AP Human Geography Unit 6: Economic Development and Industry
1/100
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Test: April 25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
Historical Context
Silk Road (late antiquity to the 1500s)
Colonialism (1600s to 1800s)
Industrialization (1800s to 1900s)
Periods of “weak” globalization
Middle Ages
WWI, Great Depression, WW2
Cold War (1947 - 1991)
What is Globalization?
The process of interaction + integration among people, companies, and governments worldwide (on a global scale)
Cultural Globalization
Language, religion, values
Economic Globalization
Capitalism / free trade (NAFTA)
Political Globalization
Multilateralism (the principle of participation by three or more parties, especially by the governments of different countries) (UN / EU / NATO)
Global Economy since 1991
increased globalization + trade
growth in industry in developing nations
decline of manufacturing in wealthy nations
rise of Asian economic power
rising inequality between richest + poorest people and countries
environmental degradation + pollution
rapid technology adoption
Why has Globalization accelerated?
Due to advances in transportation and communication technology.
Who in the Left dislikes Globalization?
Anti-capitalists (old Marxists, socialists, etc..)
Environmentalists
Anti-corporatists (hates Walmart, Target, Amazon)
Anti-American (America - Globalization)
Ex - The 99%’ers
Who in the Right dislikes Globalization?
Economic + cultural nationalists
Anti-Immigrant groups
Religious fundamentalists
Anti-American (America = immoral / decadent place)
Ex - Trumpies (MAGA)
Who in the Left likes Globalization?
Human Rights Activists
“Techies” (Amazon, Google, etc.)
Pro-multilateralists (UN = great!)
More government = more democracy, great!
Ex - Democratic party
Who in the Right likes Globalization?
Free market capitalists + entreprenuers
American exceptionalists (USA = special + unique role in world)
Less government = more democracy, yippie!
Ex - Republican party (non-MAGA)
Costs of Globalization
Loss of privacy (data mining online)
Pressure to conform to global norms
Rapid raise in costs of urbanization + industrialization
Problems once containable are now spreading to other nations more easily (crime, drugs, pollution, terrorism)
Benefits of Globalization
Rapid economic growth (for many, not all)
Reduction in barriers to trade, investment, makes economic transactions easier, more profitable
Spread of democracy + human rights for women + minorities
New advances for political access (social media)
Types of Job Sectors
Primary
Secondary
Tertiary
Quaternary
Quinary
Primary Job Sector
(Barely any education / not a lot of profit)
Providing raw materials for the economy
Ex - mining, agriculture, forestry, fishing
Secondary Job Sector
(Still not a lot of profit, more but not a lot of education)
Manufacturing things using resources
Ex - consumer goods, machinery, electronics
Tertiary Job Sector
(Need a degree (sometimes), more profit)
Providing services
Ex - hospitality, personal services, education, healthcare, finance, government
Quaternary Job Sector
(High-middle class profit / shit ton of schooling)
STEM jobs
Ex - engineers, doctors, scientists, computer / software design
Quinary Job Sector
(People who run the economy, peak profit, REALLY hard to get)
elite services / business
Ex - executives/managers, CEOs, politicians, finance, business owners, culture influencer (online, media, sports, entertainment)
Modern Country Job Sectors
Primary: 2%
Secondary: 13%
Tertiary: 60%
Quaternary: 4%
Quinary: 4%
Developing Country Job Sectors
Primary: 40%
Secondary: 30%
Tertiary: 30%
Quaternary: 2%
Quinary: 4%
Poorer Economy Job Sector Pattern
More ppl in Primary (⬆%) (lower wages + skills)
Developing Economy Job Sector Pattern
Rise in Secondary (⬆%) (lower skilled labor)
Wealthier Economy Job Sector Pattern
High number of people in Tertiary, Quaternary, + Quinary (⬆%) (higher education)
Typical Employment Pattern for Poorer Economy
Primary: 70%
Secondary: 15%
Tertiary: 15%
Quaternary: 15%
Quinary: 15%
Ex - Bangladesh
Typical Employment Pattern for Developing Economy
Primary: 40%
Secondary: 30%
Tertiary: 30%
Quaternary: 30%
Quinary: 30%
Ex - China
Typical Employment Pattern for Wealthy Economy
Primary: 5%
Secondary: 15%
Tertiary: 80%
Quaternary: 80%
Quinary: 80%
Ex - Japan
Who dominates the Primary + many Secondary jobs?
Men
Who makes up the majority of Tertiary jobs in wealthy economies?
Women
Women preform well in TQQ jobs, what does this increase?
Overall societal wealth
Are women still a large % of the unofficial job sector (untaxed) and unpaid labor (housework)?
Yes
How many hours do women in wealthy economies often spend a week more on domestic chores more than men?
15-20
More and more, jobs are being outsourced + automated, who does this place strain on?
Low skilled workers, especially in wealthier economies
What do poorer economies want their people to do?
To stop farming and to get into greater wealth generating jobs.
Site Factors
Physical features that relate to the cost of production and transportation
Situation Factors
Features of a surrounding area that are related to the cost of production and transportation
Basic Industry
The main focus of a region’s economy
Ex) Detroit = Cars, LA = Film, SanFran = Tech, DC = Gov
Non Basic Industry
Businesses that support the work of the ‘Basic Industry’
Ex) Steel + Rubber = supports Car manufacturing
What happens if the main business’ (Basic Industries) go out of business?
Everything suffers (The Non Basic Industries), a domino effect
The Multiplier Effect
How basic + non basic industries operate to grow the economy
Fixed + Variable Costs
Business have to balance the costs of things, a budget of sorts
Fixed Cost
Costs that do NOT fluctuate, stays the same
Ex) Rent
Variable Cost
Costs that DO fluctuate, changes, harder to predict
Ex) Energy bill, Tips, (Servers), Gas prices
Transportation Systems
Modern manufacturing tries to compress time and space (decrease time and distance obstacles)
Greater Distance + Weight
More cost, how to overcome?
Friction of Distance
The farther you have to get something from point A to point B, you get issues
Trucks
America, big national highway system, popular but expensive
High mobility + flexibility, high fuel cost + wear and tear
Trains
More efficient in transporting lots of things long distances
Low mobility + flexibility, very efficient over long distances, dependent on break of bulk points
Break of Bulk Points
Changing the way somethings transported (Cargo must be loaded + unloaded to a different transportation)
Airplanes
Fast, flexible, high cost + limited weight carrying
Can land lots of places, not as flexible as trucks, need an airport, not cost effective, VERY efficient to move lots of heavy things, not efficient for SUPER heavy things
Pipelines
Great for fluids, bad for everything else
Not flexible for moving gases
Ships
Low cost, slow, need port
MOST cost effective way of transportation globally, not as fuel efficient as trains, needs a port, not easy to unload
Agglomeration
When the clustering of similar businesses that can provide assistance and efficient labor and skill management
Occurs when a basic industry begins to draw in similar businesses
Advantages of Agglomeration
Shared Infrastructure
Labor + Workers
Shared Knowledge
Shared Supplies
Cumulative Causation
The continued growth due to agglomeration
Deglomeration
When a market becomes too saturated with similar businesses
What’s a problem because of deglomeration?
A market becomes too saturated with too many businesses, causes business to suffer
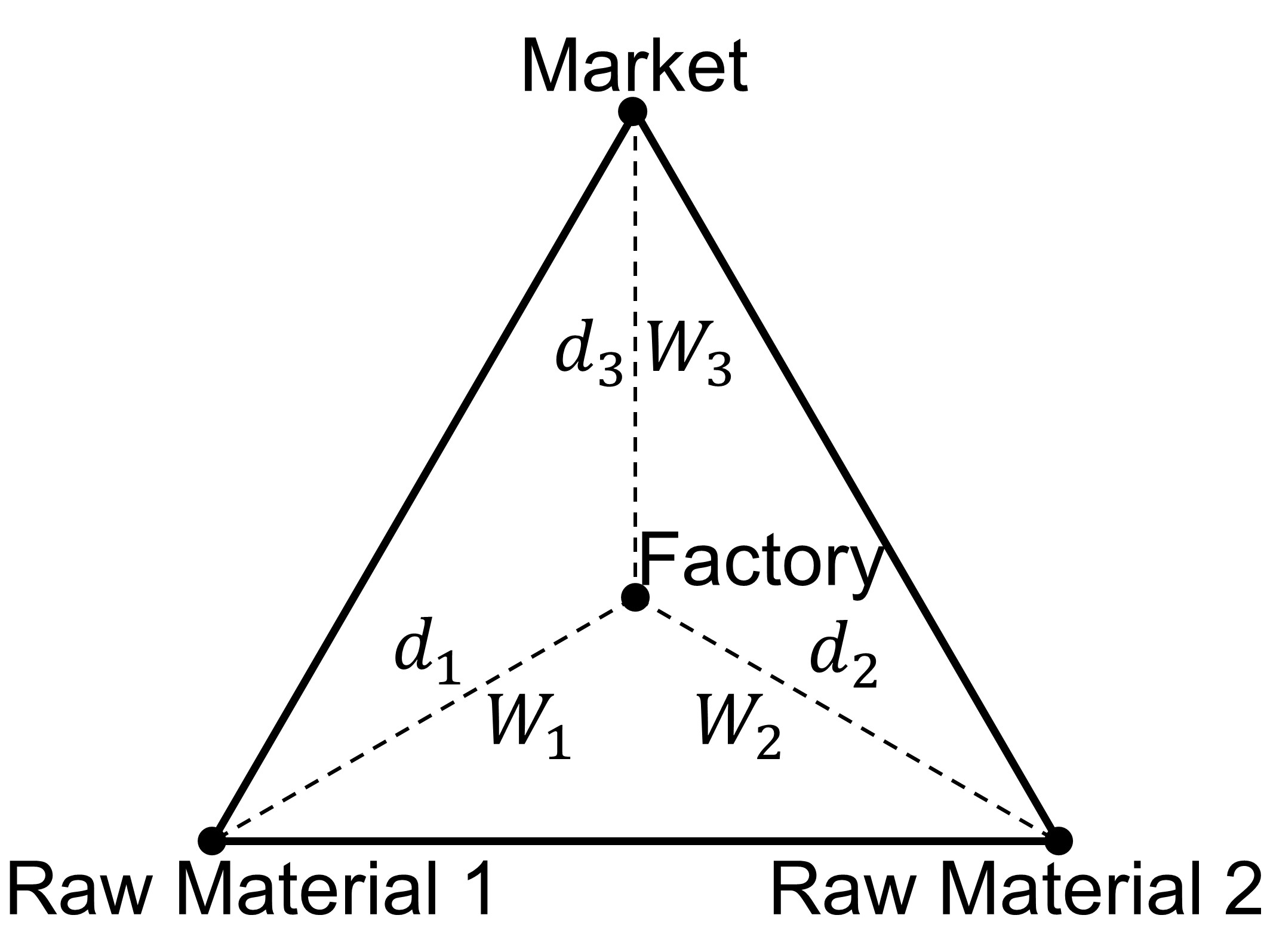
Weber’s Least Cost Theory
Think of it as a triangle
You want to be closer to the heaviest material
According to Weber’s Least Cost Theory, what is the location of a factory dependent on?
Raw materials cost (least expensive, least control)
Labor cost (most expensive)
Transportation cost (most under your control)
Weight/Bulk Gaining
Finished good weights more than the raw materials, located closer to the market
Ex) Cars, the car weighs more than the steel + rubber that goes into it
Beverages + processed food = you want to be closer to the market where you’re going to sell
Weight/Bulk Reducing
Raw materials weigh more than the finished good, located closer to materials
Ex) Potato chips, potatoes weigh more than the chips
What are the Major Industrial Zones in North America?
Ontario (Canada)
Northeastern USA (Boston-DC)
Great Lakes (Rust Belt)
Southeastern I-85 Corridor
Seattle-Portland
San Francisco Bay
Los Angeles/San Diego
Northern Mexico
Mexico City.
Which Canadian region is a Major Industrial Zone?
Ontario (including Toronto, Ottawa, Montreal)
What U.S. region is known as the "Rust Belt"?
The Eastern and Western Great Lakes area
What is the Industrial Corridor in the Southeastern U.S.?
The I-85 Corridor through North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia
Which Mexican regions are Major Industrial Zones?
Northern Mexico and Mexico City
What are China's SEZs?
Beijing, Shanghai, and Hong Kong
Focused on export processes
What is the major industrial region of Japan?
The Kanto Plain, including Osaka, Kyoto, and Tokyo.
Who are the "Asian Tigers" in global industrial zones?
South Korea, Taiwan, Singapore, and Hong Kong.
What are the major industrial countries in Western Europe?
Britain, France, and Germany
What region includes Moscow and other major cities in Eastern Europe?
Russia and Ukraine
What does GDP stand for?
Gross Domestic Product
What does GDP per capita measure?
The average economic output per person in a country.
What are common measures of development?
1) GDP/GDP per capita
2) Life expectancy
3) Education levels
4) HDI
5) GDI.
What does HDI stand for, and who created it?
Human Development Index; created by the UN in 1990.
What indicators are used in the HDI?
Life expectancy, education (literacy and school years), and income (GNI per capita)
What is the purpose of the Human Development Index (HDI)?
To measure a country's overall development, not just economic output
What does GDI stand for?
Gender Development Index.
What does the Gender Development Index (GDI) measure?
Gender gaps in human development achievements (life expectancy, education, income)
Which measure of development considers income, education, and health?
HDI (Human Development Index)
Why is life expectancy used as a measure of development?
It reflects the overall health and well-being of a population.
Why are education levels important in measuring development?
Higher education levels usually correlate with better job opportunities and quality of life.
Immanuel Wallersteins’ World Systems Theory- 3 Level Global Hierarchy
1) Core
2) Semi-Periphery
3) Periphery
Can be used at smaller scales to look at economic differences within countries and regions (Ex: USA, Core: Coasts, Semi-Periphery: Great Lakes, Periphery: Appalachia) - Solution: Wealth transfers and fairer trade deals
Immanuel Wallersteins’ World Systems Theory: Core Hierarchy Level
Ex) USA, W. Europe, Japan, (most developed, MDC)
They “rig the system” and exploit
Make the rules
Make the most profit globally
Immanuel Wallersteins’ World Systems Theory: Semi-Periphery Hierarchy Level
Ex) China, India, Latin America (developing)
Exploited by Core, but also exploit periphery
Have ‘Core’ elements, but are still mostly poor, provide most technology
Immanuel Wallersteins’ World Systems Theory: Periphery Hierarchy Level
Ex) Africa (least developed)
Exploited by Core and Semi-Periphery
Walt Rostow’s Model “Ladder” of Development
Societies progress through the 5 Stages of Development:
Traditional Society
Precondition for Takeoff
Takeoff
Drive to Maturity
Mass/Highest Consumption
Walt Rostow’s Model: Traditional Society
Most Jobs are Primary
Poorest developing nations
Ex) Niger, South Sudan, Laos
Walt Rostow’s Model: Preconditions for Takeoff
Transitional phase to early industrialization
Ex) Nigeria, Kenya, Bangladesh, Guatemala
Walt Rostow’s Model: Takeoff
Rapid growth
Agriculture changes to large scale and industrial
Huge industrial/tech growth
Most jobs are in the secondary sector, but growth in the tertiary sector
Ex) China, India, Vietnam, Brazil
Walt Rostow’s Model: Drive to Maturity
Rapid tech growth
Jobs moving out of secondary
Ex) Russia, Poland, Saudi Arabia
Walt Rostow’s Model: Mass/Highest Consumption
Most jobs are in TQQ sectors: high energy + tech use
Outsourcing of industry and increased automation
Ex) USA, Japan, Australia, South Korea
Global Resource Land Use
Oil (Ex: Petroleum)
Natural Gas
Coal
Forestry and Timber
Fishing
Alternative Energy Producers:
Hydroelectric
Solar
Wind
Nuclear
Blomass
Geothermal
Pollution
Global Resource Land Use: Oil
Most important energy resource
Main Producers: USA, Saudi Arabia, Russia, Iran
Main Consumers: USA, China, EU
OPEC: Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries
Cartel of developing nations formed in 1960 with large oil reserves; mainly from Middle East but now some African states and Venezuela. Try and control supply and demand (set price for oil)
Natural gas
Heating cold regions
Main Producer: Russia, Canada, USA
Main Consumers: EU, USA
Coal
Cheap energy source, but very polluting
Main Producers: China, India, USA
Main Consumers: China, India, USA
Forestry and Timber
Building resource
Main Producer: Canada, Russia, USA, Brazil, China
Main Consumer: China, USA
Fishing
Food Resource
Main producer: China, Indonesia, India, Vietnam
Main Consumer: China, Vietnam, Japan, USA