7SC2023 Examination
1/132
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Examination Practise
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
133 Terms
Identify a way that water ca re-enter the atmosphere:
Evaporation
Pure Substances (atom)
Cannot be Separated
Pure Substances (compound)
Can be destroyed
Composed of 2 or more different atoms bonded.
Mixture
Substance made by mixing other substances together
Solution
Mixture of solute dissolved into a solvent
Examples: Sugar & Coffee
Suspension
Mixture of gas / liquid
Insoluble Substance
Examples: Chalk & Water
Colloid
Mixture in which the particles of 1 substance spread evenly throughout another
Example: Milk
Emulsion
Dispersed in other
Example: Oil
Homogenous
Mixture in which the composition is uniform throughout the mixture
(salt water)
Heterogenous
Mixture in which the composition is uniform throughout the mixture
(soup)
Solution
Mixture of a solute dissolved into a solvent
Solvent
Substance in which a solute dissolves to form a solution
Solute
Substance that is dissolved into a solvent to form a solution
Insoluble
Collects at the bottom of the container are sediments
Soluble
Dissolvable
Dilute
Describes a solution to make it weaker by adding solvent
Saturated
Containing the maximum amount of solute
Concentrated
Amount of solute compared to the amount of solvent in a solution
Evaporation / Crystallisation
A separation technique that uses evaporation to separate the parts of a solution
Distillation
A separation technique that uses evaporation to separate substances
Decanting
A technique separating off the liquid part of a suspension, leaving the solid sediment behind
Filtration
The part of the mixture that passes through a filter
Sieving
A method to distinguish small particles from bigger particles
Centrifuging
Separates heterogeneous mixtures into their various components
(liquids to liquids)
(solids to liquids)
(liquids to gas)
Separation Funnel
Used in liquid-liquid extractions to separate the compositions of a mixture into 2 immiscible solvent phases of different densities
(Reading Elements from the Periodic Table)
Atomic Number
The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
(Reading Elements from the Periodic Table)
Mass Number
The total number of protons & neutrons in the nucleus.
(Reading Elements from the Periodic Table)
Atomic Symbol
The number of protons in the nucleus of the atom.
Periods in the Periodic Table
Each period represents a new shell
Groups in the Periodic Table
Each group represents outer electrons.
Protons in the Atomic Structure
Positive Charge
Neutrons in the Atomic Structure
Neutral / No change
Electrons in the Atomic Structure
Negative charge
Shells in the Atomic Structure
Amount of electrons that uses space
Nucleus in the Atomic Structure
Cell’s control centre
Density
The substances mass per unit of volume

This Symbol Represents?
Radiation

This Symbol Represents?
High Voltage

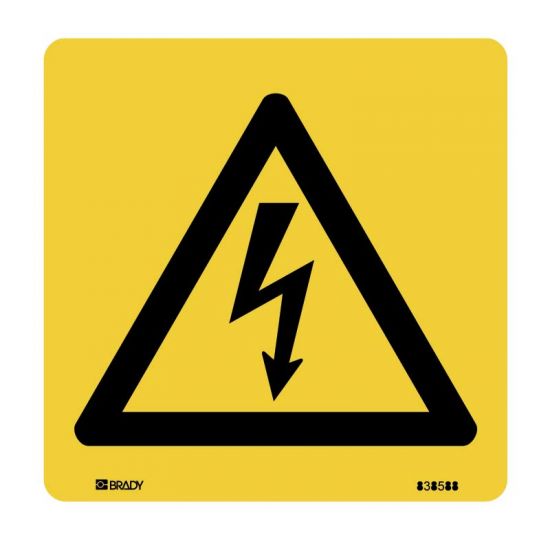
This Symbol Represents?
Oxidiser

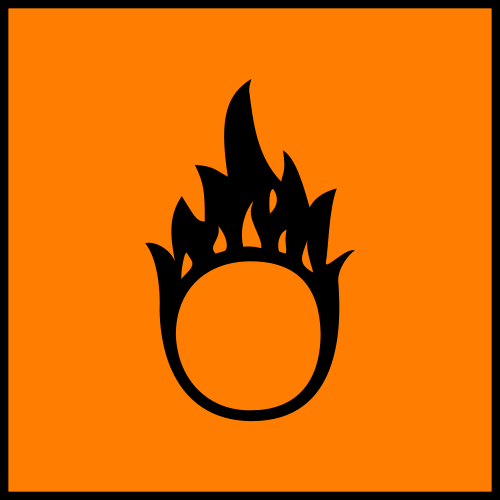
This Symbol Represents?
Harmful
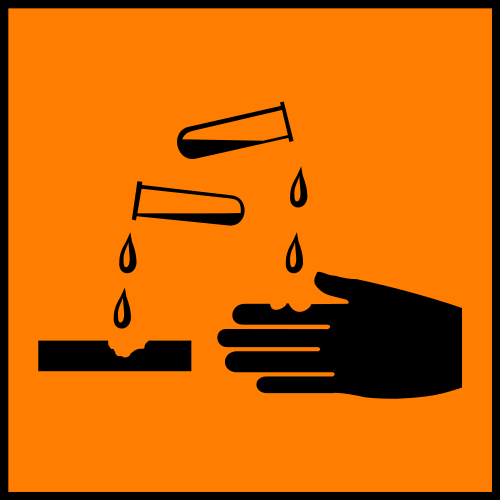

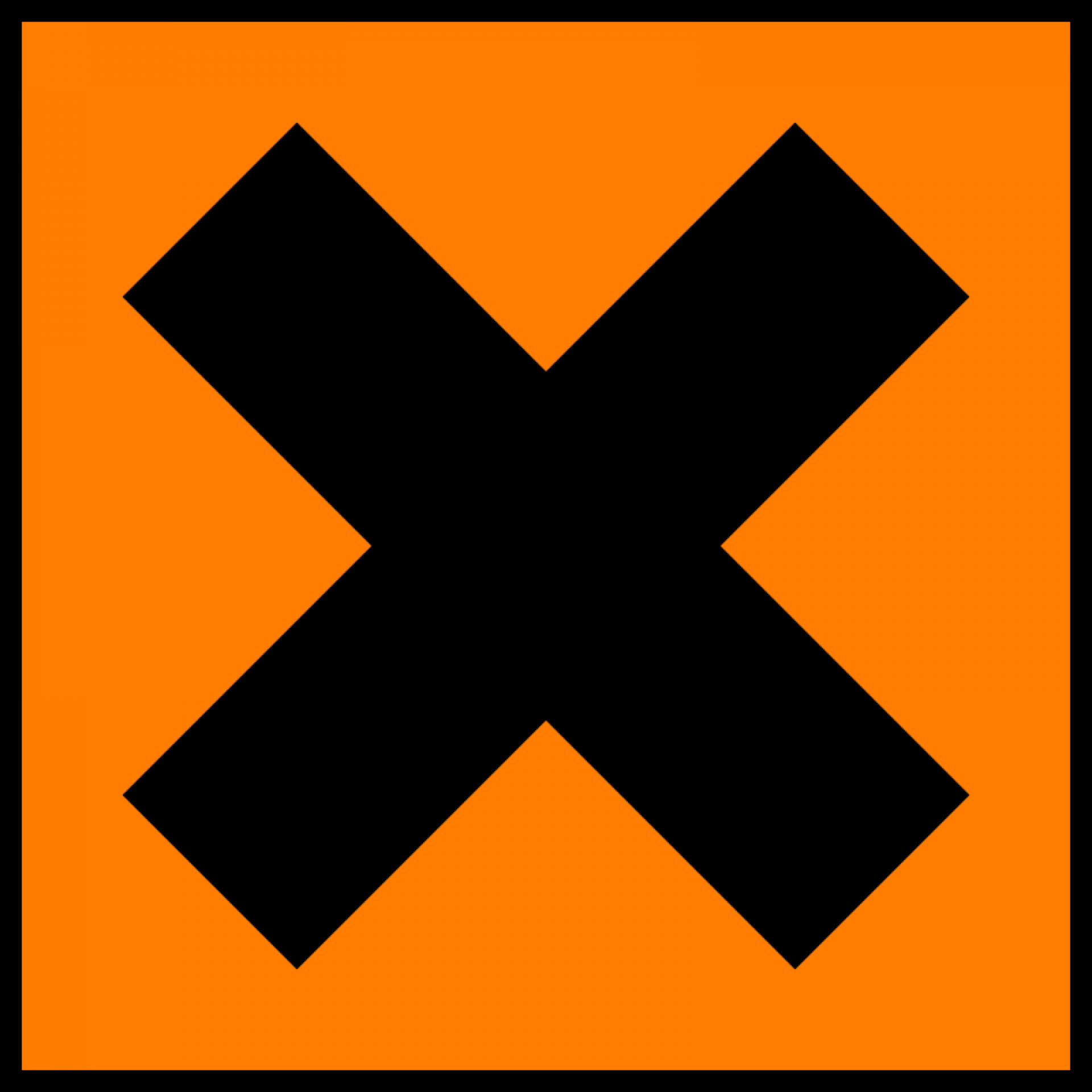
This Symbol Represents?
Corrosive, irritant effect on skin
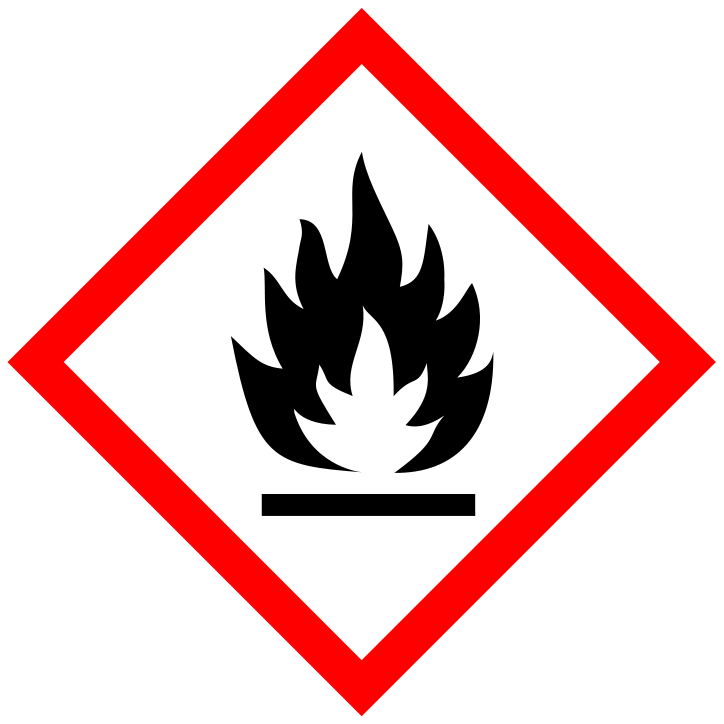

This Symbol Represents?
Flammable
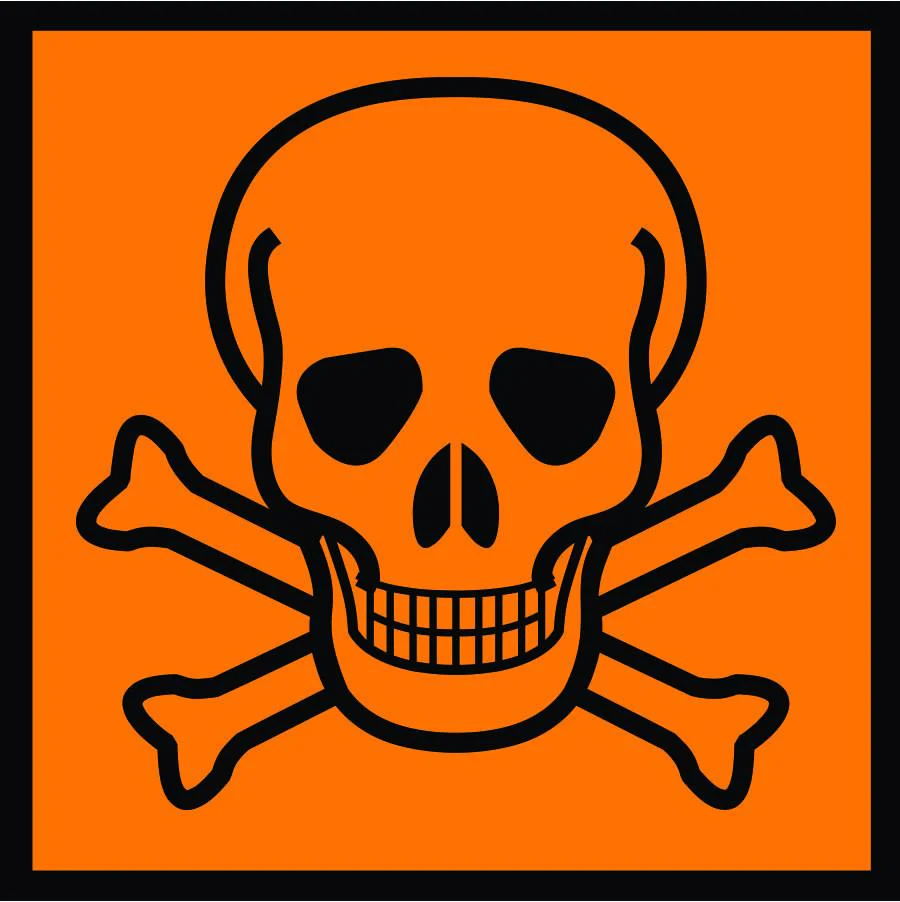

This Symbol Represents?
Toxic

This Symbol Represents?
Explosive
Biology
Study of living things
Chemistry
Study of substances
Physics
Study of Energy
Earth Science
Study of processes on earth
Space Science
Study of space
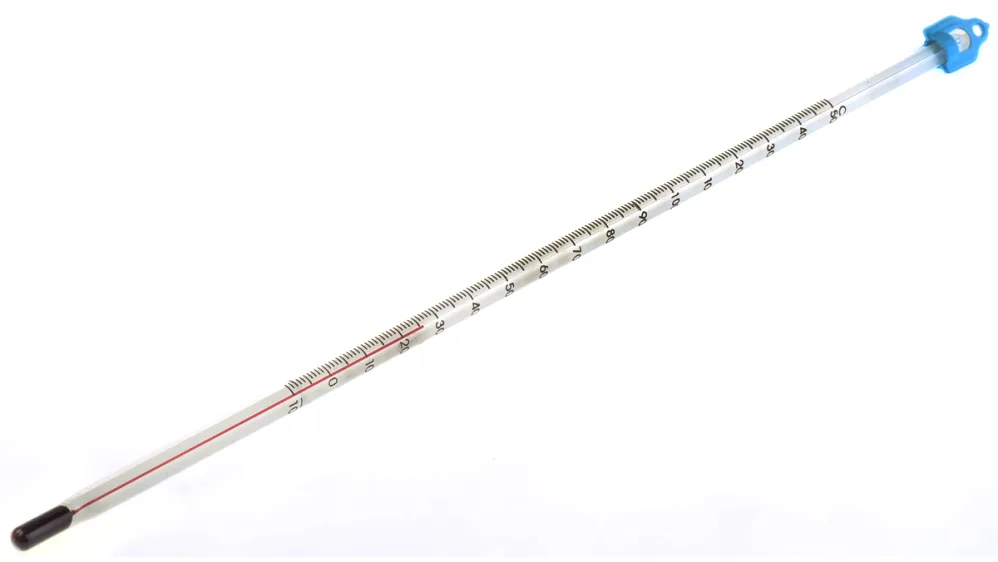

Clarify what science equipment is this?
Thermometer
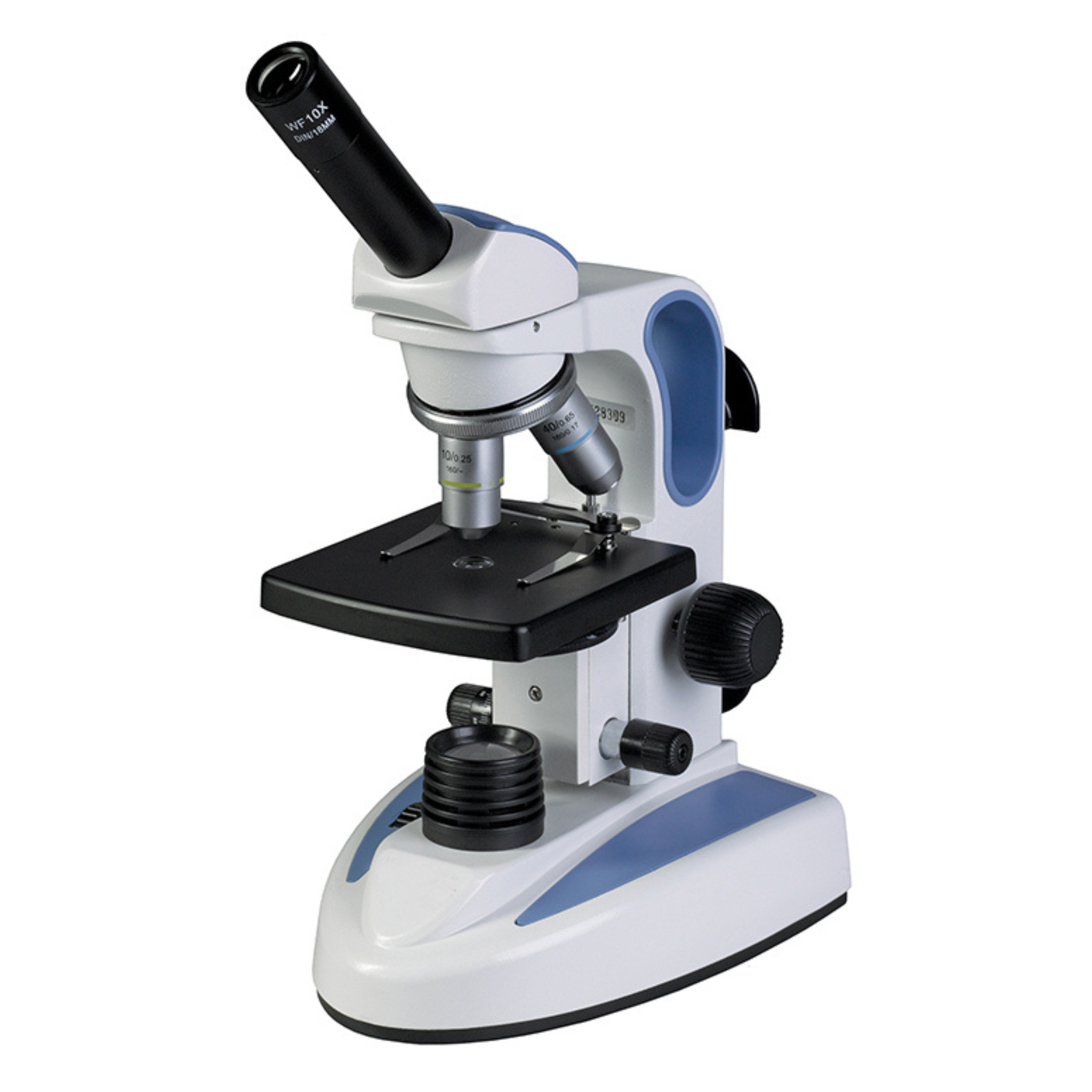

Clarify what science equipment is this?
Micro-Scope

Clarify what science equipment is this?
Beaker
Clarify what science equipment is this?
Bunsen Burner
Clarify what science equipment is this?
Tripod
Clarify what science equipment is this?
Test Tube

Clarify what science equipment is this?
Rhetort Stand

Clarify what science equipment is this?
Clonical Flask

Clarify what science equipment is this?
Filter Funnel
Independent Variable
One single variable that is changed in science
A force is a
“push”
“pull”
“twist”
A force can:
1. Change an object’s shape.
2. Speed an object up (accelerate)
3. Stop an object moving.
4. Slow an object down.
5. Change an object’s direction.
UNITS OF FORCES:
Always measured in Newtons
Definition of WORK
In science, 'work' is 'motion' caused by a force.
Equation for Work
Work (W) = Force (F) x distance (d)
Work is measured in
Joules
Force is measured in
Newtons
Distance is measured in
Metres
Vector Diagrams
“We represent forces using…
Arrows
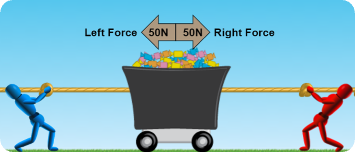
Define a Balanced Force
The left force and the right force is 50 N (Newtons)
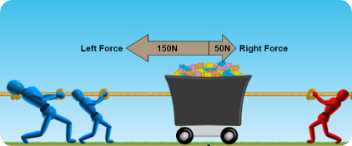
Define an unBalanced Force
The left force is greater than the right force
THE RAMP
How do they make life easier? When using a ramp, the load force remains the same but the effort force is… (Increased OR Decreased)
Decreased, as less effort Is required, thus requiring a larger distance
Definition of Weight
Weight: the gravitational force on an object
Measured in Newtons.
Definition of Mass
Mass: how much matter on object contains
Measured in kilograms.
Gravity’s influence:
Mass always stays the same, but weight can change depending on how much gravity is acting upon an object.
Definition of friction:
The resistance that one surface or object encounters when moving over another.
Factors contribution to high friction:
Rough Surfaces
Factors contribution to low friction:
Whiteboard
Buoyancy
Definition:
Buoyancy is an upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of an submerged object.
Displacement:
Definition:
: is how much water it is pushing away
Density:
Definition
Objects that are more dense than water will sink
NEWTONS 1ST LAW OF MOTION
INERTIA: Objects resistance to change.
An object in motion will continue moving
An object at rest will remain at rest.
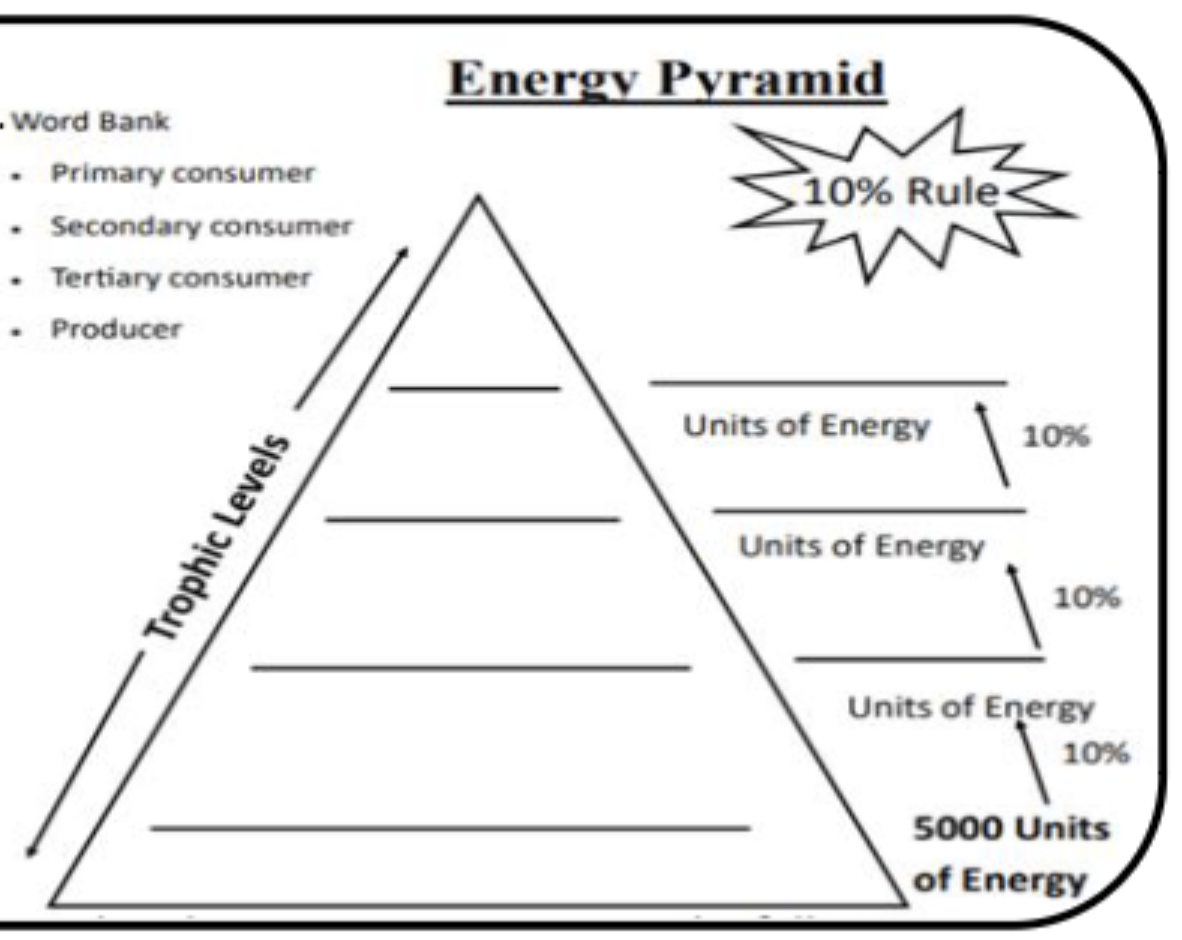
Which categories are prey:
Tertiary Consumers
Secondary Consumers
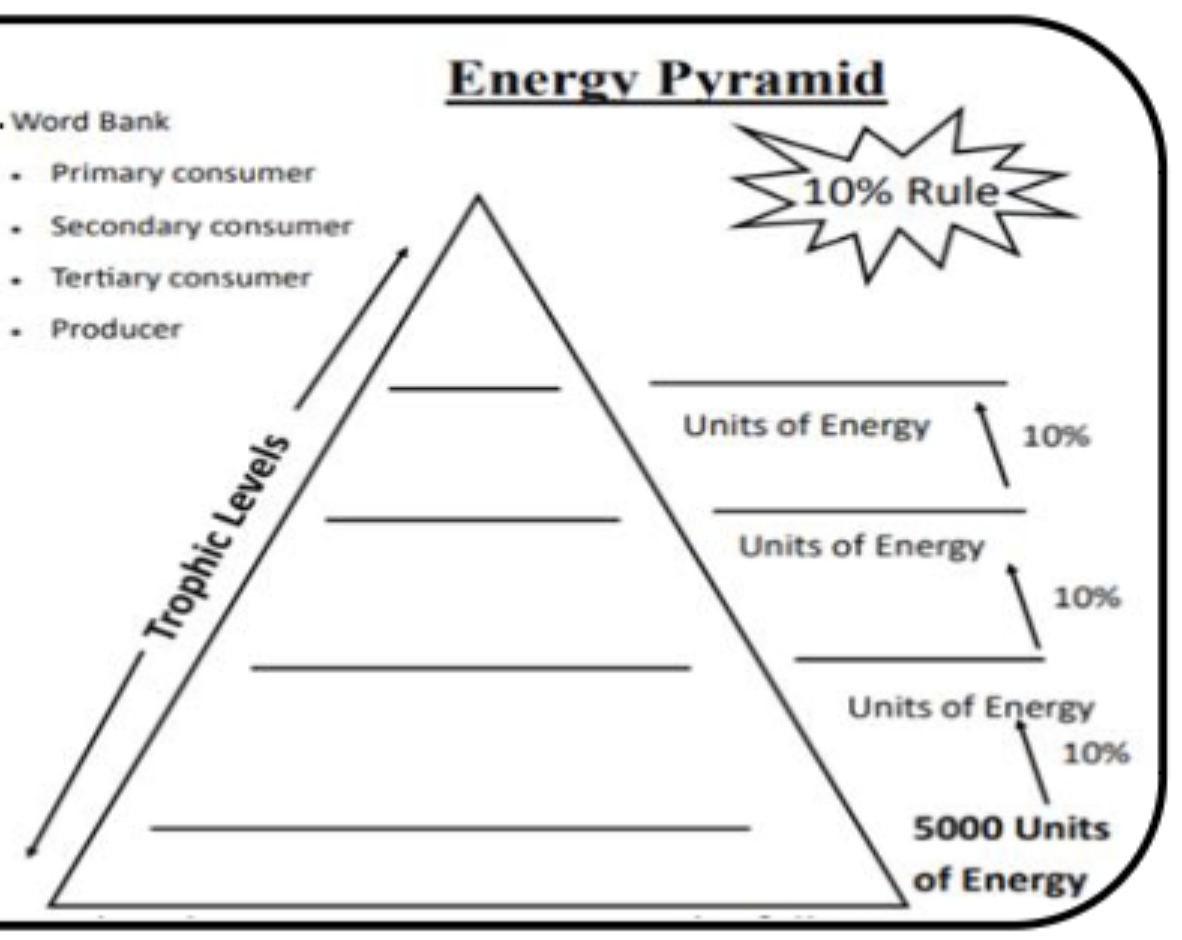
Which categories are predators:
Secondary Consumers
Primary Consumers
Definition of a Biotic Factor
A living thing, as an animal or plant, that influences or affects an ecosystem:
Definition of an Abiotic Factor
A nonliving condition or thing, as climate or habitat, that influences or affects an ecosystem and the organisms in it:
KEYTERMS:
Ecology
Study of the environment
KEYTERMS:
Biosphere
Global ecosystem composed of living organisms
KEYTERMS:
Community (INTERACTIONS BETWEEN ORGANISMS)
Diverse group of organisms that interact in a common location
KEYTERMS:
Population (INTERACTIONS BETWEEN ORGANISMS)
Group of individually of the same species living and interbreeding within a given area
Ecosystem
(BUBBLE OF LIFE) Consists of plants, animals and other organisms.
Usually ordered in categories using
Food Chains / Food Webs
Habitat
Natural home for an animal / creature
Dichotomous Key
Important scientific tool, used to identify different organisms
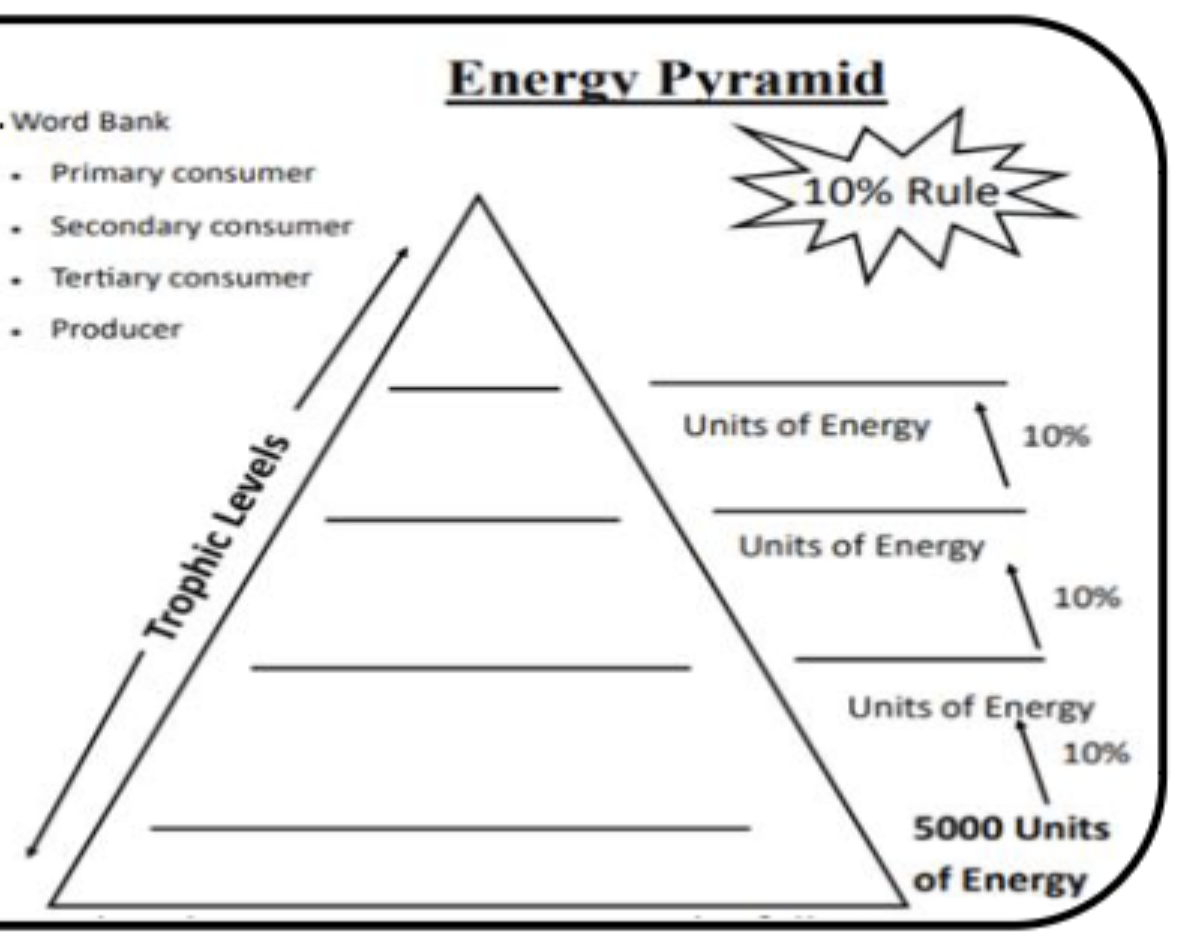
Energy Pyramid
Graphical Representation of the energy found within the tripod levels of an ecosystem
Deforestation
Loss of trees
Habitat Destruction
Food Chain
Consists of Producers, Consumers, etc…
Food Web
Consists of multiple food chains in 1 graphical representation
Producer
The beginning stage of a food web
Energy is received from the sun
Consumer
An organism that cannot produce its own food
Herbivore
Plant - eaters
Carnivore
Meat - eaters