Nucleotide Metabolism I
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
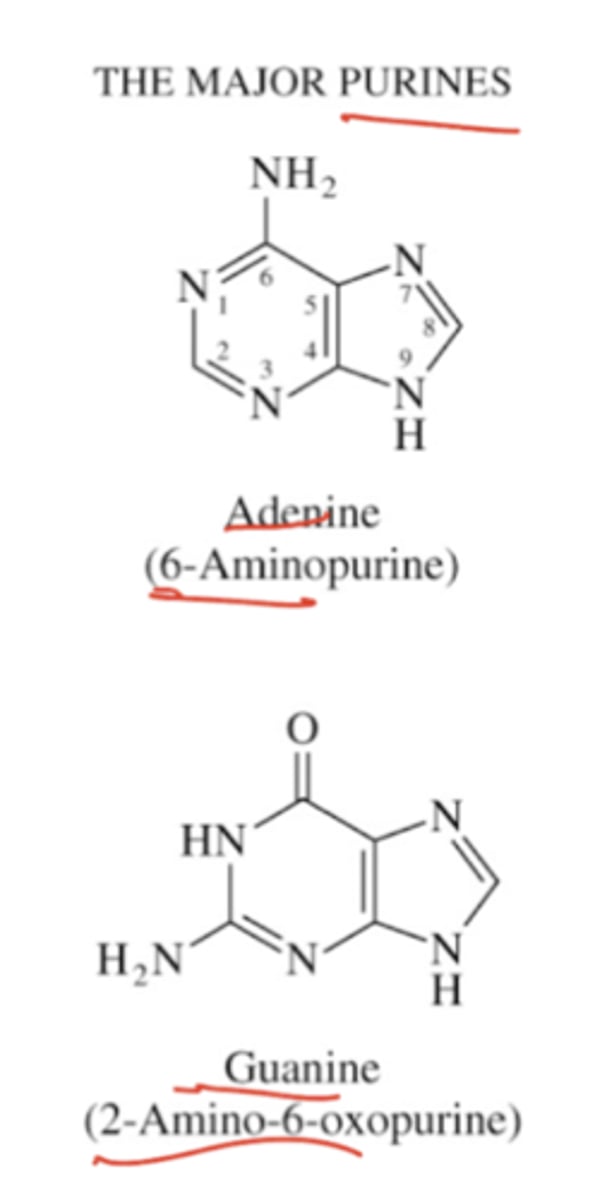
Describe the structure of the major purines.
Adenine (aka 6-aminopurine) has two conjoint aromatic rings with an amino group on the sixth carbon of the ring.
Guanine (aka 2-amino-6-oxopurine) also has two conjoint aromatic rings with an amino group on the second carbon and a ketone group on the sixth carbon.
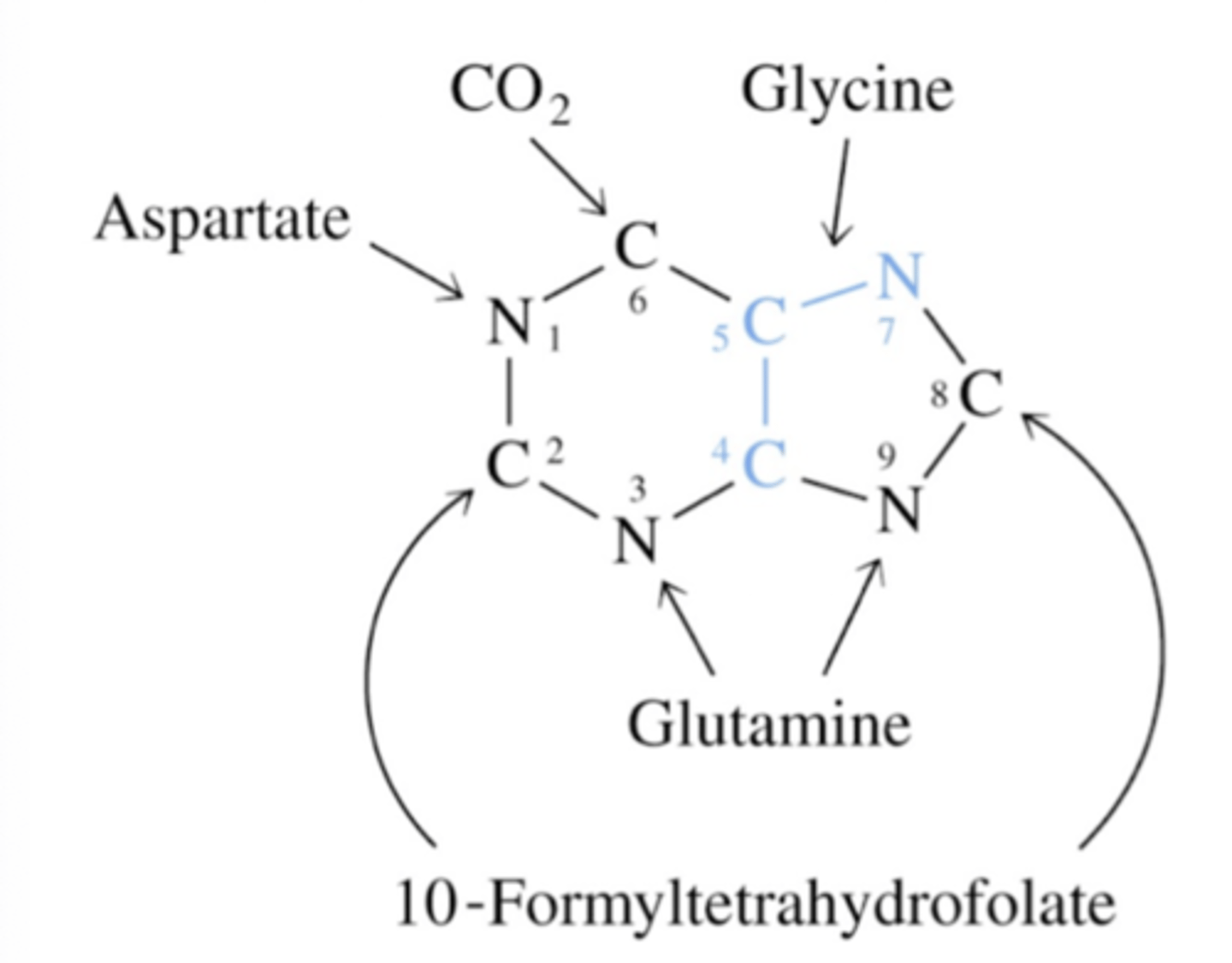
What is the base molecule of the aromatic ring found in de novo synthesis of purines? What is the origin of each of its carbon and nitrogens?
Carbon 6 is from CO2/bicarbonate
Nitrogen 3 and 9 are from glutamine
Carbon 2 and 8 are from 10-formylTHF
Nitrogen 1 is from aspartate
Carbon 4 and 5, as well as Nitrogen 7 are from glycine
What are some characteristics of adenosine?
Has hormone and neurotransmitter properties
Effects include increased blood flow, decreased blood pressure, muscle relaxation, lowering of ATP utilization
Receptors present on cell surface, affecting adenylyl cyclase activity
Caffeine increases blood pressure by binding to adenosine receptors and blocking binding
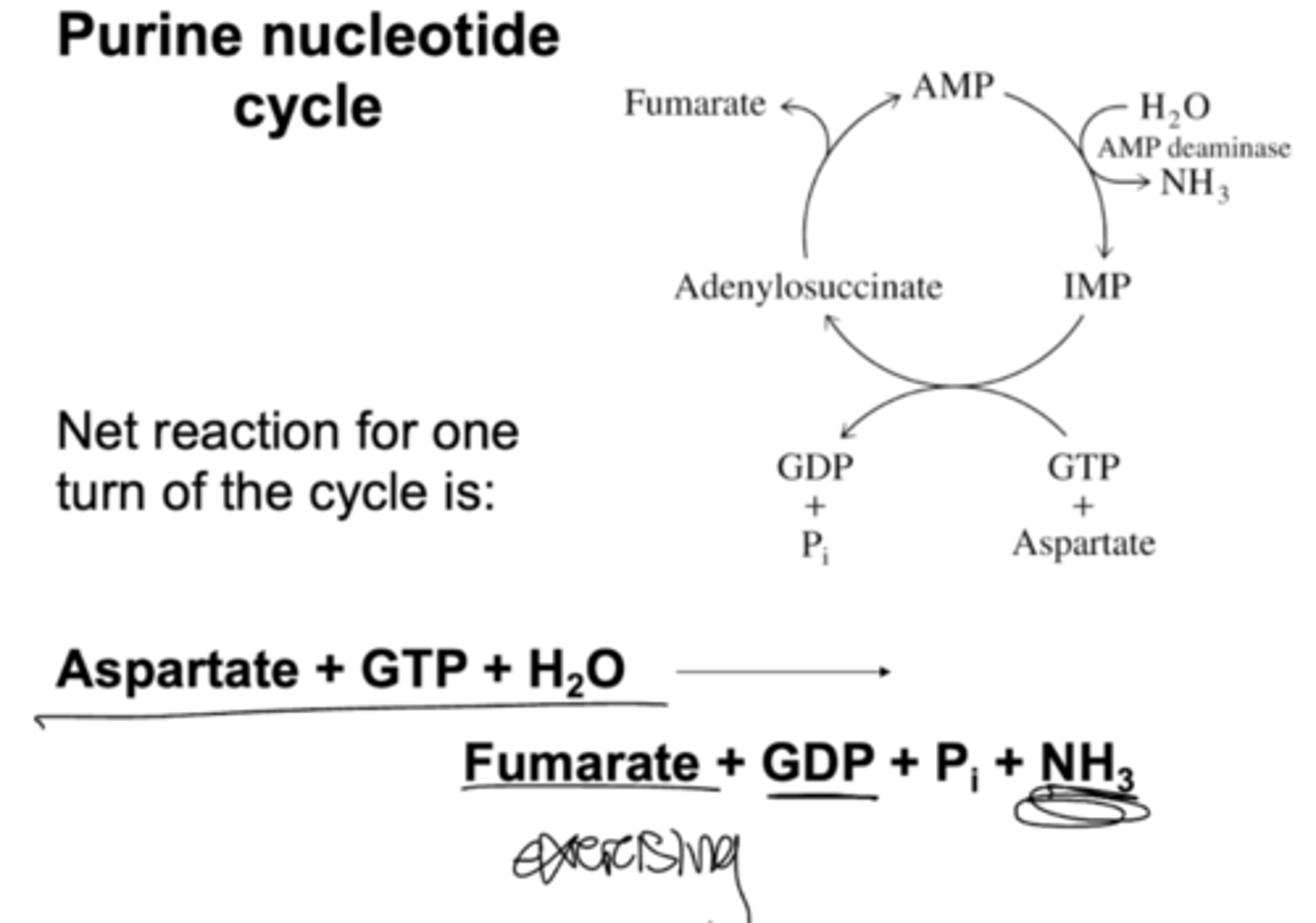
Describe the purine nucleotide cycle in muscles.
Intense exercises causes AMP deaminase to convert AMP to IMP, releasing NH3
Lower AMP levels shirt eq of adenylate kinase to produce more ATP for contraction
IMP recycled to AMP purine nucleotide cycle:
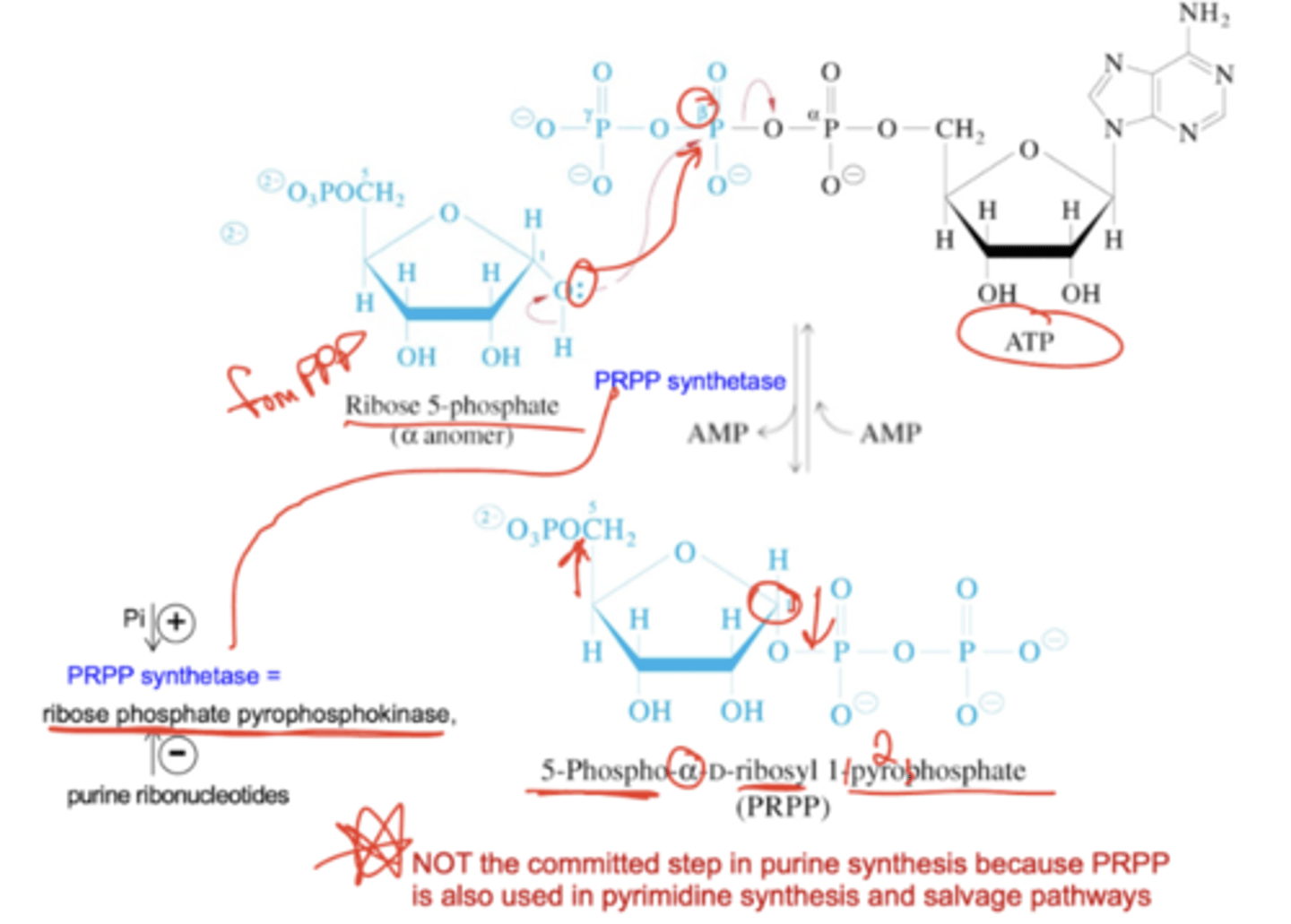
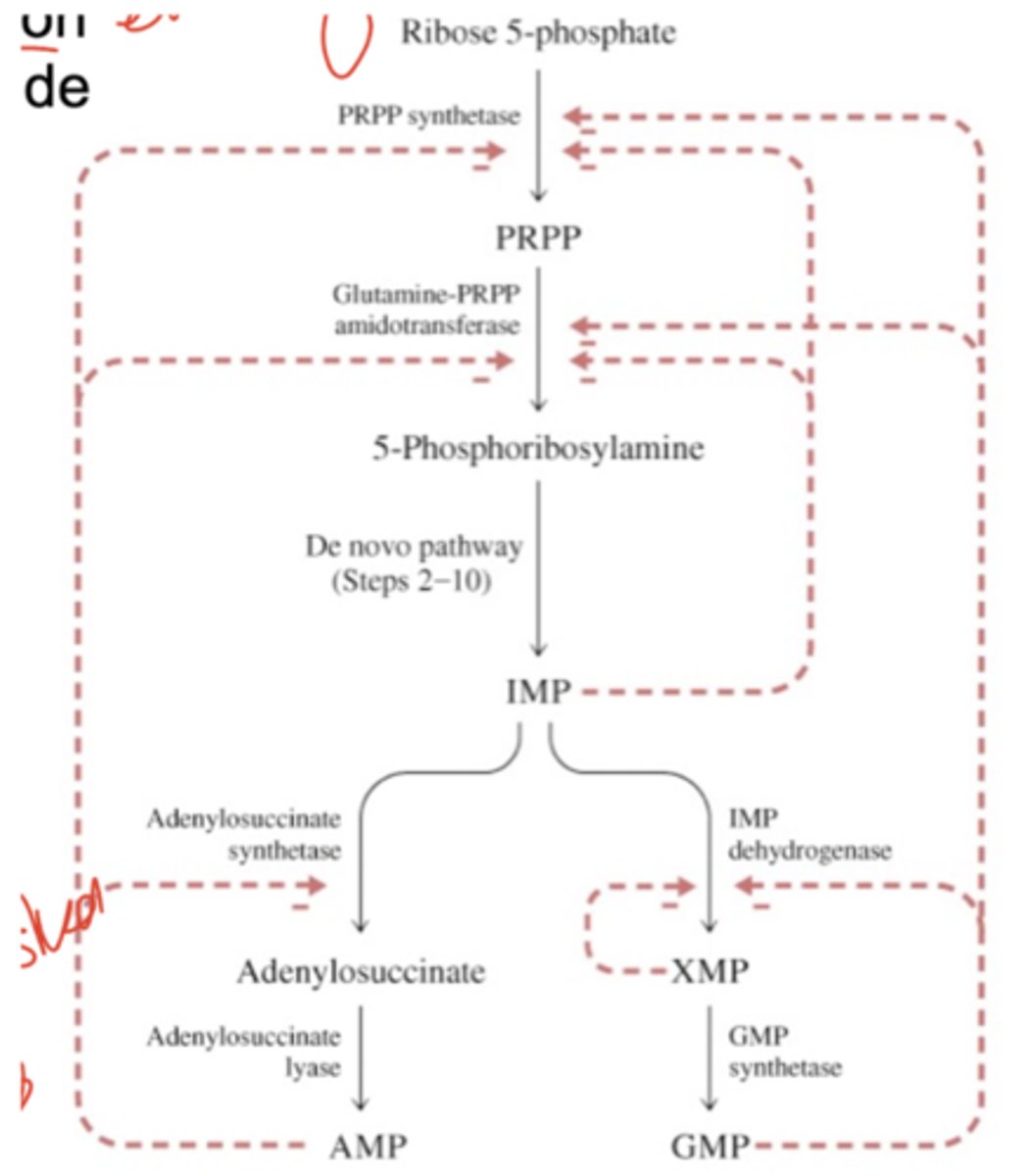
What is PRPP? Describe its synthesis.
PRPP is 5-phospho-a-ribosyl 1-pyrophosphate. Its synthesis is NOT the committed step of purine synthesis because it is also used in pyrimidine synthesis and salvage pathways.
PRPP synthase is also known as ribose phosphokinase. It is activated by Pi and inhibited by purine ribonucleotides.
Describe the committed step of the purine nucleotide pathway.
The committed step of the purine nucleotide pathway is the reactions of PRPP, GLUTAMINE, and WATER TO 5’-phosphoribosylamine (PRA), glutamate, and pyrophosphate
The enzyme is amidophosphoribosyltransferase.
This is activated by PRPP.
Inhibited by AMP, GMP, and IMP.
The END PRODUCE is IMP!
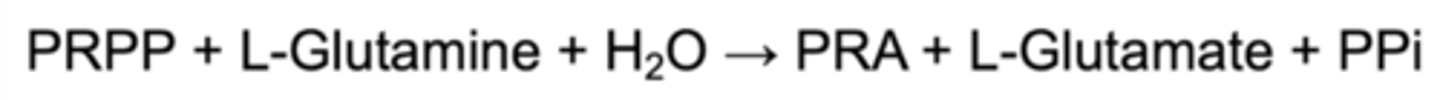
What is IMP?
The initial product of the 10-step purine nucleotide pathway. Its base is hypoxanthine. This can be converted into AMP or GMP.Descr
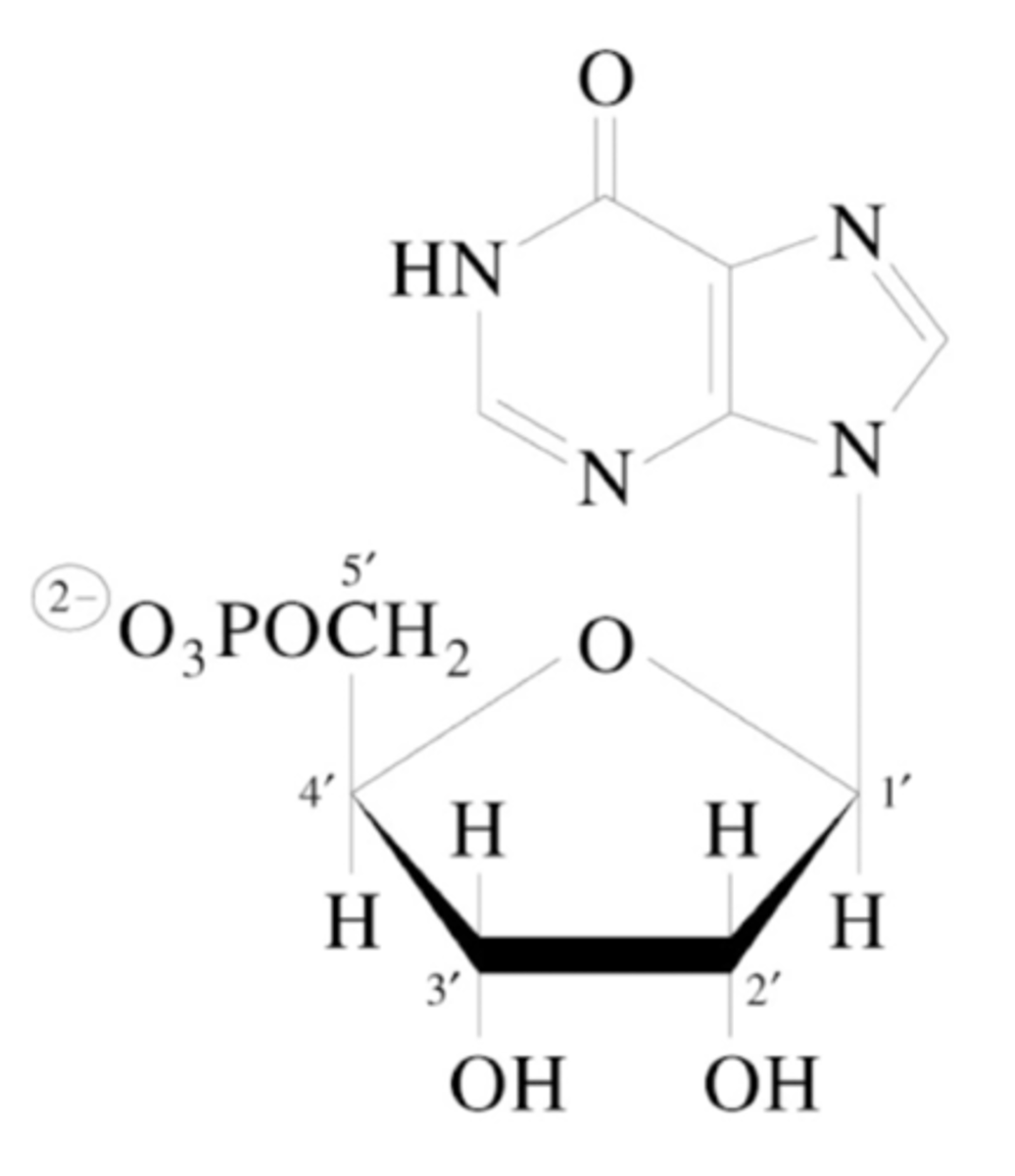
Describe the pathway of the conversion of IMP into AMP.
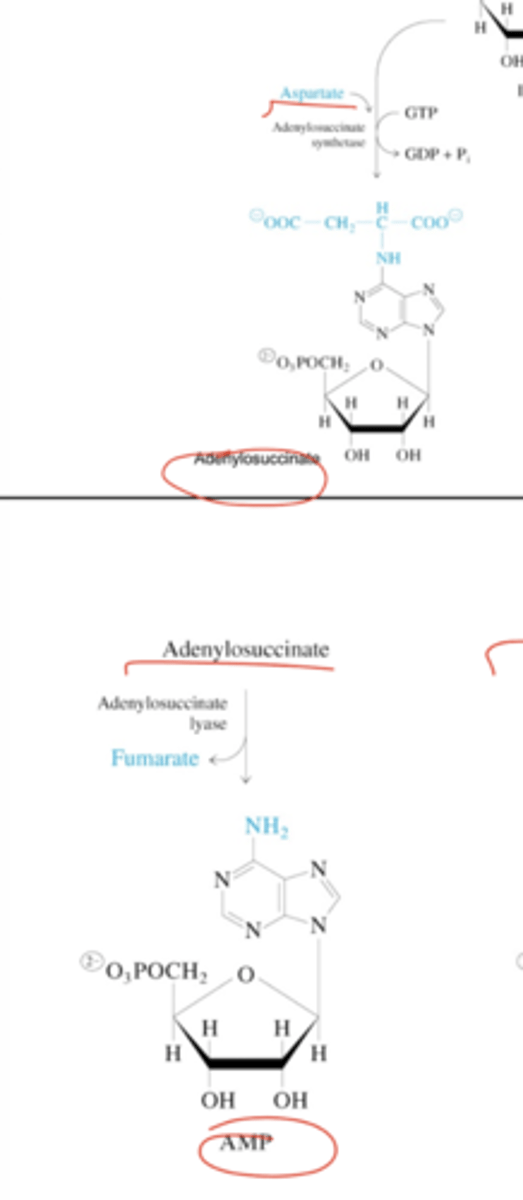
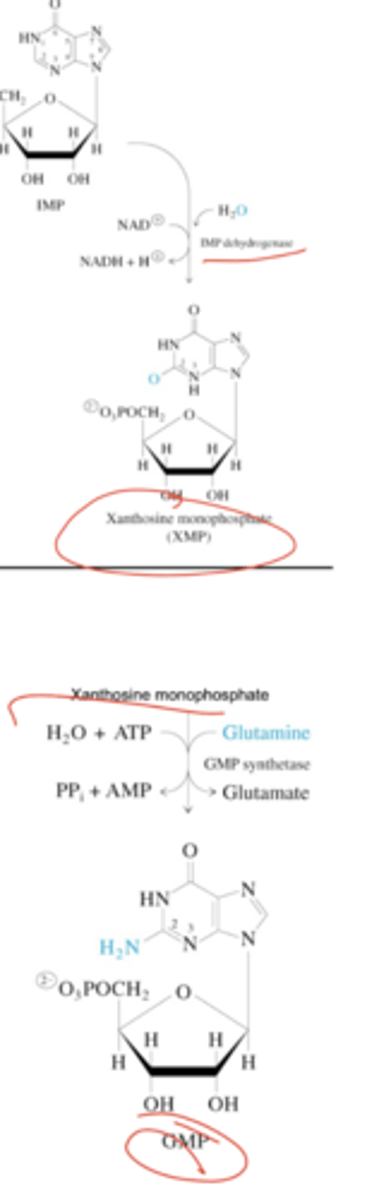
Describe the pathway of the conversion of IMP into GMP.
How is purine nucleotide synthesis regulated?
There is only feedback inhibition in purine nucleotide synthesis; all products act as feedback inhibits for everything
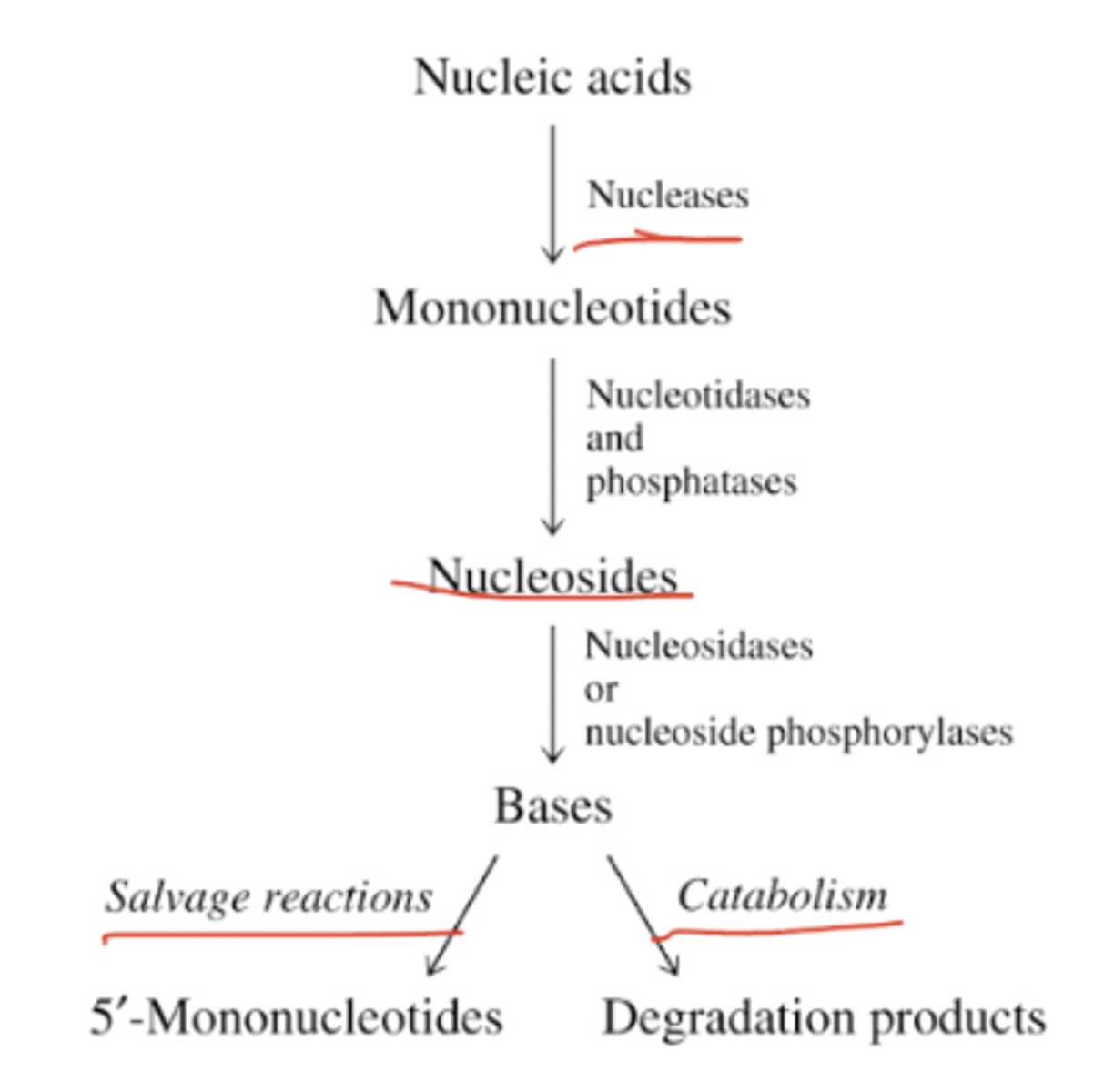
What is the purpose of nucleotide salvage?
During cell metabolism and digestion, nucleic acids are converted into heterocyclic bases.
They can be salvaged by direct conversion to 5'-mononucleotides.
PRPP donates 5'-phosphoribosyl group.
Recycling saves energy (bc of scarce reduced nitrogen sources.
Detail the salvage of purines.
Added note: 6-mercaptopurine inhibits amidotransferase (in conversion of IMP to AMP for final steps of salvage. This prevents cancer growth.
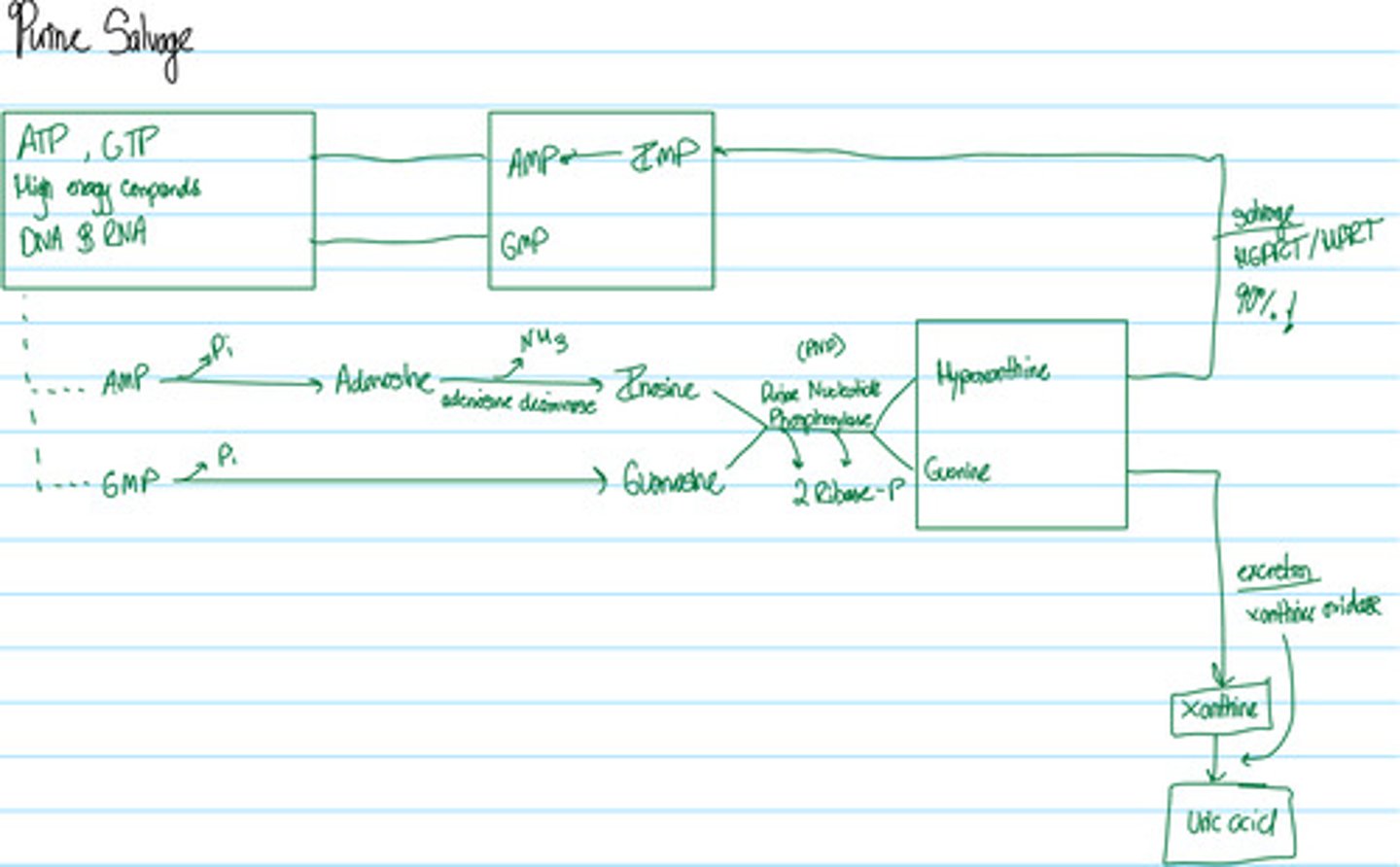
What is the alternative pathway to purine salvage?
Purine nucleotides are either salvaged or catabolized into uric acid, which is not water soluble and can crystallize in gout
What is the role of PNP
Purine Nucleotide Phosphorylase (PNP) separates the free purine base from ribose/dribose
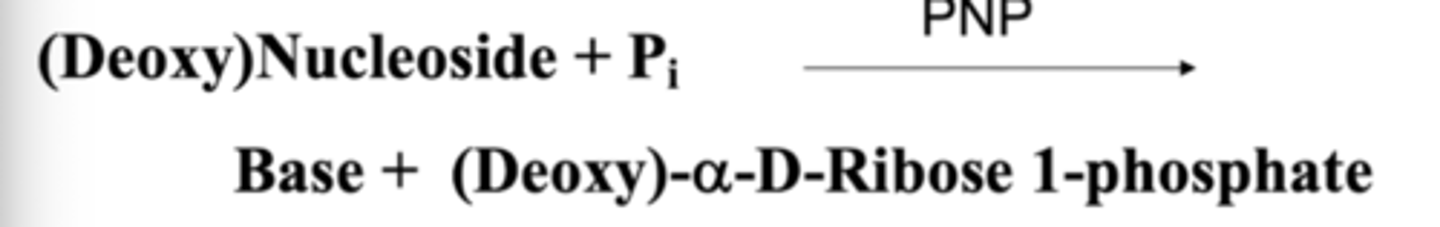
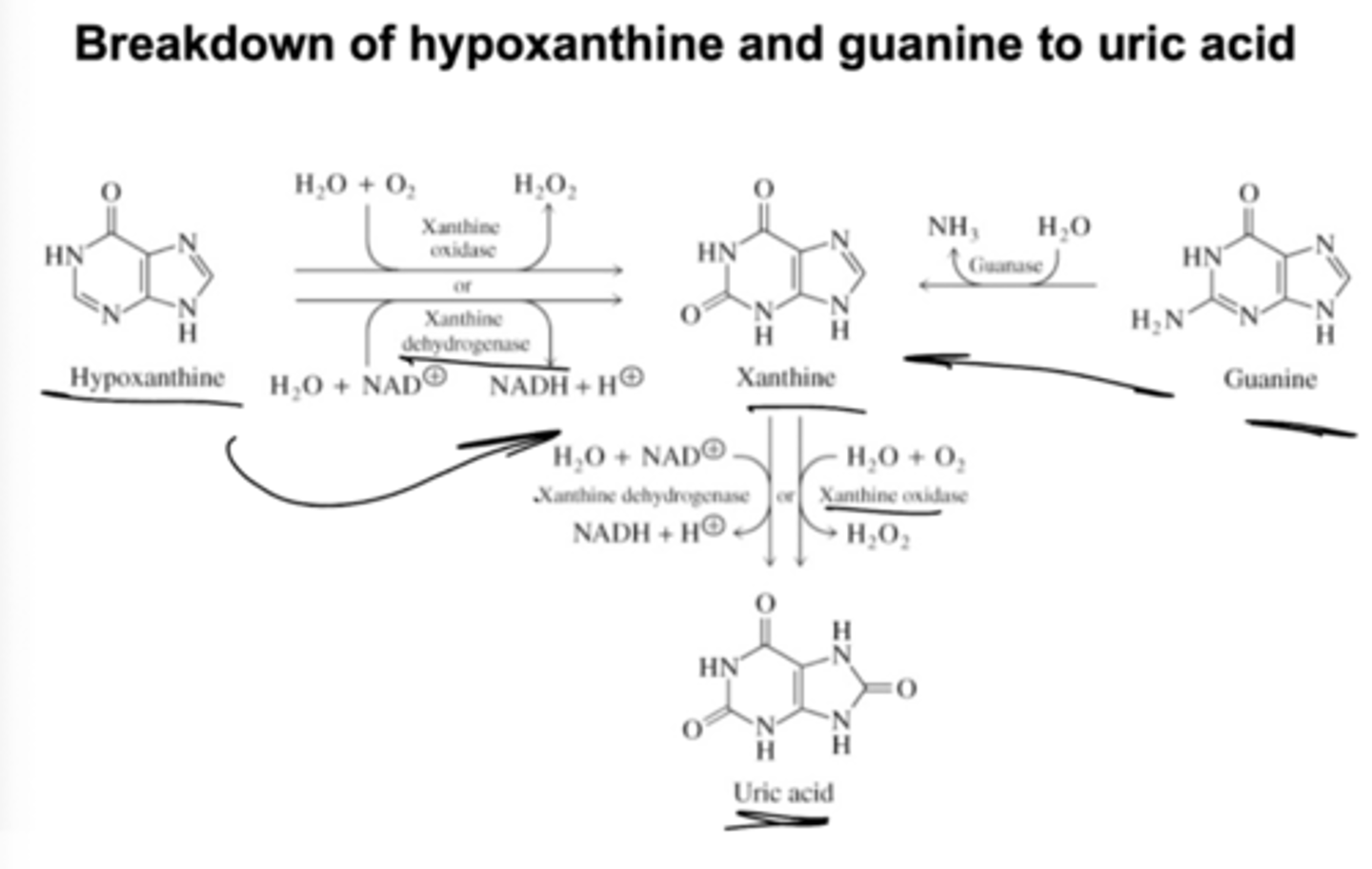
Detail the breakdown of purines into uric acid.
What is Lesch-Nyhan syndrome?
Also known as HGPRT/HPRT (hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribotransferase) deficiency. Some symptoms include spastic cerebral palsy, self-mulilation of the hands and lips, hyperuricemia, and early death.
What is ADA Deficiency?
ADA (adenoside deaminase deficiency) leads to severe combined immunodeficiency, low-t and B cells, leading to frequent infections, and is an autosomal recessive disease, such as in SCIDs disease. Ribonucleotide reducase is inhibited, leading to a lack of DNA precursors and lack of T-cell growth.
What is gout?
Gout occurs from excess sodium urate (uric acid).
Overproduction or inadequate excretion of uric acid – sodium urate INSOLUBLE and can crystallize in tissue.
Can be a result of hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase or defective regulation of purine biosynthesis.
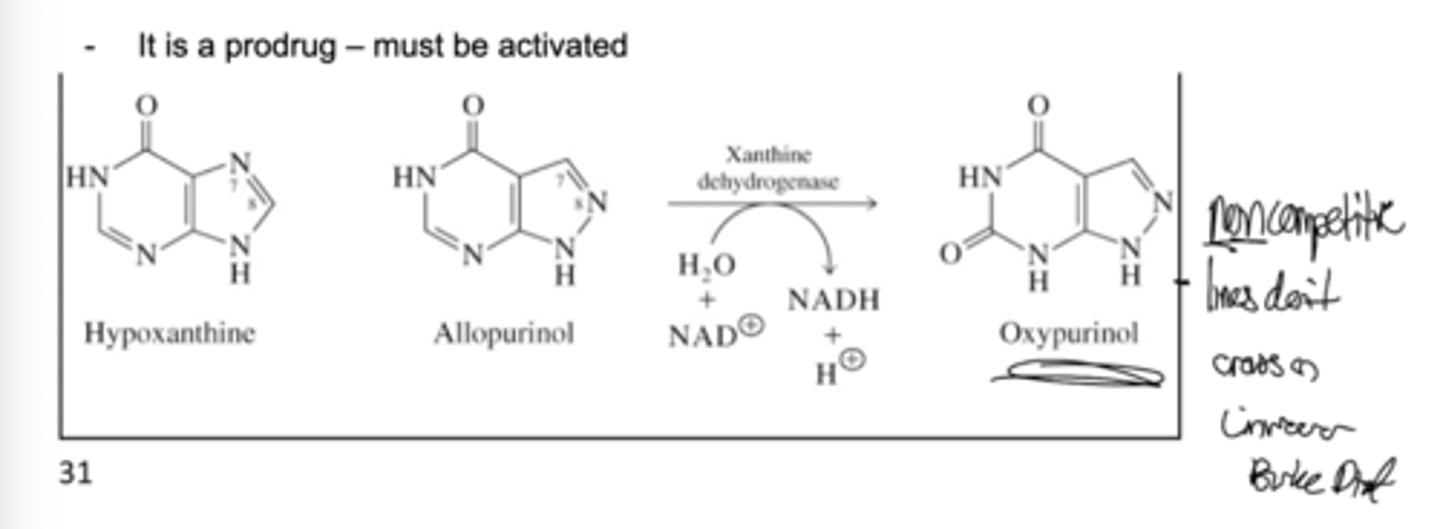
Gout is treated with allopurinol.
Converted in cells to oxypurinol – inhibits xanthine oxidase.
Prevents high uric acid
Hypoxanthine, xanthine more soluble.
What is the mechanism of action for allopurinol?
What is azathioprine?
immunosuppressant used in organ transplantation, autoimmune disease (rheumatoid arthritis), or inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn's or ulcerative colitis)
What is mycophenolate mofetil?
immunosuppressant drug used to prevent rejection in organ transplantation. Inhibits purine synthesis by blocking inositol monophosphate dehydrogenase.
What is methotrexate?
indirectly inhibits purine synthesis by blocking the metabolism of folic acid (inhibiting DHFR)
What is allopurinol?
inhibits xanthine oxidoreductase, lowering uric acid for gout treatment
What is colchicine?
reduces inflammation and has no effect on uric acid production. It reduces macrophage ingestion of uric acid crystals
What is probenecid/sulfinpyrazone?
increase uric acid excretion