Newborns and Infants
1/167
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
168 Terms
When is APGAR Scoring Done?
Immediately after delivery
Scoring for APGAR score
Based on 5 factors which each factor getting a score of 0,1,2. Total scores of 0-10.
When should you give APGAR scores?
1 minute and 5 minutes.
1 minute Apgar score reflects
Pre-delivery state
5 Minute Apgar score reflects
extrauterine transition
Repeat Apgar scoring when?
At 5-minute intervals up until 20 minutes or Apgar is >7 ideally stop at 8.
Does APGAR score determine resuscitation plan or long-term prognosis?
No...
1st sign testing in APGAR and scoring
Muscle tone activity:
0=falccid
1=some flexion of arms and legs
2=well-flexed, or active movements of extremities
2nd sign of APGAR and scoring
Pulse/HR:
0=absent
1=Below 100 per minute
2=Over 100 per minute
3rd sign of APGAR and scoring
Grimace/Reflex irritability:
0=No response
1=Grimace or weak cry
2=Good cry
4th sign of APGAR and scoring
Appearance/color:
0=blue all over or pale
1=body pink, hands and feet blue
2=pink all over
5th sign of APGAR and scoring
Respiratory effort:
0=absent
1=weak, irregular, gasping
2=Good, crying
Newborn
Birth-28 days of age
Infant
Birth to 12 months
Growth charts for preterm infants
Fenton Growth Chart
Growth Chart for full term Infants
WHO growth chart
LGA
weight above 90th percentile large for gestational age
SGA
small for gestational age (<10th percentile)
What causes SGA?
•Usually from a deficiency (baby not growing well)
•Rest of body is small compared to head
•Maternal infections can cause this.
AGA
Appropriate for Gestational Age, 10th-90th percentile
ELBW
extremely low birth weight
<1000 g
VLBW
very low birth weight
<1500 g
Low Birth Weight infant minimum
<2500 grams
Normal birth weight
2500 g
Gestational Age is determined by
•OB dating (best if less than 20 weeks ultrasound)
•Exam (Ballard - accurate within two weeks of gestational age)
Preterm
<34 weeks
Late preterm
34-36 weeks and 6/7 days
Early term
37-38 6/7 weeks
Term
39-40 6/7 weeks
Late term
•41 – 41 6/7 weeks
Post-term
42 weeks and beyond
What happens to infants born late?
They're big, the head can get stuck, now the baby has oxygen issues.
What does ballard exam measure?
Neuromuscular maturity and physical maturity
Tips to examine a newborn
•Examine the newborn in the presence of the parents
•Swaddle and then undress the newborn as the examination proceeds
•Dim the lights and rock the newborn to encourage the eyes to open
•Observe feeding, if possible, particularly breastfeeding
•Demonstrate calming maneuvers to parents (e.g. swaddling)
•Observe and teach parents about transitions as the newborn arouses
Vital ranges for birth to 1 month
Avg HR: 140 bpm
HR range: 90-165 bpm
RR:(40-60)-(30-68)
Temp: 36.5-37.5 C
Vital ranges for 1-6 months
avg HR: 130 bpm
HR range: 80-175 bpm
RR: (40-60)-(30-68)
Temp: 36.5-37.5 C
Vital ranges 6 months to 12 months
avg HR: 115 bpm
HR range: 90-170 npm
RR:25-60
Temp: 36.5-37.5 C
Best way to measure breathing
Measure for 60 seconds and watch to see if they're tachypneic >60 breaths/min from birth to 2 months
Why do we count breaths for a full 60 seconds?
Irregular periodic breathing, Cheyne Stokes
Best way to do a temperature check for an infant
Under the arm, but if the infant is cold do rectal
What to note about general Appearance
•Pink vs cyanotic (blue)
•Good tone vs hypotonic
•Are arms and legs close or spread out (can they hold their arms up)
•Respiratory effort
•They're trying to breath (diaphragmatic)
•Symmetric movements
What to look for before auscultating?
Central cyanosis
How do we assess for central cyanosis?
Look at the lips, tongue, and sublingual mucosa
Confirm with a pulse ox on the right hand and foot.
A baby is sweating while feeding what am I worried about 9/10 times?
Cardiac issues. Baby is diaphroretic. Babies only work out by eating so the baby is having issues on exertion...boom heart issues.
A newborn has peaceful tachypnea...good right?
NO. This means there's no increased work of breathing...a newborn should be working hard to breath they're lungs are still forming to take over.
Pulses: where to palpate?
•Lower extremity pulse is important (femoral)
•Vary pressure w/ femoral to make sure you're not occluding it.
•Babies can have coarctation of the aorta and you don't know till PDA closes (2-7 days of life)
•Make sure theyre strong
•Compare upper & lower extremities at the same time.
•If there's a difference in pressure check echo for coarctation.
What're thrills?
Palpable turbulence in heart or great vessels
Auscultation (APT M) what to note?
-S1, S2 w/ a split S2 on inspiration.
Auscultation, murmurs
Use timing, location, quality, intensity
Two benign systolic murmurs in newborns
•Closing ductus (PDA) – Harsh, ejective (crescendo), systolic murmur, LUSB
•Peripheral pulmonary flow murmur – Soft, ejectile, systolic LUSB radiating to lung fields and axillae
True or False: PVC or PAC are benign in a newborn
Yes, just send to cardiology to get a EKG to confirm...don't miss heart issues in a newborn
How to assess capillary refill time?
you can't do Allens test with the tiny wrist so use the infant's finger.
Most common dysrhythmia in a newborn
SVT
What to observe before auscultating for the lungs?
RR, color, nasal breathing, work of breaking and audible breath sounds.
Why nasal breathing?
Infants are obligate nasal breathers since they breath mostly with their diaphragm. They don't use their mouths. This is all due to a still developing respiratory system.
Grunting
Short, repeitive, expiratory sound. From closing of the vocal cords.
Wheezing
musical expiratory sound
Stridor
High pitched, inspiratory noise
Obstruction
Lack of breath sounds, from mucous or amniotic fluid in the lungs
Nasal flaring
COngenital atresia or excess movement of the nares to breath
Retractions
Chest indrawing
-Supraclavicular, intercostal, substernal, subcostal.
how do you confirm retractions
Not pretty but you push a G-tube
Definition of apnea
absence of breathing for 20 seconds or more
Fontanelles in a newborn: enlargement could mean
Cretinism, congenital hypothyroidism
Fontanelles are usually
soft and flat or slightly concave
A bulging fontanelle might indicate
ICP, bleeding, hydrocephalus
A deeply shrunken fontanelle might mean
Dehydration
Anterior fontanelle in a newborn
Large and diamond shaped.
Closes in 80% of infants by 18 months, 90% by 22 months.
Posterior fontanelle in a newborn
Triangular shaped, usually closes by 2 months but can take up to 6 months.
Positional Plagiocephaly (bilateral)
Can be from torticollis
Torticollis
head tilt due to shortening or spasm of one sternomastoid muscle
Positional Plagiocephaly (unilateral)
Baby is spending too much time in one position
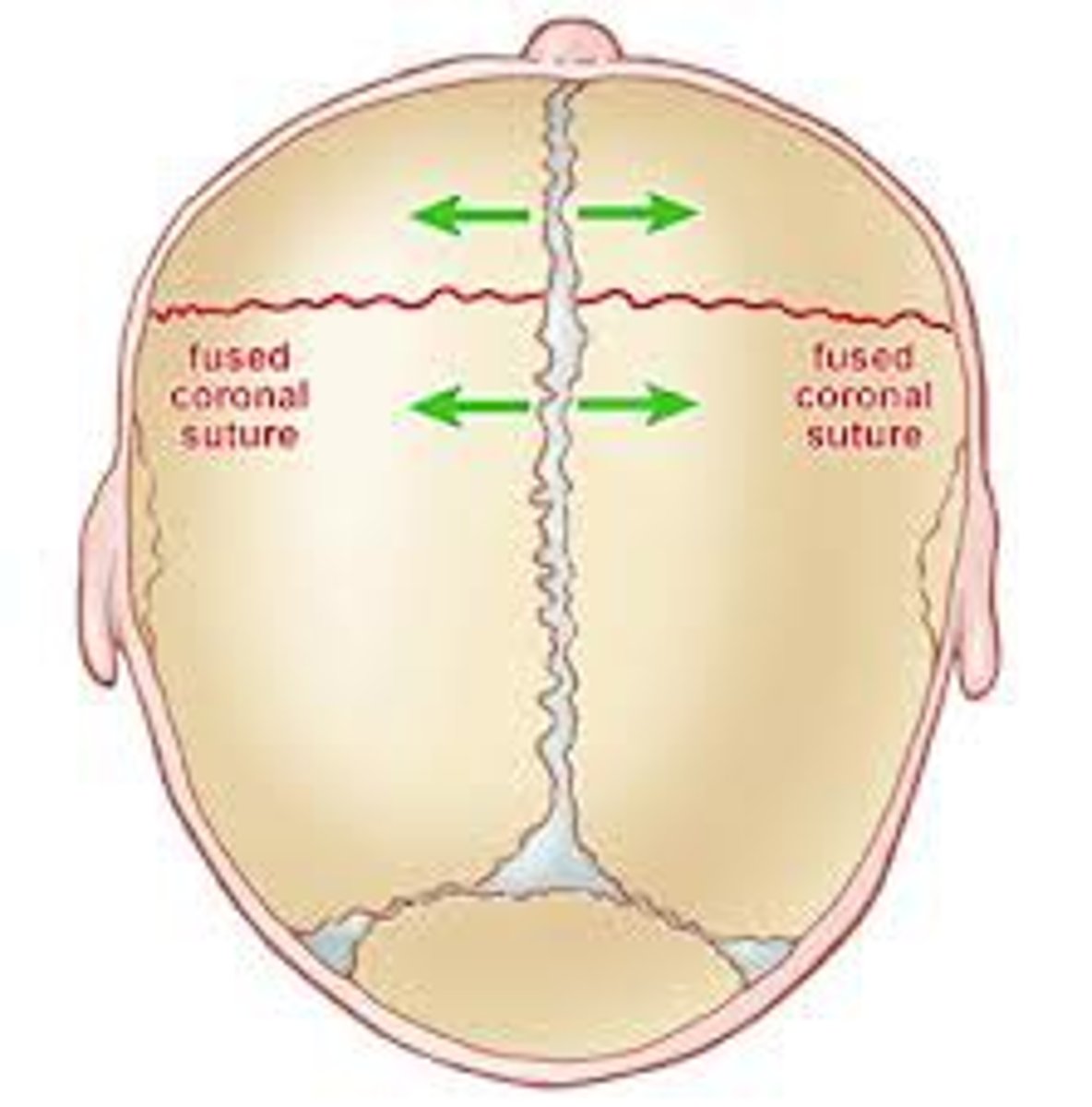
Craniosynostosis
Premature closing of cranial sutures causing an abnormally shaped skull
MC Craniosynostosis
Sagittal suture synosis causing narrow head
Sagittal suture synostosis name and shape
Scaphocephaly, boat shaped
Brachycephaly
Short broad head due to premature suture fusion
Caput succedaneum
Pitting edema in the scalp
Crosses suture lines
Resolves in 1-2 days
Occipitoparietal region

Cephalohematoma
Subperiosteal hemorrhage
Collects over 24 hrs
Does not cross suture line
Resolves in around 3 weeks
At risk for Jaundice
Can be lethal.
What do we see caput succedaneum, Cephalohematoma, and subgaleal hemorrhage with?
Vacuum delivery
Subgalea hemorrhage
Fluid wave that moves immediately to dependent locations.
Venous bleeding under galea, entire area of the scalp.
Potential for significant blood loss
Admit to SCN/NICU to monitor vitals and hematocrits.
Significant jaundice risk
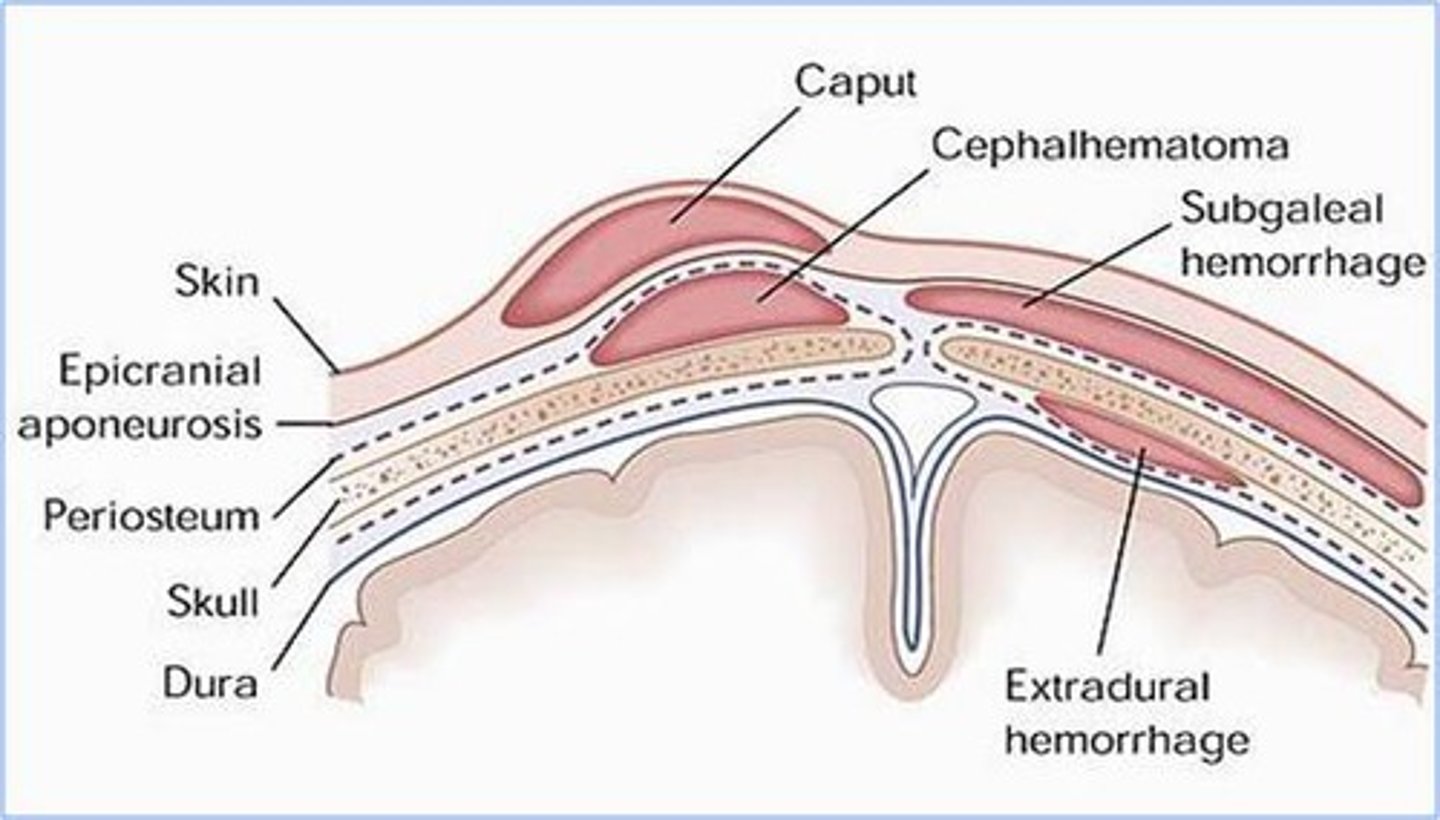
Difference between subgaleal hemorrhage and cephalohematoma
Both involved venous bleeding and jaundice, but a subgalea hemorrhage has blood collection in the entire scalp. Larger volume of blood loss. Greater risk for hemorrhagic shock.
Inspect the neck for?
Webbing, torticollis, clefts, pits, masses
Inspect the clavicles for?
Symmetry, fractures
Why would the clavicle fracture?
Extremely easy to do in vaginal deliveries.
A callus will develop
Do you need to fix a clavicle fracture in a newborn?
No theyll be fine. It heals on its own.
When inspecting the ears note
Position, ear pits, tags
When do we worry about ear pits?
If they're isolated its ok, but with other malformations we worry about kidney abnormalities.
Pits and tags are associated with
Hearing loss
Imaginary line is drawn from the
Inner and outer canthi of eyes and should cross the pinna or auricle
What happens if the ears are below this line?
Low set ears like in DS!!
How to do an otoscopic exam
Pull the auricle down and out.
Newborns are obligate
Nsal breathers
True or False: when assessing patency, you 100% should occlude both nares at the same time
False...one at a time
Ankyloglossia
Tongue tied!
What happens if a newborn has ankyloglossia and they're breastfed?
There's a clicking noise.
Mouth abnormalities
Cleft lip, cleft palate, bifid uvula.
How many primary teeth for natal teeth?
20
Rate of tooth development
1 tooth for each month between 6-26 months for a maximum of 20 primary teeth
There's a white coating on the newborn tongue differential
-residual milk (can wipe off)
-Thrush (cannot wipe it off)
A baby has a protruding tongue differential
Cretinism, Trisomy 21, Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome