave. there is only one frequency present!
what kind of wave does this spectrum represent?
a sawtooth wave. there is energy at all harmonics but it is sloping down.
what kind of wave does this spectrum represent?
a square wave. there is only energy present at ODD harmonics, but the spectral envelope slope isn’t too severe
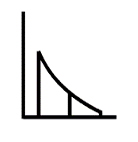
what kind of wave does this spectrum represent?
a triangular wave. there is only energy present at ODD harmonics, but the spectral envelope slope is very severe
what kind of wave does this spectrum represent?
a pulse wave
which two kinds of complex waves have a spectrum where amplitudes decrease as the inverse of the harmonic number? what is the difference between them, though?
sawtooth and square waves.
sawtooth - harmonics are at ALL frequencies.
square - harmonics are only found at ODD frequencies
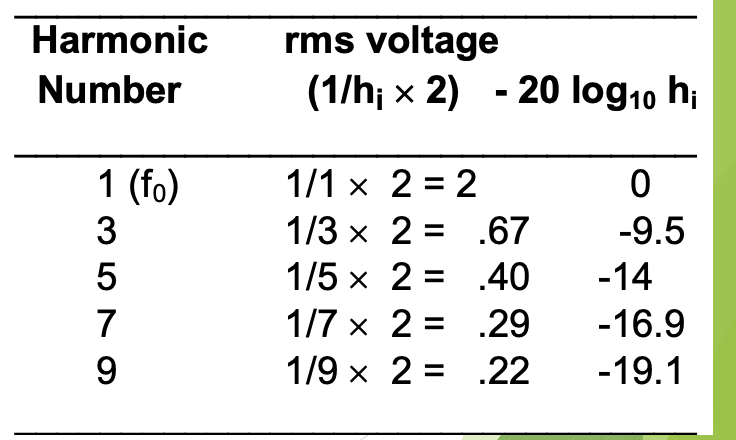
which kind of periodic complex wave has a spectrum where the amplitudes are found like this? (3rd harmonic = 1/3, 5th harmonic = 1/5, 7th harmonic = 1/7)
square wave
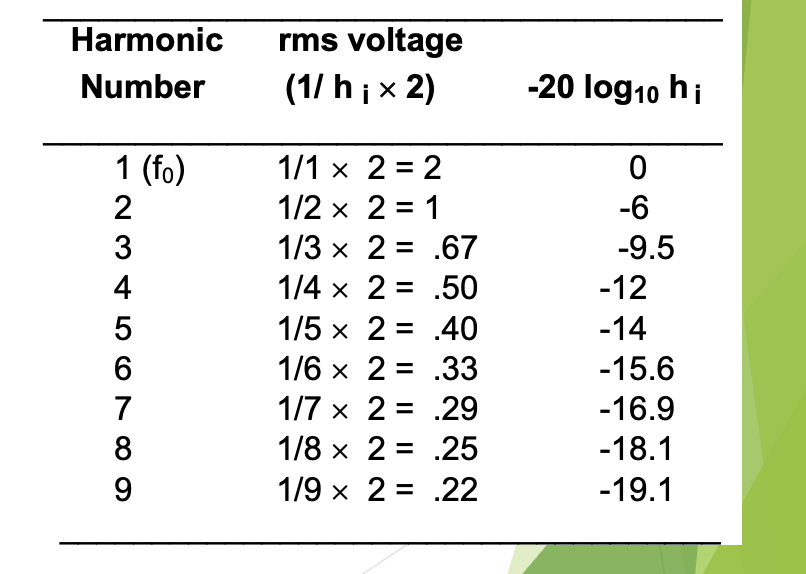
which kind of periodic complex wave has a spectrum where the amplitudes are found like this? (2nd harmonic = 1/2, 3rd harmonic = 1/3, 4th harmonic = 1/4)
sawtooth wave
which kind of periodic complex wave has a spectrum where the amplitudes decrease as the reciprocal of the square of the harmonic number?
triangular wave
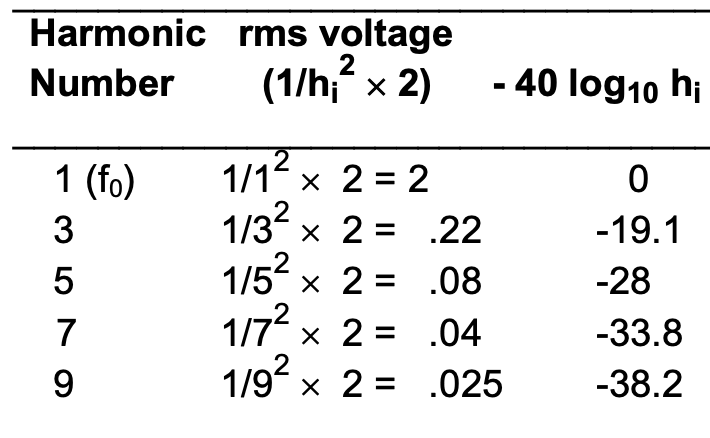
which kind of complex wave has a spectrum where the amplitudes are found like this? (3rd harmonic = 1/32, 5th harmonic = 1/52, 7th harmonic = 1/72)
triangular wave
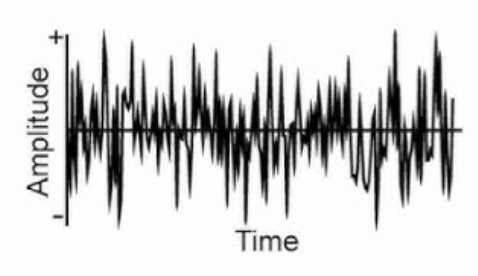
what is this an example of?
a complex aperiodic wave
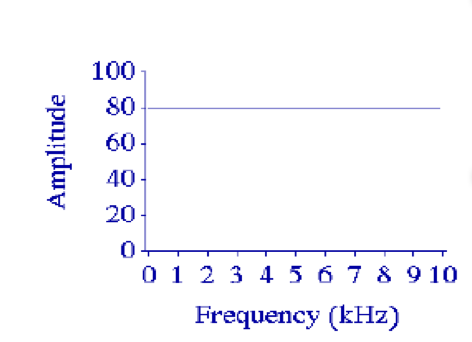
what kind of wave does this spectrum represent?
a complex aperiodic wave. energy is present at all frequencies with the SAME amplitude
what 3 kinds of changes may a sound wave undergo when it encouters an object in a medium?
reflection, diffraction, and refraction
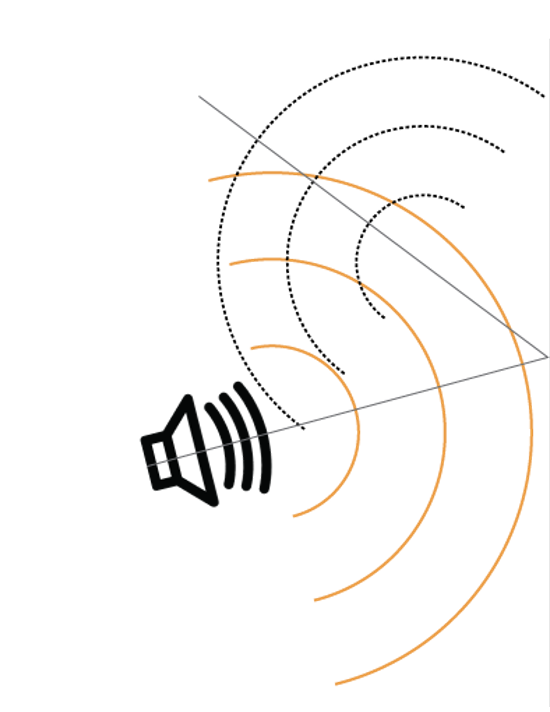

what is reflection?
an ECHO. when a sound wave encounters obstacles in a medium and changes its traveling path
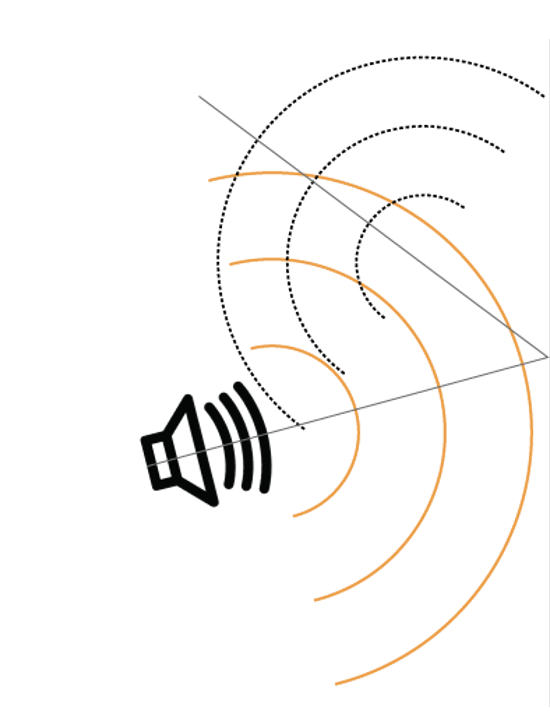

what is this image an example of?
reflection (ECHO)
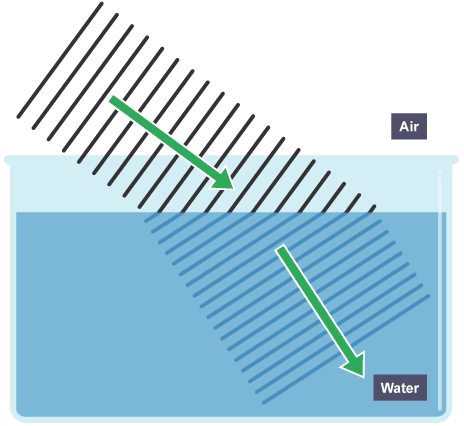
what is refraction?
BENDING when entering a different medium with any angle except 90 degrees
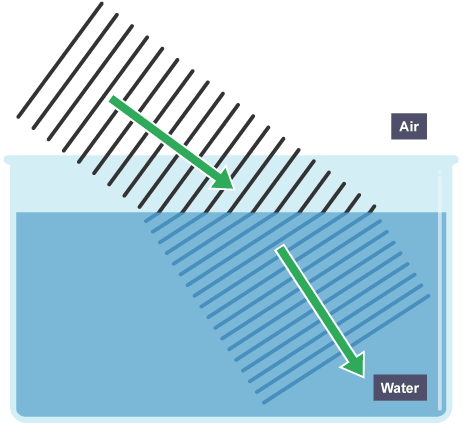
what is this image an example of?
refraction (BENDING when entering a different medium)
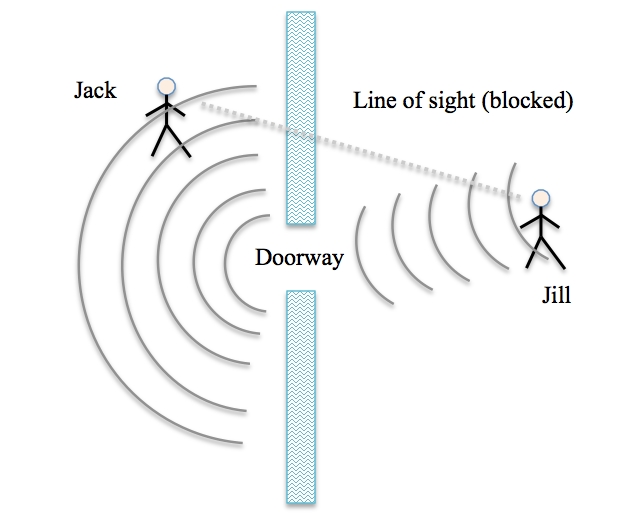
what is diffraction?
CHANGE IN DIRECTION. when sound waves change direction as they pass through an opening or around a barrier in their path
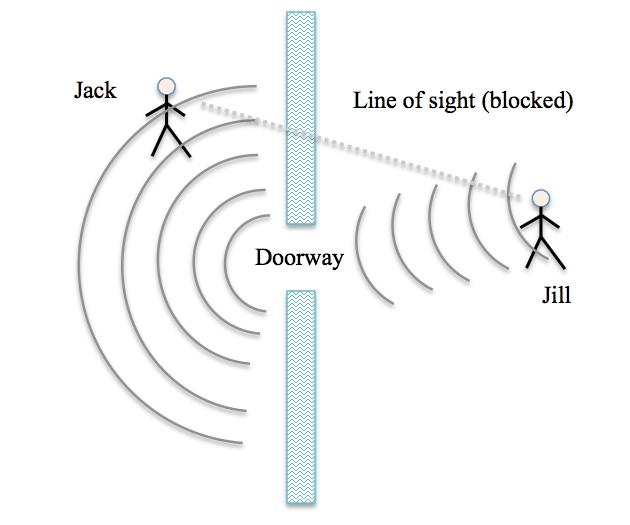
what is this image an example of?
diffraction (CHANGE IN DIRECTION)
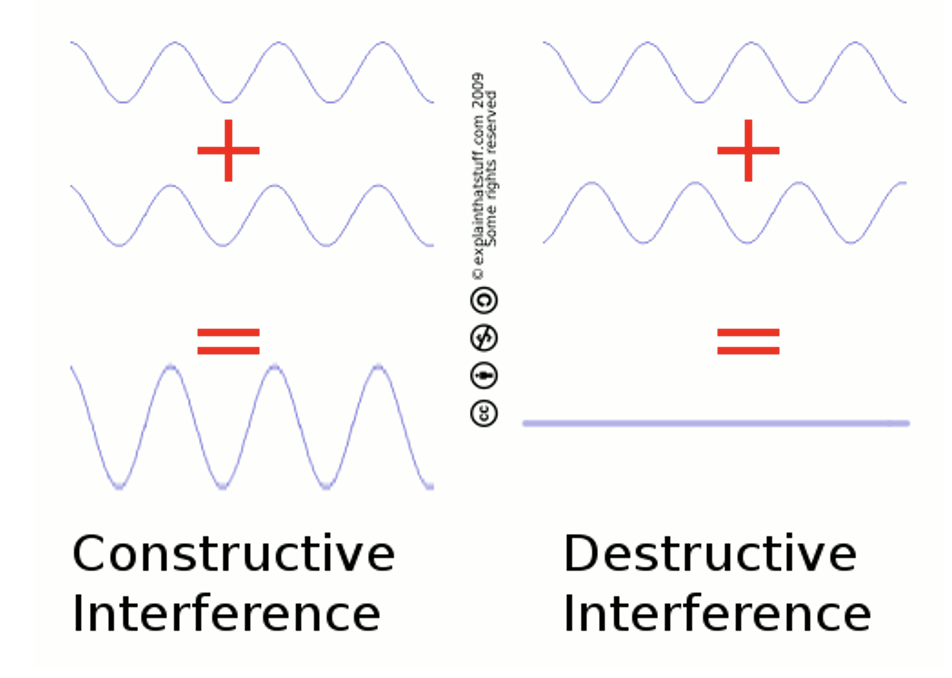
what is interference? what are the 2 kinds?
a condition when 2+ waves carrying energy meet up and overlap. constructive and destructive interference.
what determines if interference is constructive or destructive?
if the 2 waves are IN PHASE or OUT OF PHASE
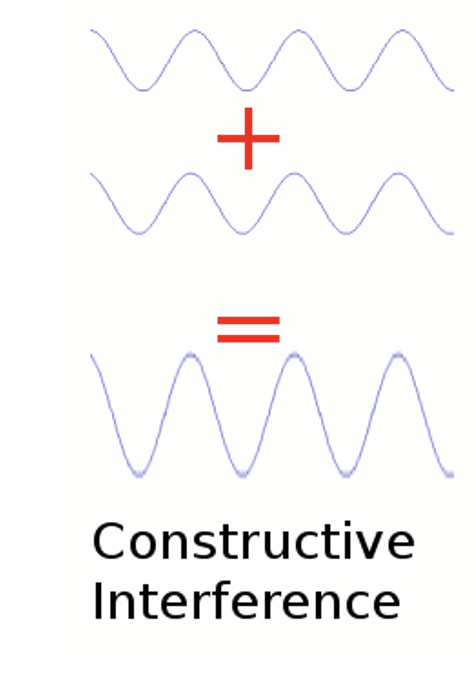
what is constructive interference?
when 2 waves that are in phase are added together, the amplitude of the final wave will be LARGER
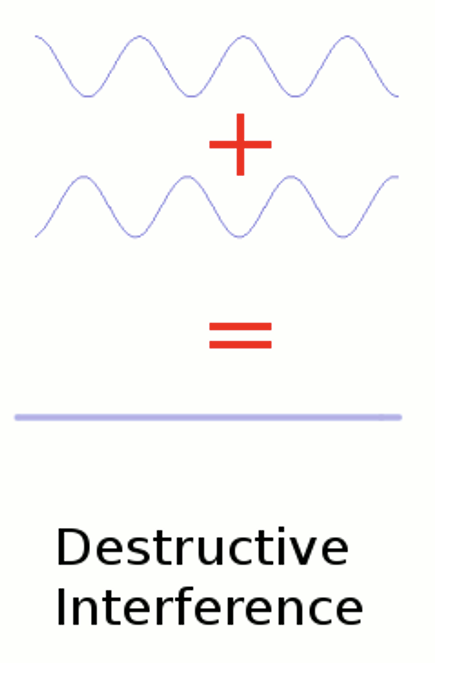
what is destructive interference?
when 2 waves that are out of phase are added together, the amplitude of the final wave will be SMALLER
what are string waves?
can be produced by stretching a string
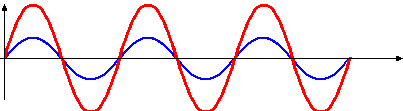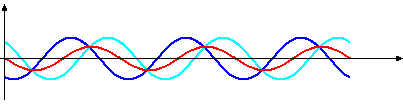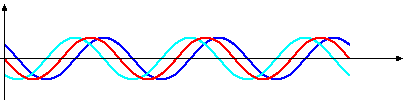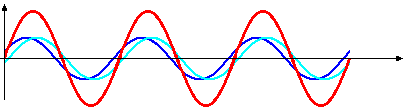
what are standing/stationary waves? which wave is the stationary wave in this image?
a result of interference between two waves travelling in opposite directions. the standing wave is the red wave.
what are nodes and anti nodes on a standing wave?
antinode: maximum amplitude/distance from 0 - moving up and down
node: minimum amplitude - stay at baseline
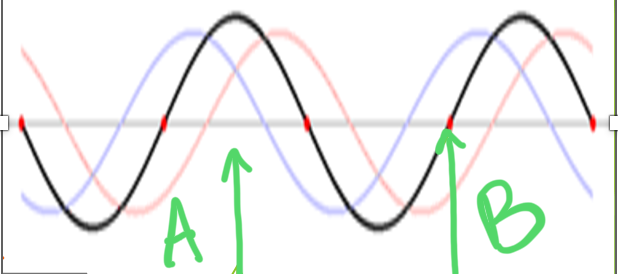
label
A: antinode
B: node
if the fundamental frequency/1st harmonic is 1000 Hz, what will the 3rd harmonic/2nd overtone be?
3000 Hz
what is a beat? how do we perceive it?
a kind of interference between two sounds of slightly different frequencies. we perceive it as periodic variations in volume (wobbling)
how do you find the rate of beats?
by taking the difference between the two frequencies
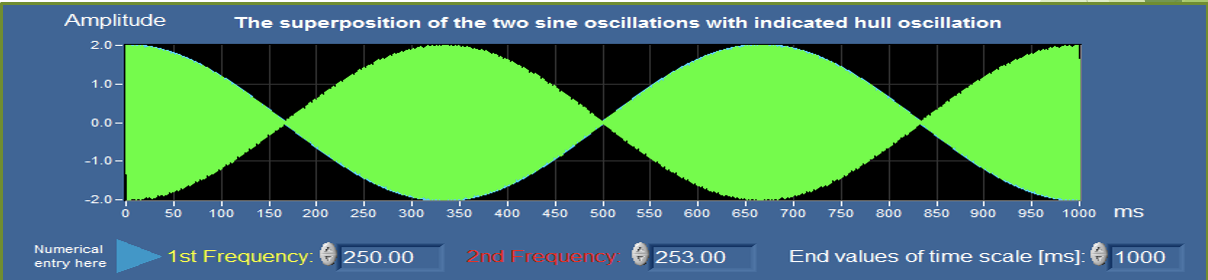
what is this an image of?
beats
if you combine a 250Hz tone and a 253Hz tone, how many beats per second will result?
3 beats per second
2 sine waves propagating in opposite direction will result in a ________
standing wave
reflection will be best if there is a [hard/loose/no] barrier
hard barrier
sound waves entering from air to water medium =
refraction
sound of a fire cracker is an example of
reflection (echo)