FSHN 2650 - Bioenergetics
1/102
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Bioenergetics, Metabolism, Catabolism, Metabolic Pathways
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
Where does glycolysis take place?
Cytosol
Function of mitochondria?
Generates most of cells energy from carbs, proteins, and fats
Hormones regulate ____&____ reactions
Catabolic, anabolic
Energy is stored in ____ of molecules making up protein, carbs, and fats
Bonds
Fast, with oxygen reactions
Aerobic
Slow, without oxygen reactions
Anaerobic
Products of betaoxidation
NADH(+) + H(+) & FADH
What is the biochemical reason ketogenesis occurs during carbohydrate deficiency?
The TCA cycle has too much NADH + H(+) being produced
The build up of ___ in the ____ promotes the synthesis of fatty acids.
Citrate, TCA cycle
What cannot use ketone bodies for ATP production?
Red blood cells
What dictates the fate of pyruvate following glycolysis?
The presence of oxygen
What’s essential for fatty acid oxidation to occur?
CoA
What’s essential for the quick synthesis of ATP in a working muscle?
Creatine phosphate, ADP, glycolysis
What would classify as a catabolic process?
Beta-oxidation
What cannot be converted into glucose by the liver?
Fatty acids
What dicates whether someone is in a state of acute starvation?
Lack of glycogen
What hormone is involved in the absorptive state?
Insulin
What hormone is involved in the post-absorptive state?
Glucagon & epinephrine
Glucokinase can ___
Churn out products faster in the liver
Involved in the fasted state, low insulin, activated by glucagon
Hormone sensitive lipase
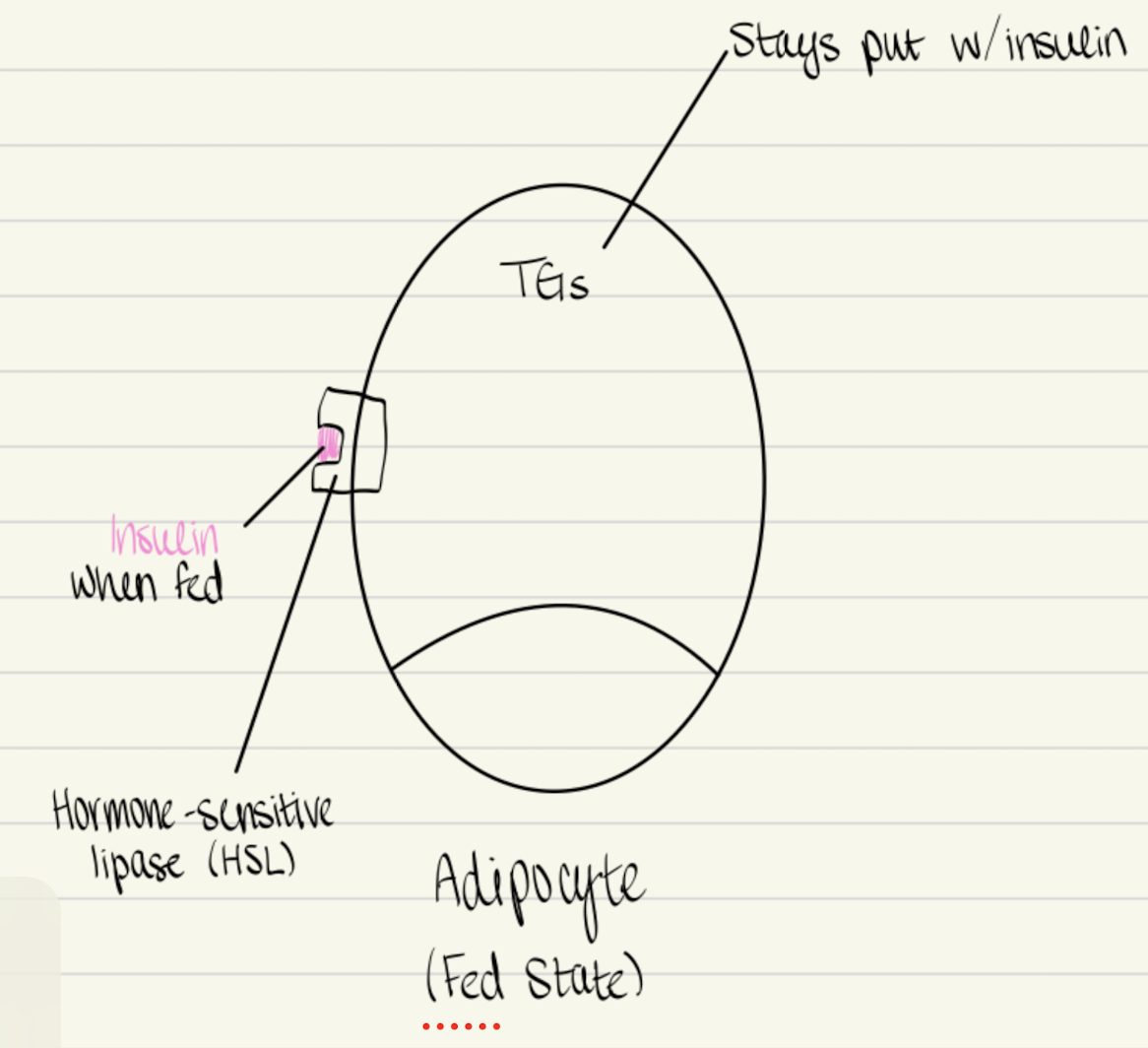
Involved in the fed state, activated by insulin
Lipoprotein lipase
What is the fuel ratio percentage of (glucose:ketone bodies) during a carb deficiency?
70:30
What compound is released when muscle protein transfers to amino acids?
NH3
Glucagon stimulates liver _____.
Glycogen
Glycogen releases ____
glucose
Where does ketogenesis take place?
liver
What 3 hormones are active during the acute starvation state?
Glucagon, epinephrine, cortisol
Carbs broken down into glucose, then a (+) ____ breaks it down to glycogen
insulin
Glucose is stored in ____ & ____
fat cells, liver
The liver prioritizes making ____.
Glycogen
How many hours does acute starvation occur?
24 hours after last meal
How many hours does the post-absorptive state occur?
4 hours
T/F: The absorptive state is when there is the MOST fuel in the blood
True
What are the products of glycolysis?
2 ATP
2 Pyruvate
2 Coenzymes
Insulin bonds to the ____ on a triglyceride when fed.
hormone-sensitive lipase
What is ATP?
Cell’s direct energy source
What is energy metabolism?
Sum of all chemical reactions
Glucose —> ____
glycogen
Amino acids —> ____
proteins
Fatty acids & glycerol —> ____
Triglycerides
In what way does a metabolic pathway relate to energy metabolism?
Metabolic pathways are chemical reactions where energy is stored or released
Cofactor:
Inorganic; tightly bound to enzyme
Coenzyme:
organic; loosely bound to the enzyme
Roles of coenzymes and cofactors:
Assist in catalyzing reactions with their non-protein components
What happens when there is EXCESS ATP present?
Acetyl CoA is turned into fatty acid and stored as fat
What happens when there is LOW ATP present?
Acetyl CoA enters the TCA cycle
The 3 main portions of the molecule ATP are: ___, ___, & ___
adenine, phosphates, & ribose
1 ___ is hydrolyzed to produce energy from ATP
phosphate
The body regenerates ATP by ___ & ___
ADP, creatine phosphate
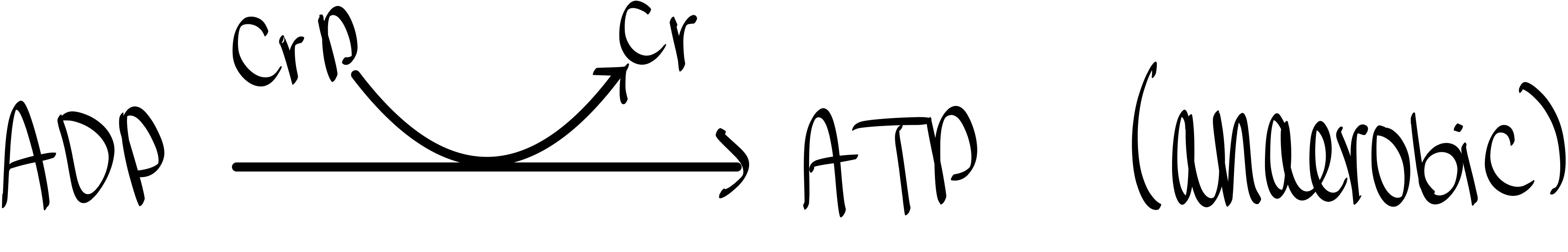
The hormonal signal for anabolic storage of energy is ___
Insulin
The signals for the catabolism (mobilization) of energy are ___, ___, & ___
Glucagon, epinephrine, & cortisol
Fate of Pyruvate: Aerobic
Acetyl CoA
Fate of Pyruvate: Anaerobic
Lactate
Where does the Cori cycle occur?
Liver
The Cori cycle: ___ —→ blood —→ ___ —→ ___ —→ blood
Lactate, pyruvate, glucose
The TCA cycle occurs in the _____ matrix.
mitochondrial
Pyruvate must convert to ___ to enter the TCA cycle
Acetyl CoA
Where does oxidative phosphorylation (ETC) occur?
Mitochondria
What are the final products of the ETC?
H2O, ATP, NAD+, FAD
How would creatine supplementation aid in the regeneration of ATP from ADP?
CrP releases a P and that’s added to ADP to form ATP.
What is the molecular focal point in lipid metabolism?
Glycerol undergoing beta-oxidation
Where does beta oxidation occur?
Mitochondrial matrix
What are the hormonal signals for lipolysis?
Lipase
Lipid Metabolism (Stage 1): Process & Product
Lipolysis
Fatty Acids
Lipid Metabolism (Stage 2): Process & Product
Beta-Oxidation
Acetyl CoA
Lipid Metabolism (Stage 3): Process & Product
TCA cycle
CO2
Lipid Metabolism (Stage 4): Process & Product
Oxidative Phosphorylation (ETC)
ATP
Lipid Metabolism
Carnitine’s role in Beta-oxidation:
transfers long-chain fatty acids to the mitochondria for B-oxidation
Practice Problem
You slam a Monster Energy drink with 2500 mg proprietary energy blend with L-carnitine for fat burning, are you burning more fat as you sit down studying?
No
Transamination
transfer of an amino group
Deamination
complete removal of an amine group
Protein Metabolism (Stage 1): Proteolysis
Proteins —→ amino acids
Protein Metabolism (Stage 2): Transamination/Deamination
NH3 & keto acids
Protein Metabolism (Stage 3): TCA cycle
NADH & FADH2
Protein Metabolism (Stage 4): Process & Product
Oxidative phosphorylation (ETC)
ATP
How’s protein metabolism different than lipid and carbohydrate in relation to entry into the TCA cycle?
Proteins —→ amino acid —→ TCA cycle
OR —→ deaminated —→ glycolysis —→ acetyl CoA
Gluconeogenesis:
generation of glucose from non-carb C substrates
(e.g.) lactate, glycerol, and glucogenic aa
Where does gluconeogenesis occur?
liver
What hormone stimulates gluconeogenesis?
cortisol
Glycogenesis:
formation of glycogen from glucose
The hormonal signal for glycogenesis is ___
insulin
The important branch point for shuttling glucose to form glycogen is ___ & ___ cells
liver, muscle
Lipogenesis:
converting glucose to fat for storage
Lipogenesis is stimulated by increased ___ & ___
carbs, insulin
Where are new triglycerides stored?
adipose tissue
Ketogenesis:
formation of ketone bodies from excess acetyl CoA
Why is ketogenesis important?
creates ketone bodies
High levels of ketogenesis lead to ________
drop in pH and ketoacidosis
Processes that occur in the absorptive state
Lipogenesis
Glycogenesis
Protein synthesis
Processes that occur in the post-absorptive state
Glycogenolysis
Lipolysis
Processes that occur in acute starvation
Gluconeogenesis
Ketogenesis
Catabolism
release of energy
In the mitochondria, the metabolic pathways used for catabolizing fatty acids are ___ and the ___ ___ which create ___ + ___ and ___ for the creatione of ATP during oxidative phosphorylation.
B-oxidation, TCA cycle, NADH + H+ and FADH2
What is the objective of the Cori cycle?
recycle lactate
B-oxidation process:
Add a CoA to the Carbon chain producing NADH + H+ & FADH
Protein —→ Amino Acid —→ Keto Acid
Why is the N removed during: Amino Acid —→ Keto Acid?
So it can be used for energy
Glucose Catabolism: Stage 1 — Glycogenolysis
Glucose —(2 hormones)—→ G-6-P
hexokinase & glucokinase
Glucose Catabolism: Stage 1 —Glycolysis
G-6-P —(hormone)—→ F-6-P
Phospho hexose isomerase
Glucose Catabolism
F-6-P —(hormone)—→ F-1,6-P
PFK1
Glucose Catabolism
During the transition of F-6-P to F-1,6-P — F,2,6-BP is made by ___ from an increase in ___.
PFK2, insulin