Chapter 11: Immunological Memory and Vaccination
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
long-lived plasma cells
plasma cells produced at late stages of primary infection that can last a lifetime and can produce clones and are the source of a low stead level of antibodies in circulation; reside in the bone marrow and don’t divide or require T cells for antibody secretion
short
Are most plasma cells that are made during the primary response short or long lived?
naive B cells
B cells that use membrane bound IgM to initiate B cell activation
IgG, IgA or IgE
What antibody classes do memory B cells express as receptor?
false
T/F: plasma cells express membrane bound B cell receptors
true
T/F: plasma cells don’t express membrane bound B cell receptors because alternative splicing has already occurred
true
T/F: secreted high affinity IgG binding to antigen prevents any additional activation of naive B cells with the same antigen specificity
quicker
Membrane bounds IgG on memory B cells triggers slower or quicker activation to become plasma cells
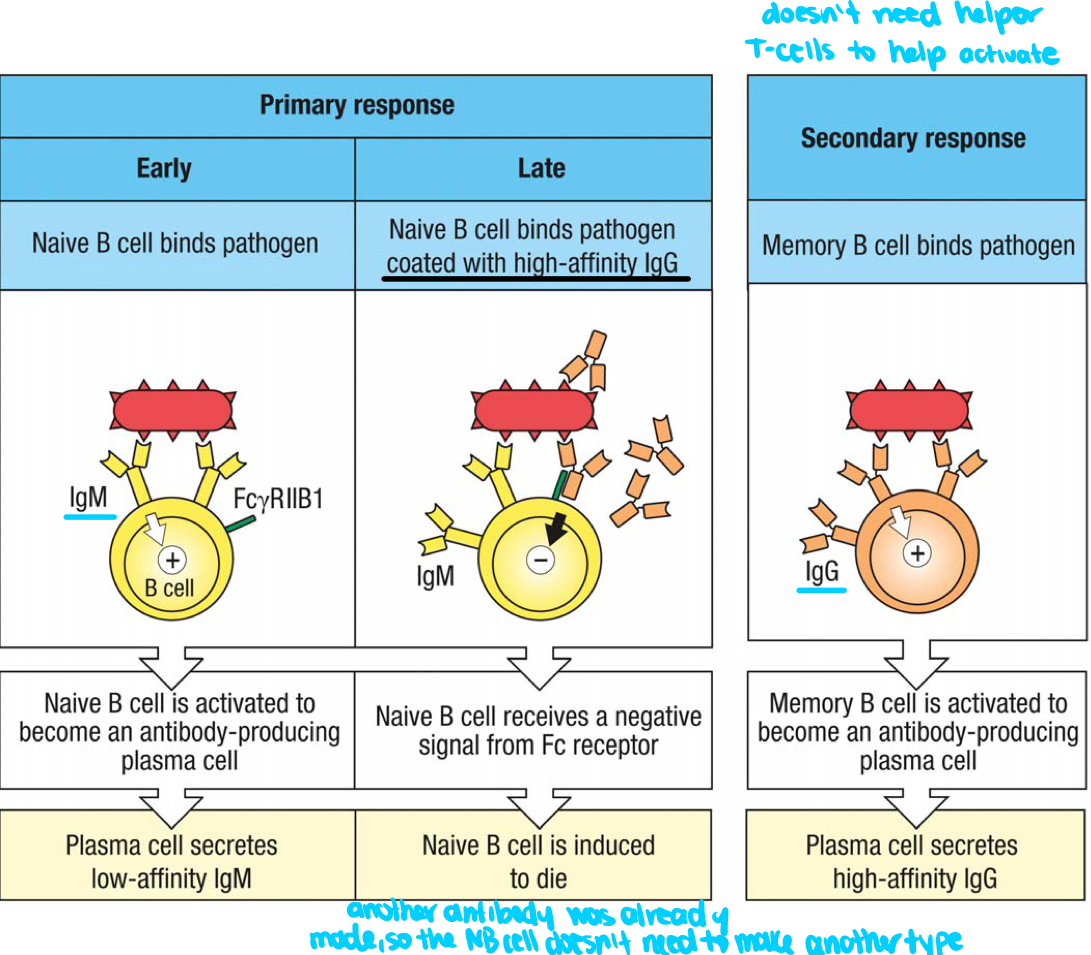
hemolytic anemia
condition where the mother is RhD- while carrying a RhD+ child; the first pregnancy is fine, but the mother develops memory B cells that can attack subsequent babies; requires infusion of anti-Rh IgG during first pregnancy to prevent development of memory B cells
true
T/F: for pathogens whose antigens remain consistent, the long-lived plasma cells are effective to prevent subsequent reinfections
true
T/F: for pathogens that undergo frequent mutations and antigen changes, the suppression of naive B cells during secondary immune responses puts the body at a disadvantage until all memory is lost
catabolism
metabolic pathway that breaks down molecules to release energy
true
T/F: naive T cells are long lived quiescent and survive through catabolism
anabolism
metabolic pathway that builds molecules using energy
false
T/F: T cell activation changes the metabolism to catabolism
true
T/F: T cell activation changes the metabolism to anabolism, enabling the T cell to synthesize macromolecules
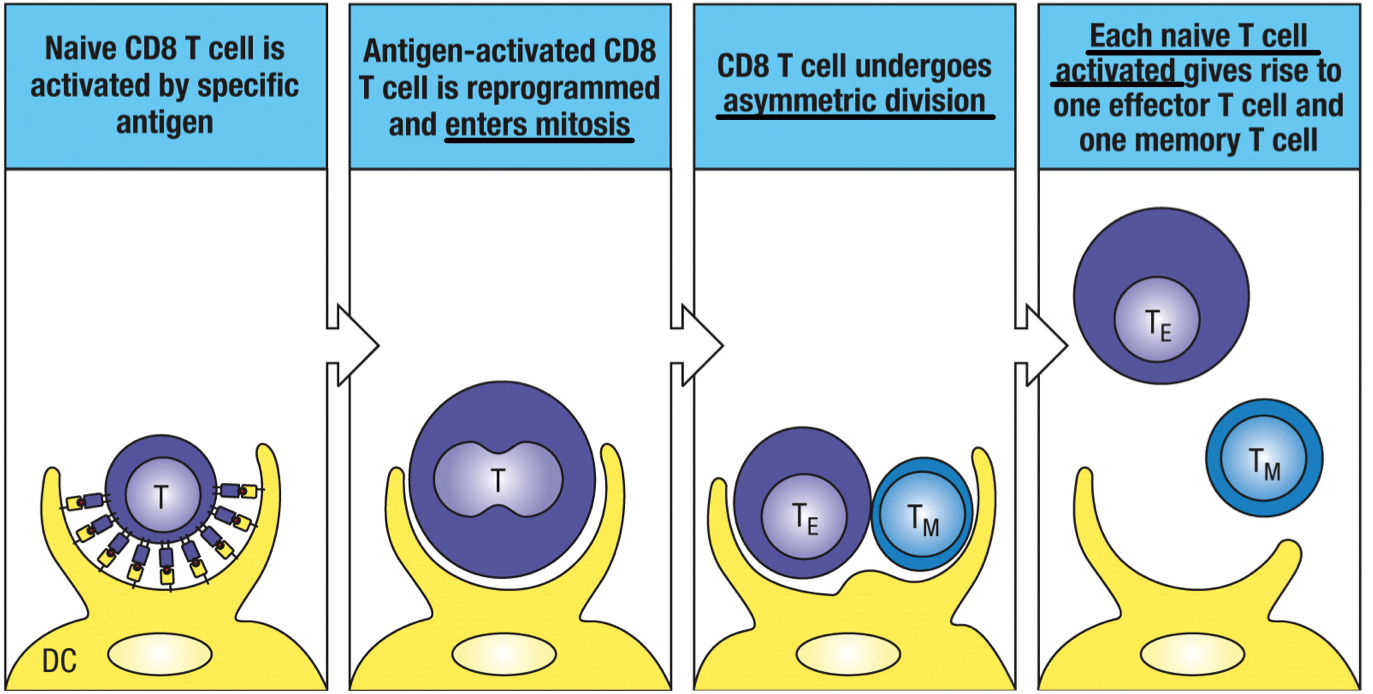
metabolic reprogramming
process that changes the metabolism from catabolism to anabolism, triggering asymmetric division of the T cell to give rise to one effector T cell and one memory T cell
central memory T cell (TCM cell)
memory T cell that circulates through the blood, the T cell zone of secondary lymphoid tissues and lymph
effector memory T cell (TEM cell)
memory T cell that circulates through the blood and all tissues
resident memory T cells (TRM cells)
long-lived memory T cells that never return to the circulation but stay in the mucosal tissue after healing from infection
shorter
Is the CD45RO isoform on memory T cells longer or shorter than the CD45RA isoform on naive T cells?
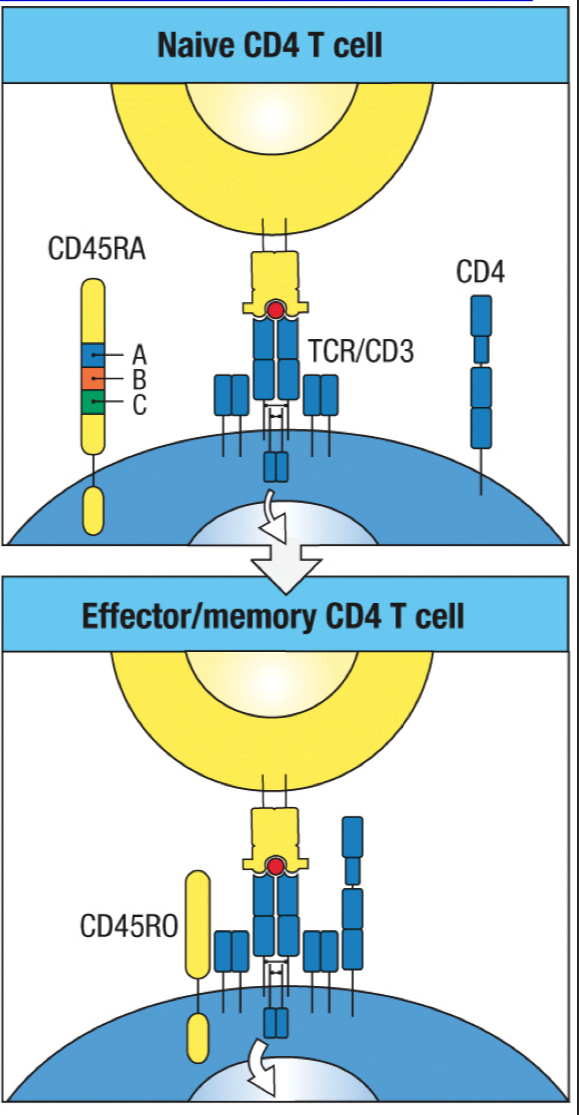
better
Does CD45RO on memory T cells have better or worse interaction with the TCR than CD45RA on naive T cells
true
T/F: the shorter CD45RO isoform on memory T cells allows interaction with the TCR without co-stimulation
small
Does the primary immune response require a small or large number of pathogen-specific cells?
large
Does the secondary immune response require a small or large number of pathogen-specific cells?
high
Does the primary immune response have a high or low threshold of activation?
low
Does the secondary immune response have a high or low threshold of activation?
true
T/F: innate immunity works alone until the primary adaptive response is activated and ongoing
true
T/F: there’s close cooperation between the innate immunity and the secondary adaptive immunity from the start of infection
false
T/F: secondary immune responses take the same amount of time as primary immune responses to become effective
false
T/F: plasma cells generated in a secondary immune response have longer life spans than those made during a primary immune repsponse
true
T/F: during a primary immune response, effector B cells outnumber memory cells
false
T/F: memory T cells require costimulation
false
T/F: memory T cells undergo somatic hympermutation
false
T/F: memory T cells undergo isotype switching