Borgon Molec Bio lecture 1 & 2 objectives
1/86
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
What is Mendel's Law of Segregation?
Each organism has two alleles for each trait, which segregate during gamete formation, ensuring each gamete carries only one allele.
What is Mendel's Law of Independent Assortment?
Genes for different traits assort independently of one another in the formation of gametes, applicable when genes are on different chromosomes.
What did Mendel observe in his pea plant experiments?
He observed 3:1 phenotypic ratios in F2 generations, leading to conclusions about dominant and recessive traits.
Why were pea plants chosen for Mendel's experiments?
Pea plants were ideal due to distinct traits, controlled mating, and rapid growth cycles.
What are alleles?
Variants of a gene found at a specific locus on a chromosome.
What is the difference between homozygous and heterozygous?
Homozygous has two identical alleles for a trait (e.g., AA or aa), while heterozygous has two different alleles for a trait (e.g., Aa).
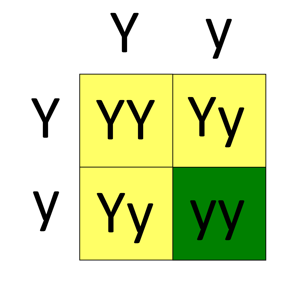
How do you perform a Punnett Square for a single trait?
Use a 2x2 grid for single trait outcomes.
What is the phenotypic ratio of a dihybrid cross?
The expected phenotypic ratio in F2 generations from a dihybrid cross is 9:3:3:1.
What is incomplete dominance?
A type of inheritance where traits are blended
Example of incomplete dominance
pink flowers from red and white parents
What defines codominance?
Both alleles are expressed fully in the phenotype
Example of codominance
AB blood types
Give an example of multiple alleles.
Blood type is controlled by multiple alleles, such as A, B, and O.
Define multiple alleles
More than two alleles control a trait
What is polygenic inheritance?
Traits that are controlled by multiple genes
Examples of polygenic inheritance
Skin color
What is epistasis?
One gene modifies the expression of another
Examples of epistasis
Coat color in dogs
What happens during mitosis?
Mitosis produces identical diploid cells, consisting of stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
What are the key differences between meiosis and mitosis?
Meiosis produces haploid gametes while mitosis produces diploid cells; meiosis involves two rounds of division.
What happens during metaphase in Mitosis?
Chromosomes align at the metaphase plate
What happens during anaphase in Mitosis?
Sister chromatids separate
What is the result of mitosis?
Two identical daughter cells (2n each)
What does Meiosis produce?
Haploid gametes (2n to n)
What is a requirement of meiosis?
crossing over
What is independent assortment in genetics?
The principle that genes on separate chromosomes assort independently during gamete formation.
How are linked genes inherited?
Linked genes show less frequent recombination and tend to be inherited together unless separated by crossing over.
Beadle and Tatum experiment
Studied mold mutants and developed the one gene- one enzyme hypothesis
Griffith experiment
Studied rough (R) and smooth (S) strains of bacteria to show transformation
Avery experiment
Digested DNA, RNA, Proteins, etc. to show that the transforming agent was DNA
Chargaff’s Rules
A=T, G=C. Disproved the tetranucleotide hypothesis
Hershey-Chase Experiment
Showed the DNA (32P) enters the host cell, not not protein (35S)
Franklins diffraction
X-ray data confirmed that DNA is helical and composed of 2 strands
Watson and Crick
Modeled the structure of the DNA double helix
Kornberg’s experiment
Showed that DNA replication was 5’ to 3’
Meselson-Stahl experiment
Showed DNA replication is semi-conservative
What is the significance of recombination frequency?
Recombination frequency indicates how often crossing over occurs between two genes and is used to calculate gene linkage.
How do sex-linked traits behave in inheritance?
Sex-linked traits are associated with sex chromosomes, such as X-linked conditions like color blindness.
What did McClintock's experiment demonstrate?
It demonstrated crossing over in corn using chromosomal markers and established linkage and crossover events.
What are two-factor and three-factor crosses used for?
To map genes and analyze gene order based on recombination frequencies.
How do you determine gene order using three-factor crosses?
By analyzing the phenotypes of offspring to identify the least frequent recombinants.
What is the connection between genetic markers and recombination frequency?
Genetic markers are used to map genes and calculate recombination frequencies, accounting for double crossovers.
What do genetic disorders linked to enzyme mutations illustrate?
They advance the understanding of metabolic pathways and genetic inheritance, such as alkaptonuria and phenylketonuria.
Genetic linkage occurs when genes are..?
located close together on the same chromosome
Linked genes tend to be inherited more/less frequently than genes on different chromosomes
More
Crossing over is the exchange of…?
genetic material between homologous chromosomes during meiosis
The frequency of crossing over between two genes is related to..?
Their physical distance on the chromosome
Genes that are closer together on a chromosome have a lower/higher chance of bering separated by crossing over
Lower
Linkage percentage ranges from..?
50% to 100%
Recombination percentage ranges from..?
0% to 50%
What is the benefit of using E. coli in genetic studies?
E. coli has a rapid generation time (~20 minutes) and a haploid genome, facilitating the observation of mutations.
What concept did the Beadle and Tatum experiment propose?
The one gene–one enzyme hypothesis, linking specific genes to specific enzymes.
What did Beedle and Tatum expose spores to?
X-rays to induce mutations, resulting in strains dependent on supplements
What happens when a mutation occurs in a sequential metabolic pathway?
A mutation can halt the pathway, leading to the accumulation of substrate.
How did biochemists categorize lipids and carbohydrates?
homopolymers or repetitive heteropolymers, can be built from single enzymes
How did biochemists categorize proteins?
polypeptide chains, non-repetitive heteropolymers
How did biochemists categorize nucleic acids?
polynucleotide chains
What is the Central Dogma of Biology?
The flow of genetic information is DNA → RNA → Protein.
How is the genetic code degenerate but not ambiguous?
Multiple codons encode the same amino acid and each codon specifies only one amino acid.
What is the significance of Vernon Ingram's studies on hemoglobin?
He identified that a single amino acid substitution (glutamate to valine) leads to sickle cell anemia.
What was the purpose of Griffith's experiment with Streptococcus pneumoniae?
To demonstrate the concept of transformation, showing that heat-killed virulent strains could transform non-virulent strains.
What did Avery’s experiment reveal about the transforming substance?
That DNA is the transforming substance responsible for genetic information transfer.
What did Chargaff's rule indicate regarding DNA base pairing?
A = T and G = C; it revealed the base composition's variability across species.
What was the outcome of the Hershey-Chase experiment?
It confirmed that DNA, not proteins, is the genetic material by showing DNA enters bacterial cells.
Identify DNA nucleosides
Deoxyadenosine, deoxyguanosine, deoxycytidine, and thymidine
Identify RNA nucleosides
Adenosine, guanosine, cytidine, and uridine
What do nucleosides consist of?
a nitrogenous base (purine or pyrimidine) bonded to a sugar molecule (ribose in RNA, deoxyribose in DNA).
What do nucleotides consist of?
Consist of a nitrogenous base, a sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), and one or more phosphate groups.
Identify DNA nucleotides
Deoxyadenosine triphosphate (dATP), deoxyguanosine triphosphate (dGTP), deoxycytidine triphosphate (dCTP), and thymidine triphosphate (dTTP).
Identify RNA nucleotides
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP), guanosine triphosphate (GTP), cytidine triphosphate (CTP), and uridine triphosphate (UTP).
How did Kornberg's experiment contribute to our understanding of DNA synthesis?
It isolated DNA polymerase I and demonstrated that DNA synthesis requires a template and occurs in the 5’ to 3’ direction.
What does the Meselson and Stahl experiment illustrate about DNA replication?
That DNA replication is semiconservative, with each daughter molecule containing one original and one new strand.
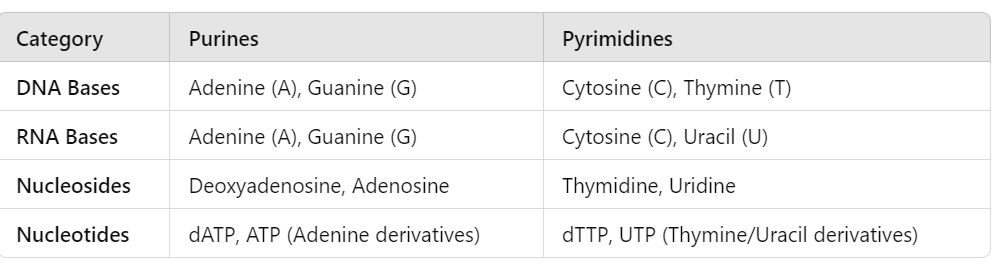
Helpful table for DNA/RNA bases and nucleosides/nucleotides
JUST A TABLE FOR REFERANCE
What are the structural differences between DNA and RNA?
DNA is double-stranded with deoxyribose sugar and thymine; RNA is single-stranded with ribose sugar and uracil.
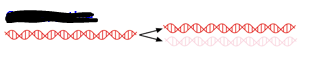
Original strands remain together; new strands pair.
Conservative DNA replication model
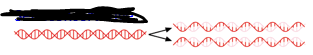
Each daughter molecule has one original and one new strand.
Semiconservative
Strands are interspersed with old and new DNA.
Dispersive
The results for the DNA replication models sup[ported the semiconservative model using ..?
density gradient centrifugation
What is the role of tRNA in protein synthesis?
tRNA carries specific amino acids and matches codons on mRNA to its corresponding anticodons.
Explain the differences between RNA and DNA structures
DNA: Double-stranded, deoxyribose sugar, thymine.
RNA: Single-stranded, ribose sugar, uracil.
Explain the differences between RNA and DNA functions
DNA stores genetic information
RNA translates and carries it for protein synthesis.
What is the significance of aminoacyl tRNA synthetases?
They charge tRNA with the correct amino acids and ensure accuracy during protein synthesis.
What did Brenner, Jacob, and Meselson demonstrate about mRNA?
That mRNA is the intermediary between DNA and protein synthesis.
What did pulse-labeling experiments reveal about protein synthesis directionality?
That proteins are synthesized from the amino (N) terminus to the carboxyl (C) terminus.
Why did Crick hypothesize that there was an adapter molecule to synthesize proteins from RNA?
He thought that adapter RNA recognition might be due to H-bonding
Recall the initiation and termination processes of transcription
Initiation: Promoter regions (-10 and -35 sequences) guide RNA polymerase binding.
Termination: Rho-dependent (helicase action, rho catalyzes the disassociation of mRNA) or rho-independent (hairpin loops, interferes with transcription).