General Pathology Laboratory Midterm Exam
1/101
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
Morgagni De Sedibus
Who said “Physicians who either performed many autopsies themselves or who regularly witnessed post mortem examinations, learnt at least to have their doubts. Those however, who are not themselves dealing with the very often depressing findings of autopsy material are floating in the clouds of uncontrolled optimism.”
The systemic examination of a dead animal.
Definition of Necropsy
The purpose of necropsy is to “answer questions”.
Why perform necropsy?
These are things we know that we know.
There are known knowns.
There are things that we know we don’t know.
There are known unknowns.
There are things we don’t know we don’t know.
But there are also unknown unknowns.
Clothing
Instruments
Fixative and Misc
tools
Necropsy Equipment
10% neutral buffered formalin
4% paraformaldehyde
Zinc Formalin
Bouin’s Fxative
Four commonly used Fixative for tissue processing in histology
Fromaldehyde Solution (37-40%) --- 100ml
Distilled Water --- 900ml
Monobasic sodium phosphate --- 4.0gm
Dibasic sodium phosphate --- 6.5gm
If the phosphates are not available, the acidity can be neutralized by adding calcium or magnesium carbonate to excess.
Preparation of 1 liter of formalin
•Provides information for assessing the effect of the environment and its pollutant on health;
•Use to establish incidence and distribution of zoonotic disease; contributing to control efforts;
•Provides new insights into the cause of death and source of information for establishing the range of manifestations of a disease
•Plays a major role for establishing risk in safety assessment of old and new products
Importance of Necropsy
Immediately after death of an animal
Time for Necropsy
Adrenal medullae
Epithelia of the alimentary tract
pancreas
liver
kidney
nerve cells of the CNS
What are organs that first to show postmortem changes?
water
ventilation
drainage
provision for the cadaver disposal
provision for lowering the chances of contaminatio9n the surroundings
The place of the necropsy should have?
in a laboratory
Where does the examination should be done in case the animal died of suspected transmissible, zoonotic, or exotic diseases?
Incineration
best method for the disposal of small animal cadaver?
Burying deep into the ground
What is the practical method to dispose the cadaver?
away from sources of feed or where underground water is pumped.
The site of the disposal should be?
Case identification
Owner’s identification
Specimen identification
clinical history
necropsy findings
results of laboratory exaination
diagnosis
examiner’s information
The necropsy record consists of?
assigned case number
the case code
date of submission and examination
Case of identification includes?
name
address
phone number
Owner’s identification includes?
species
breed
age
weight
sex
coat
coat color
animal number/name animal classification
specimen identification includes?
details of the clinical findings
signs and symptoms observed
clinical diagnosis
vet name
necropsy request
clinical history includes?
results of the necropsy examination that may be arranged by organs or system or by the sequence of examination
Necropsy findings includes?
includes the samples collected during the necropsy and the results of the examination done
results of the examination includes?
Diagnosis
It is the outcome of the examination
includes the name, qualifications, and signature of the one who did the examination and formulated the diagnosis.
examiner’s information includes?
Be objective
What is the general rule in interpreting lesions?
Interpret the lesions observed than describing the changes seen.
common fault in preparation for a report?
Organs or tissue involved
position
size and shape
weight
color
appearance
consistency
texture or intact and cut surface
odor
Description of the lesion includes (Solid organs)?
organs involved
appearance
texture of intact and opened surfaces
contents, which should be qualifies as to:
Nature
volume/amount
consistency
transparency
colour
odor
Description of the lesion includes (hollow organs)?
few but Very descriptive words as possible
how to describe accurately?
Verbose description
refrain from using_________ in describing that tend to distract attention and no clear meaning.
metric system of notation
How does the weight should be recorded?
concise
grammatically correct
anatomically precise
Description should be?
OBSERVE carefully
DESCRIBE completely
DIAGNOSE confidently
Three steps useful in VetMed?
severity - mild, moderate, marked/severe
Duration - per acute, acute, subacute, chronic, chronic-active
Distribution - focal, multifocal, coalescing, locally-extensive, diffuse, bilateral/unilateral, and others.
nature of lesion
what are the morphologic diagnoses modifiers?
10% neutral-buffered formalin
specimens should be placed in what fixative for subsequent histopathology?
½ cm and 4cm in greatest length of diameter
specimen should be trimmed with a sharp, flat blade to a thickness of_____?
poor fixation with autolysis continuing after placement of fixative.
Inadequate volume of formalin or oversized specimens result in?
Pieces of liver, kidney, urine, stomach contents
Eye fluid for nitrite poisoning
poisoning is undetermined of origin, 2 ounces of stomach
contents, urine, blood, liver, and kidney contents should be
collected.
Collection and Submission of Specimen for Toxicologic Analysis
Heart, Blood, cerebrospinal fluid
Collection and Submission of Specimen for Immunologic study
it must be free from bacterial contamination
Tissue specimen are placed in sterile, wide-mouth, cork-stoppered bottles and shipped frozen with dry ice or in 10 t0 20 volumes of sterile 50% glycerine solution refrigerated in transit
Heart, blood serum, and CSF for virus identification are shipped in sterile vials refrigerated with ice
Collection and Submission of Specimen for Virus Analysis
intestinal loop with the mesenteric lymph
nodes
sample any organ with lesion
peritoneal or thoracic fluid
For Bacteriology
2-3ml diarrheic feces for cryptosporidium
Segment of intestine and feces from the rectum for gastro-
intestinal parasites
Parasitology
Obtain and record the animal and/or herd history must be obtained
Do not approach the examination with a preconceived diagnosis.
Make sure appropriate disinfectant is available and be familiar with its use
Observe and collect samples from clinically normal animals first, if applicable
Conduct the examination of live animals with precautions needed to protect attendants, yourself, and other animals from infection or injury.
Examine and collect specimens from live animals not necessarily intended for necropsy. Select animals in various stages of disease.
Obtain permission from the owner to conduct the necropsy
explain the guidelines for pre necropsy
Remove from the kit only what is needed, so that unused equipment will not be contaminated.
Wear rubber boots, gloves, and coveralls. A mask and goggles may be used at your discretion.
Check the TABLE OF SPECIMEN COLLECTION to see what samples are required.
Pre label specimen containers to ensure all recommended specimens will be collected.
explain the preparation for necropsy
Signalment
History and clinical diagnosis
Clinical pathology
External appearance o State of nutrition
Mucus membranes
Body orifices
Gen conformation
Superficial lesions
Hair coat o Parasites
Check lips, gums cheeks, teeth
Preliminary Review and Observation
Decontaminate instruments before cleaning them.
Clean and disinfect all work surfaces.
Decontaminate self (e.g., disinfect and remove boots, gloves, and coveralls).
Record the necropsy finding
Post Necropsy
Obtain history
examine the animal externally
open the body
remove all organs and set aside for detailed examination
examine and sample the organs
write the report
The six steps of routine necropsy
Mild, Moderate, Severe
Types of Severity
peracute, acute, chronic
Types of time
describe what you see and do not use food analogies
what factor you should consider in describing colors?
a ruler
In terms of the sizing, you must use….?
patchy
distribution

multi-focal
distribution
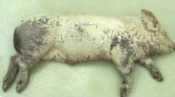
bilateral
distribution
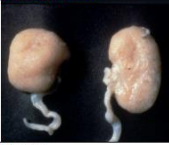
diffuse
distribution

focal
distribution
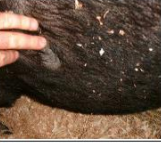
unilateral
distribution

polypoid
shape
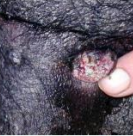
Botryoid
shape
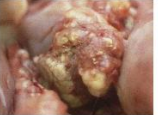
circular-flat
shape

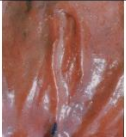
oblong
shape
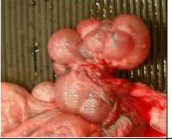
spheroid
shape
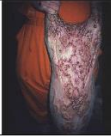
irregular
shape
wedge-shape
shape
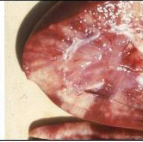
reniform
shape
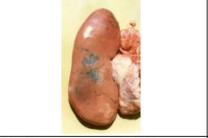
ovoid
shape
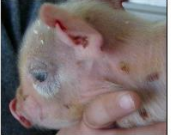
granular
Surface changes
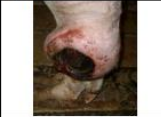
ulcerated
Surface changes
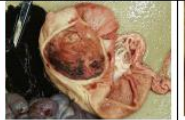
cobblestoned
Surface changes
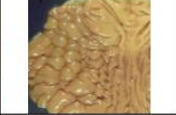
pitted
Surface changes

striated
Surface changes
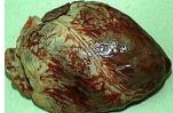
smooth
Surface changes
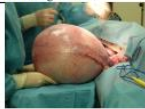
rough
Surface changes

bulging
Surface changes

verrucous
Surface changes

umbilicated
Surface changes
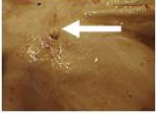
corrugated
Surface changes
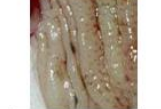
Eroded - skin only
Surface changes

crusted
Surface changes
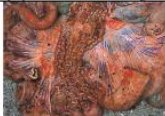
infiltrative
Margin of the lesion
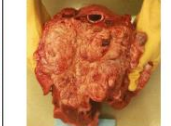
indistinct
Margin of the lesion
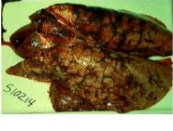
well-demarcated
Margin of the lesion

pendunculated
Margin of the lesion

villous - finger like
Margin of the lesion
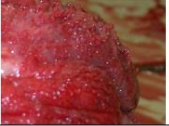
sessile
Margin of the lesion

serpinginous
Margin of the lesion
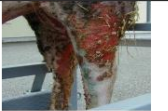
papillary
Margin of the lesion
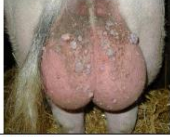
serrated
margin of the lesion
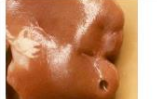
soft
Consistency

friable
Consistency

spongy
Consistency

gritty
Consistency
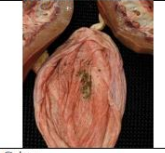
caseous
Consistency
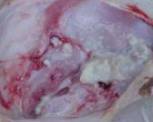
leathery
Consistency
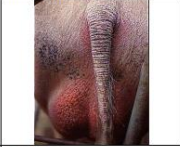
resilient
Consistency

viscous
Consistency
rubbery
Consistency
fluid
Consistency
