energy resources - non-renewable energy resources
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
What are energy resources
Fuels or resources which can be processed or harnessed to provide useful energy for humans
In what ways do energy resources vary
Their accessibility and abundance
The amount of useful energy derived
The energy lost in transformations
The energy required to harness, extract, process, and redistribute them
What are fuels
Substances containing chemical energy that is released when oxidised, most commonly through combustion
Can fuels be reused once they are consumed
No, once a fuel is used, it cannot be used again
Why does society need energy resources
To facilitate many activities in industry and in homes
What are the two types of energy resources
Renewable
Non-renewable
What are non-renewable energy resources
Sources that exist in limited deposits and cannot be replaced within timescales relevant to human lifetimes
Why are non-renewable resources considered finite
They take very long geologic timescales to be replaced and are being used faster than they are being formed
What are examples of non-renewable energy resources
Fossil fuels (coal, natural gas, petroleum)
Uranium (for nuclear energy)
Are all reserves of non-renewable resources currently accessible
No, some additional reserves may exist but are not currently accessible
What are the two categories of renewable energy
Infinite resources (inexhaustible regardless of rate of use)
Renewable but depletable resources (sustainable only if usage does not exceed replenishment rate)
What are examples of infinite renewable energy resources
Solar energy
Wind
Tidal power
Wave power
Geothermal energy
What are examples of renewable resources that could be depleted
Hydropower (running water)
Wood
Biofuel
What determines whether some renewable energy sources can be depleted
If their rate of use exceeds their rate of replenishment
What are the two main types of energy resources
Non-renewables
Renewables
What are examples of non-renewable energy sources
Fossil fuels and other non-renewable fuels
What fuels are classified as fossil fuels
Coal
Natural gas
Petroleum.
What are examples of other non-renewable fuels (besides fossil fuels)
Uranium (for nuclear energy)
What are the two categories of renewable energy resources
Infinite energy resources
Finite renewable resources
What are examples of infinite energy resources
Solar
Wind
Tidal
Wave
Geothermal
What are examples of finite renewable resources
Hydropower
Wood
Biofuels
What form of energy does coal use to create electricity
Potential chemical energy
What is the efficiency of coal in creating electricity
25% – 30% efficient
What is a positive of coal as an energy resource in Australia
Ample reserves, existing infrastructure, provides 85% of Australia’s electricity, and is one of Australia’s largest export commodities
How are fossil fuels like coal formed
From organic matter accumulated in shallow sedimentary basins, compressed over millions of years through geologic processes
What types of coal exist as fossil fuels
Lignite (brown coal) and anthracite (black coal)
How is coal usually mined in Australia
In open-cut mines
Is coal renewable or non-renewable
Non-renewable fossil fuel
What percentage does coal contribute to the enhanced greenhouse effect
45%
What environmental impacts are associated with coal mining
Mining is physically destructive and releases methane
Why do coal power stations need large quantities of water
For cooling
What kinds of air pollution are caused by coal power generation
Sulfates and nitrates
How reliable is coal as an energy source
Highly reliable
How much electricity does coal currently provide
~85% of Australia’s electricity and ~38% of the world’s electricity
How is energy produced from coal
Coal is combusted in a furnace to create steam, which turns a turbine. The turbine drives a generator that produces an electrical current
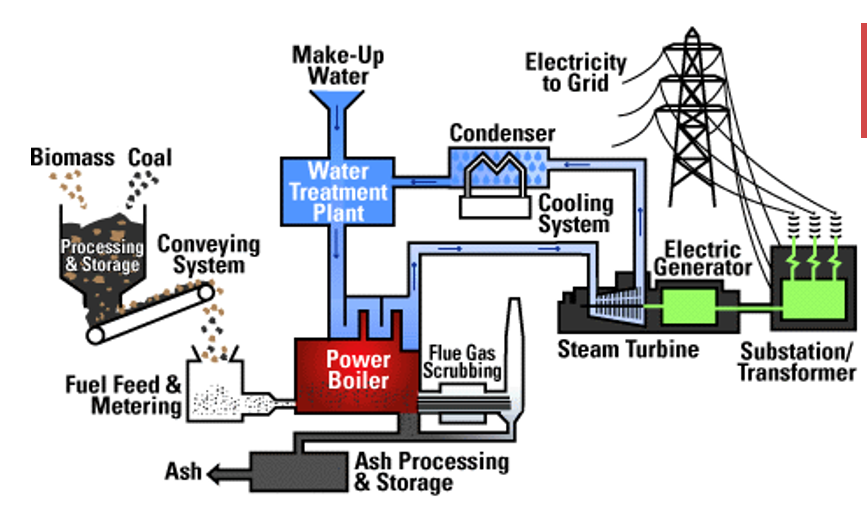
How is the electricity from coal power stations distributed
Sent along high-voltage, low-loss power lines and provided to housing and industry at appropriate levels
What are the economic aspects of coal power
Expensive to establish but relatively low cost to run
How long are the estimated coal reserves expected to last
Approximately 250–1000 years
How is coal formed
From thick layers of plant matter altered by decay, heat, and pressure
Where are the largest coal reserves in Australia located
Queensland, New South Wales, and the Latrobe Valley of Victoria
What happens to coal as you move down through the layers of formation
Pressure and heat increase, which increases the heat content of the coal type
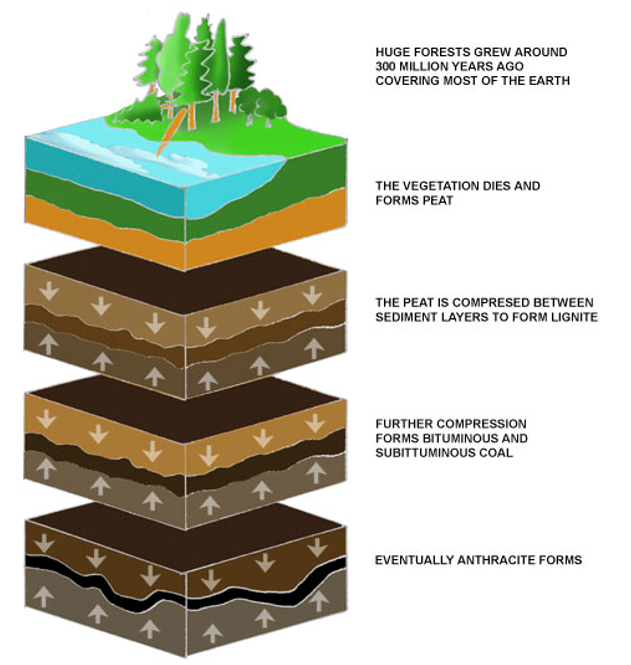
How does the energy content of oil compare to coal
Oil has a higher energy content than coal
How does oil combustion compare to coal in terms of pollution
Oil produces less pollution than coal during combustion
What products are formed from crude oil through distillation
Bitumen
Diesel
Kerosene
Petrol
Other fuels/substances
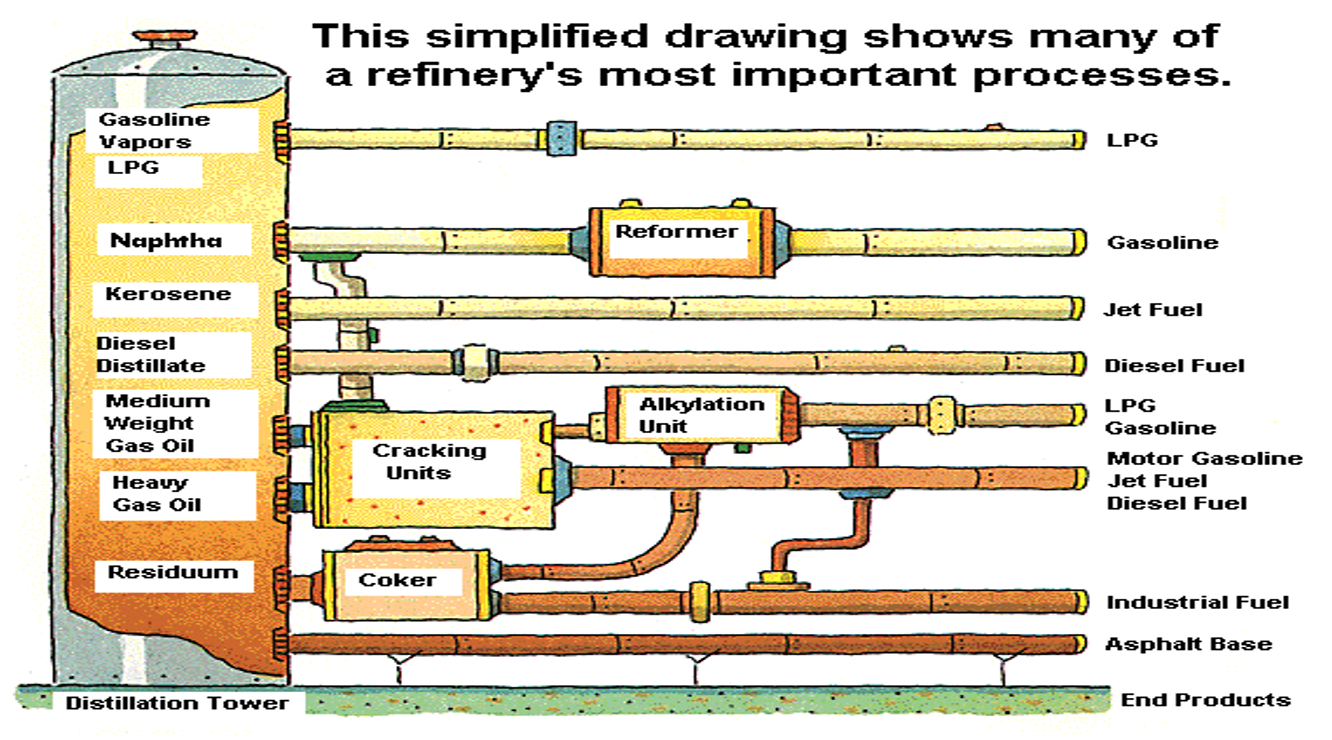
Where are major oil reserves located in Australia
Northwest Shelf of Western Australia and Bass Strait
How is crude oil processed
In a refinery to produce fuels and other useful substances
What are the main uses of crude oil
Transport, some heating, and industrial processes
How much of the crude oil reserves are estimated to remain
Approximately a 50-year supply
What are the economic aspects of oil power/usage
Expensive to establish but relatively low cost to run
How dependent is the world on crude oil
Highly dependent; it currently provides most power for transport worldwide
How is crude oil formed
Buried marine organic materials are transformed into petroleum products by intense pressure and heat in rock formations

Is crude oil renewable or non-renewable
Non-renewable fossil fuel
What percentage does crude oil contribute to the enhanced greenhouse effect
35%
Where are natural gas reserves usually found
Usually above oil deposits, though in Australia some may come from nearby coal beds
Where are major natural gas reserves in Australia
Northwest Shelf of Western Australia and Bass Strait
What is natural gas primarily composed of
Methane, with traces of ethane, propane, and butane
How is natural gas formed
Fossil fuel formed over millions of years from organisms within swamps through geological processes
How is natural gas extracted
Pumped from underground via a rig
What are the economic/infrastructure considerations for natural gas
Pipelines are expensive, so gas is sometimes burnt off instead of used
How clean is natural gas combustion
Quite clean; it produces no “other” pollutants
What are the economic aspects of natural gas
Expensive to establish but relatively low cost to run
How much of the world’s electricity is currently provided by natural gas
Approximately 17%
What is the efficiency of natural gas
30% for electricity generation; 90% for heating
How much of the natural gas reserves are estimated to remain
Approximately a 70-year supply
Is natural gas renewable or non-renewable
Non-renewable fossil fuel
How much does natural gas contribute to the enhanced greenhouse effect
18%
How does natural gas compare in abundance and cost to other energy sources
Less abundant and higher cost than coal, but relatively low cost compared to renewables and uranium
What is coal seam gas (CSG)
Natural gas that collects in underground coal seams and bonds to the surface of coal particles
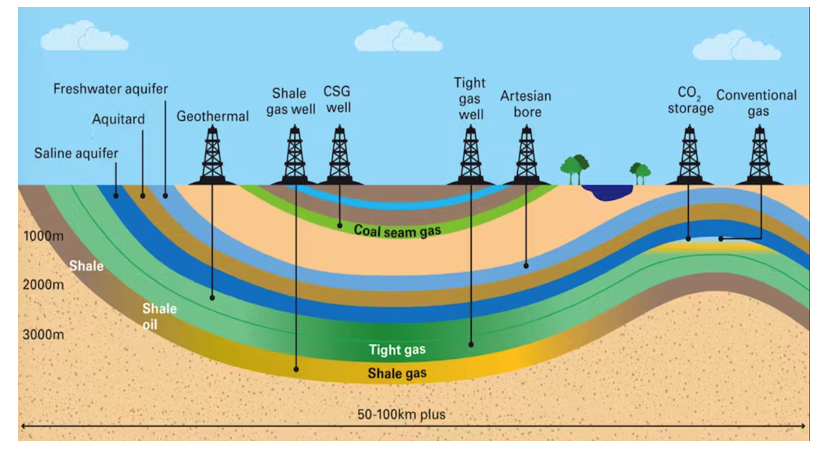
What keeps CSG attached to coal particles
The pressure of water in the coal seams, which keeps the gas as a thin film on the coal surface
At what depths are coal seams containing CSG typically found
Generally at depths of 300–1000 meters
Where are Australia’s largest coal seam gas reserves located
Particularly along the east coast
What is fracking
The process of drilling into the earth and using a high-pressure liquid mix of water and chemicals on sedimentary rock to release gases stored inside. The term refers to the fracturing of the rock
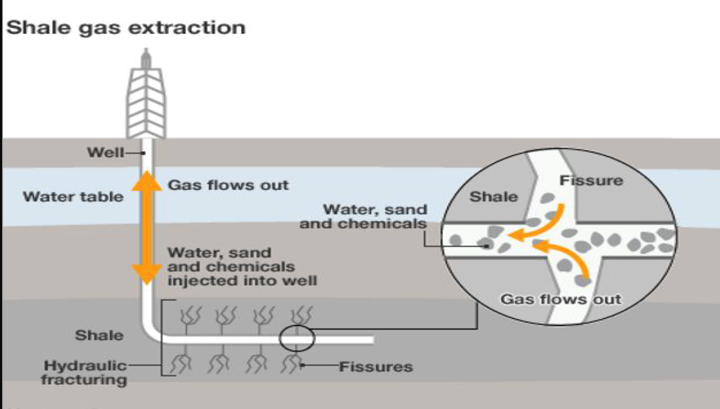
Why is fracking controversial
Environmental concerns include:
Huge water usage and transportation
Potential release of harmful chemicals
Threat of tremors and earthquakes
Why is coal seam gas considered an unconventional gas
Because it requires specialized extraction methods, such as hydraulic fracturing (fracking)
How does hydraulic fracturing (fracking) extract coal seam gas
High-pressure injections of sand, water, and chemicals are used to fracture the coal seam, allowing gas to flow to the surface
What are the major environmental concerns with fracking
Fugitive gases potentially contaminating water sources
Possible seismic activity and tremors
Which Australian states first banned coal seam gas and fracking
Victoria in 2016, followed by Tasmania
Is uranium a fossil fuel
No, uranium is a non-renewable energy source but not a fossil fuel
How is uranium used to produce electricity
Uranium is used in nuclear reactors to produce heat, which generates electricity
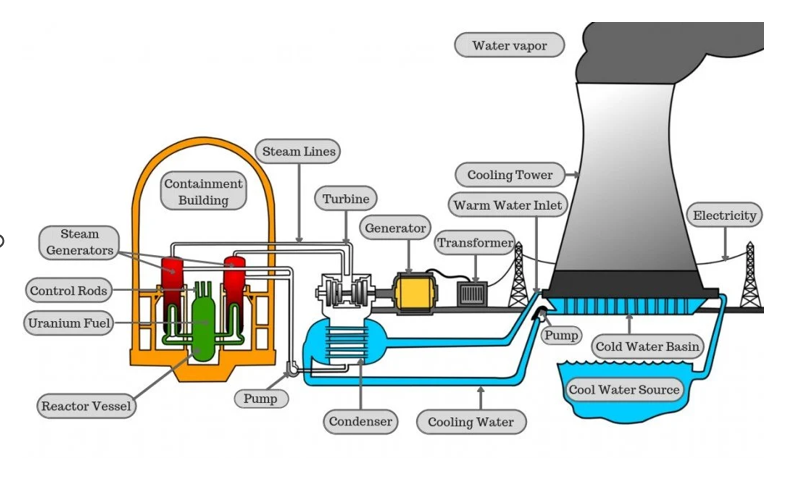
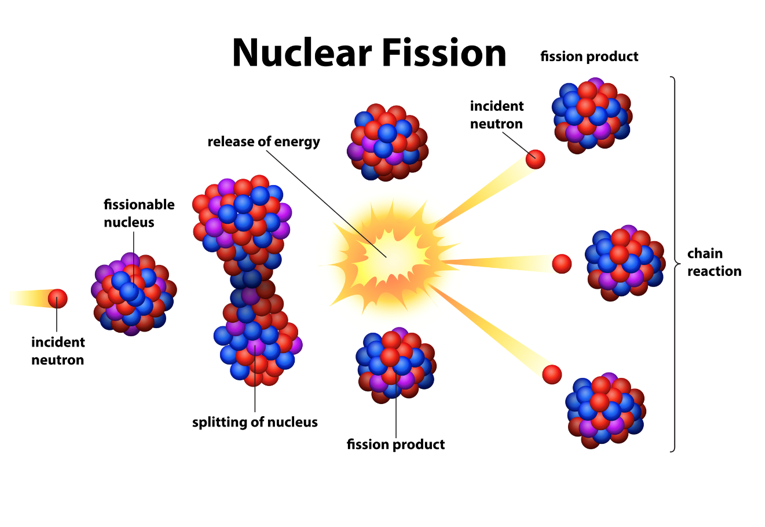
What process releases energy in a nuclear reactor
Nuclear fission chain reactions
How is a fission reaction initiated
By a neutron striking the nucleus of a large atom, causing it to split into smaller nuclei
What happens when the nucleus splits during fission
Energy and additional neutrons are released, which can strike other nuclei and continue the chain reaction
Which uranium isotope can undergo nuclear fission
Uranium-235
What happens to mass during a nuclear fission reaction
A small amount of mass is converted into energy
How efficient is nuclear energy as a fuel source
Highly efficient, with a total energy efficiency of approximately 90%
What is nuclear fusion
A reaction where energy is released when two atoms are forced together
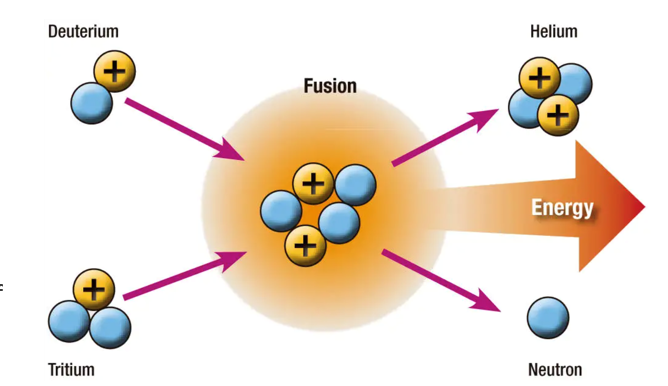
Where does fusion occur naturally
In the Sun, producing solar energy
What is a human-made example of fusion
The hydrogen bomb
Which isotopes are used as fuel in fusion power
Heavy hydrogen isotopes deuterium (hydrogen-2) and tritium (hydrogen-3)
Why is fusion considered an attractive future energy source
It is clean, sustainable, and the fuel is so abundant it could meet the world’s electricity needs for millions of years
Has controlled fusion been achieved on a large scale
No, controlled fusion has only occurred on a small scale in laboratories, and full-sized reactors are not yet feasible