Introduction to Forensic Toxicology and Sample Analysis
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
Toxicology
Study of adverse effects of agents on organisms.
Forensic Toxicology
Analyzes drugs in biological samples for legal purposes.
Human Performance
Effects of substances on human capabilities and behavior.
Postmortem Toxicology
Analysis of substances after death for cause determination.
DFC
Drug Facilitated Crimes involving substances used to incapacitate.
Forensic Drug Testing
Testing biological samples for drug presence in legal cases.
Dose vs. Poison
Paracelsus' principle: dosage determines toxicity or remedy.
M.J.B. Orfila
Father of Forensic Toxicology, published first treatise.

Stas-Otto Method
Technique for extracting alkaloids from biological materials.
Erik Widmark
Developed the Widmark Formula for alcohol concentration.

Rolla Harger
Invented the Drunk-o-meter for measuring intoxication levels.
Robert Borkenstein
Created the Breathalyzer for alcohol detection.
CNS Depressants
Drugs causing relaxation and impaired coordination.
CNS Stimulants
Drugs mimicking 'fight or flight' response effects.
Hallucinogens
Substances causing distorted sensory perceptions or hallucinations.
Pupil Size
Indicator of drug influence on the nervous system.
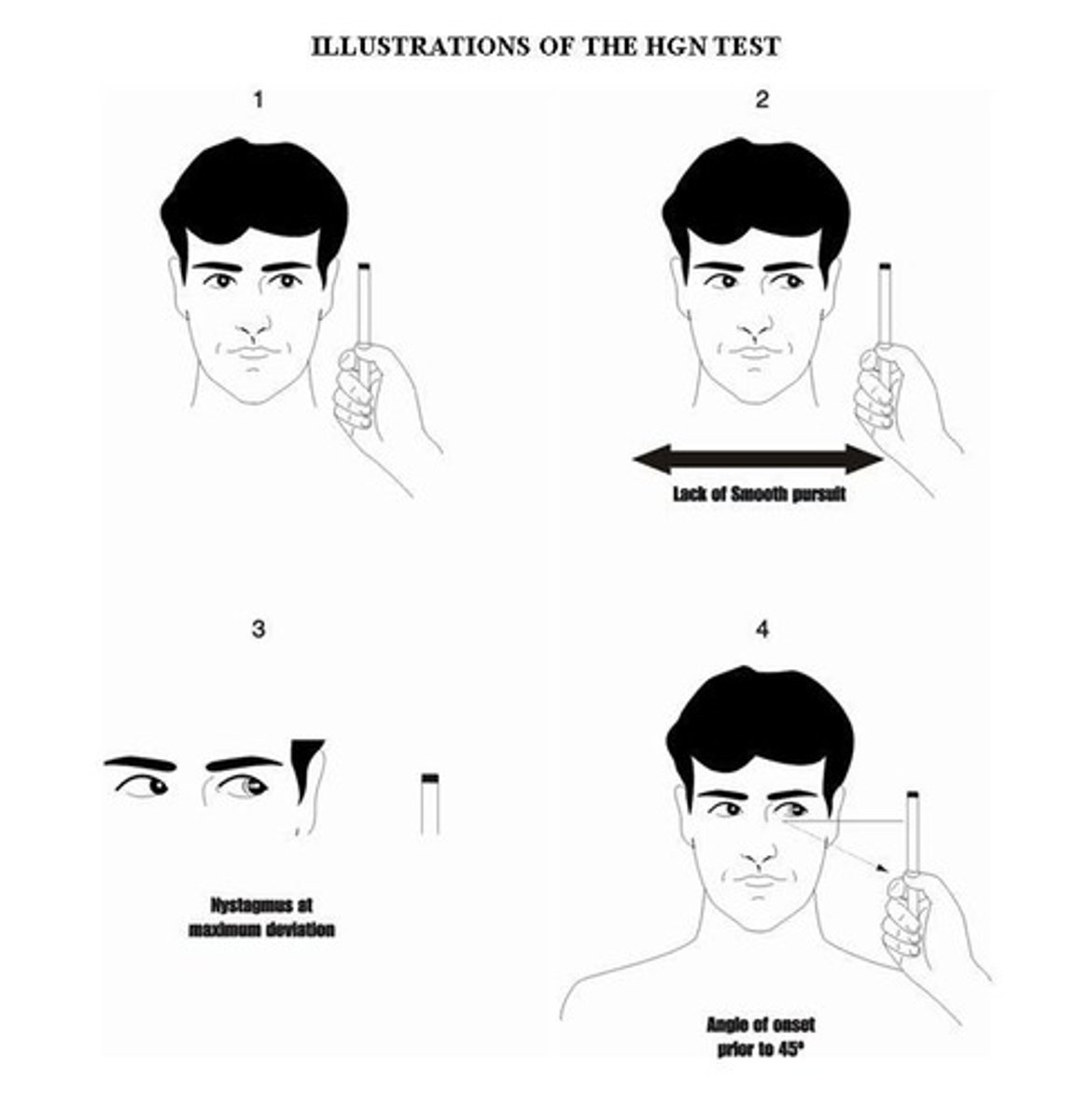
HGN
Horizontal Gaze Nystagmus, eye movement indicator of intoxication.
Therapeutic Dose
Amount of drug providing desired medical effect.
Toxic Dose
Amount of drug causing harmful effects.
Lethal Dose
Dose of substance that can cause death.
Additive Effects
Increased effects when substances are combined.
DRE - Drug Recognition Expert
Specialist in identifying drug influence in individuals.
Sign and Symptom Based
Categorization based on observable effects of drugs.
Alexander Gettler Award
Prize for contributions to forensic toxicology.
Dilated Pupils
Enlarged pupils indicating potential drug influence.
Elevated Vital Signs
Increased heart rate and blood pressure from substances.
Horizontal Gaze Nystagmus
Involuntary eye movement not caused by certain drugs.
Synesthesia
Mixing of senses, e.g., hearing colors.
Inhalants
Substances including solvents, aerosols, anesthetic gases.
Chemical Odors
Indicators of inhalant use on the user.
Impaired Gait
Unsteady walking, similar to alcohol intoxication.
Bloodshot Eyes
Red eyes commonly associated with drug use.
PCP (Phencyclidine)
Dissociative anesthetic with hallucinogenic effects.
Vertical Gaze Nystagmus
Involuntary eye movement indicating PCP influence.
Constricted Pupils
Narrowed pupils typical of narcotic analgesics.
Sedation
State of calmness and reduced activity from drugs.
Tachycardia
Accelerated heart rate, often from cannabis use.
Coroner System
Investigates suspicious deaths, often non-physician.
Medical Examiner System
Physician-led investigation of unusual deaths.
Autopsy
Postmortem examination to determine cause of death.
Forensic Toxicology
Study of drugs' effects in death investigations.
Manner of Death
Classification: Homicide, Accident, Suicide, Natural.
Blood Specimen
Represents drug concentrations at time of death.
Urine Specimen
Indicates exposure but not current blood levels.
Vitreous Specimen
Isolated from blood, useful for ethanol confirmation.
Pharmacology
Study of drug effects and mechanisms.
Pharmacokinetics
Study of drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion.
Pharmacodynamics
Study of drug effects on biological systems.
Electrolytes
Minerals in blood essential for bodily functions.
Glucose
Simple sugar used for energy in cells.
Chronic Exposure
Long-term contact with drugs or metals.
Repetitive Exposure
Repeated contact with substances over time.
Hair Analysis
Method to assess drug exposure over time.
Segmentation
Dividing samples to determine exposure timeframe.
Liver Screening
Testing organ for substance quantification.
Tissue Analysis
Examining organs for toxic substance presence.
Lung Specimen
Used for suspected inhalation poisoning analysis.
Spleen Analysis
Conducted for carbon monoxide (CO) detection.
Postmortem Redistribution
Movement of substances after death affecting results.
Peripheral Blood
Preferred for toxicological analysis, less affected.
Cardiac Blood
Used for screening but influenced by redistribution.
Venous Femoral Blood
Collected postmortem for toxicological evaluation.
Fluoride Salt Preservation
Used to stabilize blood samples for testing.
Plasma
Liquid portion of blood, contains proteins and electrolytes.
Serum
Liquid after clotting, lacks cells and clotting factors.
Whole Blood
Contains all blood components: cells and plasma.
Water Content Analysis
Study of liquid proportions in blood samples.
Mean Distribution Ratio
Average serum to blood ratio: 1.16:1.
BAC
Blood Alcohol Concentration, average 130 mg/dL.
Collection Procedure
Steps for obtaining blood, plasma, or serum.
Vitreous Humor
Transparent fluid located behind the eye lens.
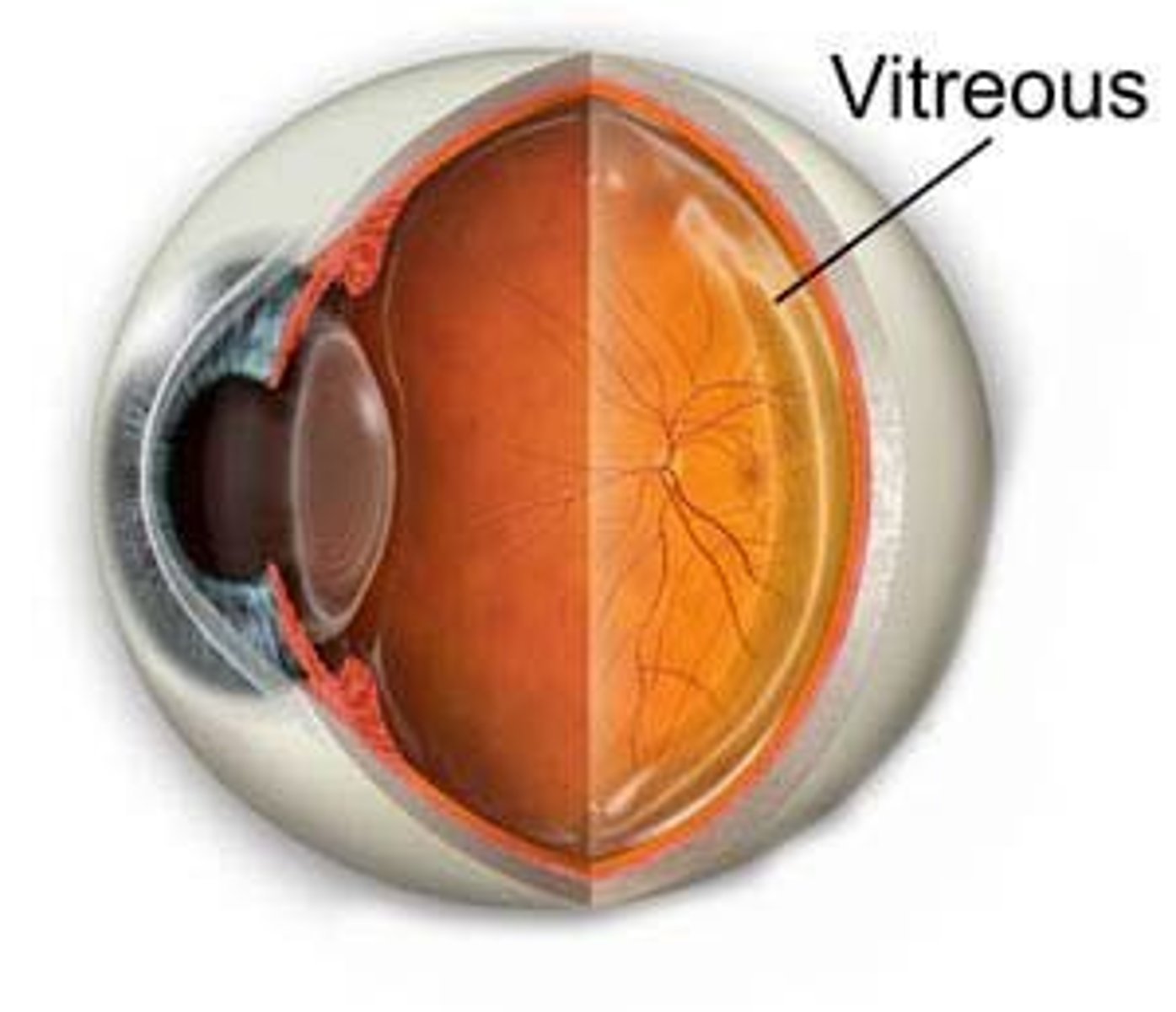
Vitreous Fluid
Jelly-like substance, stable and isolated.
Postmortem Interval Determination
Estimation of time since death using vitreous fluid.
Ethanol Determinations
Testing for alcohol levels in vitreous fluid.
Electrolyte Determinations
Measurement of electrolyte levels in vitreous fluid.
Glucose Determinations
Assessment of glucose concentration in vitreous fluid.
Microbial Activity Resistance
Vitreous fluid less prone to microbial contamination.
Urine Specimens
Contain higher drug concentrations than blood.
Screening Samples
Urine used for initial drug screening.
Quantitative Analysis Limitation
Urine not reliable for correlating impairment.
Absorption and Distribution
Processes of drug uptake and spread in body.
Metabolism and Excretion
Body's breakdown and elimination of substances.
LLOQ
Lowest limit of quantification in analysis.
LOD
Limit of detection for substances in samples.
Tissue
Biological material used for drug concentration analysis.
Liver
Primary site for drug metabolism and concentration.
Spleen
Secondary specimen for carbon monoxide and cyanide.
Kidney
Useful for determining heavy metal concentrations.
Muscle
Sample type when remains are minimal.
Bile
Waste fluid representing liver drug concentrations.
Gastric Contents
Analyzed in overdose cases for pill fragments.
Hair
Used for chronic drug exposure analysis.
Sample Collection
First step ensuring proper labeling and handling.
Specimen Storage
Conditions affecting sample integrity over time.
Fluoride Preservation
Inhibits glucose conversion to ethanol in samples.
Injection Sites
Locations for administering drugs in subjects.
Distribution Assessment
Evaluating how drugs spread in biological systems.
CO Determination
Measuring carbon monoxide levels in specimens.
Ethanol
Alcohol analyzed for forensic toxicology.
Drug Screening
Testing for the presence of drugs in samples.