Natural Sciences CLEP
1/290
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
291 Terms
Evolution
the gradual change of characteristics within a population, producing a change in a species over time.
Natural Selection
a feature of population genetics that is the driving force behind evolution.
Gene Pool
the entire collection of genes within a given population.
Differential Reproduction
individuals within a population that are most adapted to the environment and are also the most likely individuals to reproduce successfully; tends to strengthen the frequency of expression of desirable traits across the population.
Mutation
a change of the DNA sequence of a gene, resulting in a change of the trait.
Genotype
the combination of alleles that make a particular trait.
Phenotype
the trait expressed.
Genetic Drift
over time, a gene pool (particularly in a small population) may experience a change in frequency of particular genes simply due to change fluctuations.
Gene Migration
the introduction of new genes from an immigrant, which results in a change of the gene pool.
Hardy-Weinberg Law of Equilibrium
in situations where random mating is occurring within a population (which is in equilibrium with its environment), gene frequencies and genotype ratios will remain constant from generation to generation.
Allopatric Speciation
occurs when two populations are geographically isolated from each other.
Sympatric Speciation
genetically different members reproduce with each other, producing a population, which is separate from the original species.
Adaptive Radiation
a single species can develop into several diverse species over time; over time a species will specially adapt to live more effectively in a new environment.
Punctuated Equilibrium
scientific model that proposes that adaptations of species arise suddenly and rapidly; specific species undergo a long period of equilibrium, which at some point is upset by environmental forces causing a short period of quick mutation and change.
Homologous
structures that exist in two different species because they share a common ancestry.
Analogous
structures that are similar because of their common function, although they do not share a common ancestry.
Extinction
when the entire population of a particular species is eliminated.
Taxonomy
study that organizes living things into groups based on morphology or, more recently, genetics.
Organism Classification System
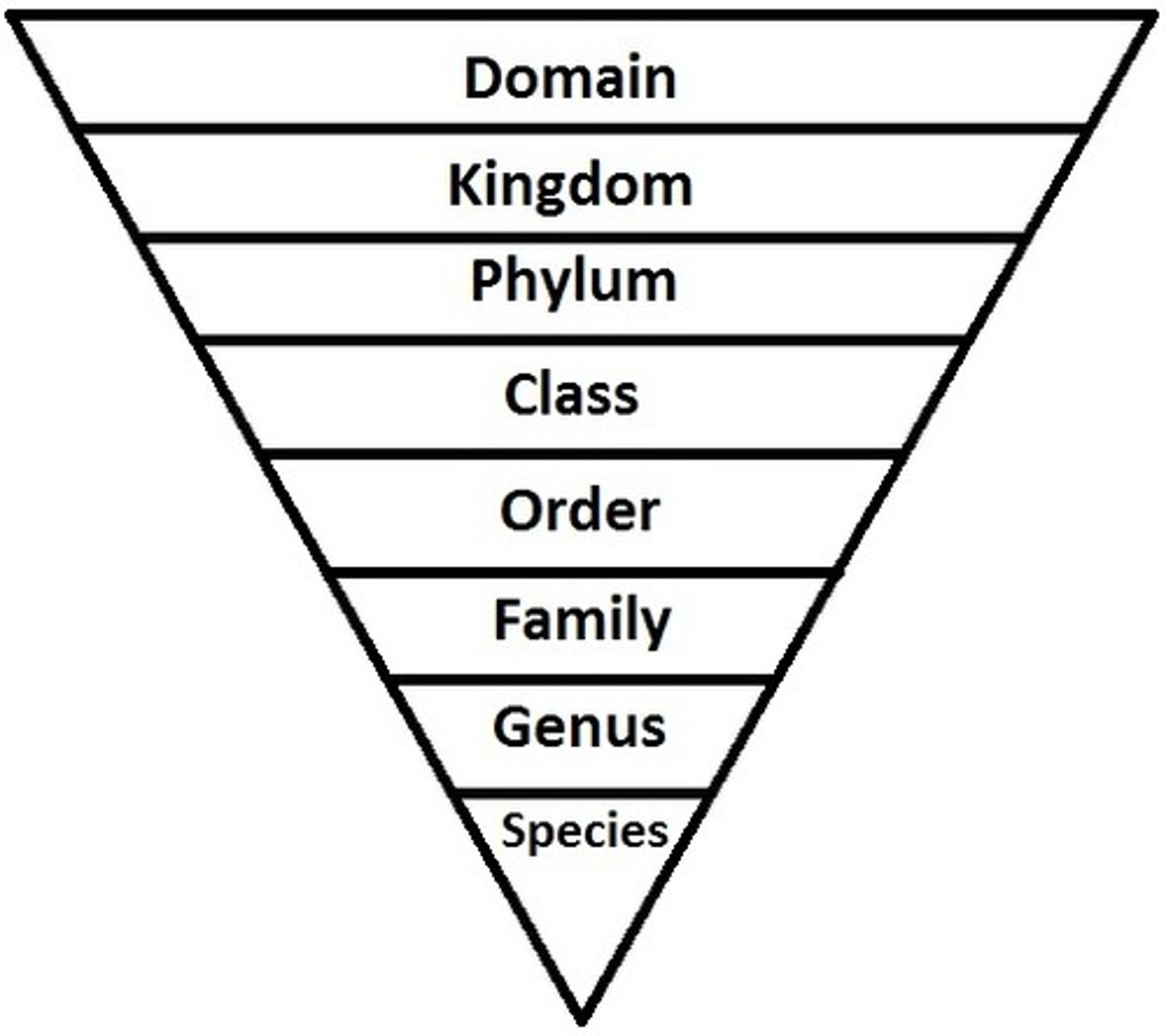
Domains
classification category even more general than kingdoms.
Cell
the smallest and most basic unit of most living things.
Prokaryotic Cells
cells with no nucleus or any other membrane-bound organelles.
Eukaryotic Cells
cells the contain membrane-bound intracellular organelles, including a nucleus.
Organelles
cells components that perform particular functions.
Viruses
smaller than even the smallest cells; survive and replicate by invading a living cell.
Cell Membrane
structure that encloses the cell and separates it from the environment; also known as the plasma membrane.
Microvilli
projections of the cell extending from the cell membrane; increase the surface area of the cell membrane, increasing the area available to absorb nutrients.
Cytoskeleton
provides structural support to a cell.
Cytoplasm
region between the nucleus and cell membrane.
Ribosomes
the site of protein synthesis within cells.
Endoplasmic Reticulum
large organization of folded membranes; responsible for the delivery of lipids and proteins to certain areas within the cytoplasm (a sort of cellular highway).
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
has attached ribosomes; instrumental to protein synthesis.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
network of membranous channels; does not have attached ribosomes.
Golgi Apparatus
instrumental in the storing, packaging, and shipping of proteins; also known as Golgi bodies or the Golgi complex.
Secretory Vesicles
carry substances produced within the cell to the cell membrane; packets of material packaged by the Golgi apparatus or endoplasmic reticulum.
Exocytosis
the export of substances from the cell.
Lysosomes
membrane-bound organelles containing digestive enzymes; digest unused material within the cell, damaged organelles, or materials absorbed by the cell for use.
Mitochondria
center of cellular respiration
Nucleus
an organelle surrounded by two lipid bilayer membranes that is located near the center of the cell and contains chromosomes, nuclear pores, nucleoplasm, and nucleoli.
Nucleolus
a rounded area within the nucleus of the cell where ribosomal RNA is synthesized.
Nuclear Membrane
the boundary between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
Cell Walls
made of cellulose and lignin, they enclose the cell membrane providing strength and protection for the cell.
Chloroplasts
the site of photosynthesis within plant cells.
Chlorophyll
pigment molecules that give the chloroplast their green color.
Stroma
the body of the chloroplast.
Passive Transport
substances freely pass across the membrane without the cell expending any energy.
Active Transport
uses energy to move molecules across a cell membrane against a concentration gradient.
Diffusion
the process whereby molecules and ions flow through the cell membrane from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration; mixing of particles in a gas or liquid.
Osmosis
a special process of diffusion that occurs when the water concentration inside the cell differs from the the concentration outside the cell; the water on the side of the membrane with the highest water concentration will move though the membrane until the concentration is equalized on both sides.
Facilitated Diffusion
allows for the transfer of substances across the cell membrane with the help of specialized proteins.
Endocytosis
the process whereby large molecules are taken up into a pocket of membrane; the pocket pinches off, delivering the molecules, still inside a membrane sack into the cytoplasm.
Anabolism
the process whereby cells build molecules and store energy.
Catabolsim
process of breaking down molecules and releasing stored energy.
ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
energy currency of cellular activity; consists of a nitrogenous base (adenine), a simple sugar (ribose), and three phosphate groups.
Photosynthesis
a crucial set of reactions that convert the light energy of the sun into chemical energy usable by living things.
CO(little)2 Fixation
the second phase of photosynthesis in which six CO(little)2 molecules are linked with hydrogen (produced in photolysis), forming glucose (a six-carbon sugar); also known as the dark reaction.
Aerobic
steps in the cellular respiration process that require oxygen.
Anaerobic
steps in the cellular respiration process that do not require oxygen.
Krebs Cycle
the first step in aerobic respiration that occurs in the matrix of a cell's mitochondria and breaks down pyruvic acid molecules (three carbons each) into CO(little)2 molecules, H+ (protons), and 2 ATP molecules; also liberates electrons.
Glycolysis
the breaking down of the six-carbon sugar (glucose) into smaller carbon-containing molecules yielding ATP.
Electron Transport
the second step of aerobic respiration that captures the energy created by the release of electrons from the Krebs cycle.
Fermentation
another name for anaerobic respiration, which breaks down the two pyruvic acid molecules (three carbons each) into end products (such as ethyl alcohol, or lactic acid), plus carbon dioxide.
Gene
length of DNA that encodes a particular protein.
Genomes
sum total of genetic information.
Transcription
the formation of an RNA molecule, which corresponds to a gene.
mRNA
RNA strand that migrates form the nucleus to the cytoplasm; also known as messenger RNA.
Translation
phase of photosynthesis that requires a second type of RNA.
tRNA
a chain of about 80 nucleotides that provide the link between the "language" of nucleotides (codon and anticodon) and the "language" of amino acids; also known as transfer RNA.
Structural Genes
code proteins that form organs and structural characteristics.
Regulatory Genes
code proteins that determine fictional or physiological events.
Transduction
the transfer or genetic material (portions of a bacterial chromosome) from one bacteria cell to another.
Transformation
a process in which bacteria absorb and incorporate pieces of DNA from their environment (usually from dead bacterial cells).
Cell Division
the process of cell reproduction that centers on the replication and separation of strands of DNA.
Histones
short length of DNA wrapped around a core of small proteins.
Chromatin
the combination of DNA with histones.
Chromatids
the two identical strands of duplicated chromatin in a cell that is getting ready to divide.
Cell Cycle
a particular sequence of events ending in cell division, which produces two daughter cells.
Interphase
the period when the cell is active in carrying on its functions.
G1 Phase
first phase of interphase; metabolism and protein synthesis are occurring at a high rate, and most of the growth f the cell occurs at this time.
S Phase
second phase of interphase where cell begins to prepare for cell division by replicating the DNA and proteins necessary to form a new set of chromosomes.
G2 Phase
final phase of interphase; more proteins are produced, which will be necessary for cell division, and the centrioles are replicated as well.
Mitosis
the process by which a cell distributes its duplicated chromosomes so that each daughter cell has a full set of chromosomes.
Prophase
step one in mitosis; chromatin condenses into chromosomes within the nucleus, the centrioles move to opposite ends of the cell, and spindle fibers begin to extend from the centromeres of each chromosome toward the center of the cell.
Metaphase
step two of mitosis; occurs when the spindle fibers pull the chromosomes into alignment along the equatorial plane of the cell, creating the metaphase plate.
Anaphase
step three in mitosis; when the centromere divides, chromatids are separated from each others and become a chromosome; the two identical chromosomes move along the spindle fibers to opposite ends of the cell.
Telophase
step four in mitosis; occurs as nuclear membranes form around the chromosomes and disperse through the new nucleoplasm; spindle fibers also disappear.
Meiosis
the process of producing four daughter cells, each with single unduplicated chromosomes.
Haploid
single unduplicated chromosomes.
Diploid
the parent cell that has a normal set of paired chromosomes.
Gametes
the four haploid cells (egg and sperm) that are found in reproductive organs as a result of meiosis.
Division
distributes the remaining set of chromosomes in a mitosis-like process.
Synapse
point at which homologous chromosomes pair up during meiosis.
Enzymes
protein molecules that act as catalysts for organic reactions.
Catalyst
a substance that changes the speed of a reaction without being affected itself.
Substrate
particular substance of an enzyme that fits within the active site.
Regulation
enzyme control that may occur when the product of the reaction is also an inhibitor to the reaction.
Vascular
plants that have tissue organized in such a way as to conduct food and water throughout their structure; also known as tracheophytes.
Agiosperms
plants that produce flowers as reproductive organs.
Gymnosperms
plants that produce seeds without flowers.
Flower
the primary reproductive organ for a plant.