Clemson University: Microbiology 3050 Prof Rudolph: Unit 1 ( WHAT ARE MICROBES?)
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/134
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
135 Terms
1
New cards
Microorganisms
oldest form of life; most populous and diverse group of organisms; found everywhere on the planet
2
New cards
Underground
Where are most microorganisms found?
3
New cards
Microbiology
The study of the dominant form of life on earth and the effect that microbes have on our planet and all of the living things that call it home
4
New cards
Microorganisms
Living things made of cells that have defined structures and unique evolutionary histories important to the biosphere
5
New cards
Microrganisms
organisms and acellular entities too small to be clearly seen by the unaided eye (there are exceptions)
6
New cards
1 mm
microorganisms are usually less than \_________ in diameter
7
New cards
Microbial culture
a collection of cells that have been grown in or on a nutrient medium
8
New cards
Medium
a liquid/solid nutrient mixture that contains nutrients required for growth
9
New cards
Fungi, Protists, Bacteria, Archaea
What are the 4 cellular organisms studied by microbiologists?
10
New cards
No highly differentiated tissue
What classifies microbes as microbes?
11
New cards
Viruses, Viroids, Satellites, Prions
What are the 4 acellular organisms studied by microbiologists?
12
New cards
Prion
an acellular biological entity composed of protein
13
New cards
Satellite
an acellular biological entity composed of nucleic acid (often RNA); can cause animal disease
14
New cards
Viroid
an acellular biological entity composed of RNA
15
New cards
Virus
an acellular biological entity composed of protein and nucleic acid
16
New cards
Prokariotic
cells that lack a true membrane bound nucleus (however, not absolute)
17
New cards
Eukariotic
cells that have a membrane enclosed nucleus and other membrane bound organelles
18
New cards
Eukariotic
cells that are more complex morphologically and larger than other types of cells
19
New cards
All cells
cells that have a permeable barrier (cytoplasmic membrane) that separates the inside of the cell from the outside; Has cytoplasm, ribosomes, and DNA genome
20
New cards
Bacteria and Archaea
What groups are known as prokaryotic cells?
21
New cards
Less
prokaryotic cells are \_______ complex than eukaryotic cells
22
New cards
Prokaryotic
what kind of cell?
-cells wall (some)
-cytoplasmic membrane
-nucleoid
-cytoplasm
-plasmid
-ribosomes
-cells wall (some)
-cytoplasmic membrane
-nucleoid
-cytoplasm
-plasmid
-ribosomes
23
New cards
Eukaryotic
what kind of cell?
-cell wall
-cytoplasmic membrane
-mitochondrion
-nuclear membrane
-nucleus
-ribosomes
-endoplasmic reticulum
-cytoplasm
-golgi
-cell wall
-cytoplasmic membrane
-mitochondrion
-nuclear membrane
-nucleus
-ribosomes
-endoplasmic reticulum
-cytoplasm
-golgi
24
New cards
plants, animals, algae, protists, fungi
Name categories in which the species have eukaryotic cells
25
New cards
Eukarya
what is archaea most similar to?
26
New cards
All cells
-structure
-metabolism
-growth
-evolution
Properties of...
-metabolism
-growth
-evolution
Properties of...
27
New cards
Eukaryotic
these cells are much larger because they have many organelles
28
New cards
0.8 micrometers-millions of micrometers
average cell size range of eukaryotic cells
29
New cards
Cell structure
what is cell size influenced by
30
New cards
0.2 micrometers-750 micrometers
average cell size range of bacteria and archaea
31
New cards
0.01 micrometers-2.3 micrometers
average cell size range of viruses
32
New cards
Size
although this characteristic helps define microorganisms, there is often overlap so you can't define solely on this characteristic
33
New cards
high surface area to volume ratio
smaller cells can do metabolic processes faster because of what?
34
New cards
decreases
as a cell increases in size, its surface area to volume ratio \_______________
35
New cards
morphology
the physical appearance of a cell as determined by shape and size
36
New cards
cocci and bacilli
most common shape for prokaryotic cells
37
New cards
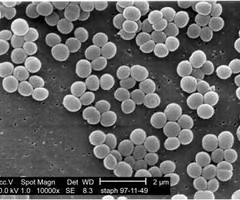
coccus/cocci
what bacterial shape is this
38
New cards
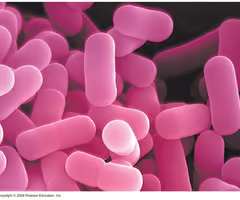
rod/bacilli
what bacterial shape is this
39
New cards
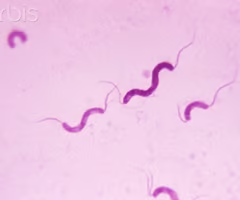
spirillum/spirilla
what bacterial shape is this
40
New cards
spirochete
what bacterial shape is this

41
New cards
appendage
these grow on some bacteria for attachment or to increase surface area
42
New cards
filamentous
what type of cell shape is this

43
New cards
arrangement
this is determined by plane of division and degree of separation after division of a cell
44
New cards
coccus/cocci
spherical shaped bacteria
45
New cards
rod/bacilli
Rod shaped bacteria
46
New cards
spirillum/spirilla
spiral shaped bacteria; rigid helices; not flexible
47
New cards
spirochete
spiral shaped bacteria; flexible; tightly coiled; have flagella inside; burrow into host tissue
48
New cards
size; shape
when classifying microbes, you should first look at cell \_____, then consider cell \______
49
New cards
diplococci
cocci growing in pairs
50
New cards
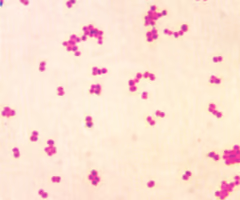
diplococci
round bacteria growing in pairs
51
New cards
streptococci
round bacteria that form a chain
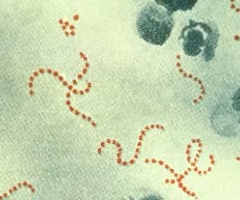
52
New cards
staphylococci
round bacteria forming grape like clusters
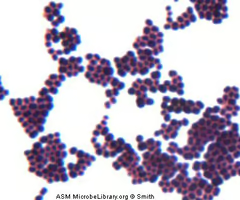
53
New cards
tetrads
4 round bacteria ordered in a square shape
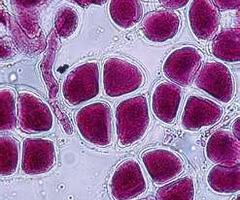
54
New cards
sarcinae
cubic configuration of 8 round bacterias

55
New cards
coccobacilli
very short rods; longer than it is wide
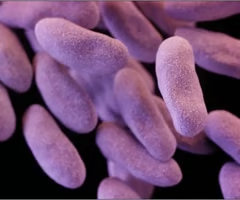
56
New cards
vibrios
resemble rods; comma shaped
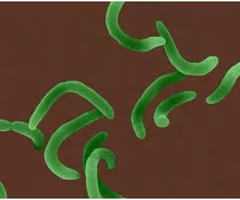
57
New cards
mycelium
a filamentous, root like structure; grows like fungi; network of long multicellular filaments
58
New cards
star
what is this unique shape of bacteria
59
New cards
pleomorphic
cell morphology that is variable in shape; non distinct
60
New cards
palisade
a unique arrangement of columnar shaped cells; connected at an end; when it divides, 1 end is curved so it sticks to the next one

61
New cards
neisseriae
coffee-bean shaped cell
62
New cards
streptomycetes
*Mold-like* filamentous bacteria
63
New cards
evolution
how do microbes increase diversity
64
New cards
haploid
An organism or cell having only one complete set of chromosomes.
65
New cards
haploid
haploid or diploid
66
New cards
they are haploid
what is unique about bacteria and archaea chromosomes that helps them increase diversity
67
New cards
horizonatal
bacteria and archaea (prokaryotes) increase genetic diversity by \___________ gene transfer within the same generation
68
New cards
horizontal gene transfer
transfer of genes between cells of the same generation
69
New cards
haploid
when cells that are \_________ become mutated, the effect is immediate. there is no masking of a dominant trait
70
New cards
highly differentiated tissue
what do all microbes lack
71
New cards
4.6 by
about how old is earth
72
New cards
bacteria and archaea
these were this first microbes to appear on earth (around 4 bya)
73
New cards
phototrophic bacteria
these were the second types of microbes to appear on earth (around 3.5 bya)
74
New cards
phototrophic bacteria
this microbe lived in an oxygen absent environment until about 2.3 bya
75
New cards
cyanobacteria
this was the third type of microbe to appear about 2.3 bya
76
New cards
cyanobacteria
these were the first type of microbes to live in an oxygenated atmosphere; 1st microbes
77
New cards
eukarya
this was the fourth type of microbe that appeared about 2 bya
78
New cards
last universal common ancestor
what does LUCA stand for
79
New cards
cyanobacteria
first microbes to start producing oxygen; this was determined by looking at fossils; prokaryotic bacteria that created an oxygenated atmosphere
80
New cards
eukarya
first living multicellular microbes
81
New cards
cellular
a phylogenetic tree is used only for \_____________ organisms
82
New cards
phylogenetic tree
a three domain system, based on the comparison of the DNA encoding small subunit ribosomal DNA
83
New cards
phylogenetic tree
divides microorganisms into bacteria, archaea, and eukarya
84
New cards
prokaryotic
bacteria are \____________________ cells
85
New cards
prokaryotic
archaea are \________________ cells
86
New cards
eukaryotic
eukarya are \______________ cells
87
New cards
number of common nucleotides divided by total number of nucleotides
to determine the relationship between cells for a phylogenetic tree placement, what do you compare?
88
New cards
they have DNA that encodes for ribosomes
why are chloroplasts and mitochondria included in phylogenetic trees?
89
New cards
endosymbiotic theory
a theory that states that certain kinds of prokaryotes began living inside of larger cells and evolved into the organelles of modern-day eukaryotes
90
New cards
no
do prokaryotes undergo endocytosis?
91
New cards
endocytosis
A process in which a cell engulfs extracellular material through an inward folding of its plasma membrane.
92
New cards
animals, plants, some fungi
what are the tree macroorganisms?
93
New cards
yes
do eukarya undergo endocytosis?
94
New cards
archaea and eukarya
which two are most closely related?
bacteria, archaea, eukarya
bacteria, archaea, eukarya
95
New cards
Protista
algae, protozoa, slime molds, and water molds belong to which kingdom?
96
New cards
green algae
we get 75% of our oxygen from \_______________ \____________
97
New cards
Capitalize and italicize
when writing the name of a domain you must.....
98
New cards
Eukarya
Which domain contains micro AND macro organisms?
99
New cards
Take organisms you want to compare, isolate DNA through DNA extraction, make copies of region of DNA that codes for the small subunit ribosomal RNA (using polymerase chain reaction), do a DNA sequence on the copies, align sequences to easily see where nucleotides match. To determine relationship, divide number of nucleotides they have in common by the total number of nucleotides in the sequence
Describe how a phylogenetic tree is generated
100
New cards
No
Do phylogenetic trees tell you which organism appeared first?