Intro to Patient Care Lecture 1 - Introduction to Patient Care and the Pharmacists' Patient Care Process
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
physiology
the study of normal functions of the living organism and its parts
pathophysiology
the study of abnormalities in bodily functions as a cause or result of disease
idiopathic
describes a condition when the cause is unknown
pharmacotherapy
the pharmacological treatment of a disorder
etiology
the cause of a disease
epidemiology
the distribution (incidence, prevalence) and determinants (causes, risk factors) of a disease condition
incidence
the number of cases of a disease that are newly diagnosed within a population during a specific period of time
prevalence
the number of cases of a disease that are currently present within a population during a specific period of time
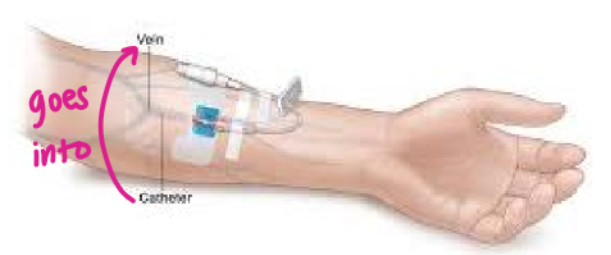
peripheral IV
IV access through a vein, generally in the hand, arm, foot, and sometimes the scalp
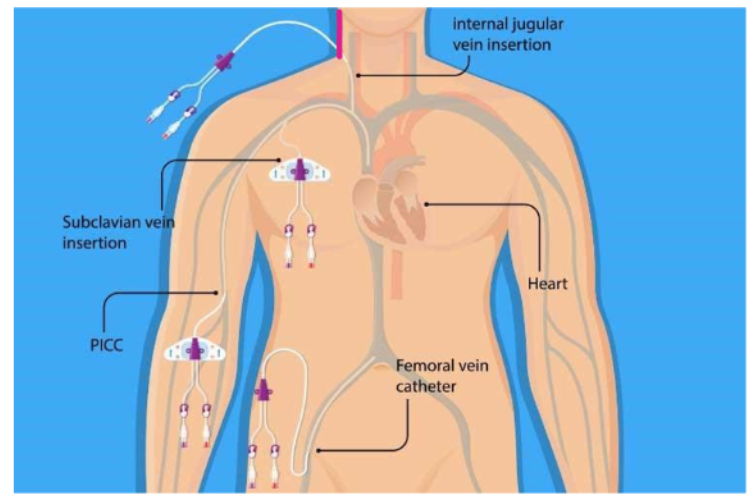
central IV
IV access through a larger vessel, generally placed in the neck, groin, or upper chest
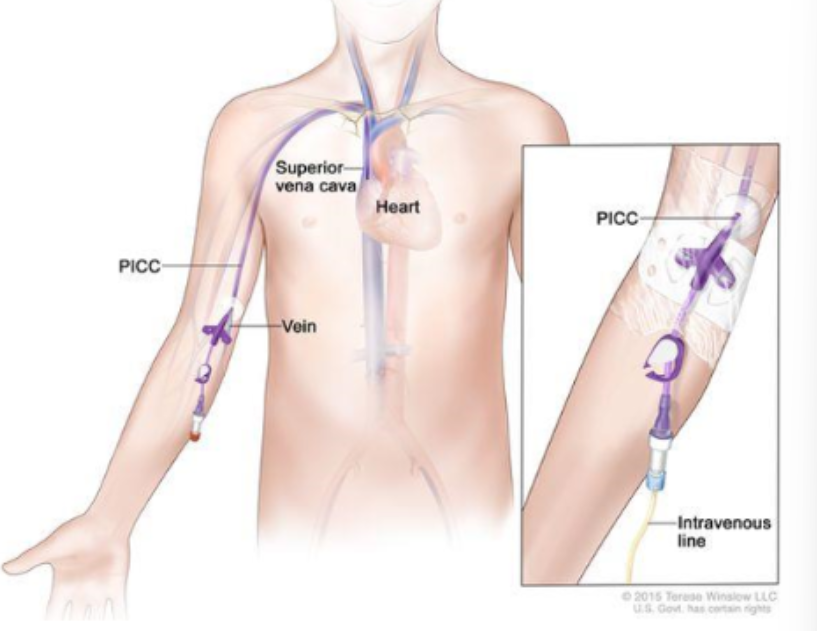
peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC)
a form of central access that is achieved by threading a catheter from a peripheral site (generally the arm) to a larger vessel
things that can be given through an IV line
medications, fluids, nutrition
fluid bolus
an IV infusion (without medication) in which a large volume of fluid (0.5 - 2 L) given to patients over 1-2 hours
maintenance infusion
an IV infusion (without medication) in which fluids are given at a specific rate (ml/hr) to maintain adequate hydration for patients who cannot have fluids by mouth
continuous IV
IV infusion (with medication) in which:
IV medications are infused continuously
often used for medications with short half-lives or narrow therapeutic ranges
will commonly see this in intensive care units
intermittent IV piggyback
a type of IV infusion (with medication) in which:
a smaller IV bag containing medication is connected to the patient’s main IV line
the smaller bag is “piggy-backing” off the patients main IV line to provide the medication
often used for medications that have long half-lives but can’t be given via IV push due to the drug properties (kinetics, toxicity, etc.)
IV push injection
a type of IV infusion (with medication) in which:
a medication can be drawn up in a syringe and be given rapidly (15 minutes or less)
the medication is “pushed” out of the syringe into an IV access point = IV push
often used for medications with long half-lives or that act quickly
intramuscular (IM) injection
a parenteral site of administration in which:
an injection given into deep muscle tissue (thigh, deltoid, gluteus)
needle angle: 90 degrees
example: flu shot
subcutaneous (SQ) injection
a parenteral site of administration in which:
an injection given into the subcutaneous fat tissue
needle angle: 45 degrees
example: insulin
intradermal injection
a parenteral site of administration in which:
an injection given into the dermis
not often used
needle angle: 10-15 degrees
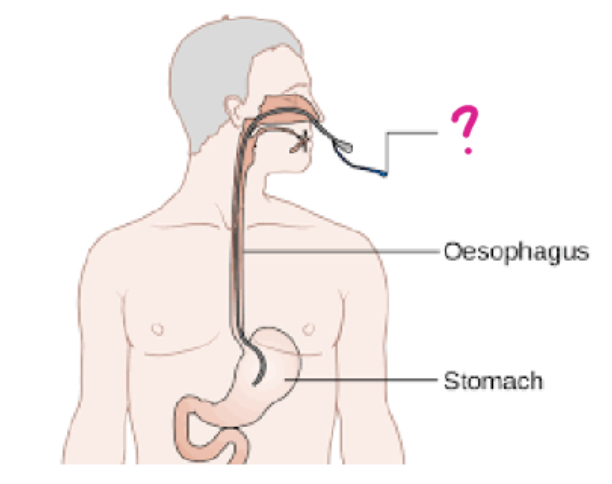
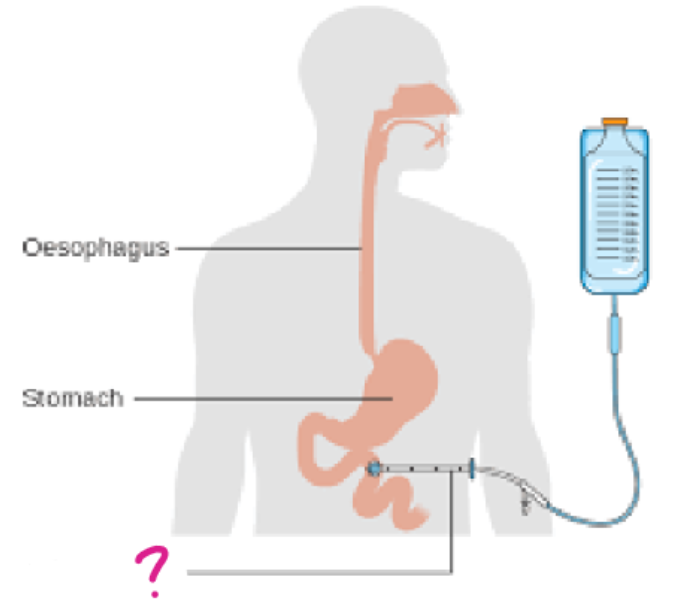
nasogastric (NG) tube
a form of enteral administration in which:
a flexible, plastic tube is inserted through the nose down into the stomach
used to administer nutrition and medications
percutaneous endoscopic gastrotomy (PEG) tube
a form of enteral administration in which:
a tube is inserted through the abdomen into the stomach
used to administer nutrition and medications
balloon is inflated so it doesn’t fall out
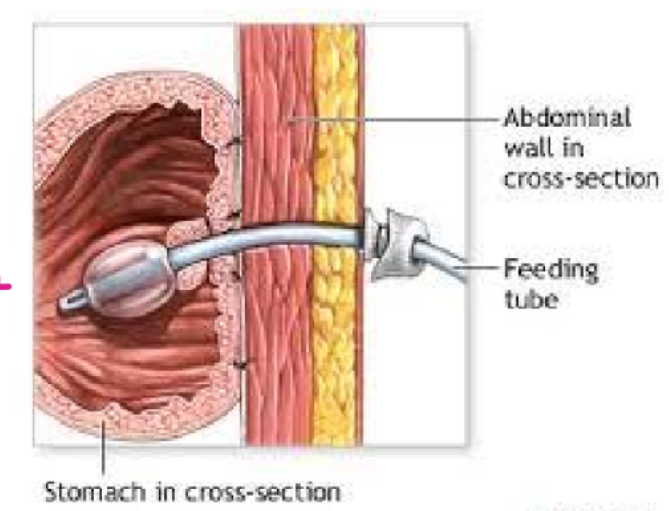
jejunostomy (J) tube
a form of enteral administration in which:
a tube is inserted through the abdomen into the jejunum (located in the small intestine)
used to administer nutrition and medications
foley catheter
a type of urinary catheter in which:
a flexible tube is placed through the urethra into the bladder
used for patients who are unable to control their bladder (incontinence, retention, sedated patients, etc.)
Texas catheter
a type of urinary catheter in which:
AKA a “condom” catheter
a less invasive approach for patients who need a catheter
PureWick catheter
type urinary catheter
a non-invasive approach to catheterization in women
uses suction to draw urine into a collecting system
health information technology
electronic health systems that health care professionals use to store, share, and analyze health information
electronic health records (EHRs)
electronic prescribing (E-prescribing)
Mobile Health (mHealth)
apps
medication adherences
examples: Medisafe, mymeds, ROUNDhealth
mental health
examples: Mindshift, QuitNow!, Headspace, PTSDCoach
wearables
smartwatches
continuous glucose monitors (CGM)
telemedicine and telehealth
demand for these services grew because of the COVID-19 pandemic
providers relied on technology to deliver virtual services to patients
telemedicine
Using telecommunications equipment to diagnose and treat illness remotely
Exchanging treatment notes, lab reports and prescriptions
Providing long-term care and treatment after hospitalization
telehealth
Conducting remote patient monitoring
Holding therapy sessions for mental and physical illness
Reviewing and exchanging medical and lab reports
role of pharmacists
to help identify digital health tools
to set-up and configure medical devices and health apps
to interpret data from digital health tools
the pharmacist’ patient care process (PPCP) definition
Definition: A process created and implemented to promote consistent, comprehensive patient care
PPCP components
Collect
Assess
Plan
Implement
Follow-up/Monitor
knowledge to perform the PPCP
Pathophysiology
Pharmacotherapy
Diagnostic testing
Laboratory testing
skills to perform the PPCP
communication with pts
communications with providers
physical assessment
subjective info
Information provided by the patient or patient's caregiver that cannot be perceived by the examiner
Information is obtained through patient interviewing
Patient interviews should utilize open ended questions
objective info
information obtained from the pt’s medical record or that was identified by an examiner
vitals
physical exam
labs
other info: imaging, diagnostic testing, calculations
problem list
what collected information (PPCP) is assessed to create
“differential” diagnosis
during Assess in CAPIF (PPCP)
in which the subjective and objective info match more than one possible condition and requires further testing to make a definitive diagnosis
additional testing can confirm or rule out a diagnosis
therapeutic plan characteristics (what they should be & components)
should be:
patient-centered
evidence-based
cost-effective
components:
non-pharmacological therapy
pharmacological therapy
safety monitoring
efficacy monitoring
pt education
follow-up
who are the ppl involved & what does implementing the plan in CAPIF (PPCP) look like in different pharmacy settings
ppl involved:
other members of the healthcare professional team
pt
in hospital, looks like entering orders on behalf of the physician
in community, looks like counseling pts
in ambulatory, looks like conducting pt visits
why we follow-up in CAPIF (PPCP)
purpose:
to ensure that the therapy is safe and effective
to assess adherence to the therapeutic plan
timing depends on:
setting
therapy changes (time to see effect of therapy, risk of safety concerns)
what you’re monitoring
actual body weight (ABW)
pt’s measured weight
ideal body weight (IBW)
a calculated value that estimates a pt’s lean tissue while considering sex and height
IBW equation male
IBW (kg) = 50 + 2.3(height in inches - 60 inches)
IBW equation female
IBW (kg) = 45.5 + 2.3(height in inches - 60 inches)
adjusted body weight (AdjBW)
a calculated value that estimates a pt’s lean tissue while considering the pt’s actual body weight, sex, and height (typically for obese ppl)
AdjBW equation
AdjBW (kg) = IBW + 0.4(ABW-IBW)
indications for use of AdjBW
indications:
drug dosing for hydrophilic medications with a low Vd (i.e., aminoglycosides)
calculating nutritional needs
intake and output
comparisons of these values are used to measure fluid balance for pts
conditions where fluid balance matters
matters in these conditions:
heart failure
kidney failure
septic shock
intake
oral fluids
IV solutions
tube feedings
output
urine
stool
vomiting
insensible losses (surgical pts)
methods of measurement of temperature
methods:
oral
rectal
axillary
ear
skin
normal oral temp
normal temp for this method of measurement: 98.6 F (37 C)
normal rectal temp
normal temp for this method of measurement: 0.5-1 F increase
tympanic temp
normal temp for this method of measurement: 0.5-1 degree F increase
axillary temp
normal temp for this method of measurement: 0.5-1 degree F decrease
temporal temp
normal temp for this method of measurement: 0.5-1 degree F decrease
Fahrenheit to Celsius conversion
C = [5(F-32)]/9
Celsius to Fahrenheit conversion
F = [9(C)/5] + 32
unit for blood pressure
measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg)
normal blood pressure
greater than 120/80 mmHg
hypertension
greater than 130/80 mmHg
hypotension
less than 90/60 mmHg
laying down has this effect on blood pressure
blood pressure is higher in this body position
standing up has this effect on bp
blood pressure is lower in this body positiion
how bp changes when pts go from lying or sitting to standing
bp decreases
orthostasis
profound change in blood pressure (SBP decreases 20 mmHg OR DBP decreases 10 mmHg)
respiratory rate units
measured in breaths per minute
normal rate for respiratory rate
12-16 breaths/minute
tachypnea
greater than 20 breaths/minute
pulse units
measured in beats per minute
normal rate for pulse
60-100 BPM
bradycardia
less than 60 BPM
tachycardia
greater than 100 BPM
magnitude of the pulse scale
described on a scale from 0 (absent) to 4 (bounding)
oxygen saturation
percentage of oxygen-saturated hemoglobin in the blood relative to total hemoglobin
normal range of oxygen saturation
95-100%
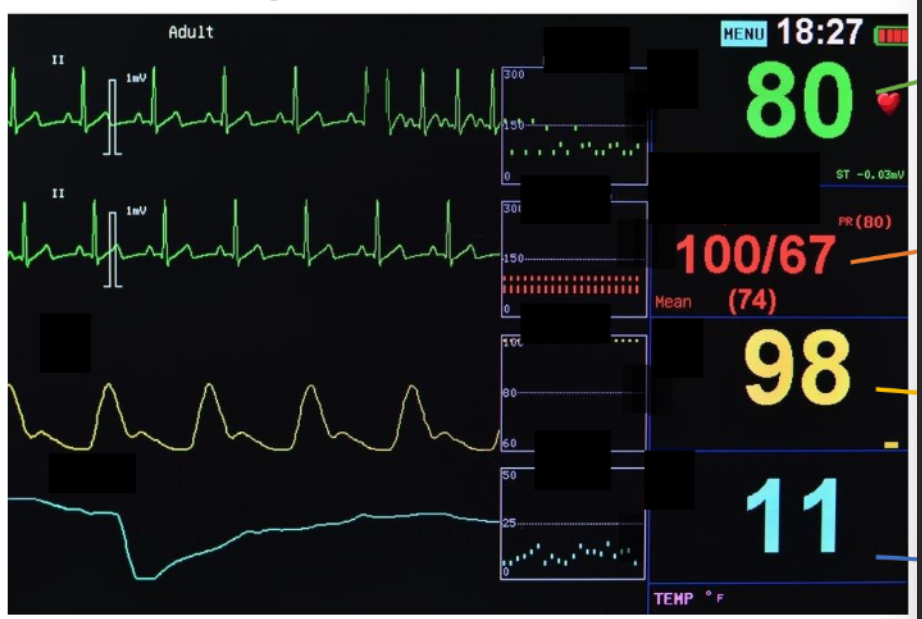
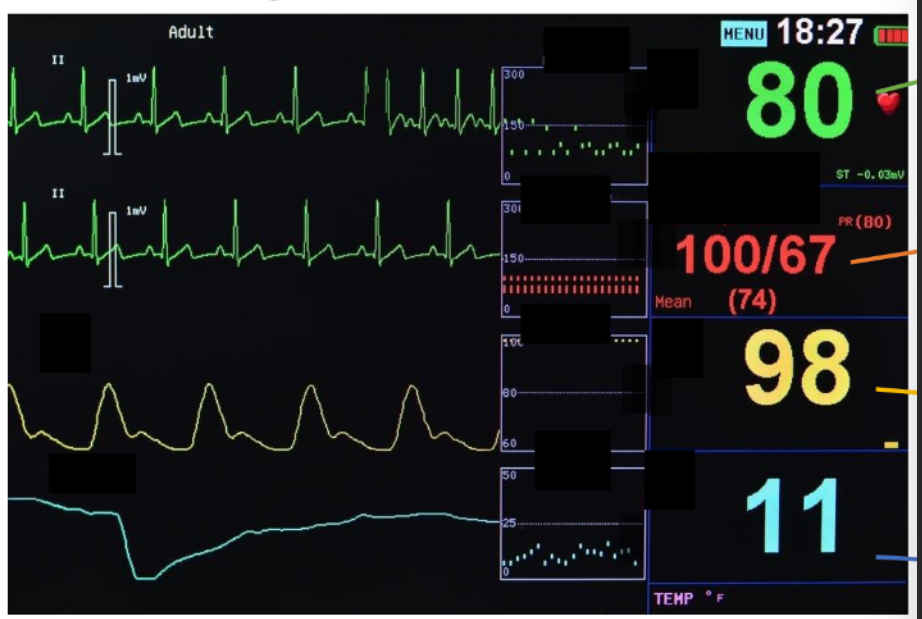
numbers on this? (top to bottom)
numbers on this (top to bottom)
heart rate
bp
oxygen saturation
respiratory rate
physical exam
a review of each bodily system for abnormalities obtained during the pt interview
considered objective date
review of systems
a review of each bodily system for abnormalities assessed by the pt
considered subjective data
fever definition
100.4+ F for over one hour OR 101+ F for any period of time