Sound Waves Quiz
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Waves transfer ______ through a medium or empty space.
Energy
A section of a sound wave where the particles are crowded together is called a ________
Compression
A substance through which a wave can travel is a ______
Medium
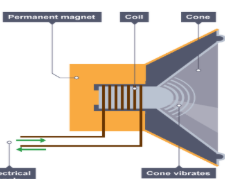
How does a speaker work? Refer to the diagram below.
One of the speaker's magnets is a permanent magnet (meaning that it is always magnetized) and the other is an electromagnet meaning it needs electricity to run through it to work.
When an electrical signal is sent to the speaker, it creates a fluctuating magnetic field that pushes and pulls the coil, (push and pull force) causing it to move back and forth with the attached speaker cone.
The cone vibrates and causes air molecules to collide with each other
transferring energy like a domino effect, until it reaches our ears.
When you increase the frequency of a transverse wave, will the wavelength increase or decrease?
Decrease
Explain how bats locate their insect prey with low and high frequency sound waves. Use the word Echolocation.
Using a process called echolocation, bats emit high-frequency sound waves (ultrasound) that bounce off objects in the environment, and then interpret the returning echoes to determine the location, size, and shape of its prey.
Fill in the blank:
A ______ ruler vibrates more slowly, so has a lower frequency. A shorter ruler vibrates more quickly so has a ______ frequency.
Longer, higher
Energy Wave
disturbances that transfer energy through space or a medium (like water, air, or fields) without permanently moving the matter itself
Sound
vibrations that travel through the air or another medium and can be heard when they reach a person's or animal's ear.
Vibration
something moving up and down
Electromagnetic force
a fundamental interaction governing charged particles, attracting opposite charges (like protons and electrons) and repelling like charges, holding atoms together and creating phenomena from magnetism to light

Label each part of the wave
A = Trough
B = Ampltude
C = Crest
D = Wavelength