08 Muscular System
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Axial Division
Axial muscles support and position axial skeleton
-head, neck, trunk
appendicular division
Appendicular muscles support, move, and brace the limbs
-upper and lower extremities
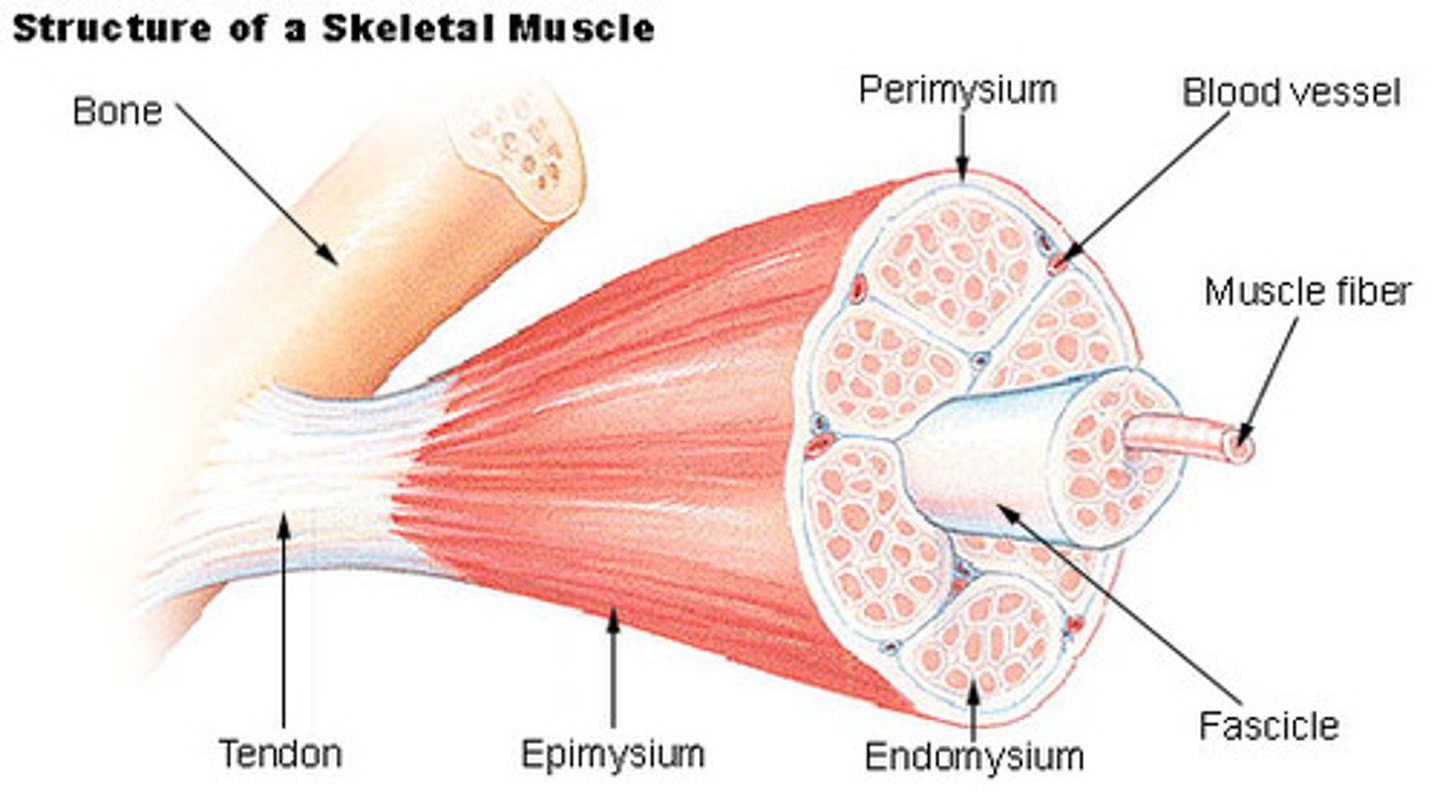
Tendon
Attaches muscle to specific point on a bone
Aponeurosis
strong sheet of tissue that acts as a tendon to attach muscles to bone
-broad flat tendon
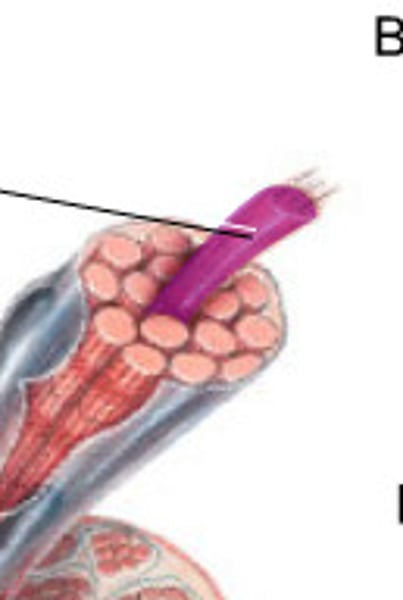
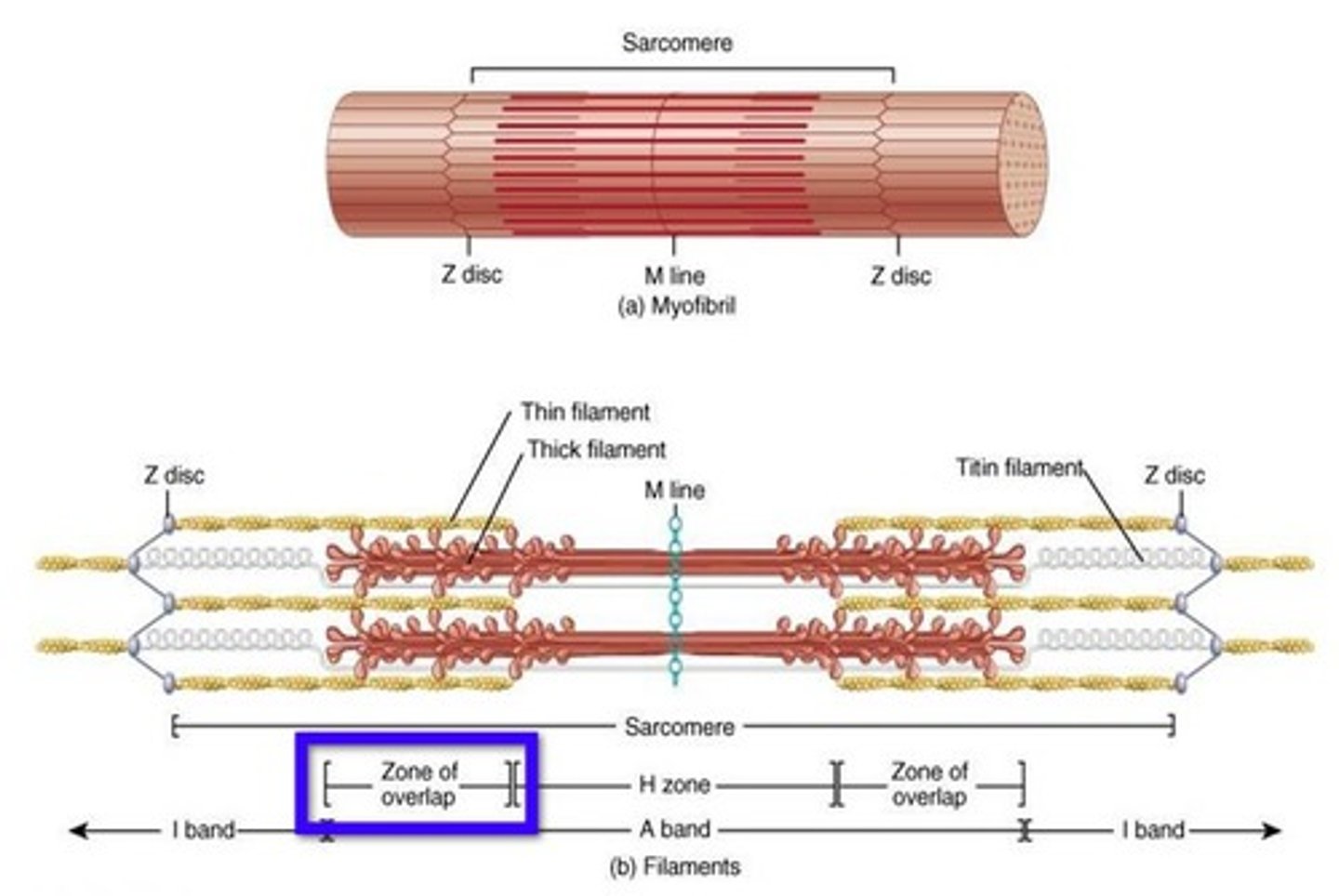
Myofibril (muscle fiber)
Cylindrical structures arranged parallel inside muscle fiber; run length of muscle fiber
Endomysium
Thin layer of areolar connective tissue around each muscle fiber
Collagen & elastic fibers, blood vessels, nerves
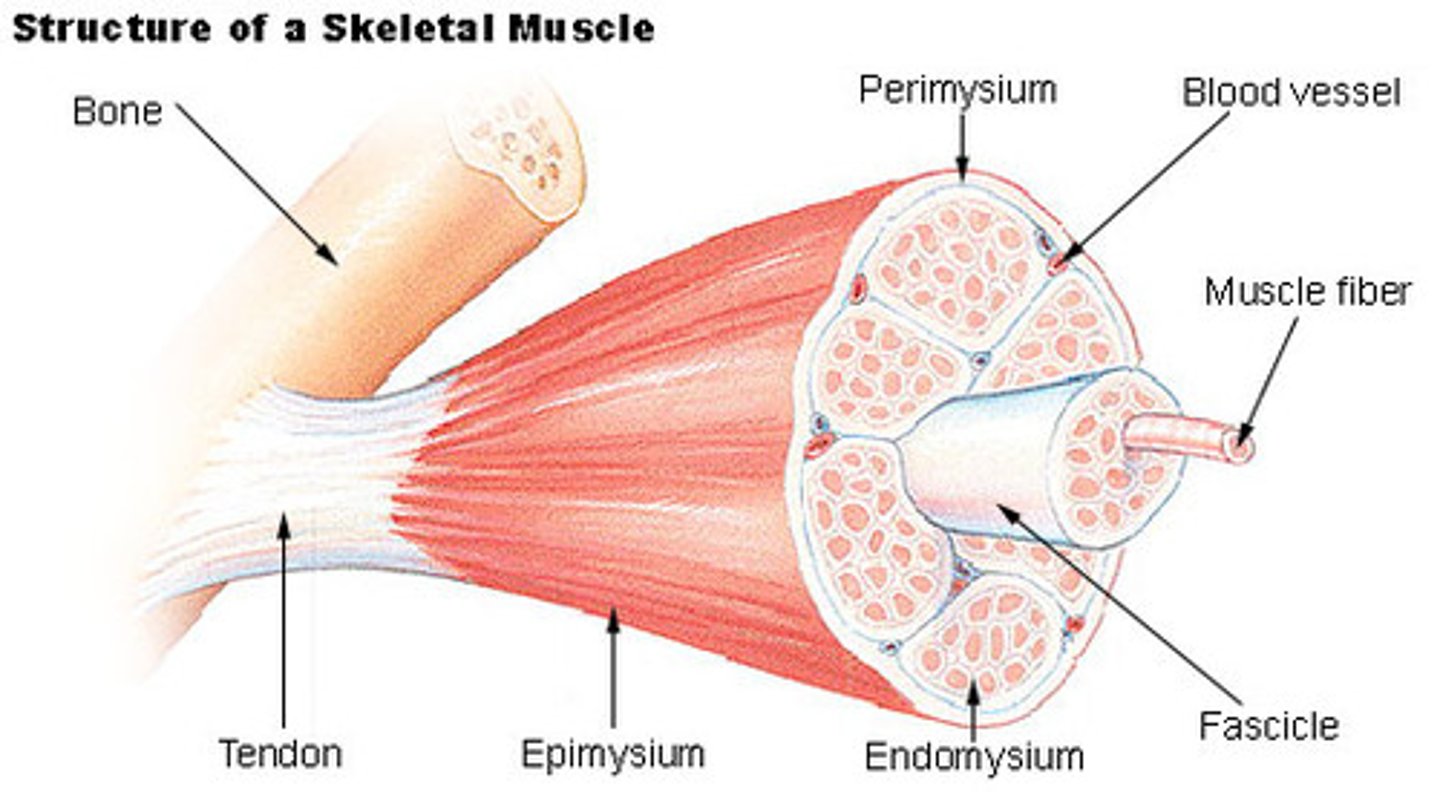
muscle fascicle
Bundle of muscle fibers/cells & surrounding endomysium
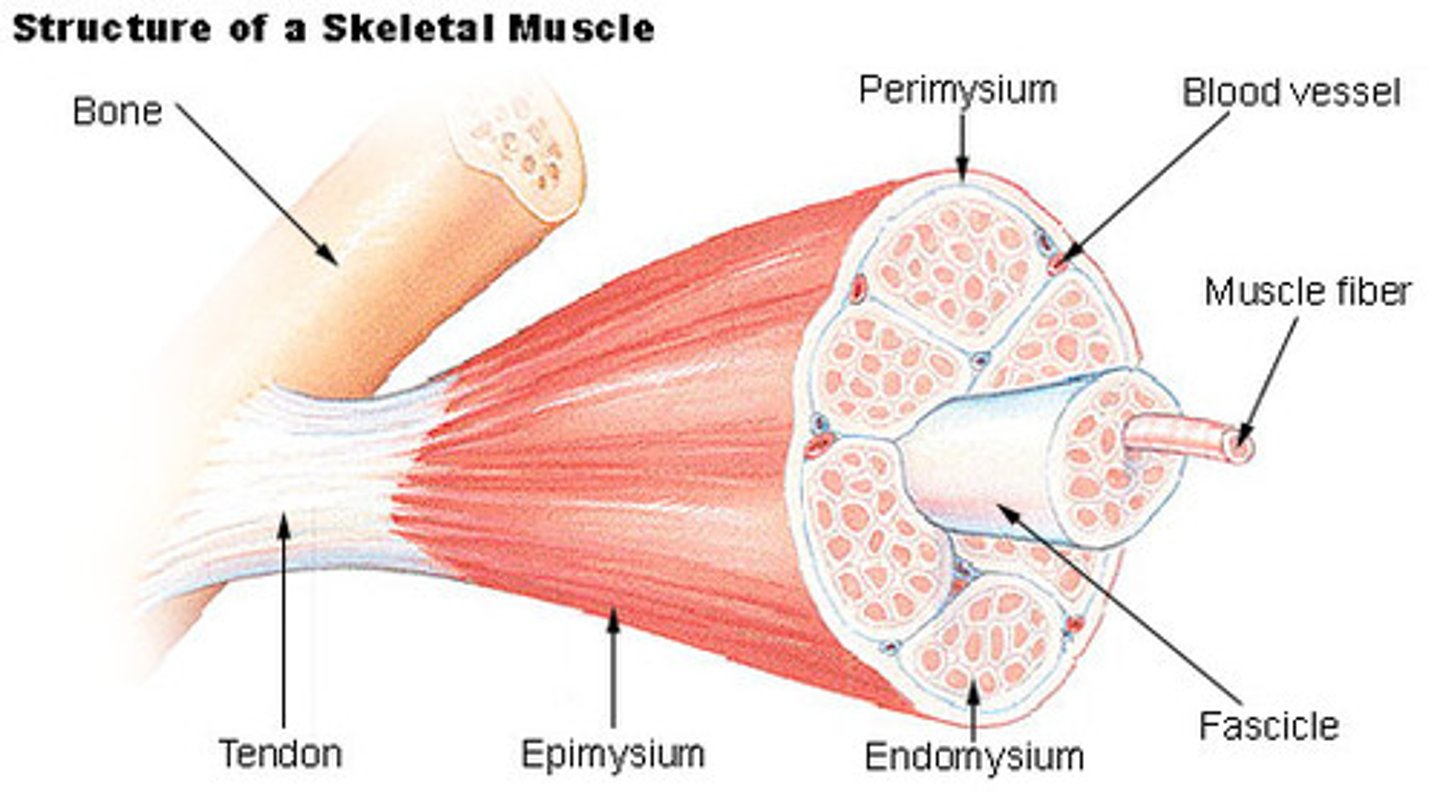
Perimysium
Fibrous layer dividing fascicles
Muscle
tissue composed of fibers that can contract, causing movement of an organ or part of the body
Epimysium
Dense sheath of collagen fibers around muscle
Separates muscle from other tissues/organs
Connected to deep fascia
Sarcolemma
plasma membrane of a muscle fiber
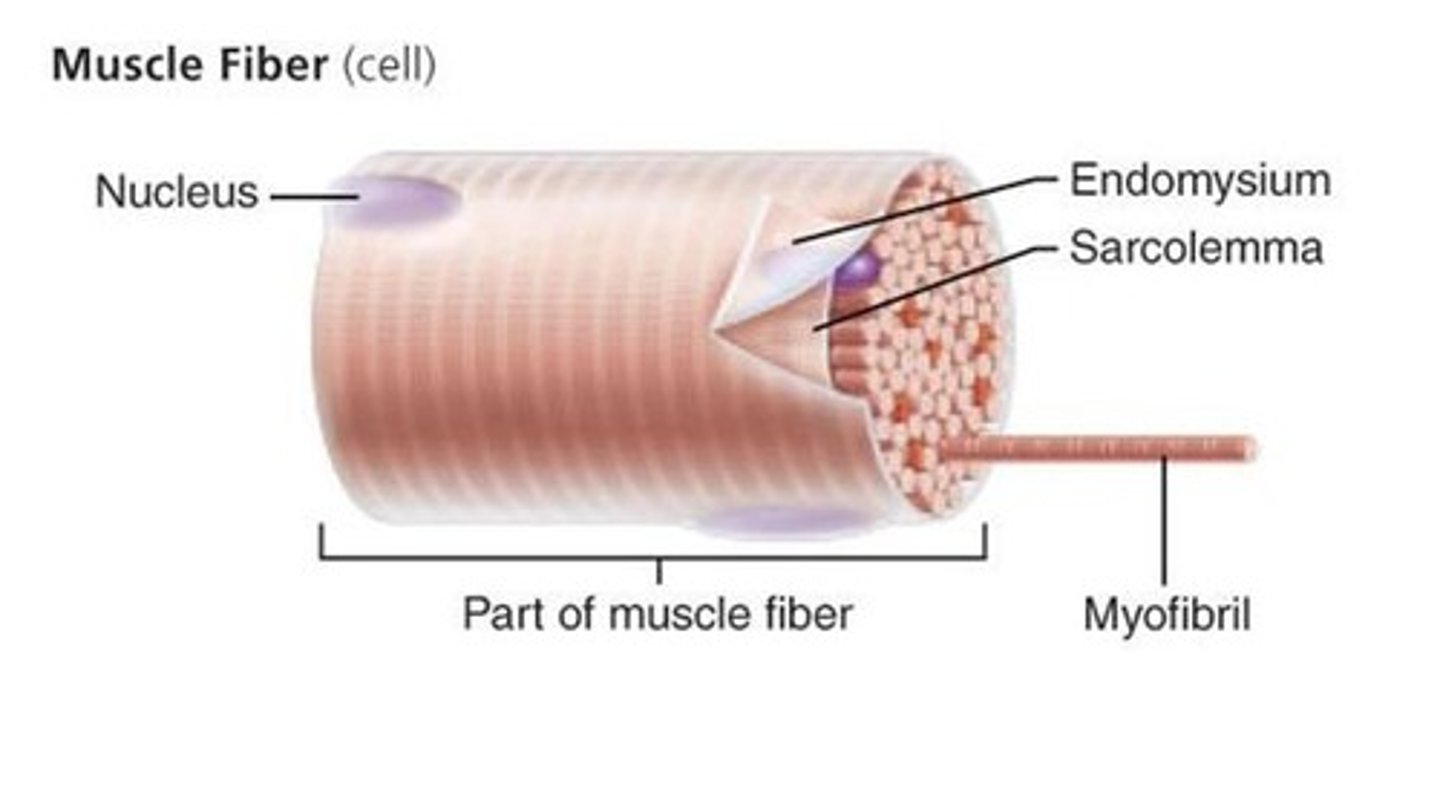
Sarcoplasm
Cytoplasm
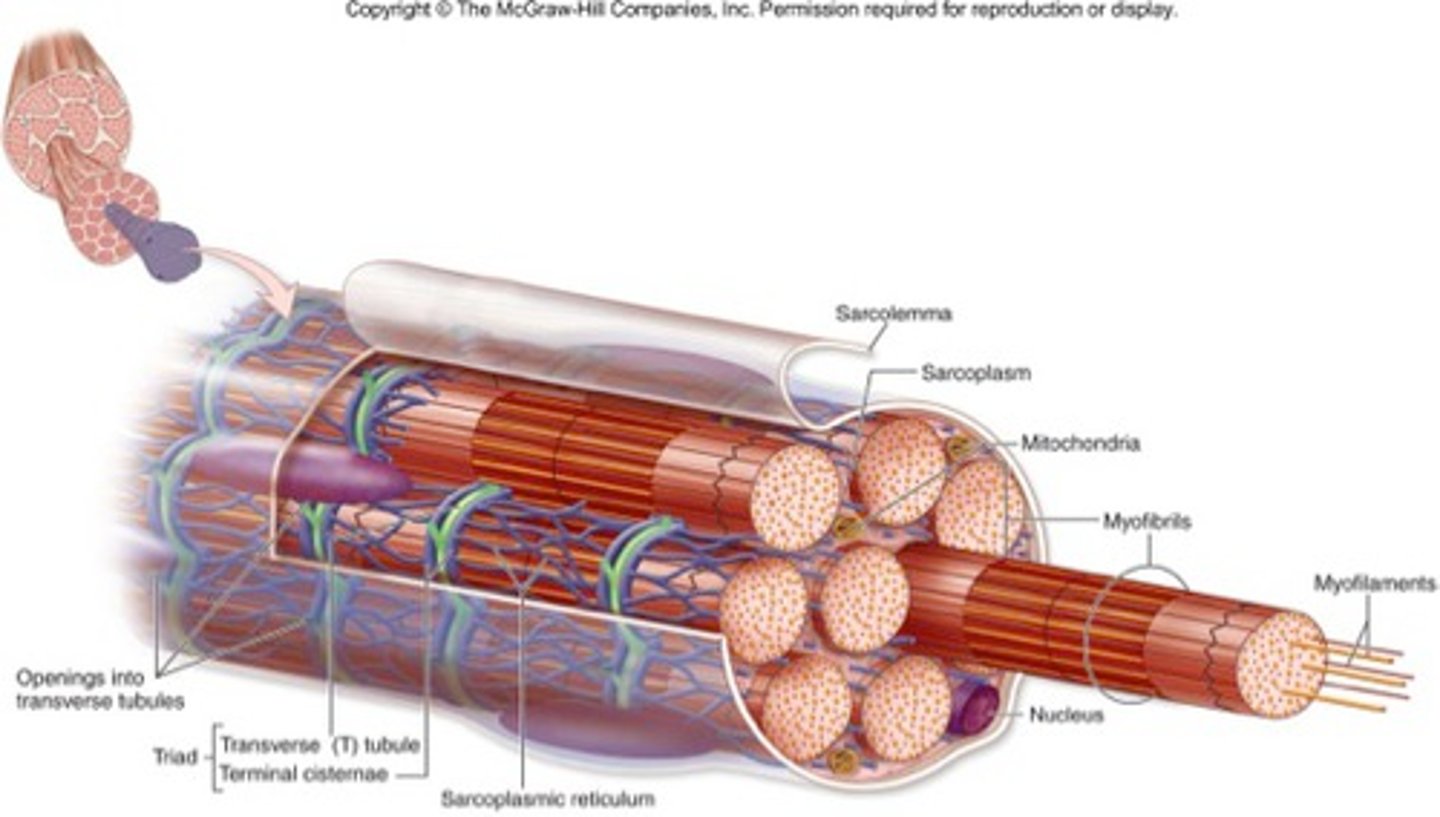
Transverse Tubule
Continuous with sarcolemma and extend into sarcoplasm
Form passageways through muscle fiber and encircle sarcomere
Allows events at cell surface to penetrate "into" the cell
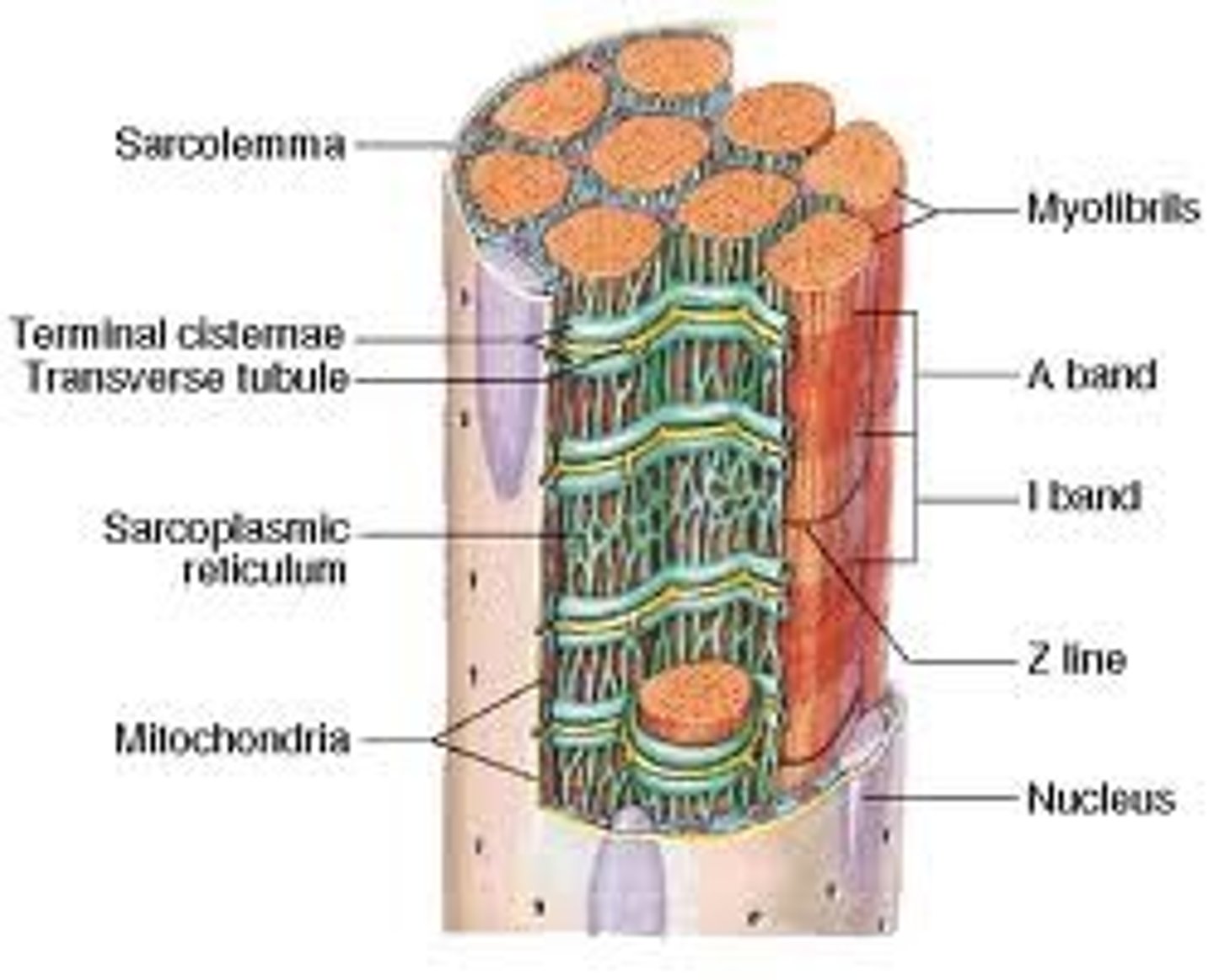
sarcoplasmic reticulum
Similar to smooth endoplasmic reticulum of other cells
Makes contact with T-tubule
Surrounds each muscle cell
Stores calcium ions (actively pumped in from cytosol) Major role in muscle contraction
Myofilament
Bundles of protein filaments inside myofibrils
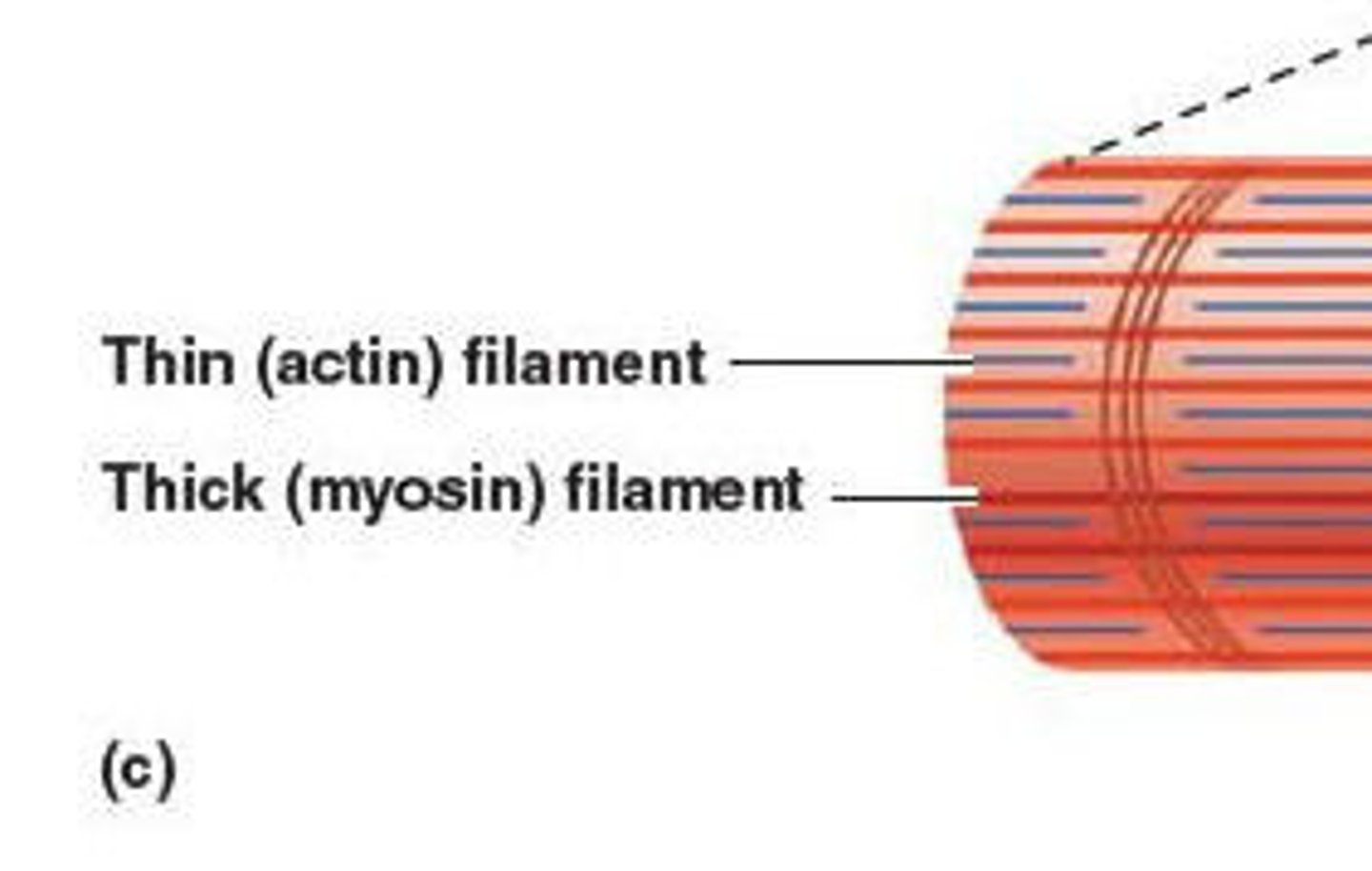
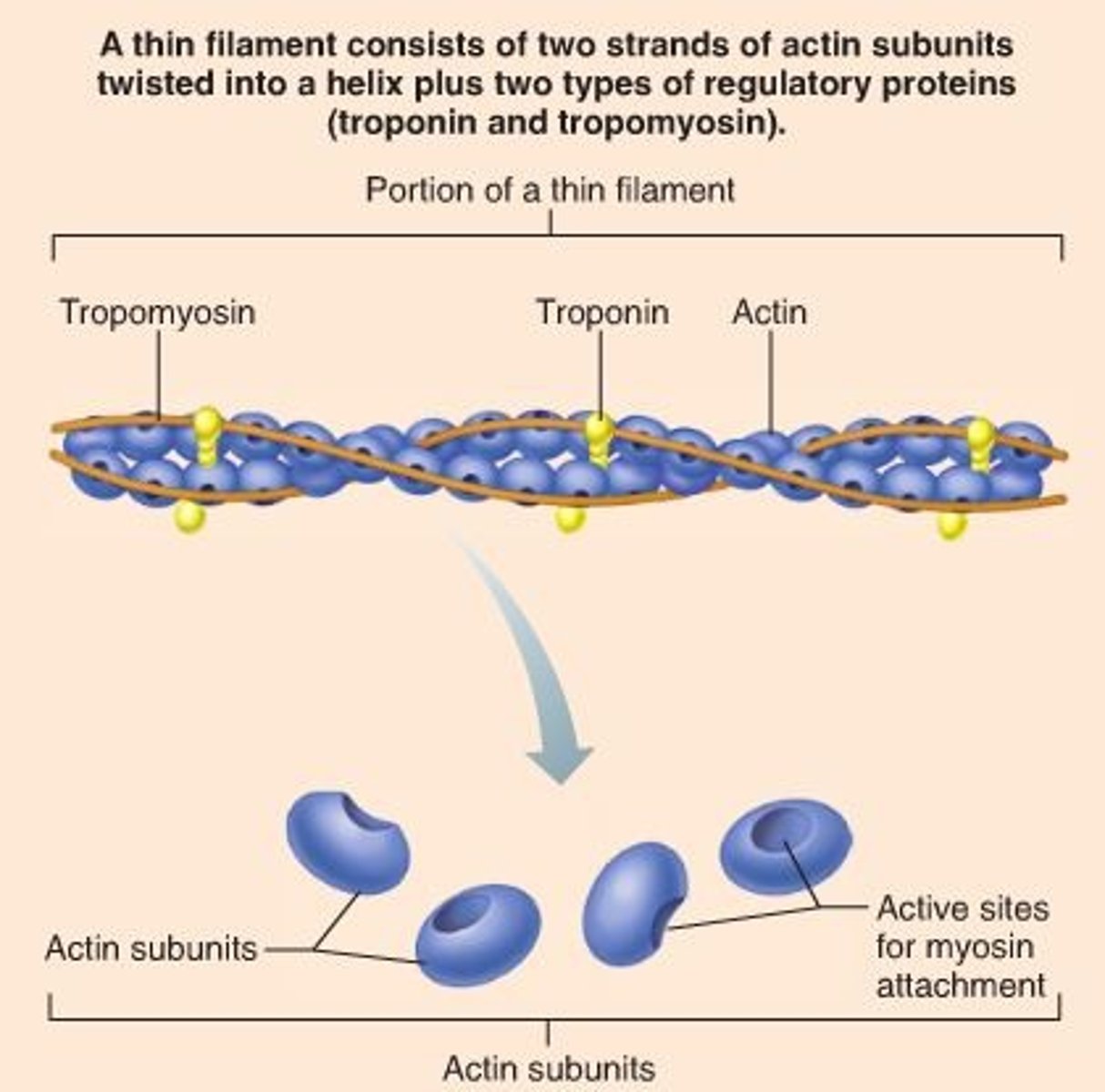
thin filaments
mostly composed of actin
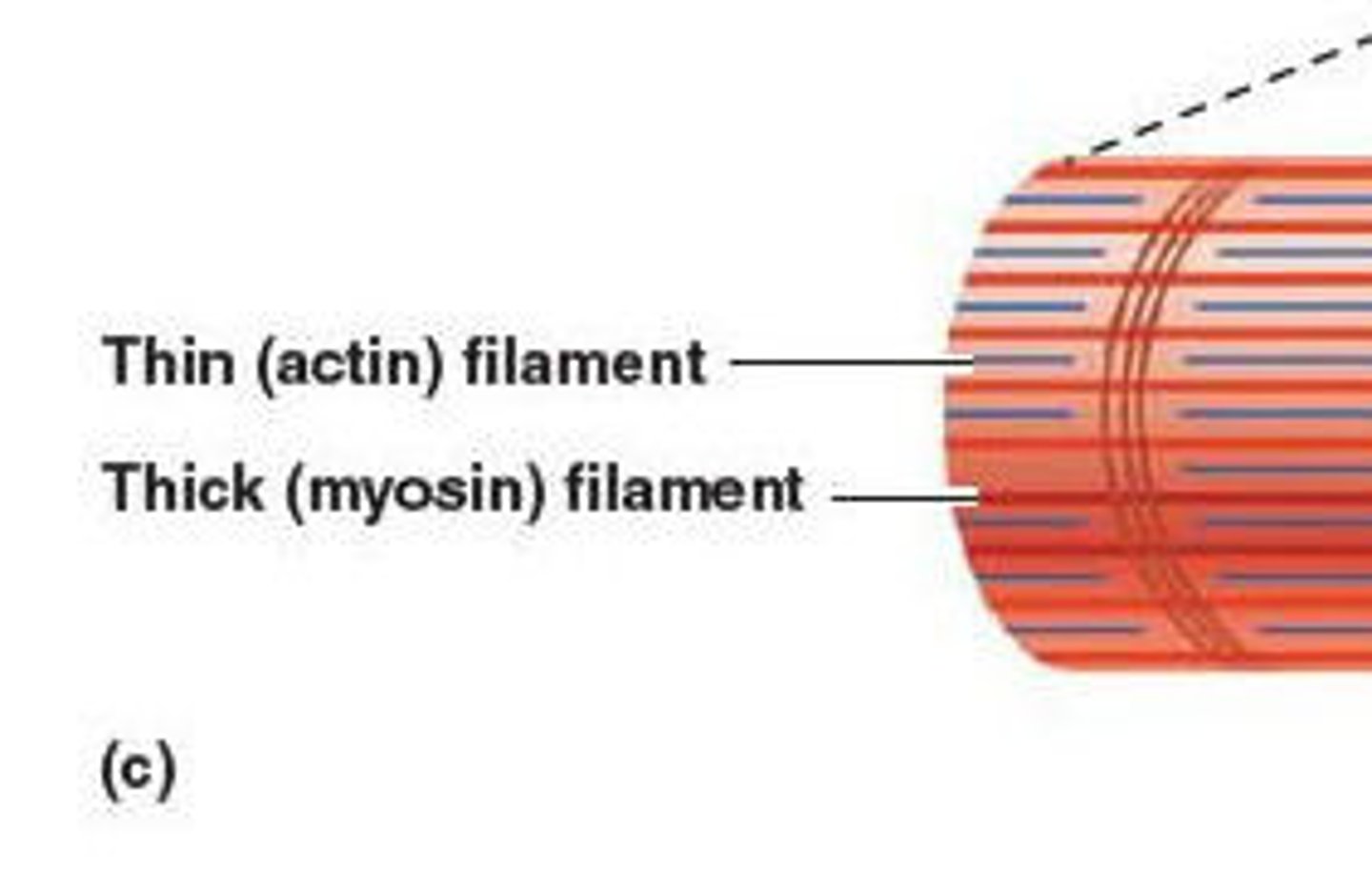
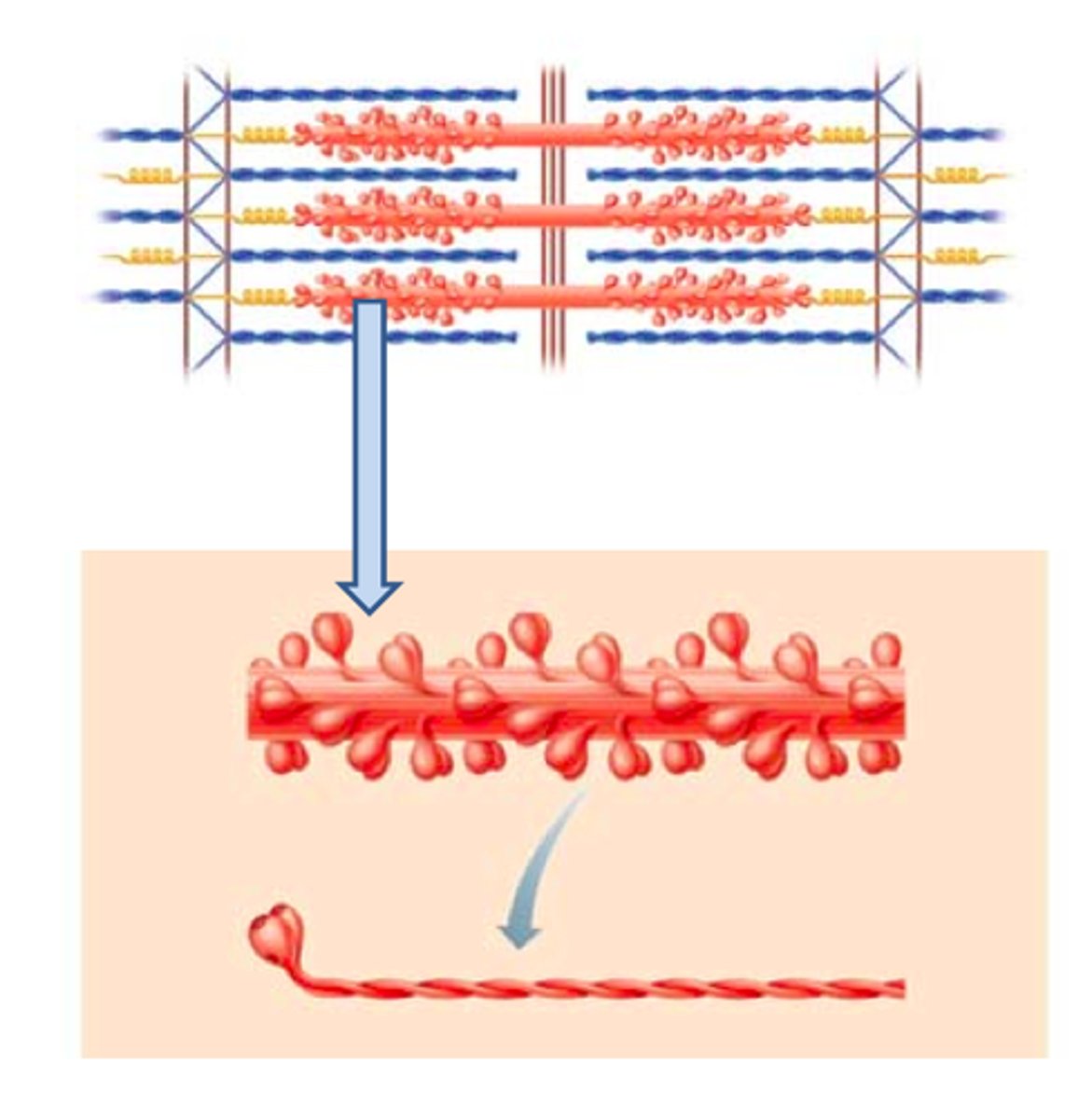
thick filments
mostly composed of myosin
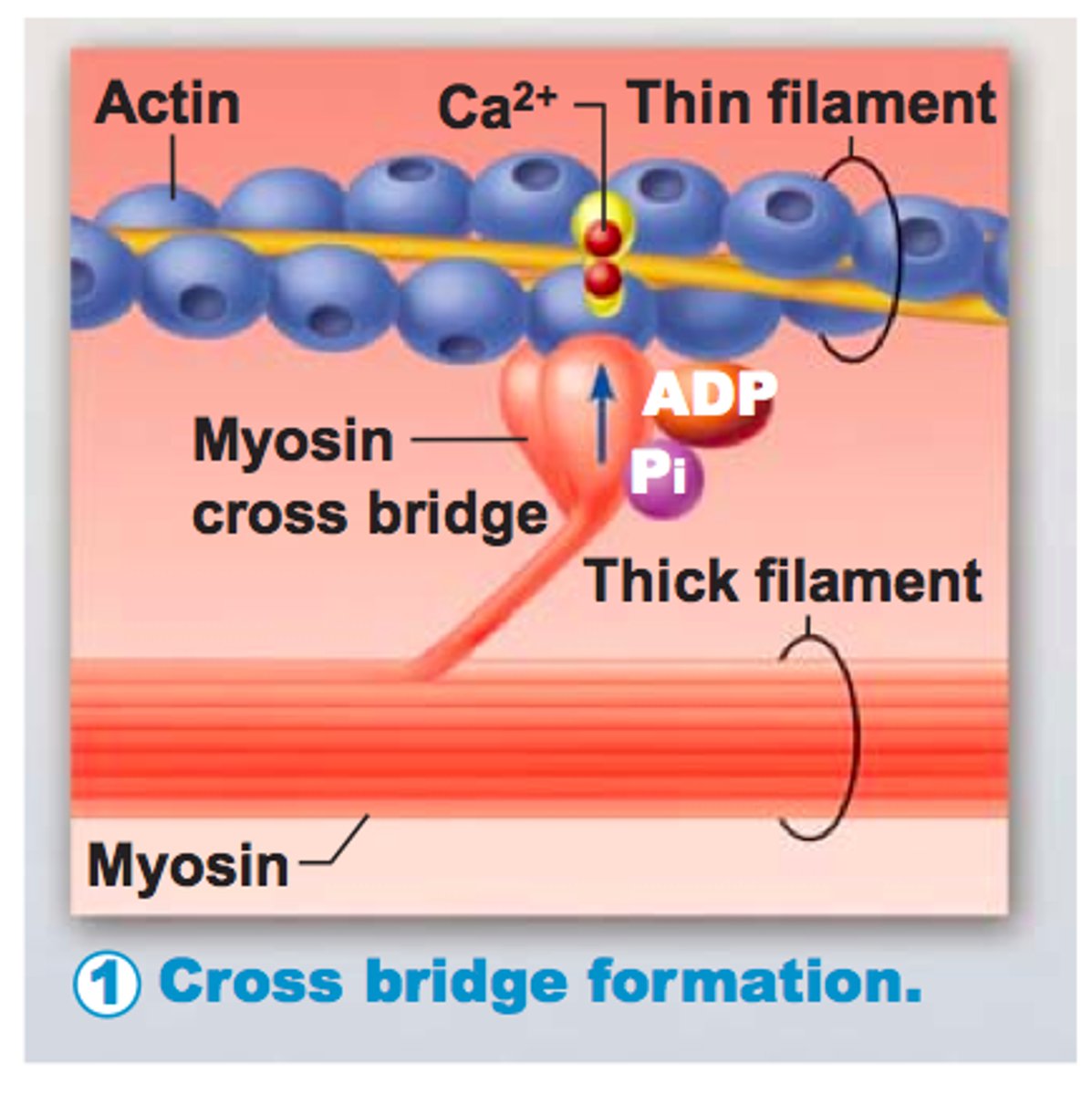
Actin
A globular protein that links into chains, two of which twist helically about each other, forming microfilaments in muscle and other contractile elements in cells.
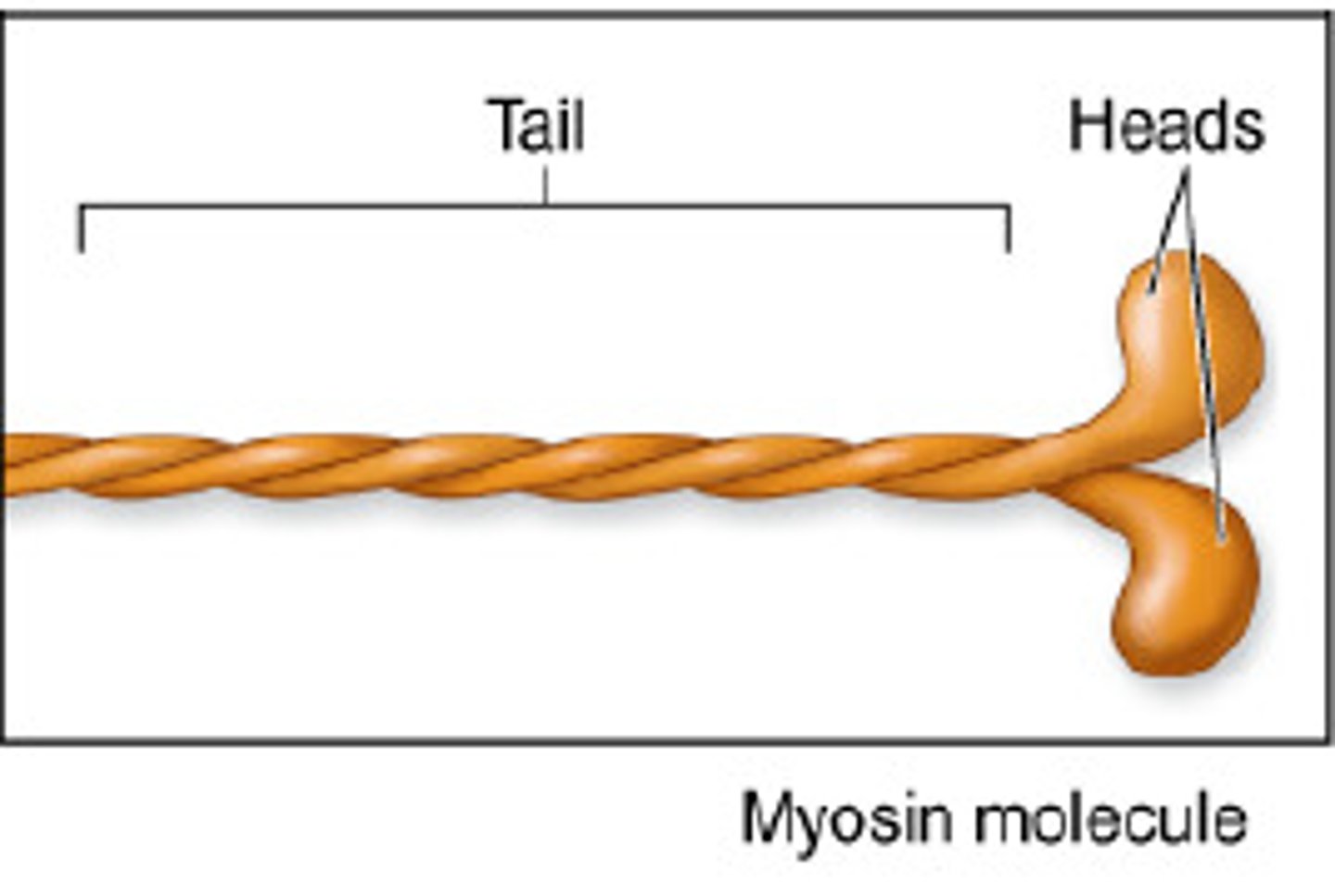
Myosin
A protein present in muscle fibers that aids in contraction and makes up the majority of muscle fiber
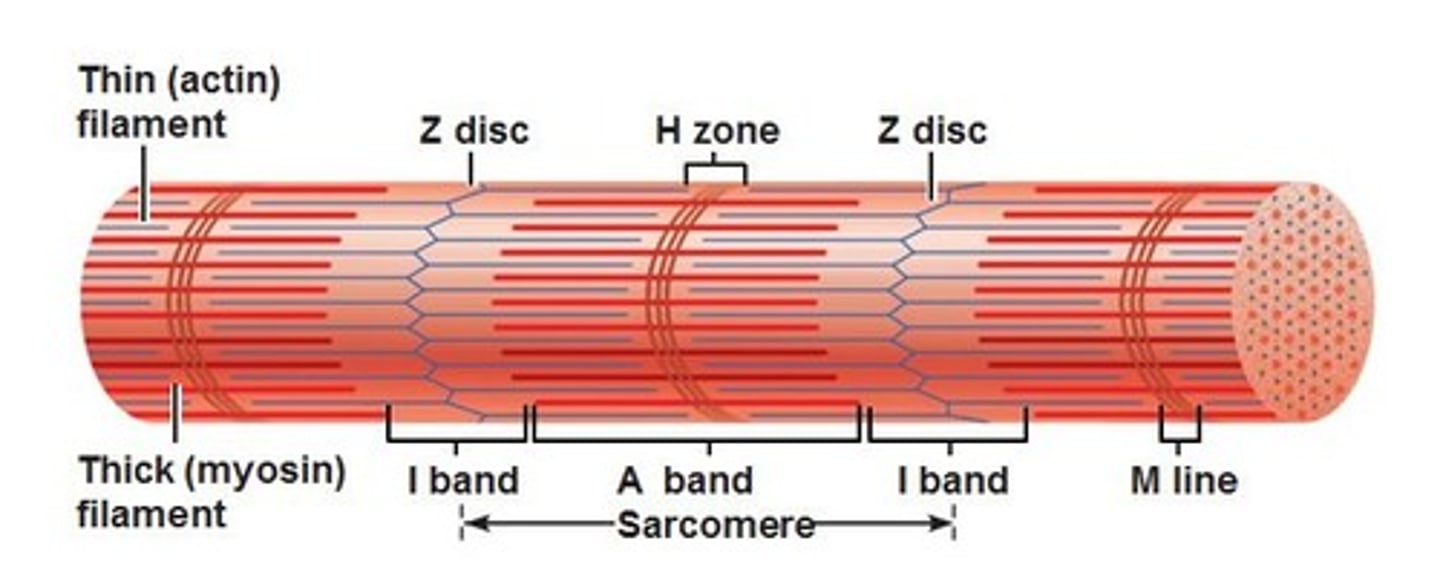
Sarcomere
Repeating functional units of skeletal muscle fiber
Overlapping sections of thick & thin filaments
~10,000 sarcomeres/myofibril, each ~2 µm resting length
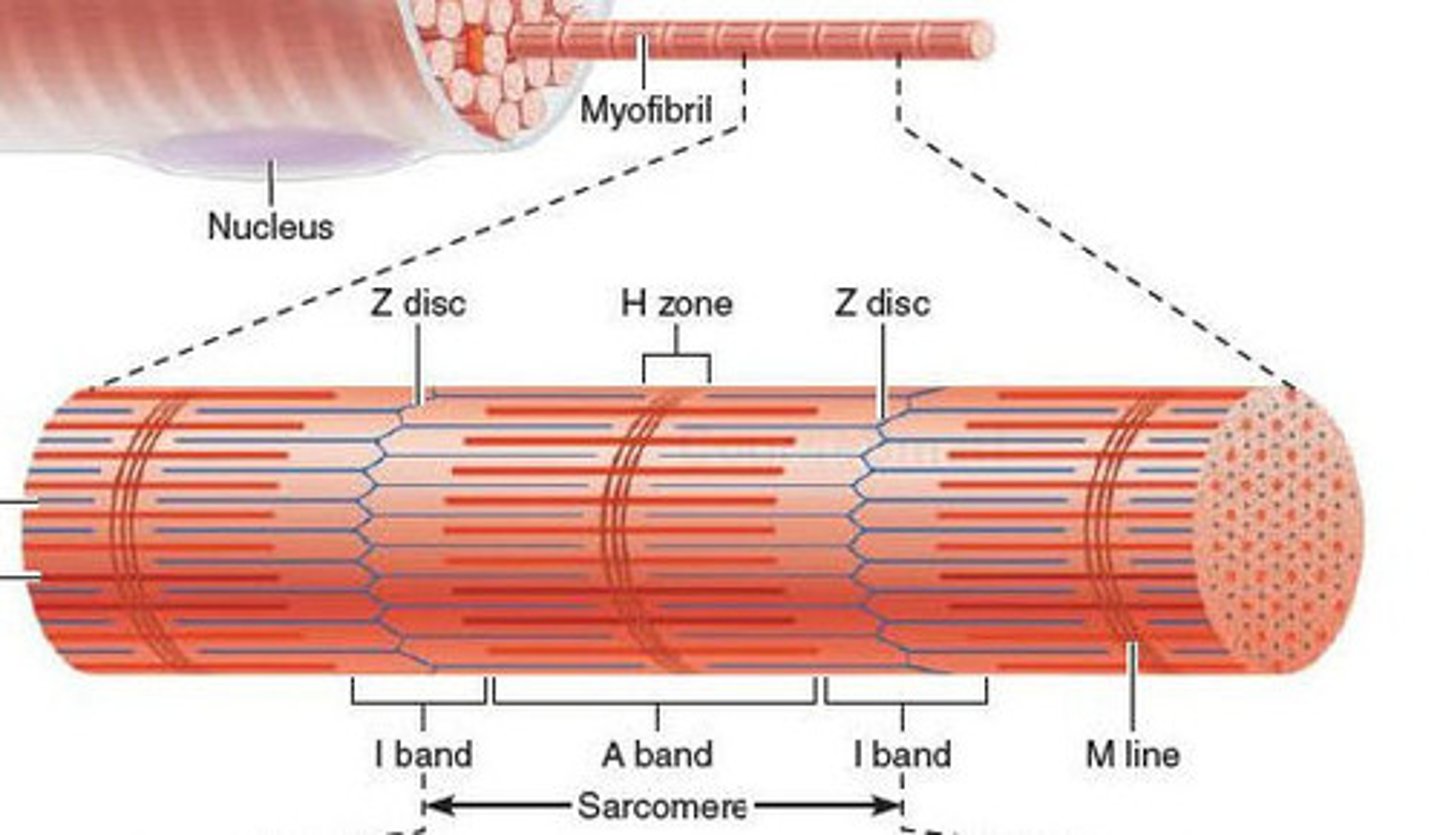
Z line
Junction of adjacent sarcomeres
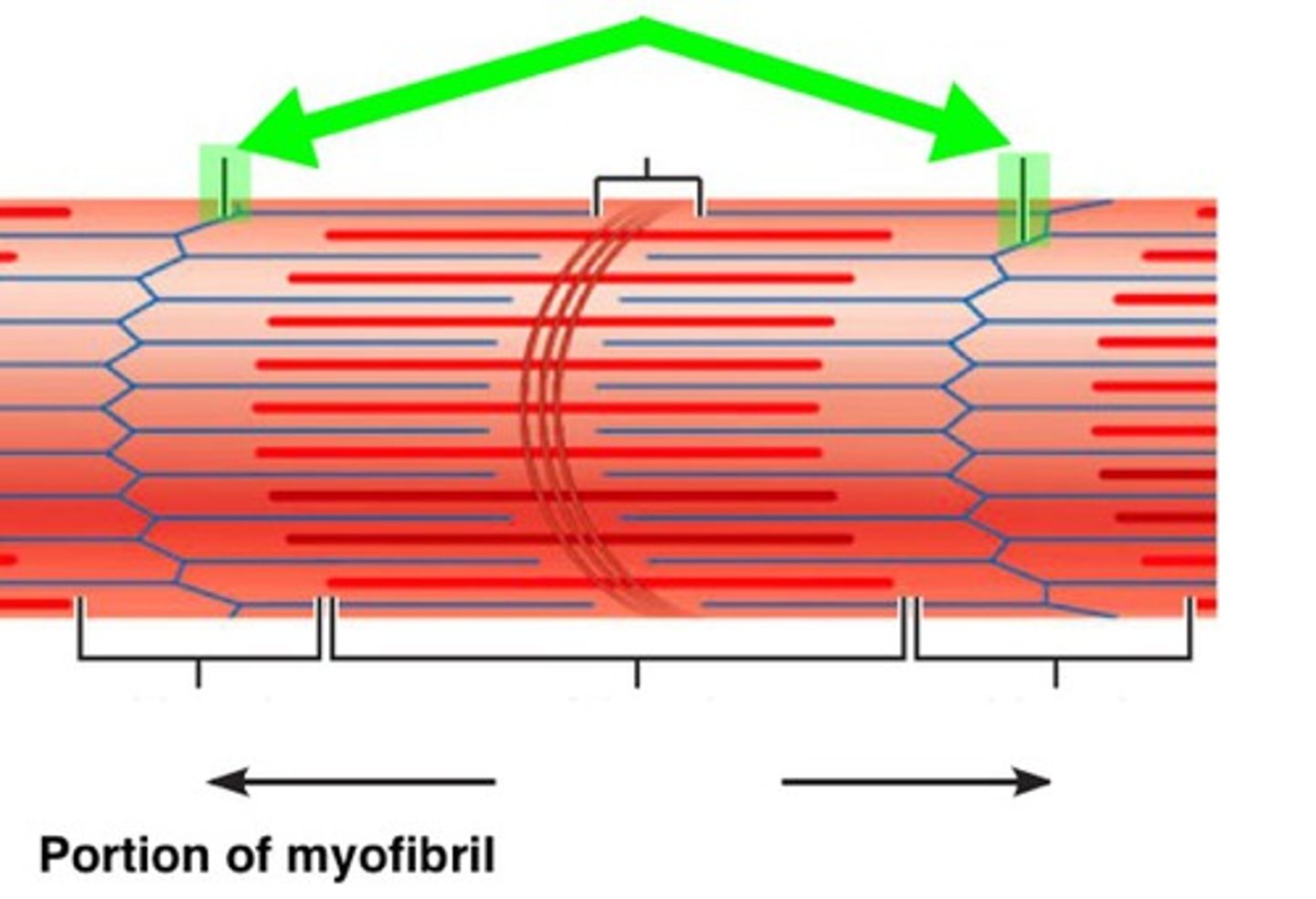
I band
Lighter band with only thin filaments (l-I-ght)
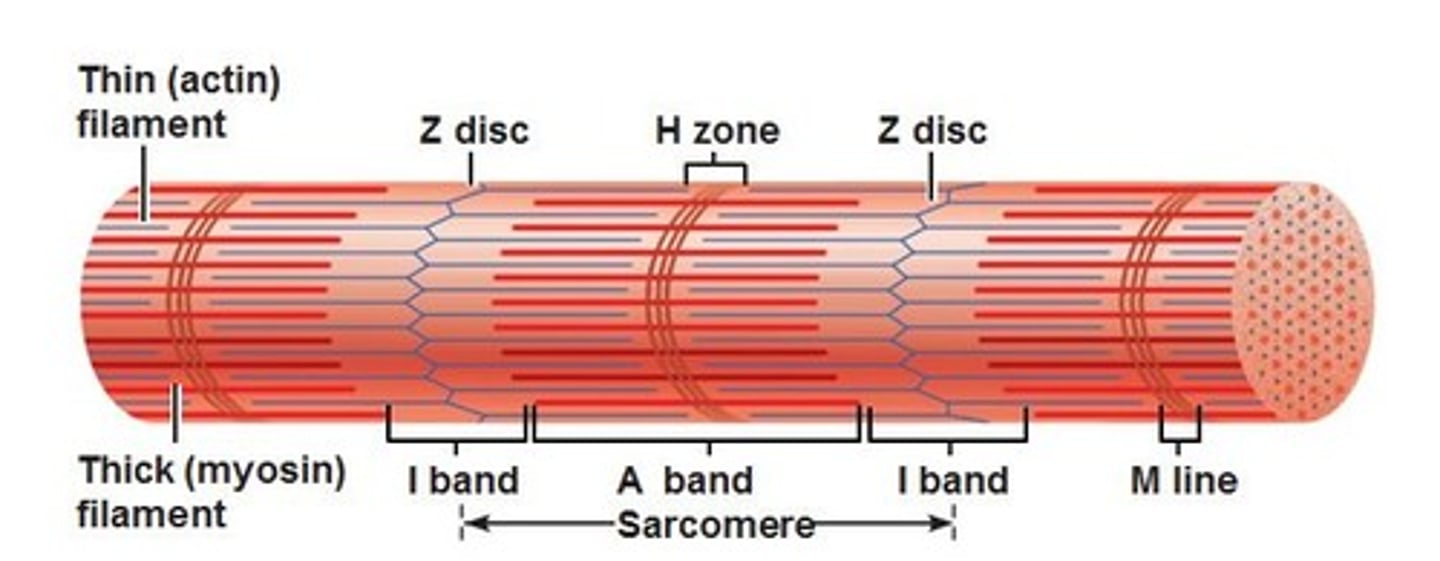
A band
Dark/dense region containing thick filaments (d-A-rk)
M line
Center of A band where adjacent thick filaments connect
H band
Region on each side of M line with only thick filaments
zone of overlap
Within A band; overlapping thick/thin filaments
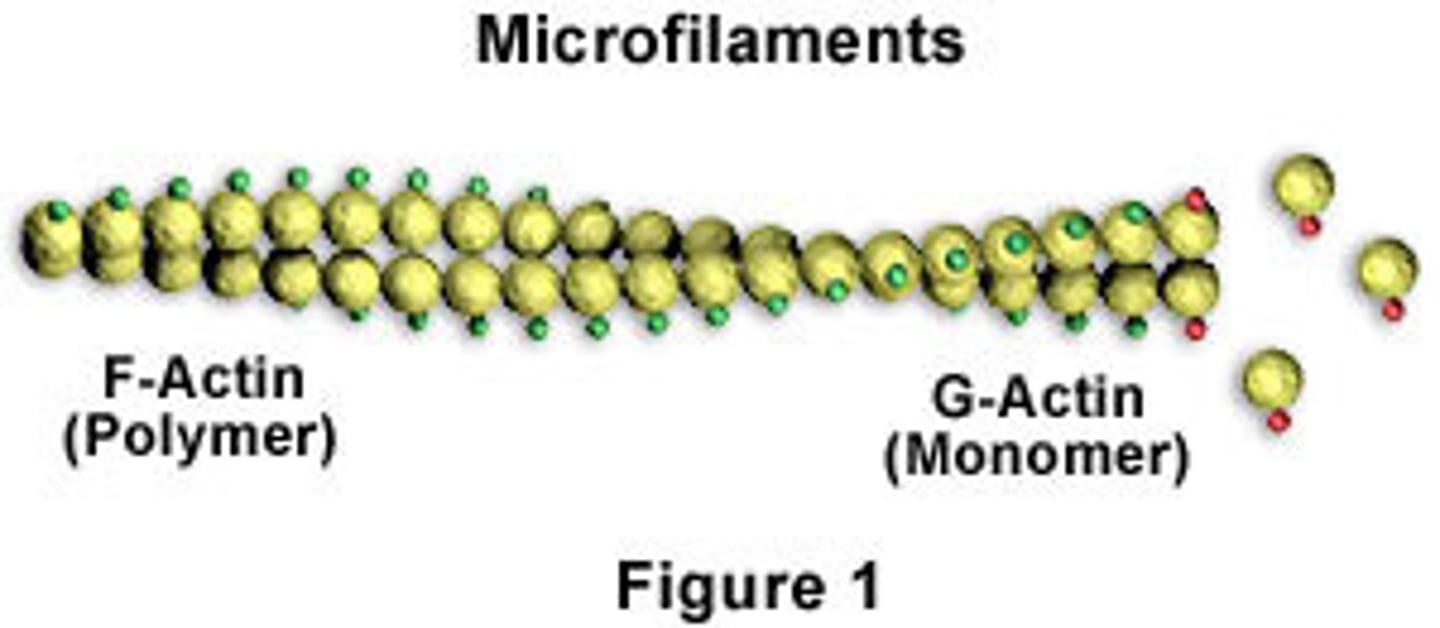
F-actin
A fibrous protein made of a long chain of G actin molecules twisted into a helix; main protein of the thin myofilament
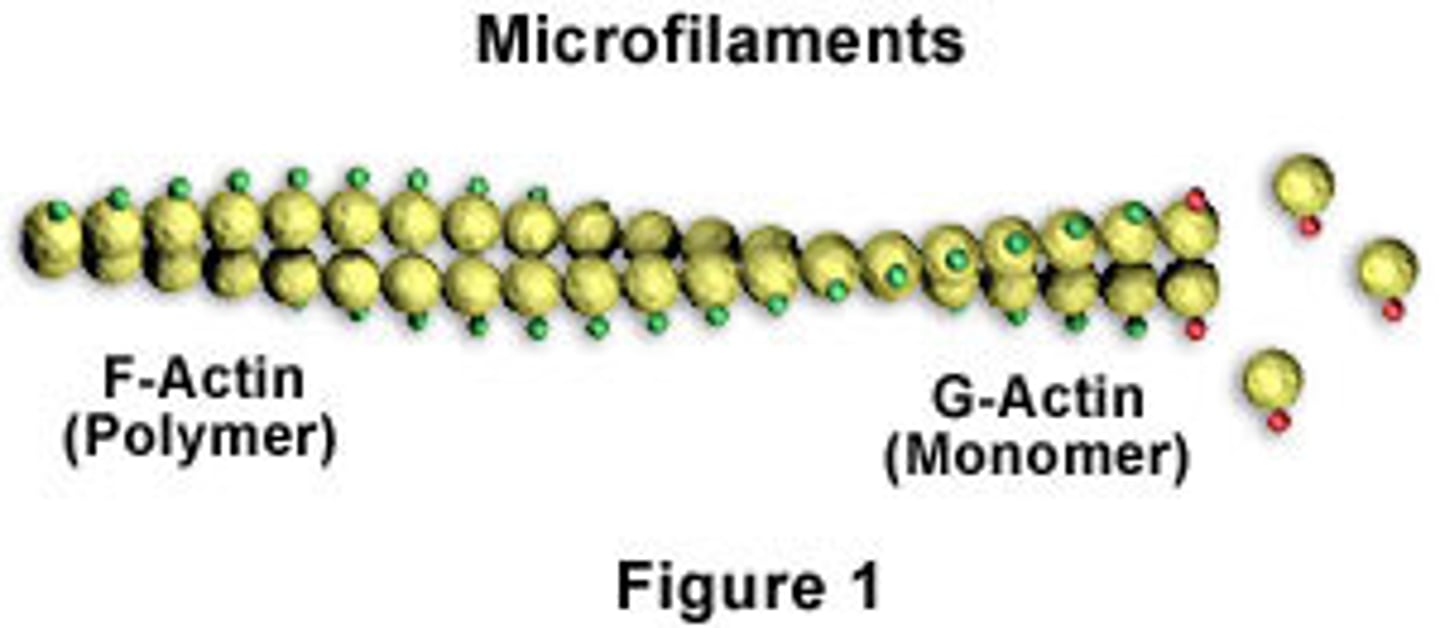
G-actin
a globular subunit of F actin with an active site for binding a myosin head
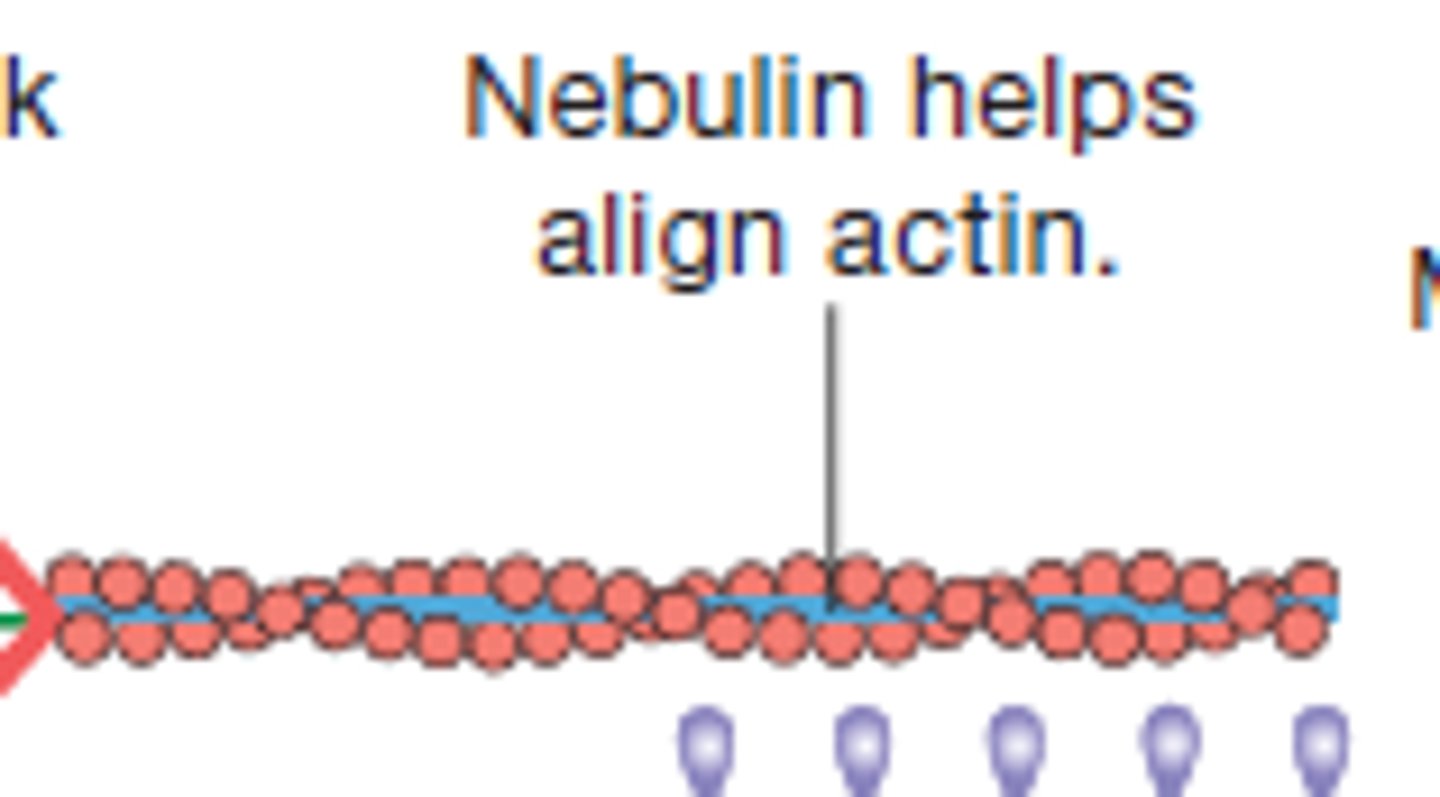
Nebulin
Holds F-actin strands together
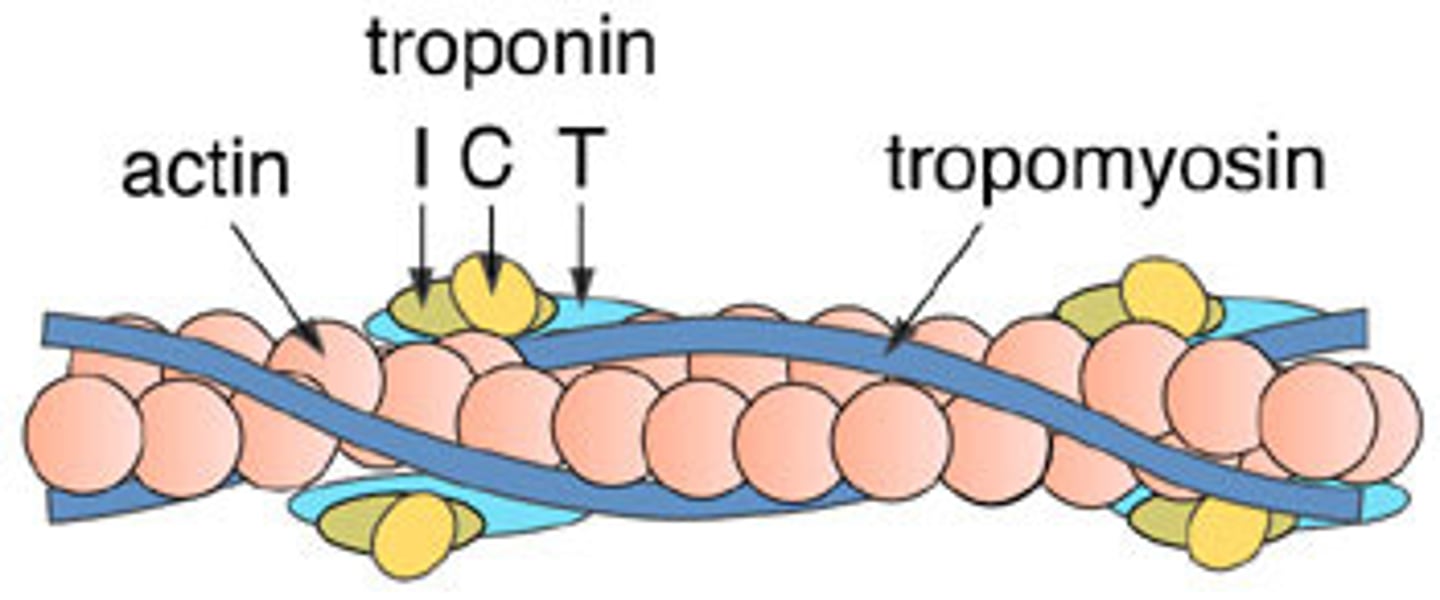
Tropomyosin
A protein of muscle that forms a complex with troponin regulating the interaction of actin and myosin in muscular contraction
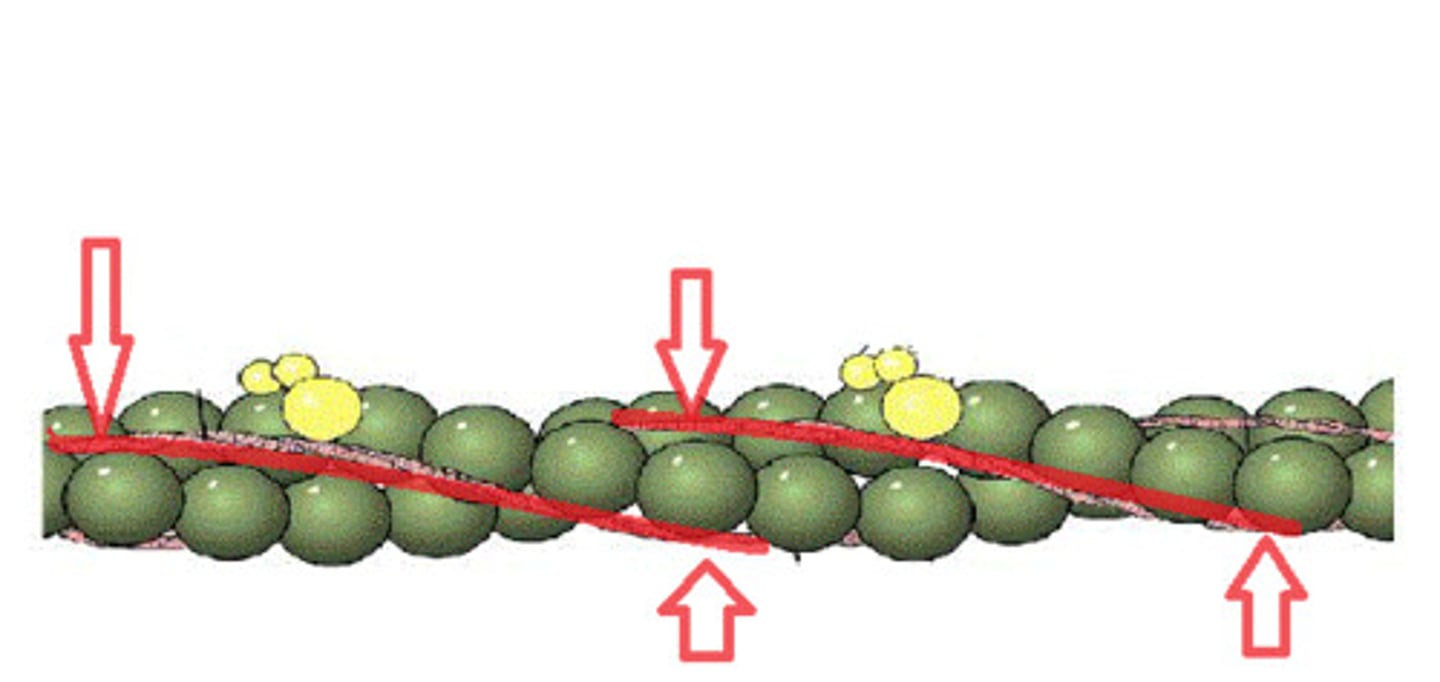
Tropinin
Part of the thin actin filament that has a binding site for calcium ions
myosin tail
(Twisted golf club handles); points toward the M line in the center of the sarcomere; tails of neighboring myosin molecules lie parallel to one another, forming the shaft of the thick filament.
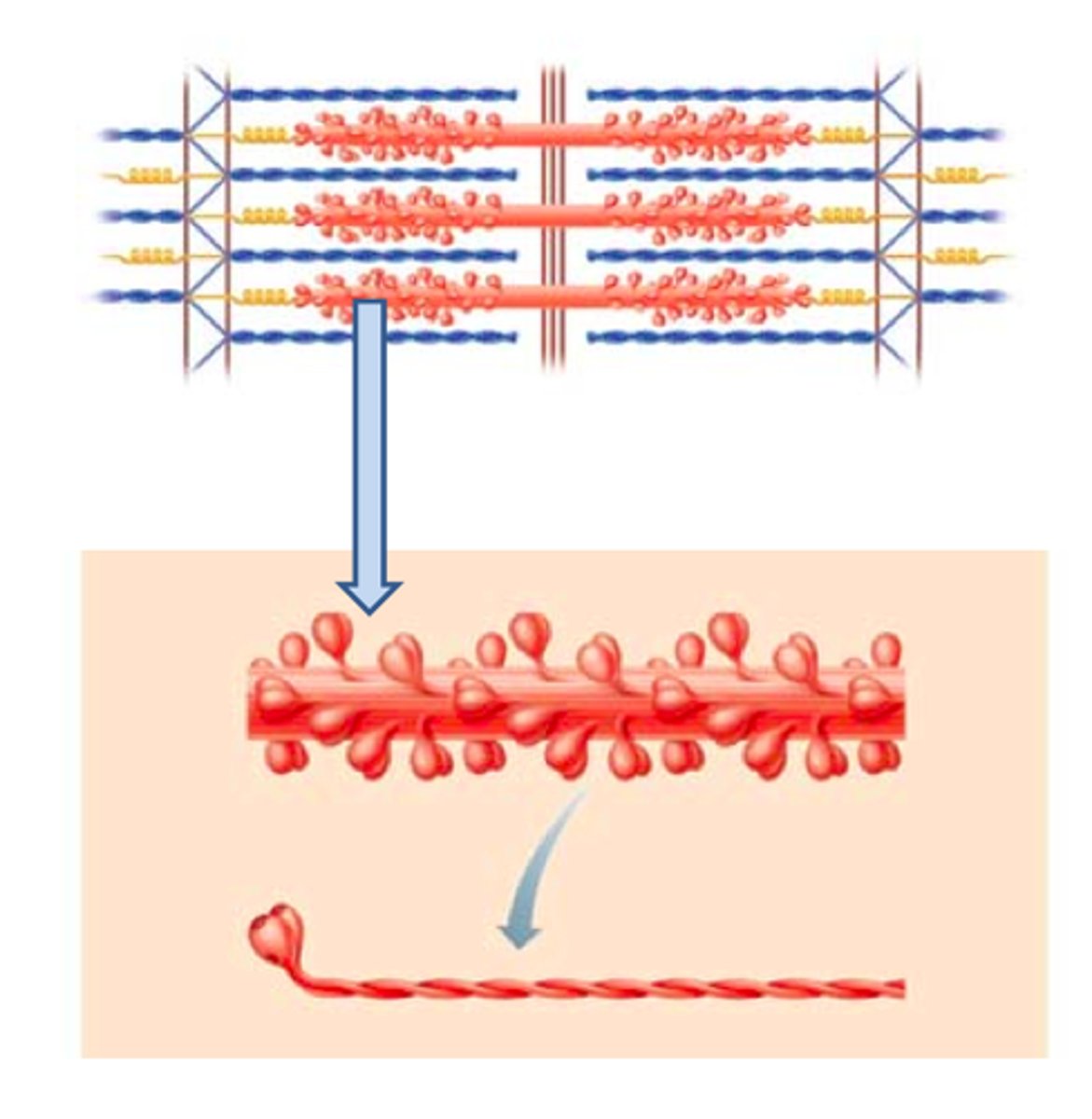
myosin heads
Bind to specific sites on actin molecules to form cross bridges
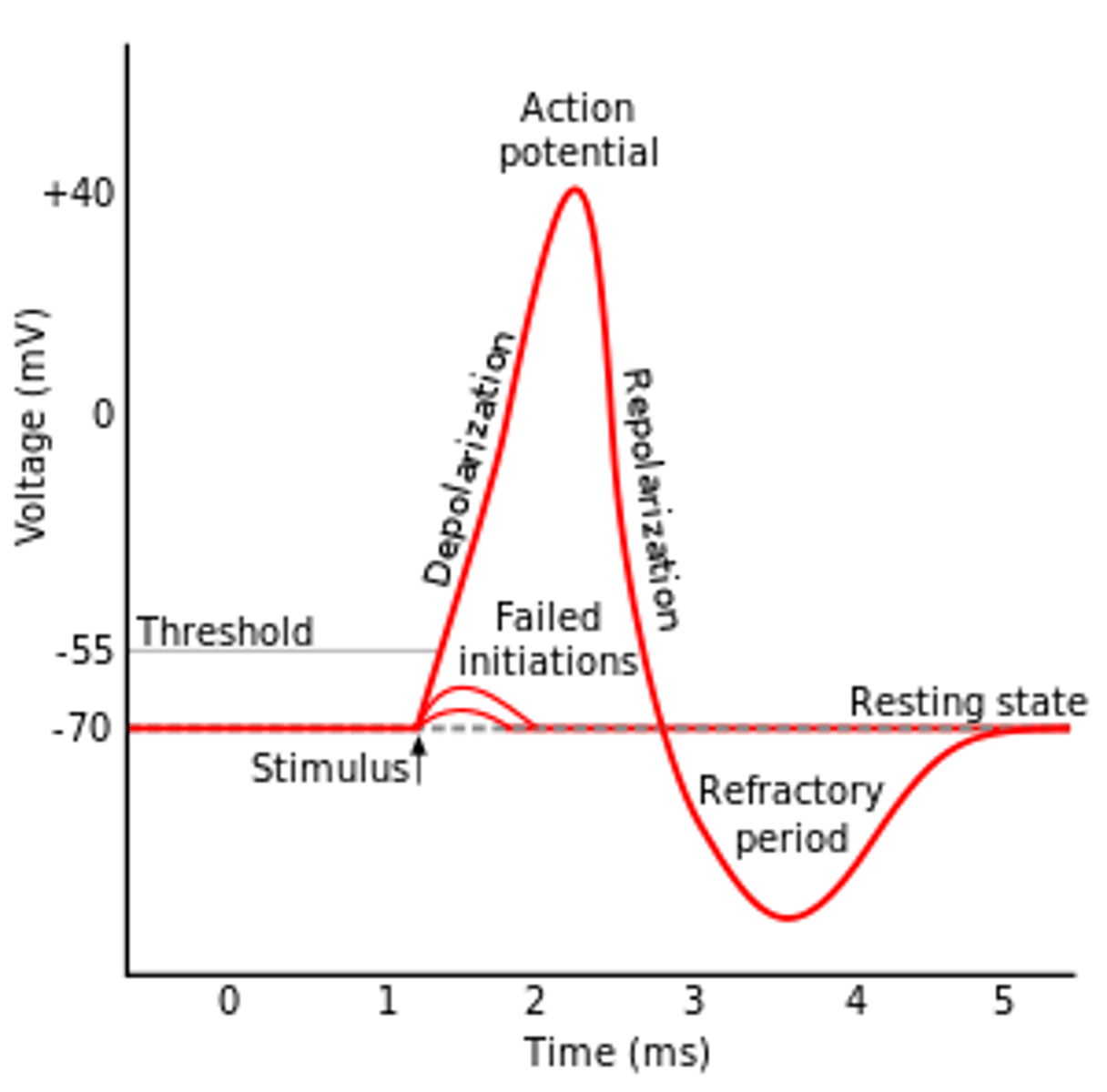
resting membrane potential
the electrical charge of a neuron when it is not active
-70mV
action potential
a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon
Change in membrane potential due to ion movement
Depolarization
Change of membrane potential to positive
Repolarization
Membrane potential returns to polarized state
refractory period
Time when firing an AP is impossible or difficult
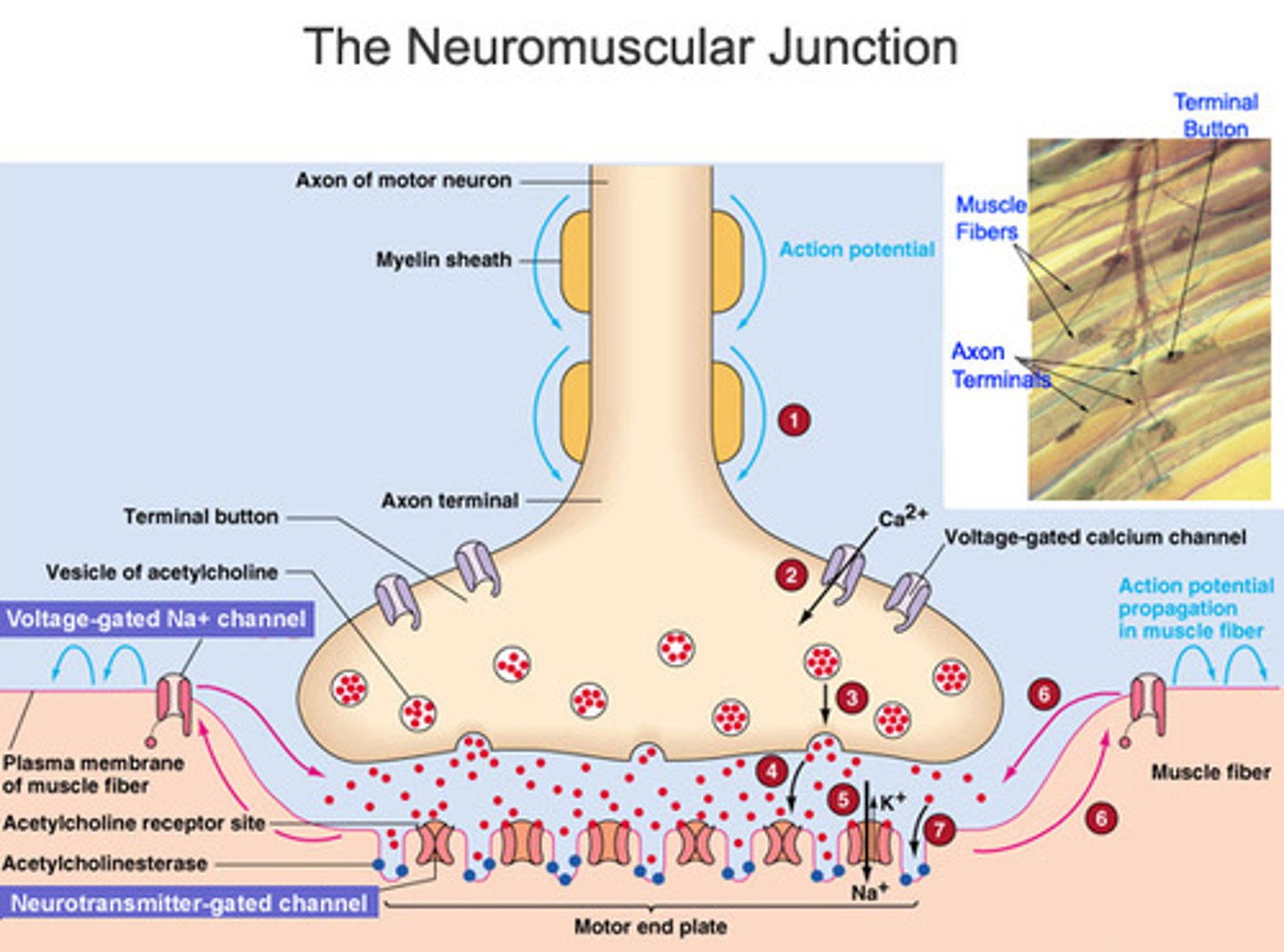
Acetylcholine
A neurotransmitter that enables learning and memory and also triggers muscle contraction
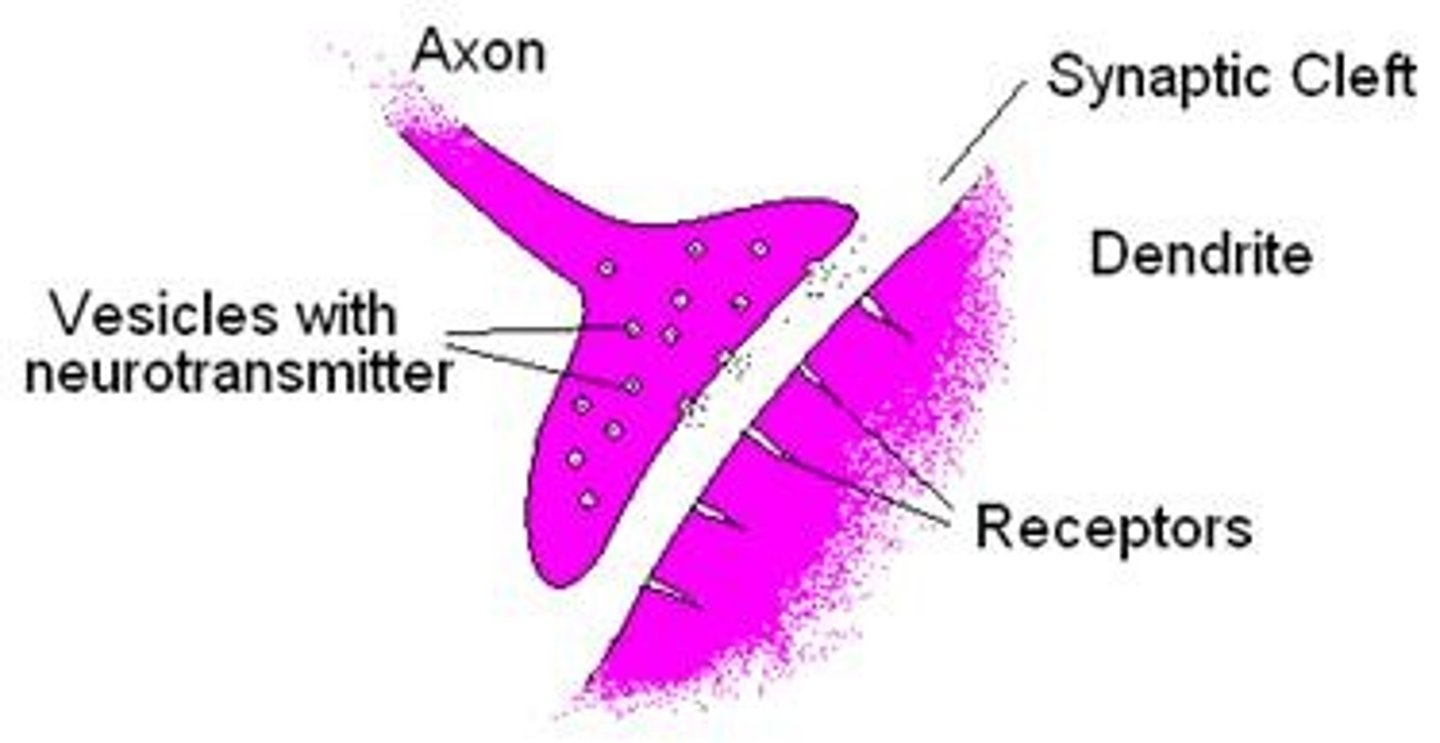
Neurotransmitter
chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons
motor end plate
Portion of muscle fiber that receives nerve signal
Has ACh receptors able to bind ACh
Junctional folds (creases) increase # of ACh receptors
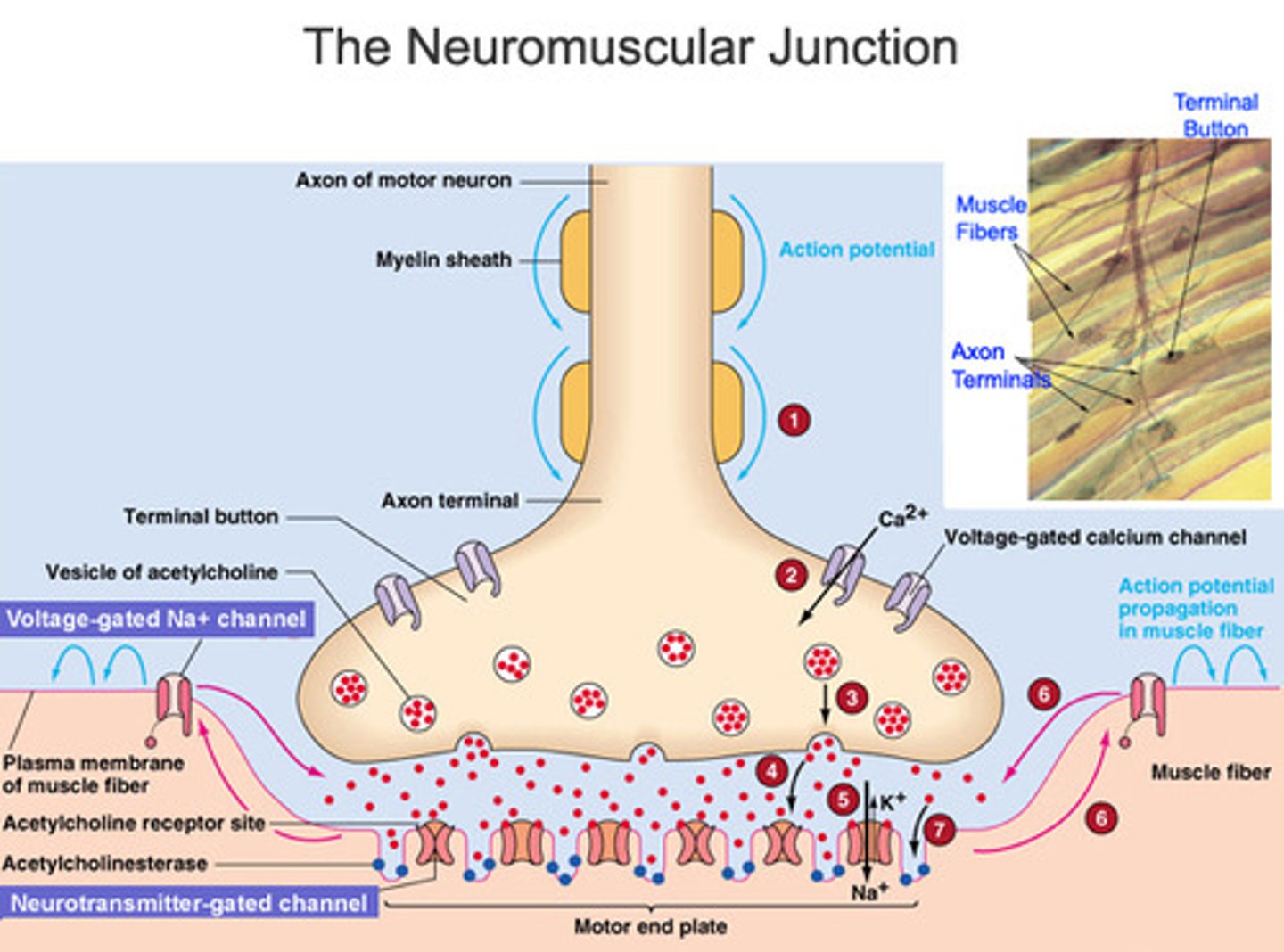
synaptic cleft
space between axon terminal and motor end plate
-Contains acetylcholinesterase (AChE)
-Breaks down ACh
Acetylcholinesterase
the enzyme that breaks down acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft
Cross bridge
The connection of a mosin head group to an actin filament during muscle contraction (the sliding filament theory).
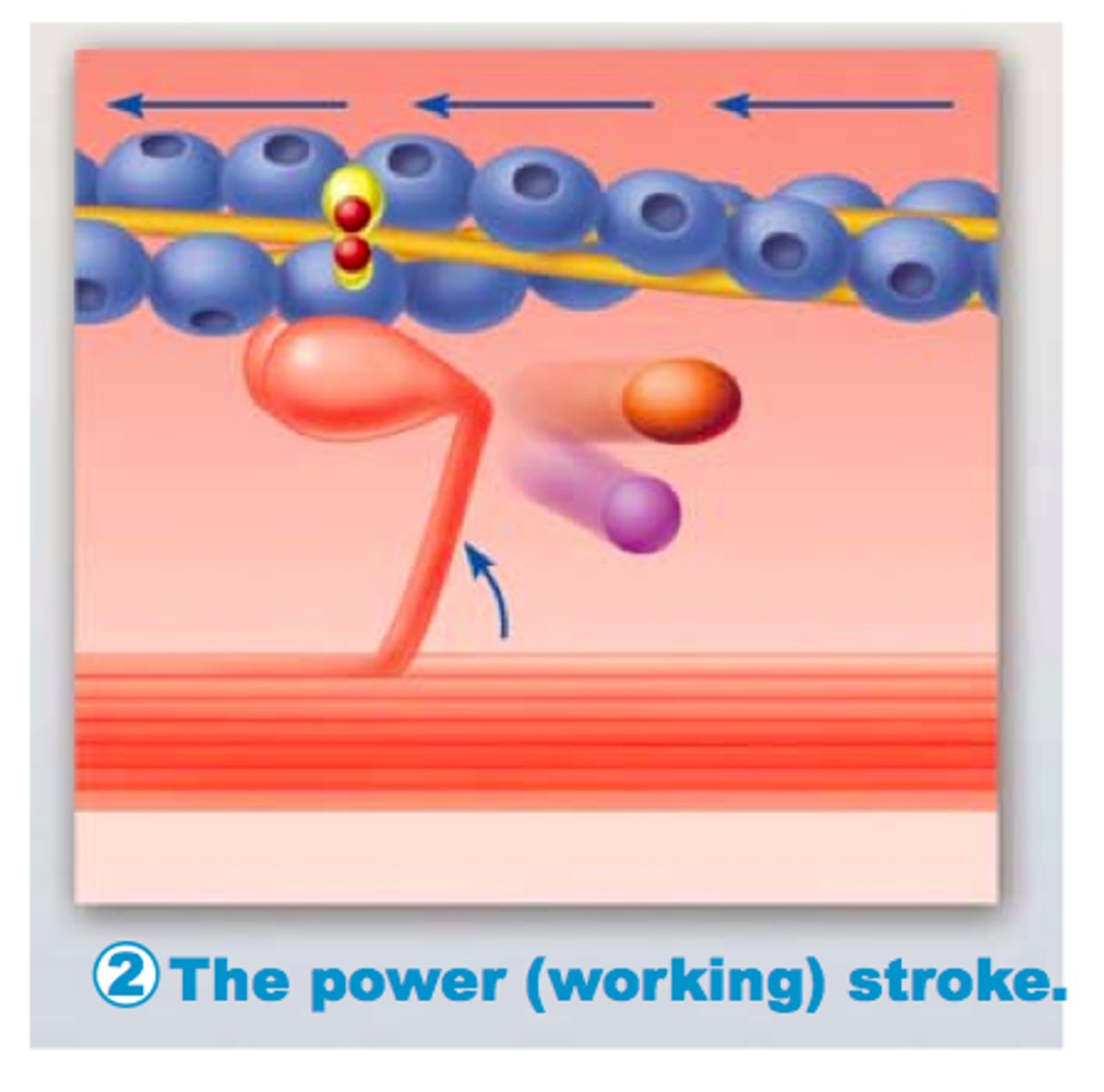
Power stroke
action of myosin pulling actin inward (toward the M line)
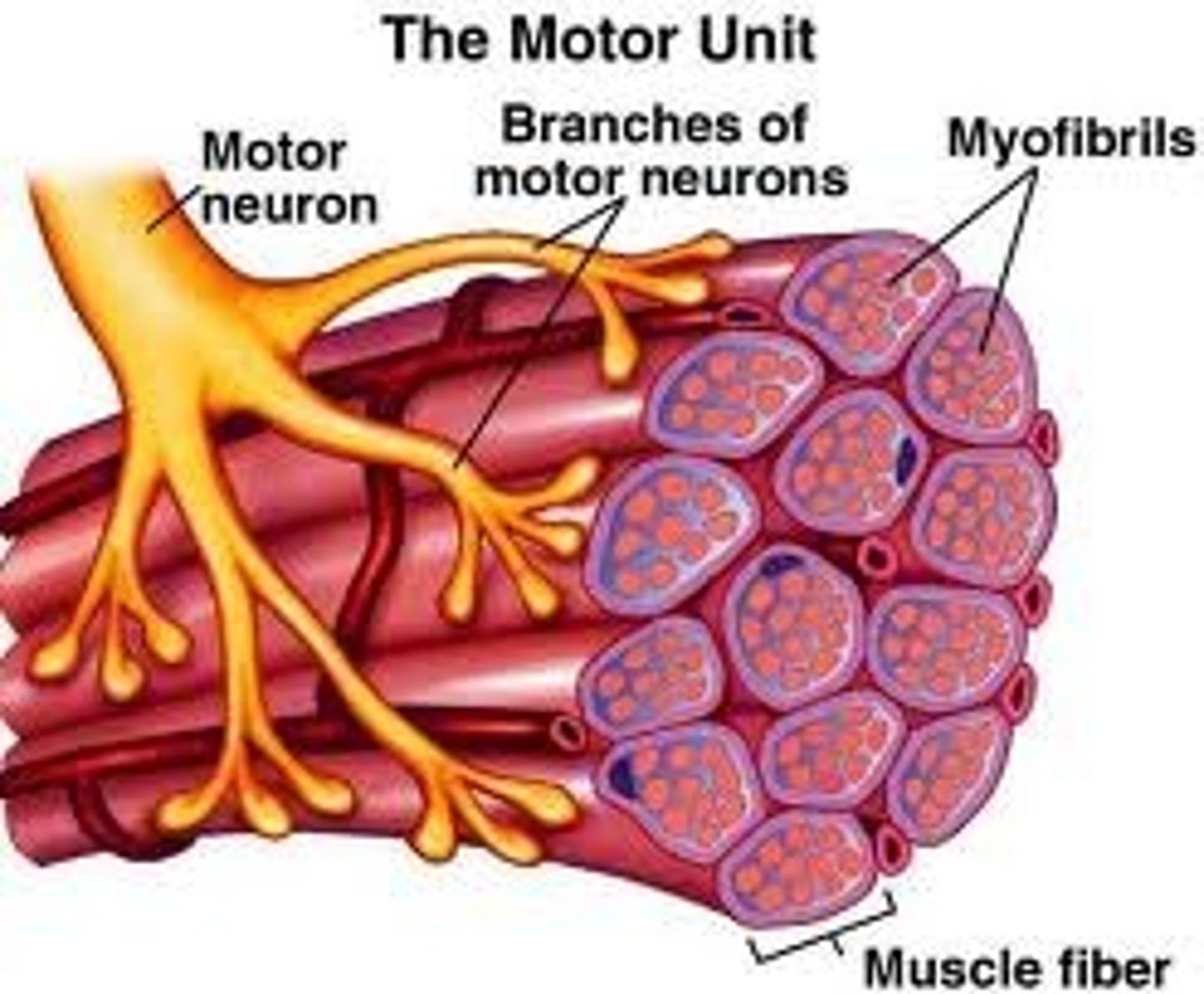
motor unit
A motor neuron and all of the muscle fibers it innervates
One motor neuron for multiple muscle fibers
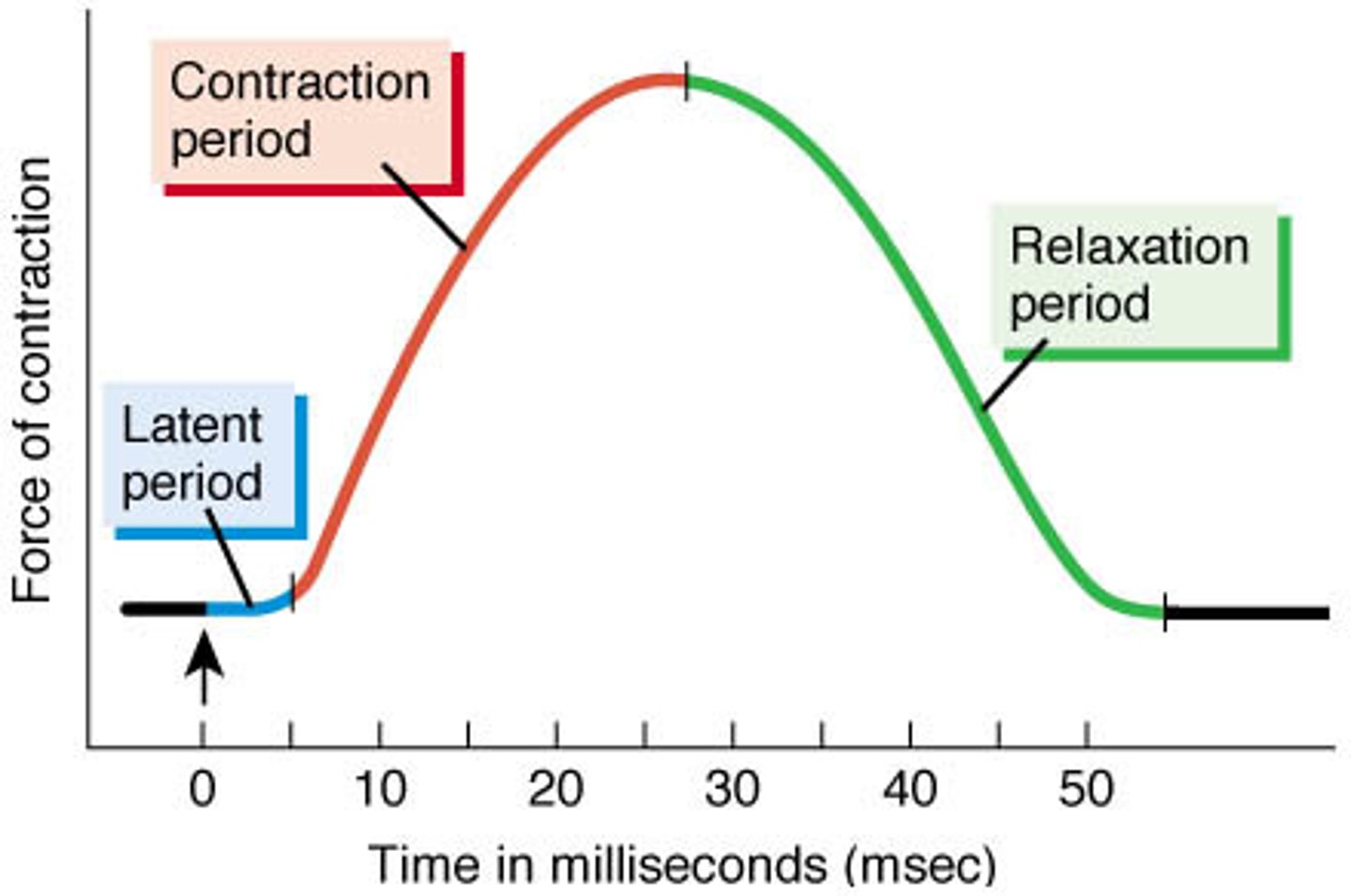
muscle twitch
Single stimulus-contraction-relaxation sequence in a muscle fiber
Duration varies by muscle type, location, environmental factors
Fasciculation
involuntary "muscle twitch" under skin
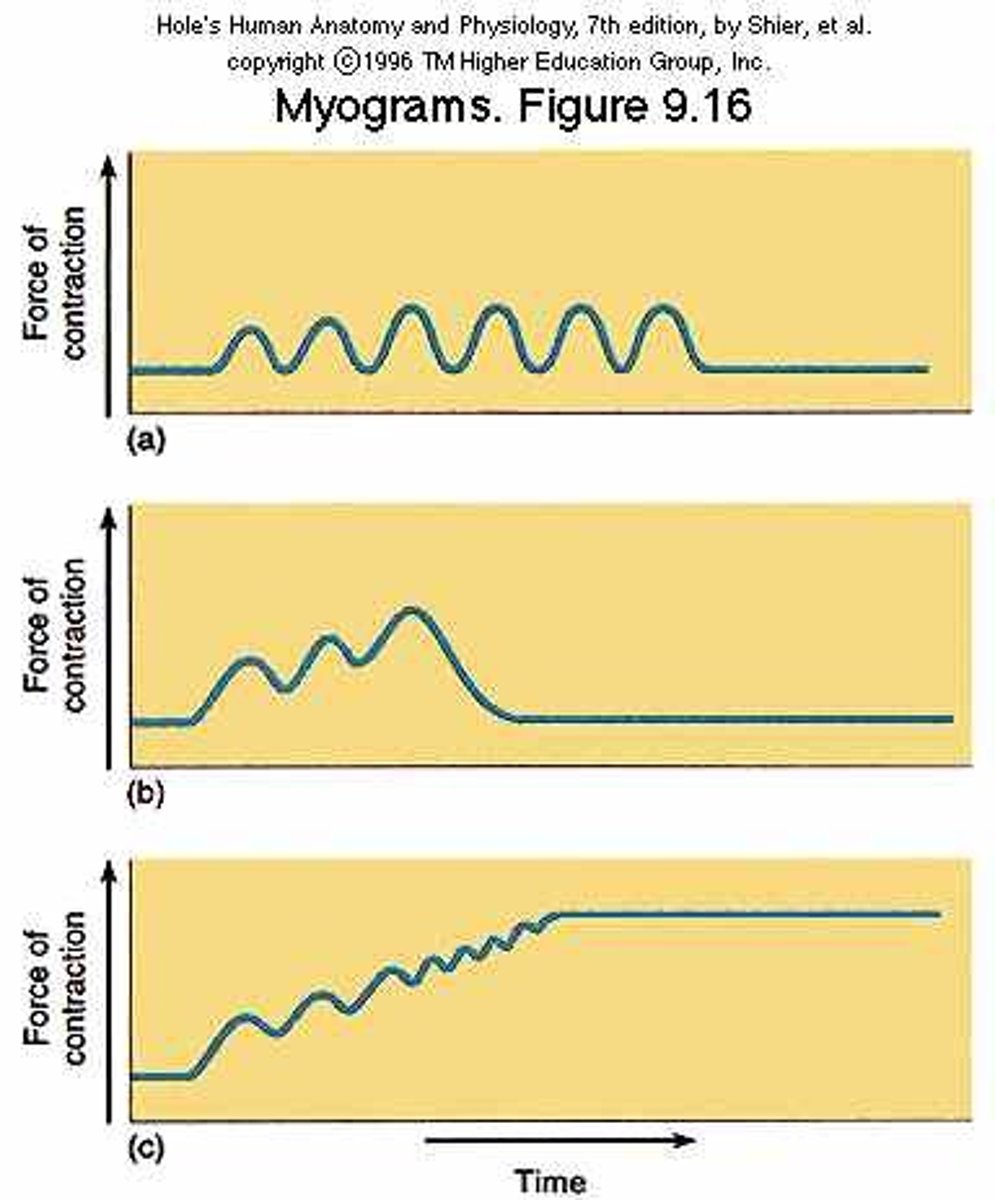
myogram
Shows development of muscle tension
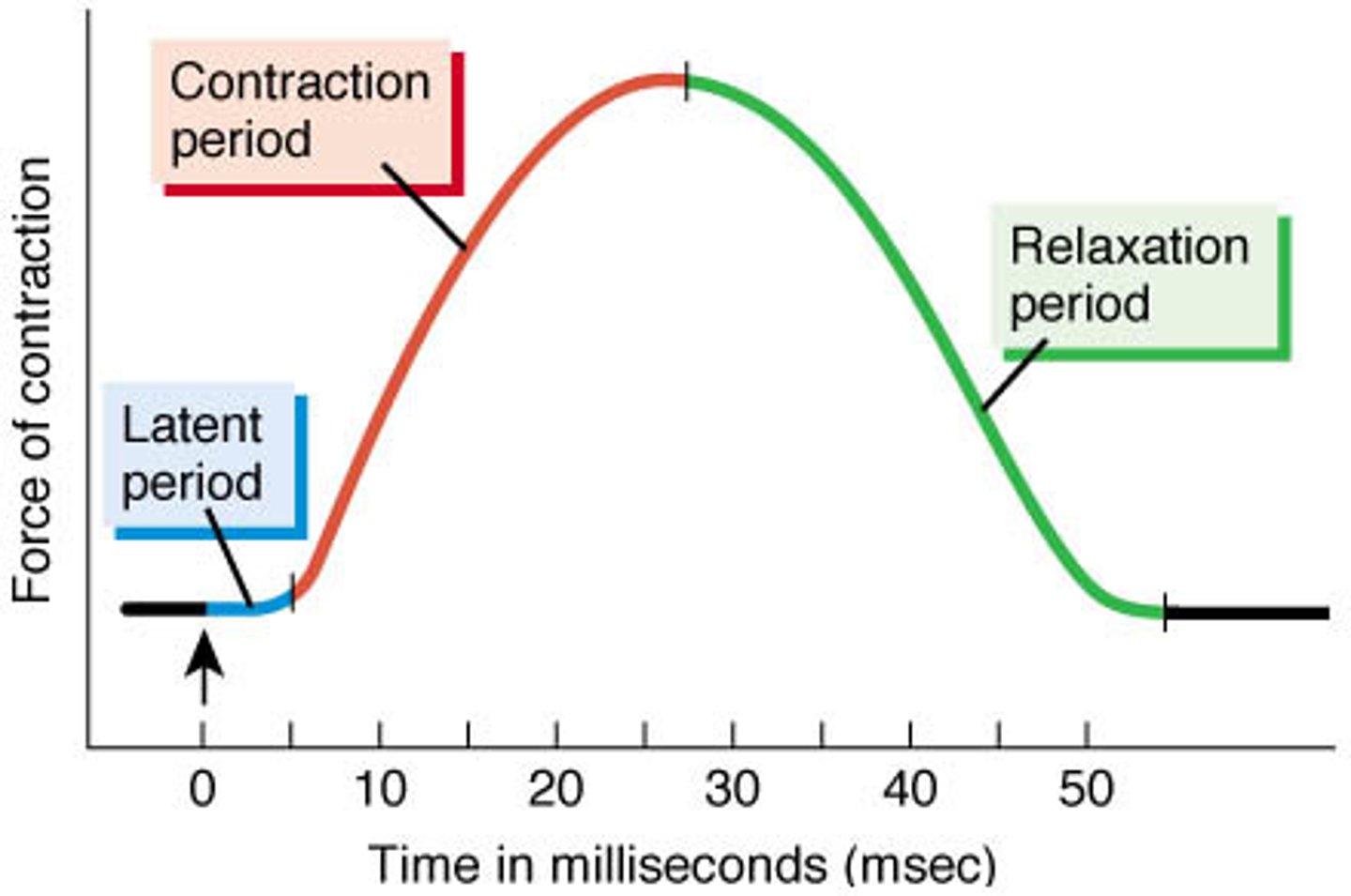
latent period
Action potential stimulates sarcolemma
Calcium released from sarcoplasmic reticulum
No tension yet
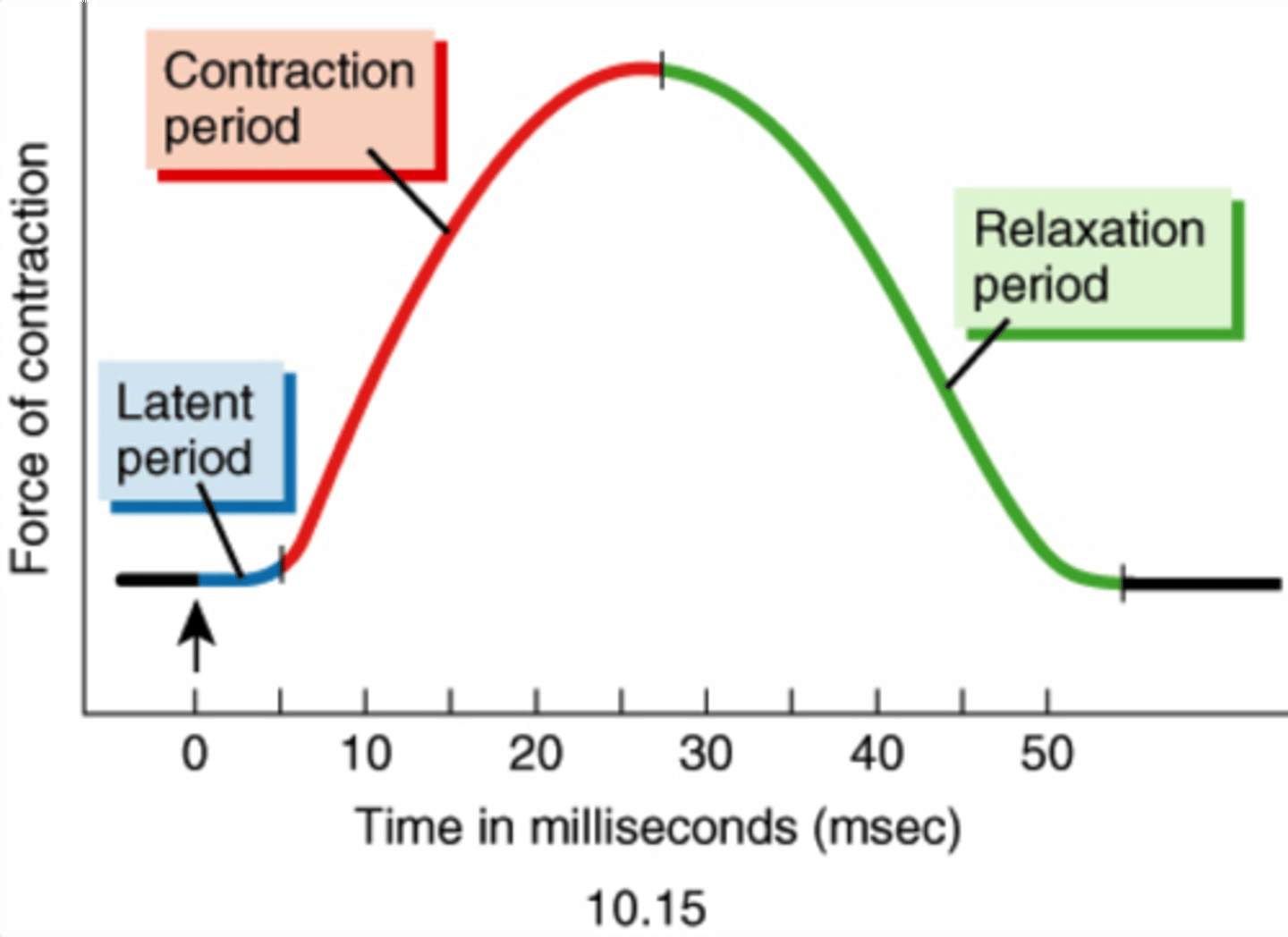
contraction phase (of a muscle twitch)
Calcium binds to troponin
Cross-bridge cycling
Start of tension development to peak tension
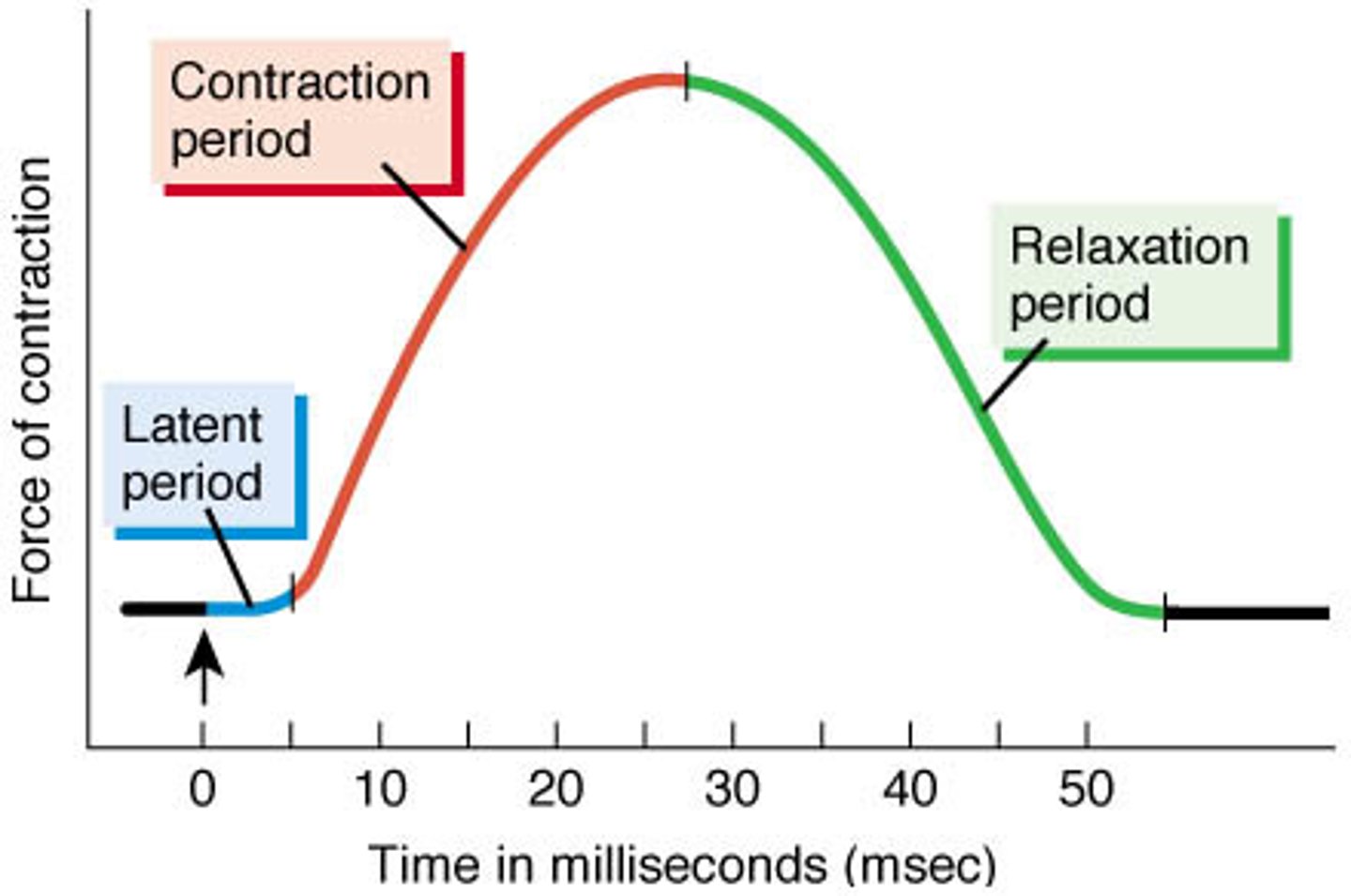
relaxation phase
Calcium drops; cross-bridges detach; active sites covered
Tension returns to resting levels
From peak tension to end of twitch (about 25 msec)
Treppe
stepwise increase in contraction tension
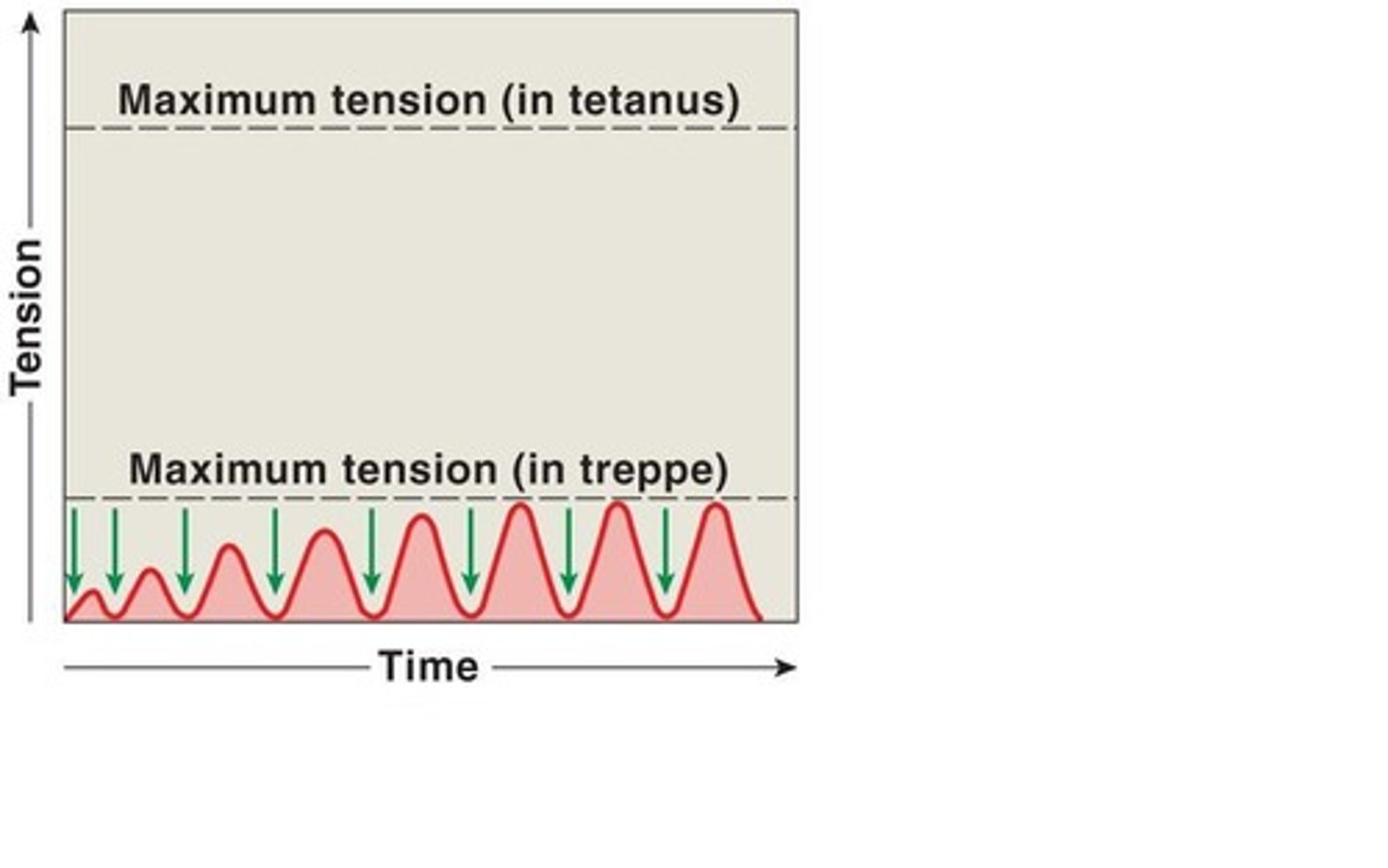
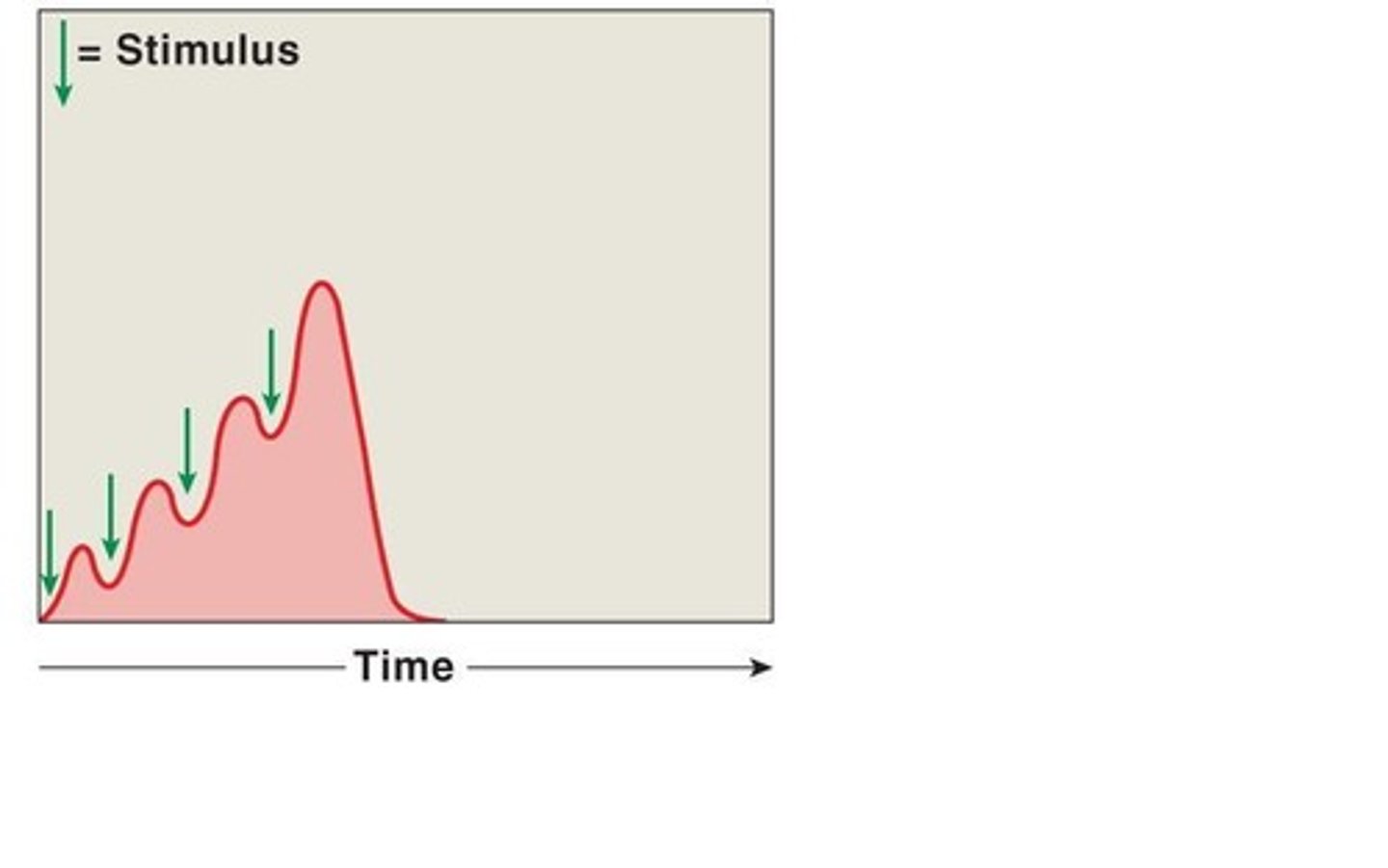
wave summation
this occurs when a second stimulus is received before the muscle fiber has relaxed, creating a second contraction that is stronger than the first
incomplete tetanus
muscle fibers partially relax between contraction
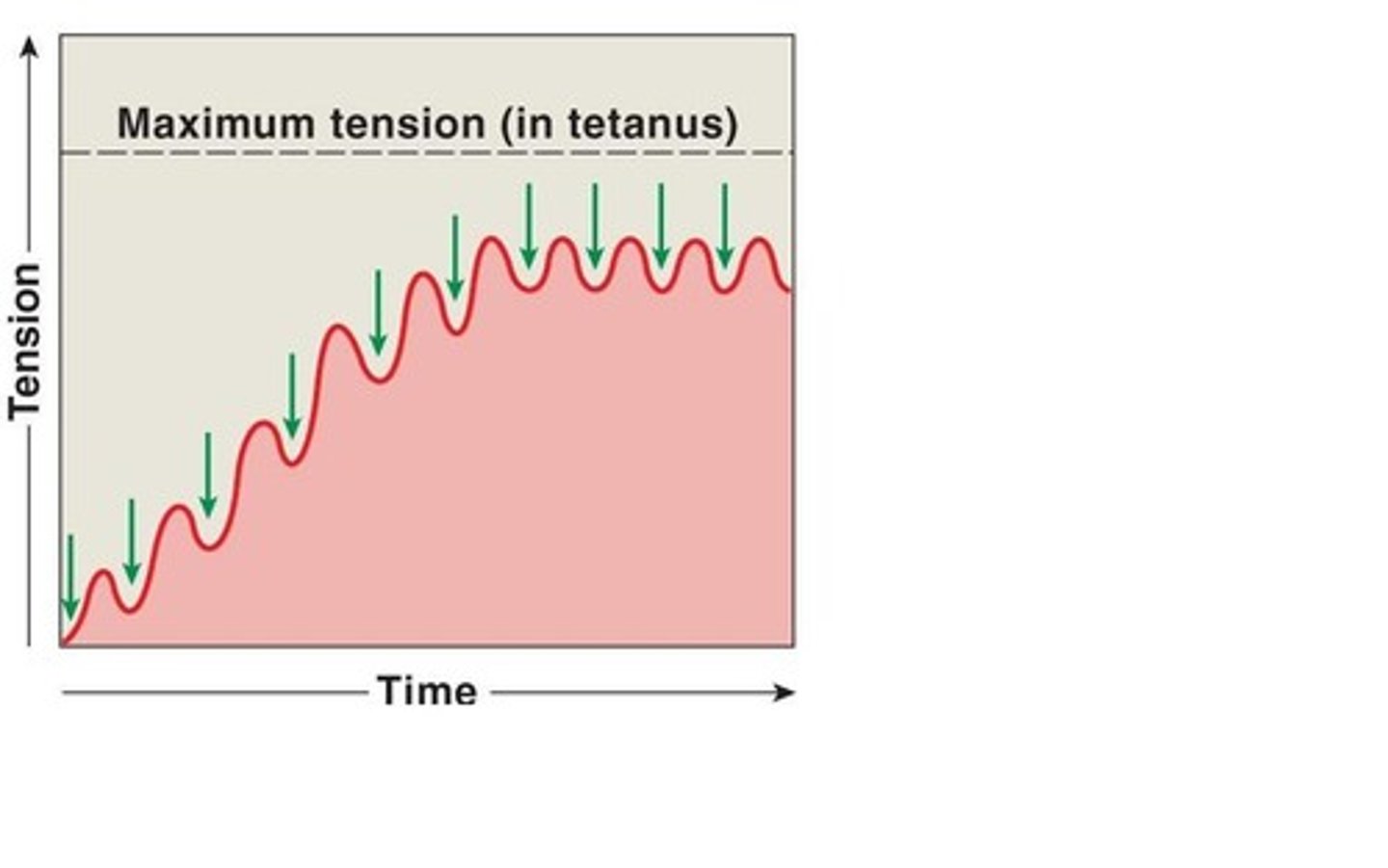
Tetanus
a sustained muscular contraction resulting from a rapid series of nerve impulses
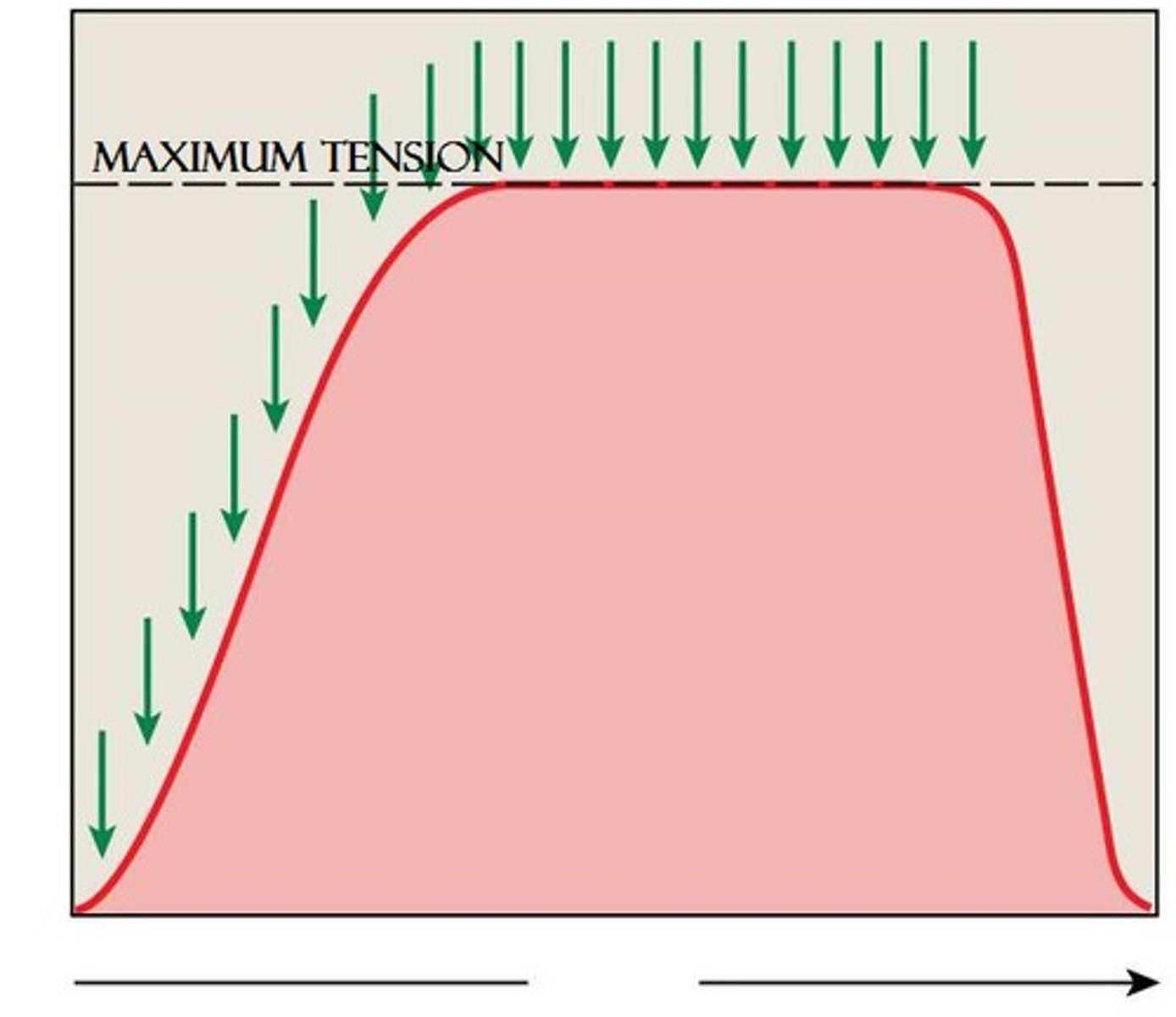
asynchronous motor unit summation
motor units activated on a rotating basis to maintain a sustained contraction
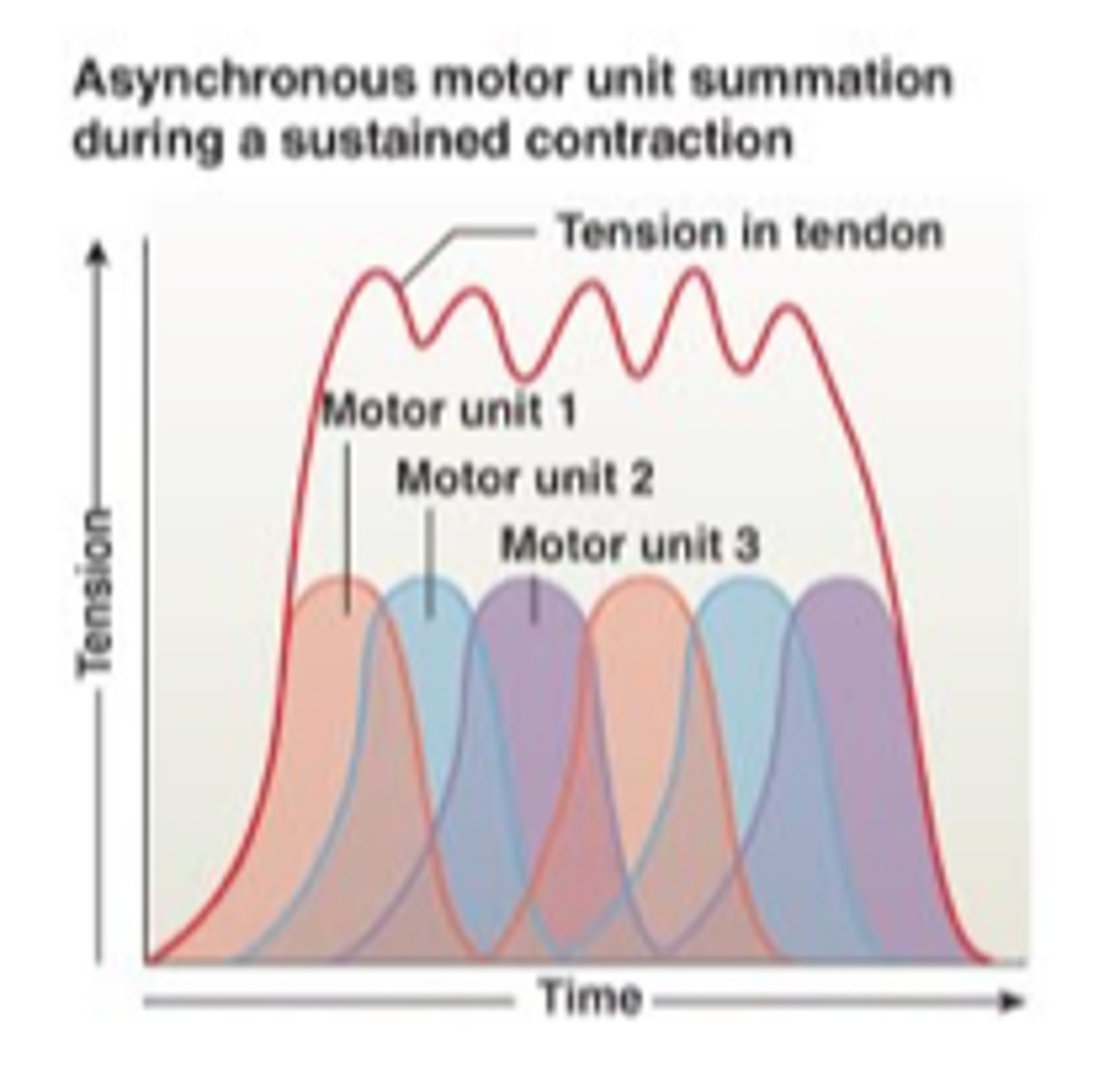
muscle tone
Resting tension in a skeletal muscle
-uses energy
isotonic contraction
muscle shortens because muscle tension exceeds load
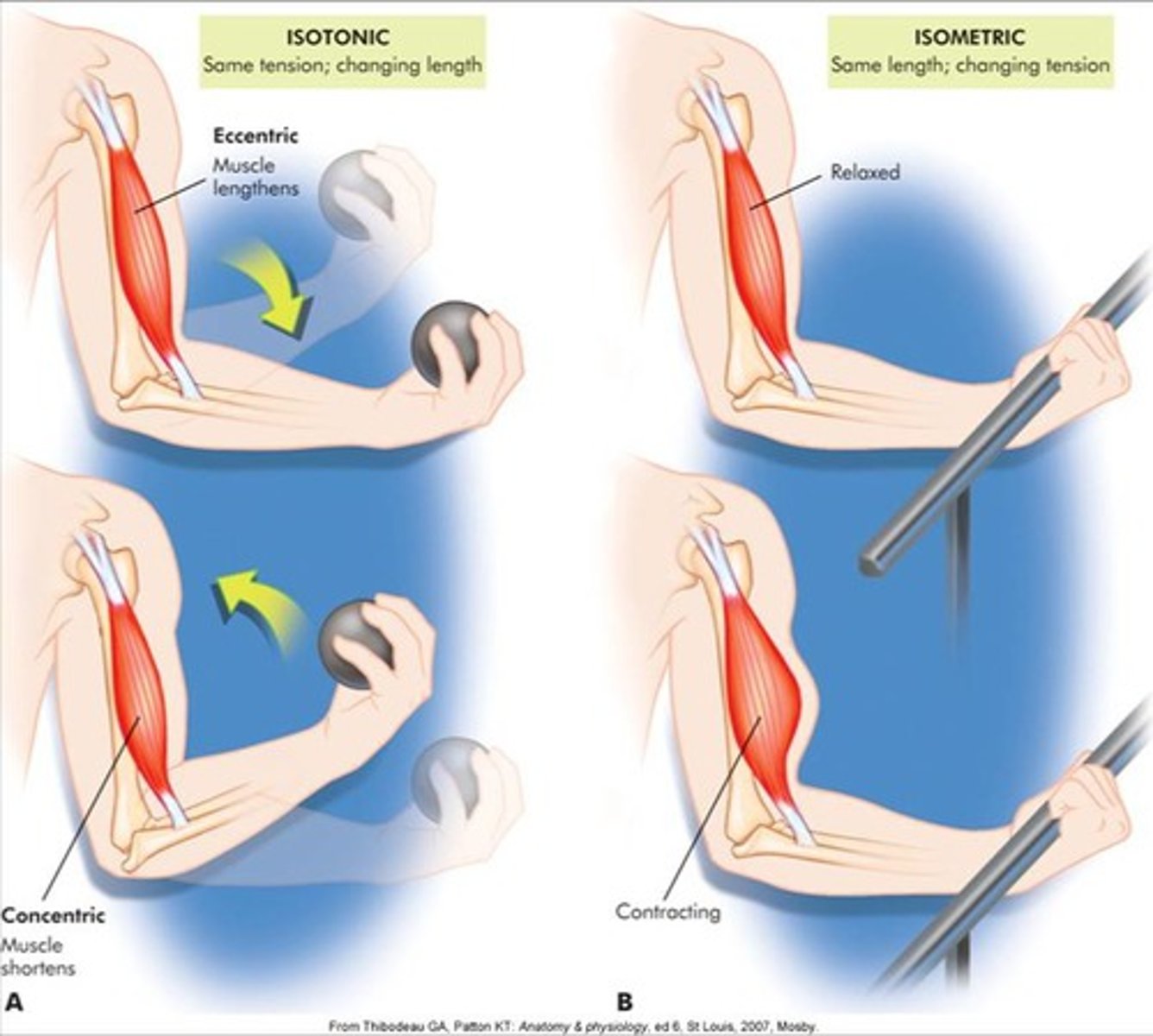
isometric contraction
Muscle contracts but there is no movement, muscle stays the same length
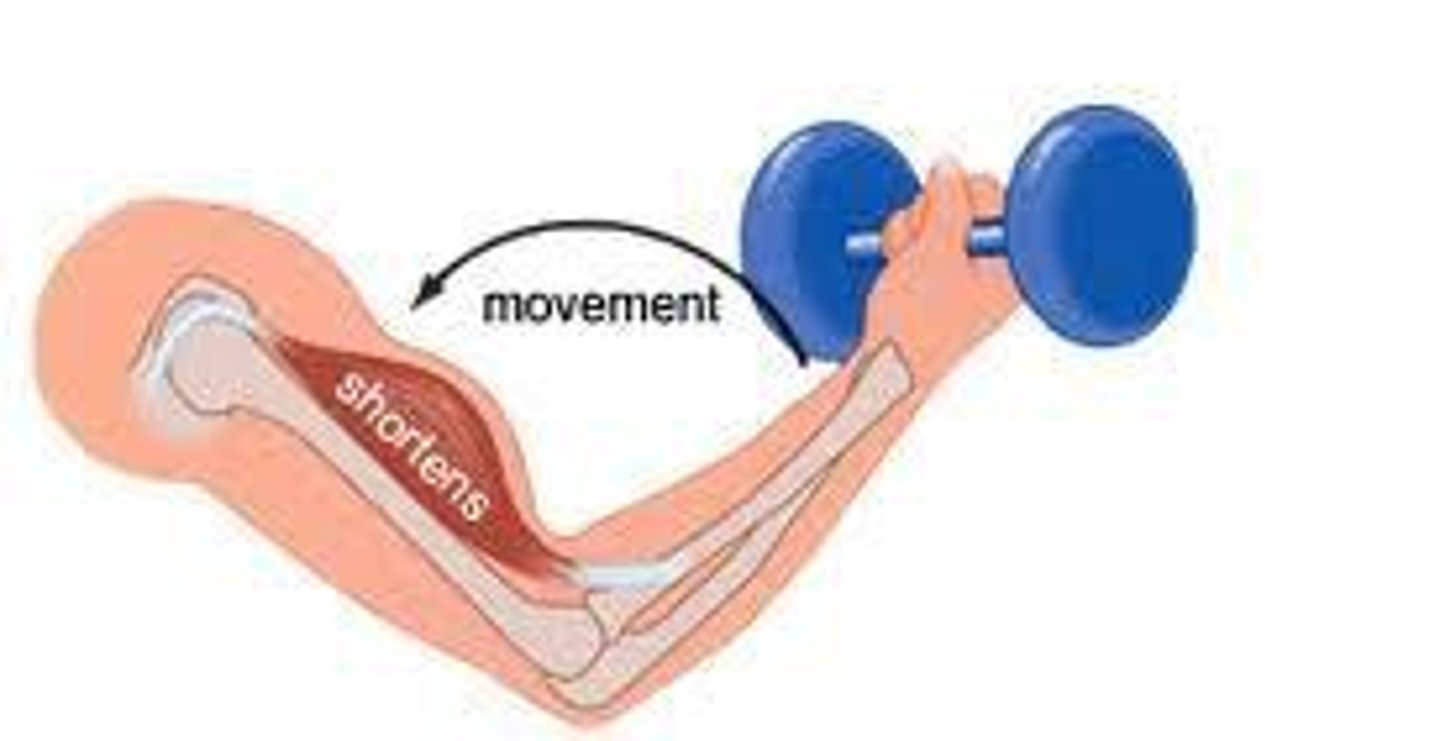
concentric contraction
muscle shortens as it maintains tension
eccentric contraction
muscle lengthens as it maintains tension
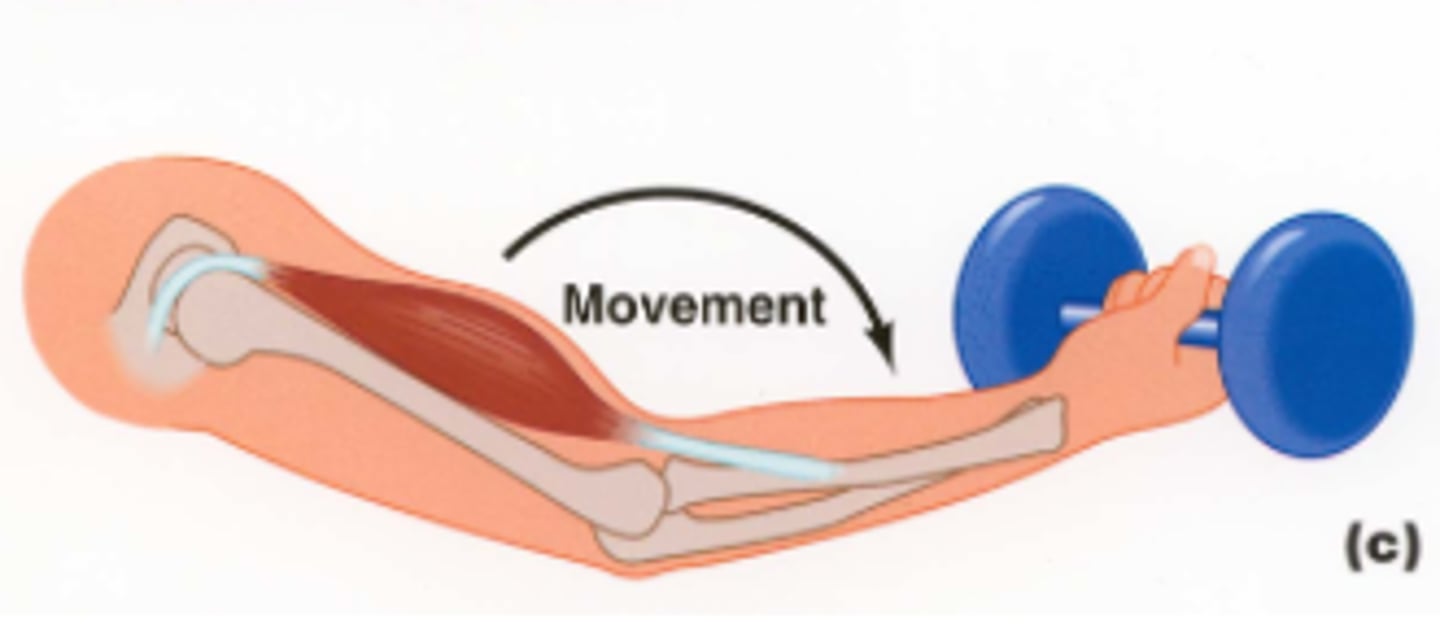
origin
attachment of a muscle that remains relatively fixed during muscular contraction
Insertion
The attachment of a muscle tendon to a moveable bone or the end opposite the origin
action
Specific movement produced by a skeletal muscle
Agonist
muscle whose contraction is mostly responsible for producing the movement
Example: biceps brachii - elbow flexion
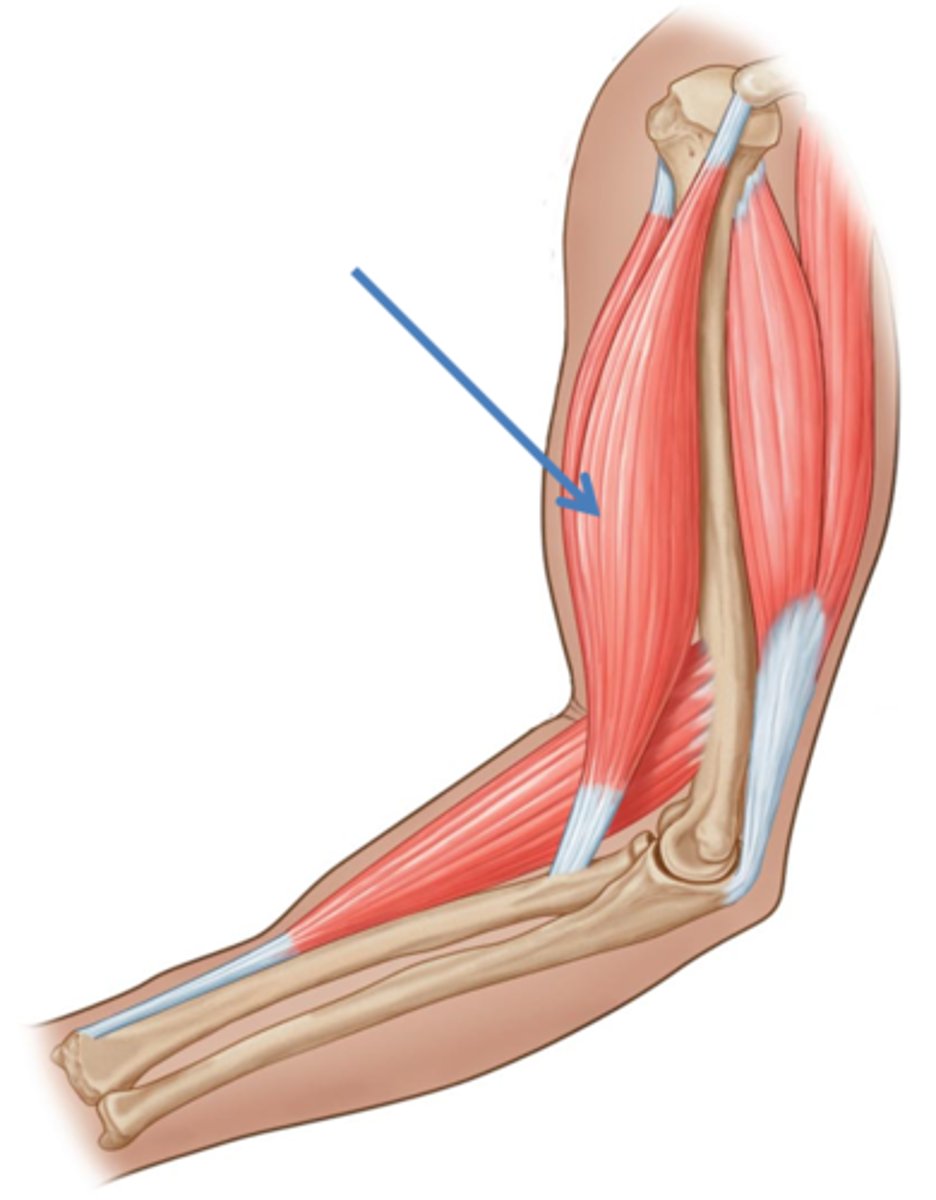
Antagonist
Muscle whose action opposes a particular agonist
Example: triceps brachii for elbow flexion
Antagonist to biceps brachii
Agonist for elbow extension
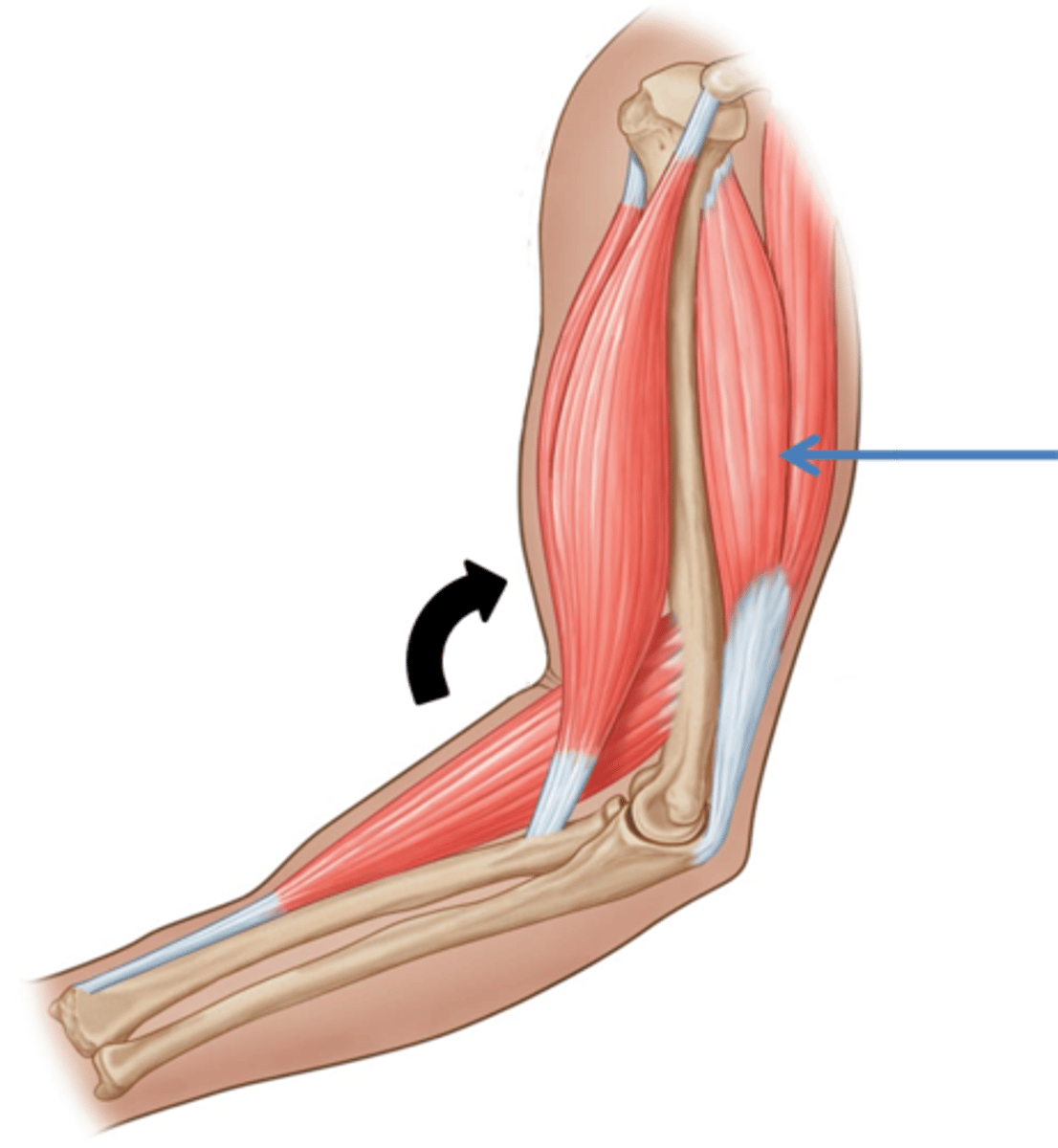
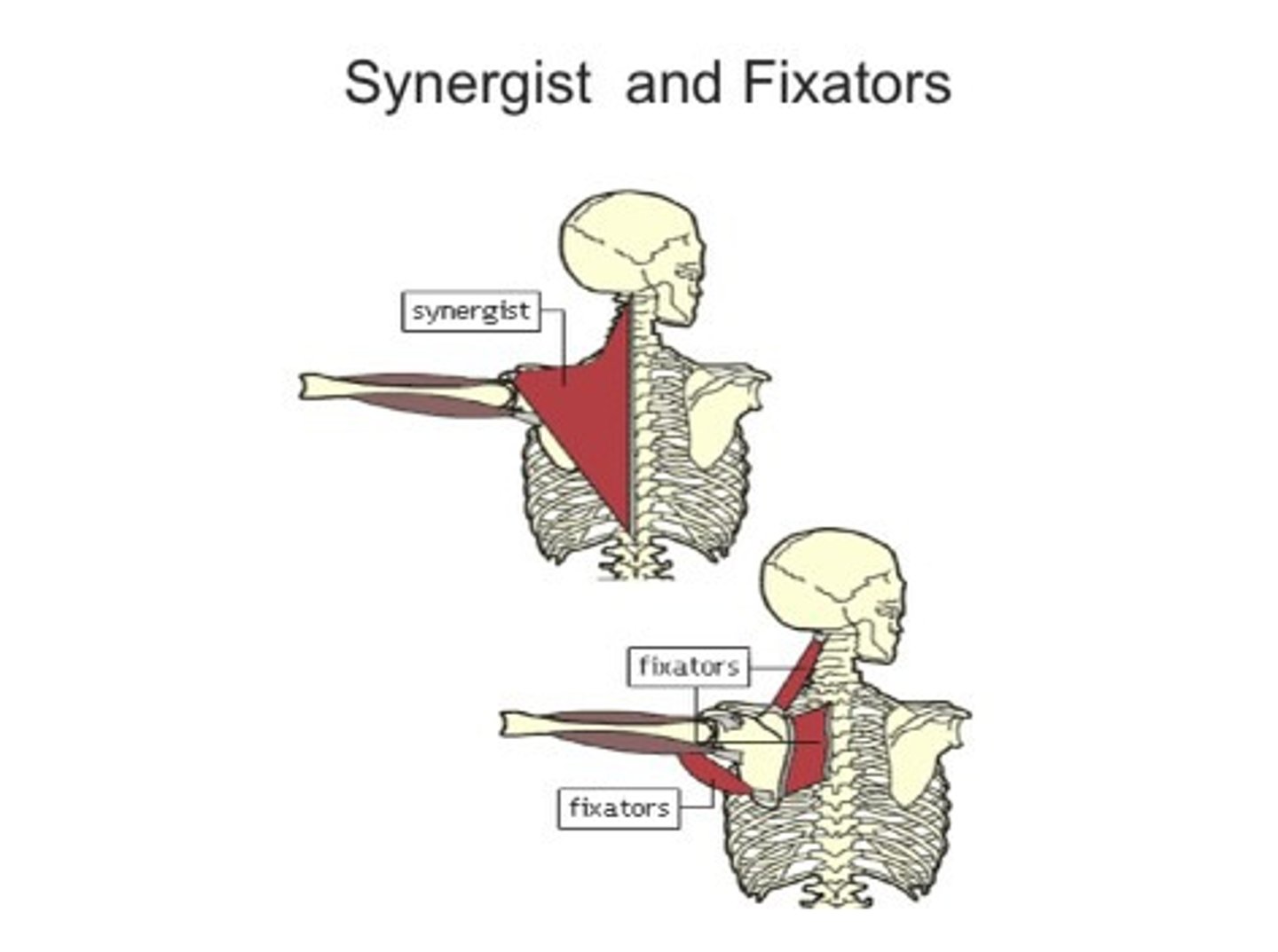
Synergist
Muscle that helps a larger agonist work efficiently
May provide additional pull or stabilize origin
Example: brachioradialis for elbow flexion
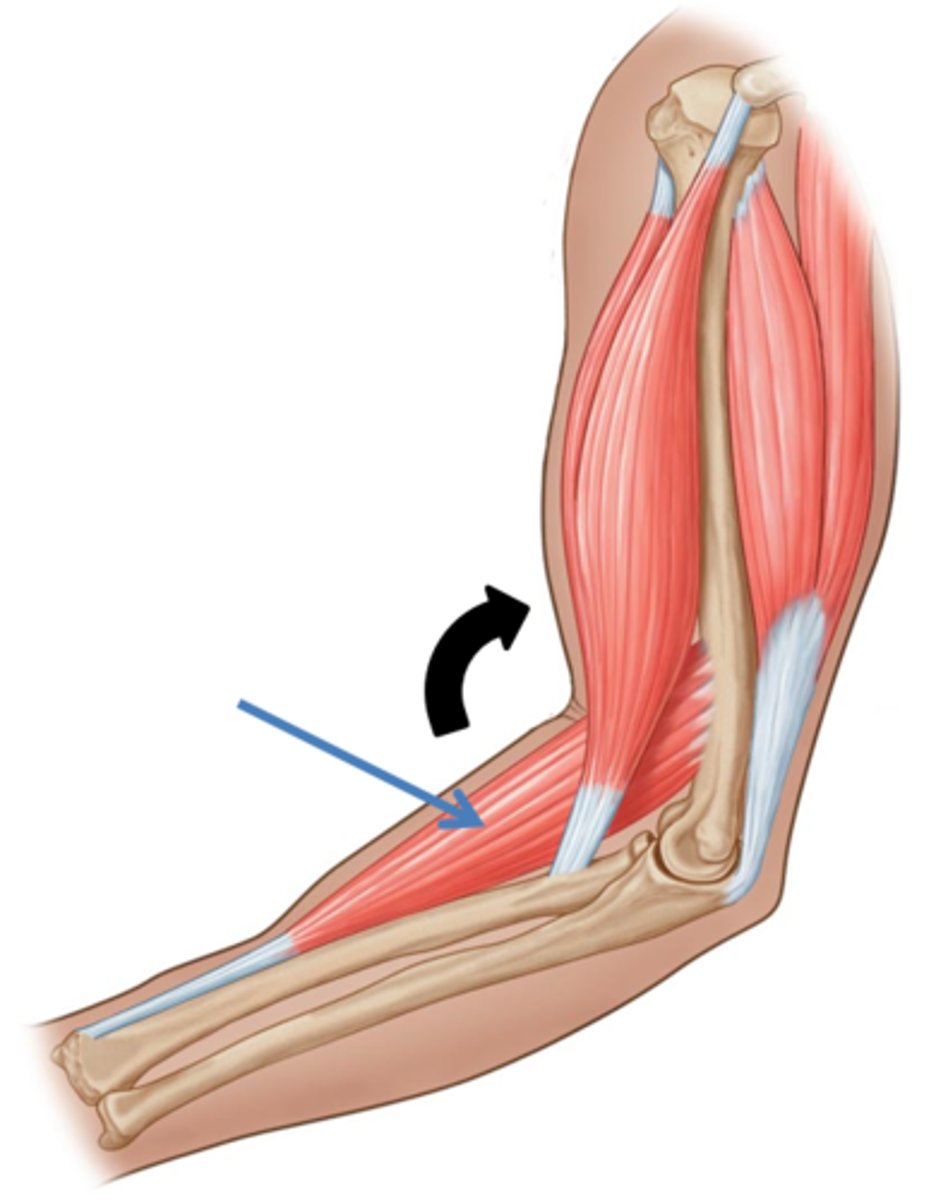
Fixator
Synergists that assist by preventing movement at another joint
creatine phosphate
Reforms ATP (ADP + Pi ATP)
Up to 15s of energy
muscle fatigue
-Muscle can no longer perform at required level
-Decreased pH
-Decreases calcium/troponin binding
-Alters enzyme activities
recovery period
Time needed to return to pre-fatigue conditions
Activity decreases
Oxygen now available
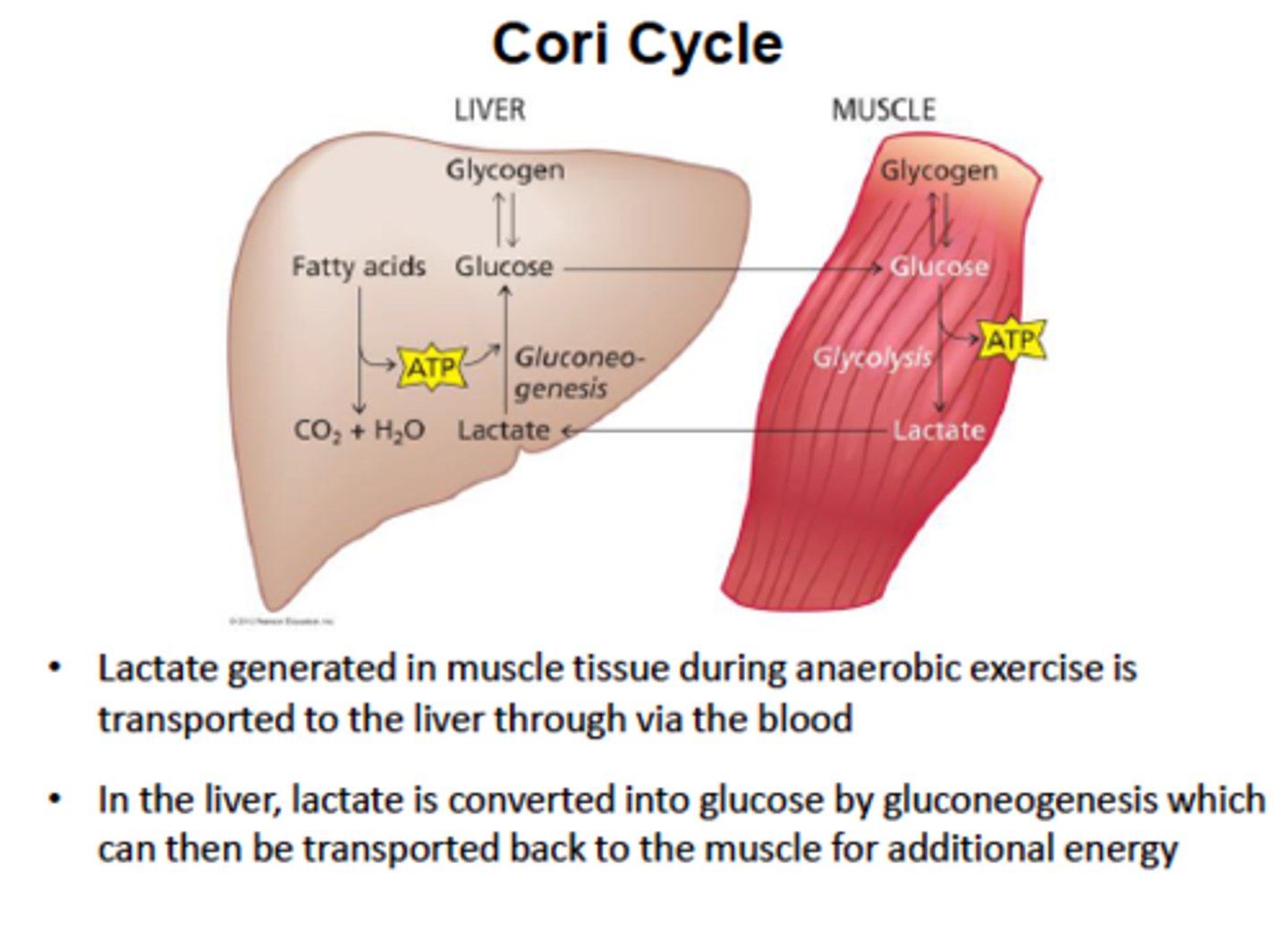
The cell resets the system Lactate converted back to pyruvate Pyruvate makes ATP (aerobic) or recycled to glucose/glycogen
Cori Cycle
Shuttling of lactate to liver, glucose back to muscles
oxygen debt
Amount of oxygen required to restore normal, pre-exertion conditions
In muscles Restore ATP, creatine phosphate, and glycogen levels
In liver Produce ATP to convert excess lactate to glucose
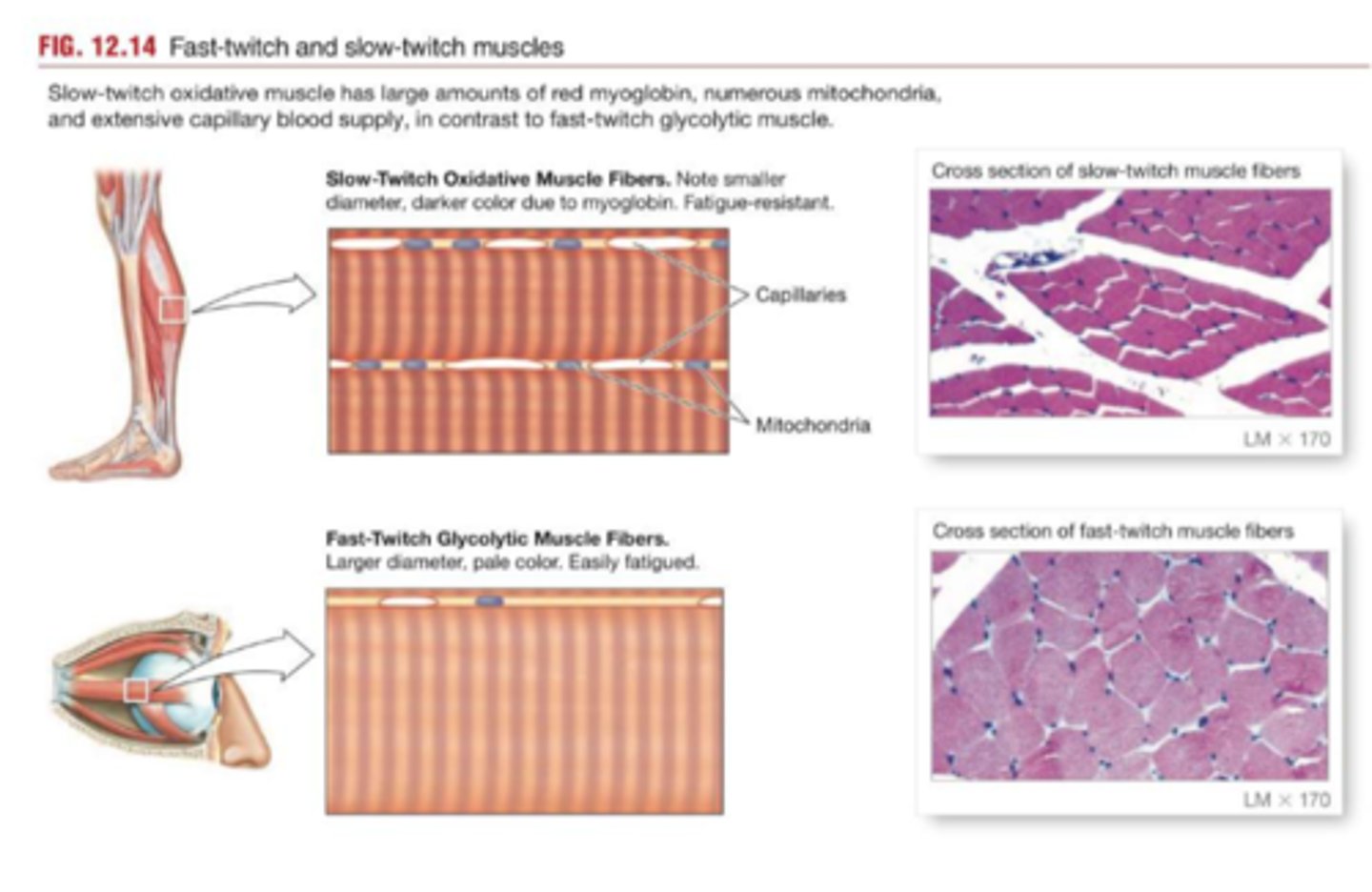
Slow fibers (Type I)
Contractions
-Take 3× longer than fast fibers
-Longer sustained
-Slow to fatigue
Energy
-Mostly aerobic ATP production
-Use more oxygen
-Extensive capillary network
-Myoglobin pigment (binds O2)
Appearance
-Half the diameter of fast fibers
-Appear dark red(myoglobin/blood)
Fast fibers (type IIx)
Contractions
-Reach peak tension in
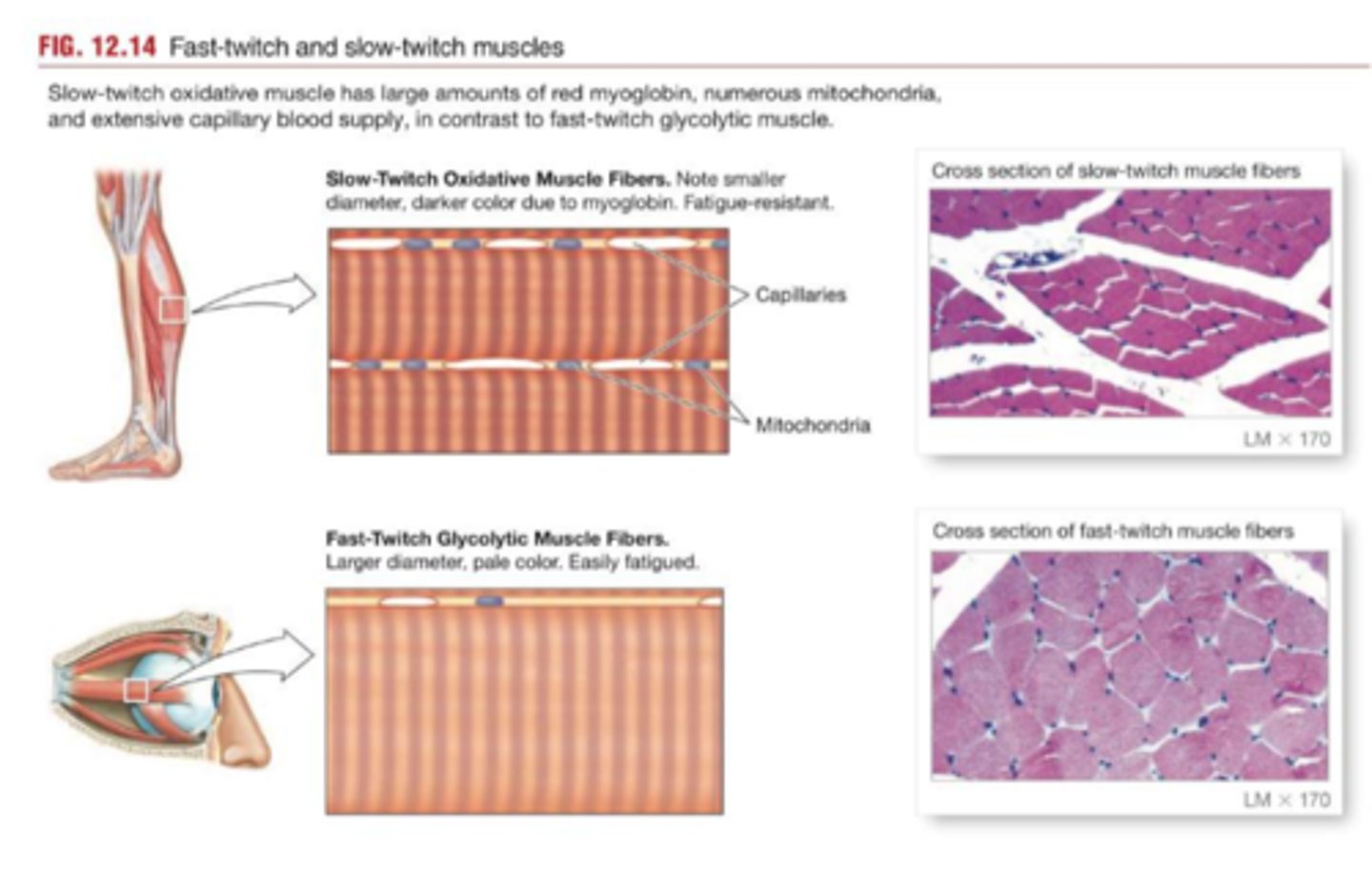
Intermediate fibers (type IIa)
More closely resemble fast fibers (little myoglobin; pale color)
More capillaries and more fatigue-resistant than fast fibers
hypertrophy
increase in muscle size
atrophy
(n.) the wasting away of a body organ or tissue; any progressive decline or failure; (v.) to waste away
An isotonic contraction causes changes in a muscles
length
Muscle tone refers to
the amount of tension present in a resting muscle
Which part of the myofibril is myosin attached to?
M-line
The H-band contains which of the following?
Myosin only
When two Z-lines come closer together, what has occurred?
Concentric isotonic contraction
What change would turn an incomplete tetanus into a complete tetanus?
Increased action potential frequency
Which muscle tissue moves bones?
Skeletal Muscle
Which muscle tissue moves the digestive system, blood vessels, and other internal organs?
Smooth Muscle
A thick myofilament is made of what protein structure?
Actin
______ tension is produced when fewer motor units are recruited in a contraction
less
During a muscle shortening, the Z-line
does not change size
Which region of a myofibril contains myosin and actin?
A-band
During a muscle lengthening, which regions of a myofibril become shorter?
Zone of overlap only
Which muscle tissue has striations?
Skeletal and cardiac muscle
An isometric contraction causes changes in a muscles _______
tone
Unequal distribution of ______ create a membrane potential
ions
What is a muscles insertion?
The muscle connection that moves when the musce is activated
What is a muscle's origin?
The muscle connection that does not move when the muscle is activated
During a muscle shortening which regions of a myofibril become shorter?
H- and I- bands
During a specific body movement, a muscle that functions to limit other secondary movement is called the_______
fixator
What type of activity would anaerobic metabolism be a good use for?
A one-minute sprint