Diagram of Rivers GCSE AQA GEOGRAPHY | Quizlet
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
Abrasion
rocks carried along by the river scratch away the river bed and banks.
Attrition
erosion caused when rocks transported by waves bang into each other and break up into smaller and rounder pieces.
(Channel) straightening
removing meanders from a river to make the river straighter.
Cross profile
the side-to-side cross-section of a river channel and/or valley.
Dams and reservoirs
a barrier (made of earth, concrete or stone) built across a valley to interrupt river flow. they store water and generate hydroelectric power , but are very expensive
Discharge
the quantity of water that passes a given point on a stream or river-bank within a given period of time.
Embankments
Raised banks constructed along the river. Hence the river can hold more water, protecting the buildings on a flood plain.
Estuary
the tidal mouth of a river where it meets the sea.
Flood
occurs when river discharge exceeds river channel capacity.
Flood plain
the relatively flat area forming the valley floor on either side of a river channel.
Flood relief channels
building new artificial channels, which are used when a river is close to maximum discharge.
Flood risk
the predicted frequency of floods in an area.
Flood warning
providing reliable advance information about possible flooding. Damage to possessions is less.
Fluvial processes
processes relating to erosion, transport and deposition by a river.
Gorge
a narrow, steep sided valley, often formed as a waterfall retreats upstream.
Greenfield site
a plot of land, often in a rural or on the edge of an urban area, which has not yet been subject to any building development.
Hydraulic action
the force of the river against the banks can cause air to be trapped in cracks and crevices.
Hydrograph
a graph that shows the discharge of a river, related to rainfall, over a period of time.
Interlocking spurs
A series of ridges projecting out on alternate sides of a valley and around which a river winds its course.
Lateral erosion
It widens the valley and the channel , it is dominant in the middle and lower course of the river.
Levée
Where natural embankments form during floods on the side of the river. (becasue the flow of water is slower)
Long profile
the gradient of a river, from its source to its mouth.
Meander
a pronounced bend in a river.
Ox-bow lake
an arc-shaped lake which has been cut off from a meandering river.
Saltation
particles bouncing along the river bed.
Solution
soluble particles are dissolved into the river.
Suspension
fine solid material held in the water while the water is moving.
Traction
the rolling of boulders and pebbles along the river bed.
Transportation
the movement of eroded material.
Urban sprawl
the unplanned growth of urban areas into the surrounding countryside.
Vertical erosion
Downward erosion of a river bed. It is prominent in the upper course of the river because high turbulence causes particles to be scraped along the river bed.
Waterfall
sudden descent of a river or stream over a vertical or very steep slope in its bed.
Precipitation
any source of moisture reaching the ground e.g. rainfall, snow, hail etc...
Interception
water being prevented from reaching the surface by trees or grass.
Surface storage
water held on the ground surface e.g. puddles, lakes.
Infiltration
water seeping into the soil layer from the ground surface above
Soil moisture storage
water held in the soil layer
Percolation
water seeping into the permeable rock layer
Groundwater
water stored in the rock
Groundwater flow
water flowing through the rock layer parallel to the surface
Throughflow
water flowing through the soil layer parallel to the surface
Surface run-off
water flowing over the surface of the land
Evaporation
water lost from ground/vegetation surface
Transpiration
water lost through pores (stomata) in leaves
Channel flow
water lost via flowing in the river channel
Evapotranspiration
the total of all the water lost from drainage basin back up into the atmosphere
Upper course (gradient)
Steep
Middle course (gradient)
Medium
Lower course (gradient)
Gentle
Upper course (valley shape)
V-shaped valley, steep sides narrow, shallow channel
Middle course (valley shape)
Gently sloping valley sides, wider deeper channel
Lower course (valley shape)
Very wide, almost flat valley very wide, deep channel
Waterfalls are formed when...
...waterfalls flow over an area of hard rock and then soft rock
-form a step (the soft rock is eroded by hydraulic action and abrasion more than by the hard rock)
-hard rock is undercut by erosion. It becomes unsupported and collapses.
- The collapsed rocks are swirled around at the foot of the waterfall where they erode the softer rock by abrasion, this creates a deep plunge pool.
- Over time more undercutting will cause more collapses, the waterfall will retreat leaving a steep-sided gorge.
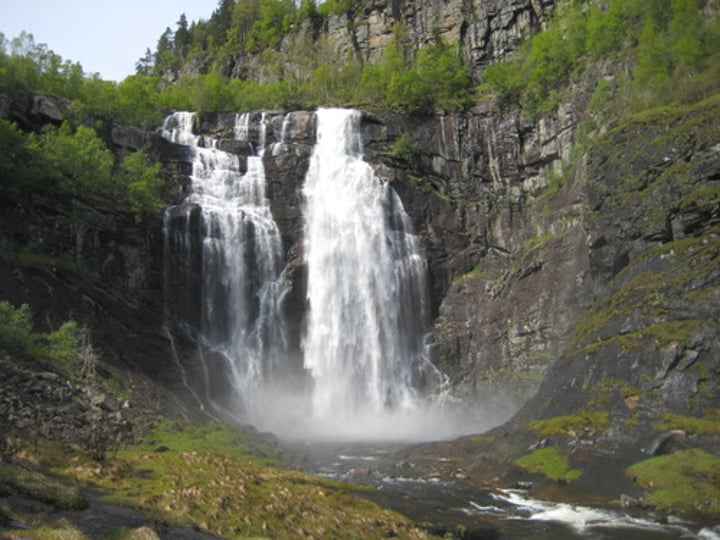

Waterfalls are found in...
... the upper course of the river
Gorges are formed when...
... the waterfall keeps retreating and undercutting to form ___________
Landforms in the upper course...
...Waterfalls, gorges and interlocking spurs (Erosion)
Interlocking spurs...
...Upper course of the river has steep sides because the rivers don't have enough energy to erode laterally
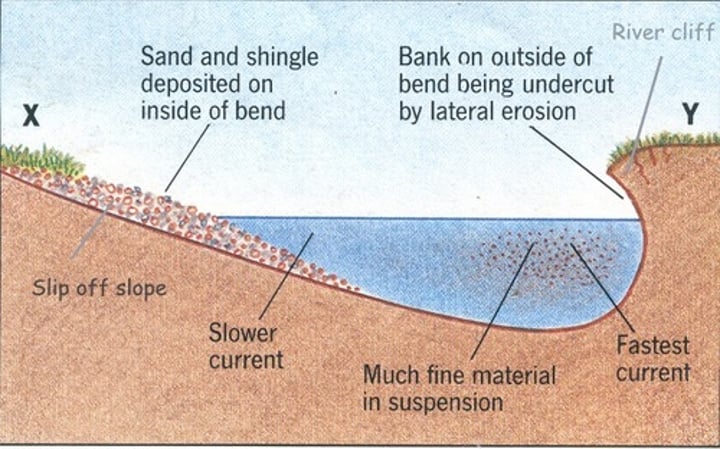
The flow of water is the fastest on the...
...outside bend on the river because the river channel is deeper, so there is less friction to slow the water down.
More erosion takes place on the outside bend causes...
River cliffs to form
When the river is shallower...
...the water flows slower because there is more friction with the river bed
Ox bow lakes form when...
...Erosion causes the outside of the 2 bends to get closer
-During a flood the river breaks through and then takes the shortest route
-forms a ox bow lake where the river used to be
- water flow is slow so sand is deposited to cut meander off
River land forms found in the middle course...
...Meanders and ox bow lakes (erosion and deposition)
Most erosion in a river happens by
abrasion and hydraulic action
Flood plains are...
...the wide valley floor either side of the river
Flood plains are formed when...
...when the river floods the flow of water slows down and the river deposits all of the sediment which it is carrying
-Meanders can also migrate across the floodplain making it wider
-deposition on the side of slip off slopes also builds up the flood plain
slip off slopes
eroded material is deposited on the inside bend
Estuary's are...
...the widest point of the river before the sea the water here is tidal
Estuary's are formed when...
...Since the estuaries are tidal, it means that the water level rises and falls each day, the water floods over the banks and slows down so it deposits its silt and sand.
-overtime more and more builds up creating large areas of mudflats
-at low tide the muddy banks are exposed
Flood warnings
The environment agency warns people about potential flooding via the radio, TV or the internet Buildings are modified to reduce flood damage; people make plans before the flood. Warnings don't stop a flood, people may not have access to warning or not even hear them
Preparation
The impact of flooding is reduced as people make plans for what they do in a flood - keep items like torches and blankets in a handy place.
Flood plain zoning
Planning restrictions prevent building on parts of the flood plain that are likely to flood The risk of flooding is reduced, impermeable surface are not created, the impact of flooding is reduced if there are fewer buildings on the floodplain It can limit expansion in a time me when there is pressure for more homes to be built, It is no help to areas where there are already buildings on the flood plain
Planting trees
Planting trees increases interception through the roots and leaves and slows down the lag time Discharge and flood risk are reduced, vegetation reduces soil erosion, trees provide a habitat for wildlife. Less land available for farming
River restoration
Removing man-made levees - making the river look more natural - upstream means that there is a lower risk of flooding downstream because discharge is reduced. Little or no cost involved as the river is in its natural state. Better habitats for wildlife. This involves removing man-made levees to allow the flood plain to flood naturally.
Dams and reservoirs
Dams are built across the upper course of a river a reservoir (artificial lake) s formed behind the dam. Reservoirs store water which reduces the risk of flooding downstream during periods of heavy or prolonged rainfall, water in the reservoir can be used for drinking water for nearby settlements, the dam can generate electricity through hydroelectric power Local flood risks can increase if there is no intervention in risky areas. If water rises above them, they can be breached and there will be severe and sudden flooding
Channel straightening
The rives course is straightened meanders are cut out by building artificial straight channels Water moves out of the area more quickly because it does not travel as far. This reduces the risk of flooding in that area. Flooding may happen downstream instead as water is carried there faster.
Flood relief cannels
Flooding is prevented because river discharge is reduced, gates on the flood relief channel will mean the release of water can be controlled Channels are built to divert water around the important areas when the water level in the river gets to high There will be increased discharge where the relief channel re-joins the river further down stream or where it meats and other river which could caused flooding in other areas if the water level gets too high the flood channel could also flood
Levees are formed when...
...during a flood eroded material is deposited over the whole flood plain
-The heaviest material is dropped first because that gets dropped first when the river slows down
-Over time the deposited material builds up.
Interlocking spurs are formed when...
The rivers are not powerful enough to erode laterally so most of the erosion happens vertically, this creates steep-sided v-shaped valleys.
The river does not have enough power to erode laterally around the hill sides so just erodes around them
social issues
issues related to culture, work, lifestyle
economic issues
Issues related to money, taxes, and production of goods and services.
Environmental issues
How the environment is effected.
deposition
when a river drops the material that it is carrying, this happens when it slows down.
Why do rivers slow down and deposit materials?
- the volume of water in the river falls
- the amount of eroded material in the water increases
- the water is shallower, e.g. on the inside of a bend
- the river reaches its mouth
meanders are formed when
the currant is faster on the outside of the bend because that is where the river is deeper. So more erosion takes place on the outside of the bend, forming river cliffs. Since the currant is slower on the inside of the bend it means that more deposition happens here, this forms slip off slopes.
the currant is faster on the outside bend because...
it is deeper so there is less friction
the currant is slower on the outside bend because...
it is shallower so there is more friction
cross section of a meander
river clyde
the rivers estuary is about 34km west of Glasgow and is 3 miles wide. It comes from the southern uplands region of Scotland. Glasgow is built on a floodplain of the river Clyde. There are 4 waterfalls and a gorges in the highlands near Lanark.
Flood plain (river cyde)
Glasgow is built on the flood plain of the River Clyde The land is about 5m above sea level on either side of the river.
upper course (river Clyde)
there's a gorge, formed by the waterfalls retreating, there are steep cliffs along the banks of the river. There are 4 waterfalls in total. There are interlocking spurs in Crawford.
Middle course (river clyde)
there is an ox bow lake forming, there are meanders between Motherwell and Glasgow
peak discharge
the highest discharge in the period that you are looking at
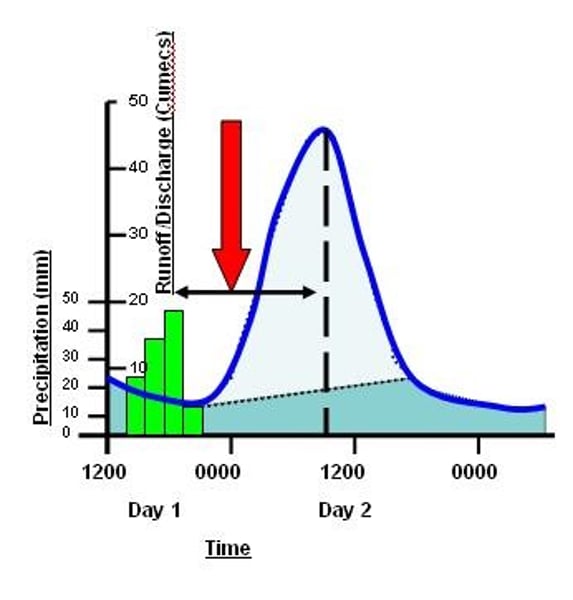
Lag time
the delay between the peak rainfall and peak discharge
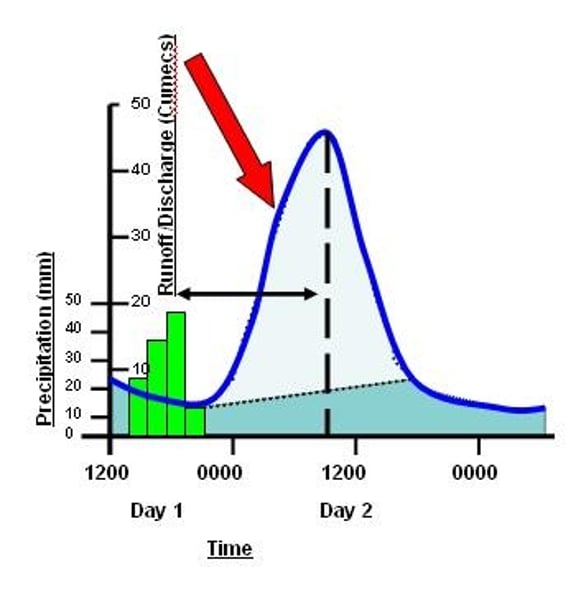
Rising limb
The increase in river discharge as rainwater flows into the river
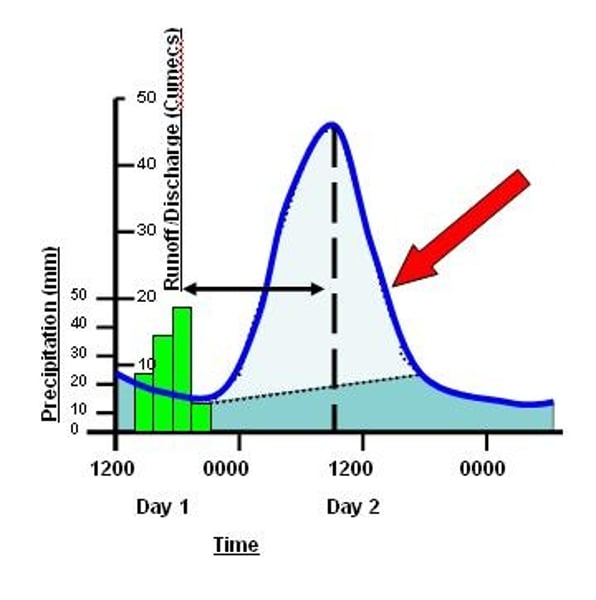
Falling limb
The decrease in river discharge as the river returns to its normal level
Prolonged rainfall
After a long period of time the soil becomes saturated. Any further rainfall can't infiltrate, which increases runoff into rivers. This increases discharge quickly, so flooding is more likely.
Lag time happens because
most of the rainwater doesn't land directly in the channel, it gets there by flowing quickly overland (surface runoff), or by soaking into the ground (infiltration) or flowing slowly underground (groundwater flow).
Heavy rainfall
means that the water arrives too quickly for infiltration, this means that there is a lot of surface runoff, so water gets to the rivers too quickly.
Geology
clay soils and some rocks e.g. granite and shale, are impermeable so runoff is increased. When it rains, discharge increases quickly, which can cause a flood.
relief
If a river is in a steep-sided valley, water will reach the river channel much faster because water flows more quickly on steep slopes. Discharge increases rapidly, increases the risk of a flood.