American YAWP - Chapter 21
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
An assassination that led to WWI.
Assassination of Archduke Ferdinand

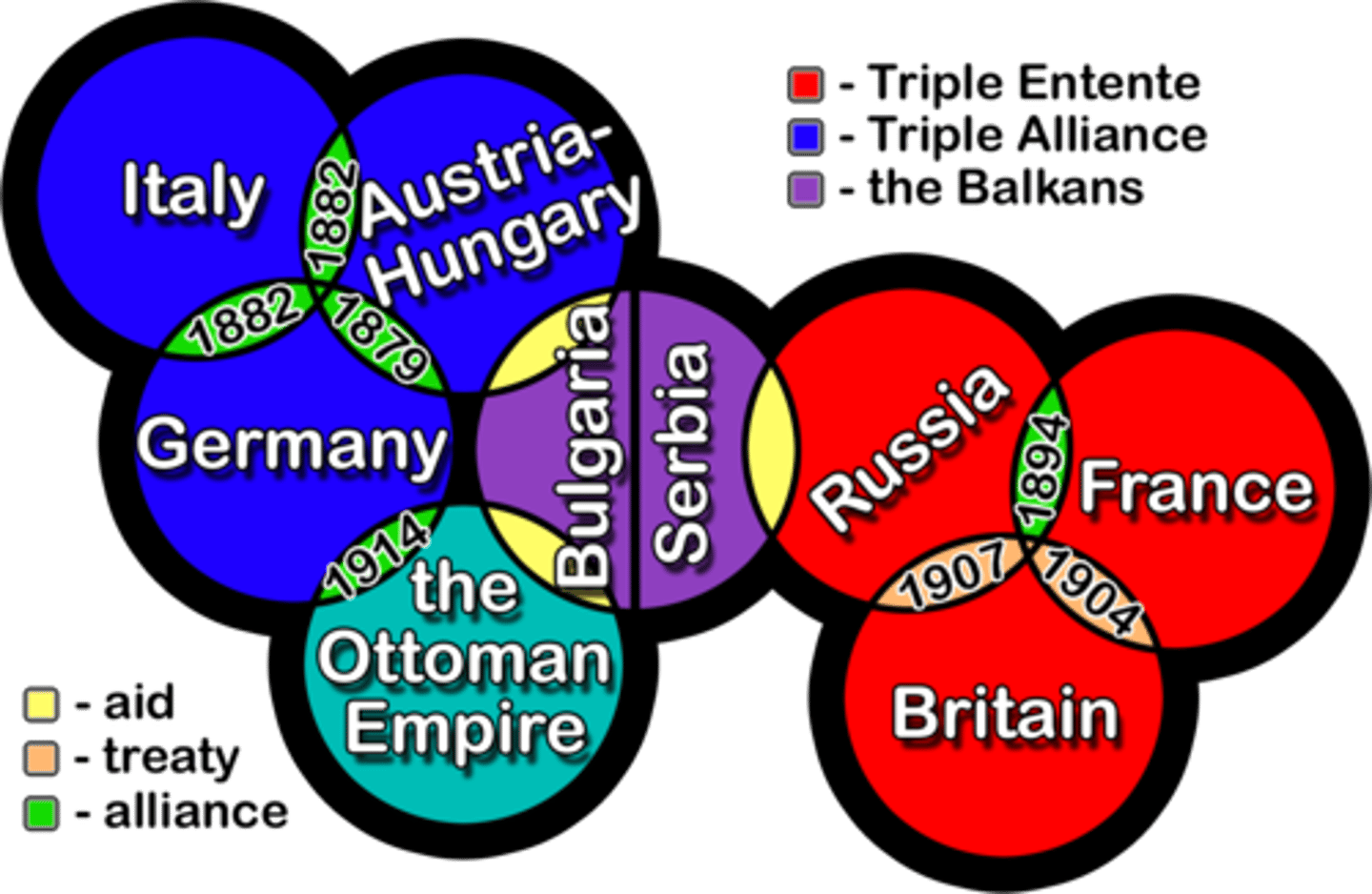
Triple Entente
A military alliance between Great Britain, France, and Russia in the years preceding World War I.

Neutrality
A position of not taking sides in a conflict

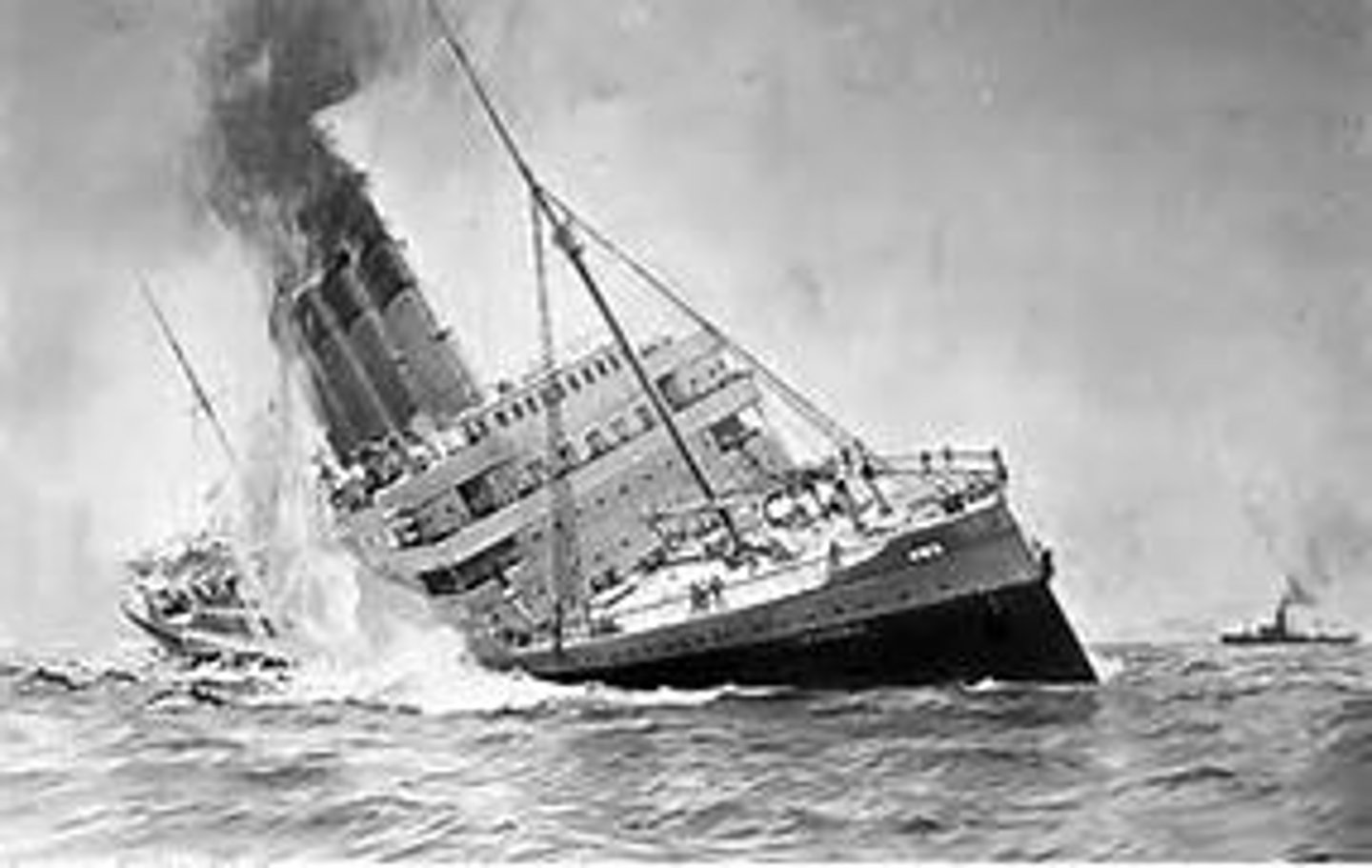
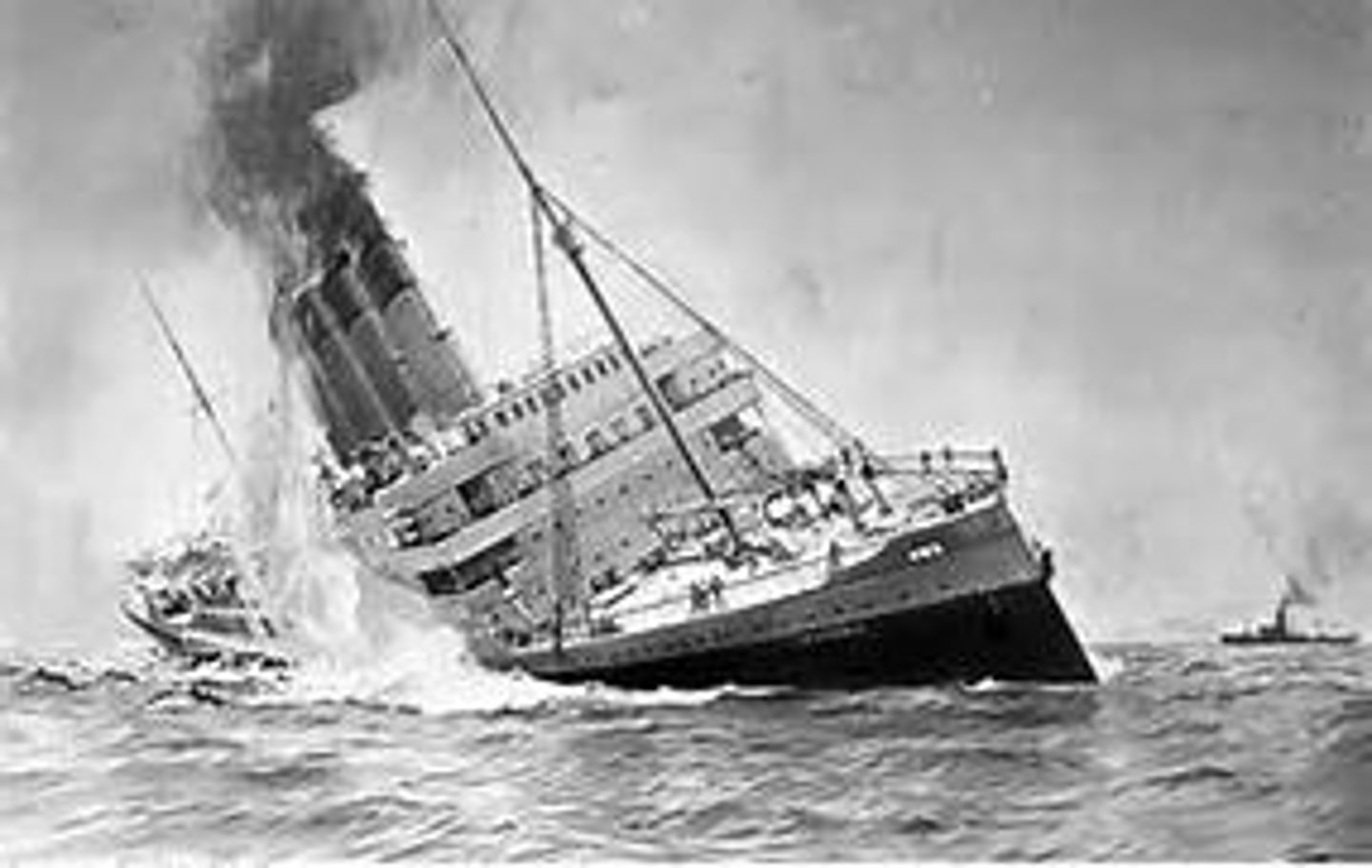
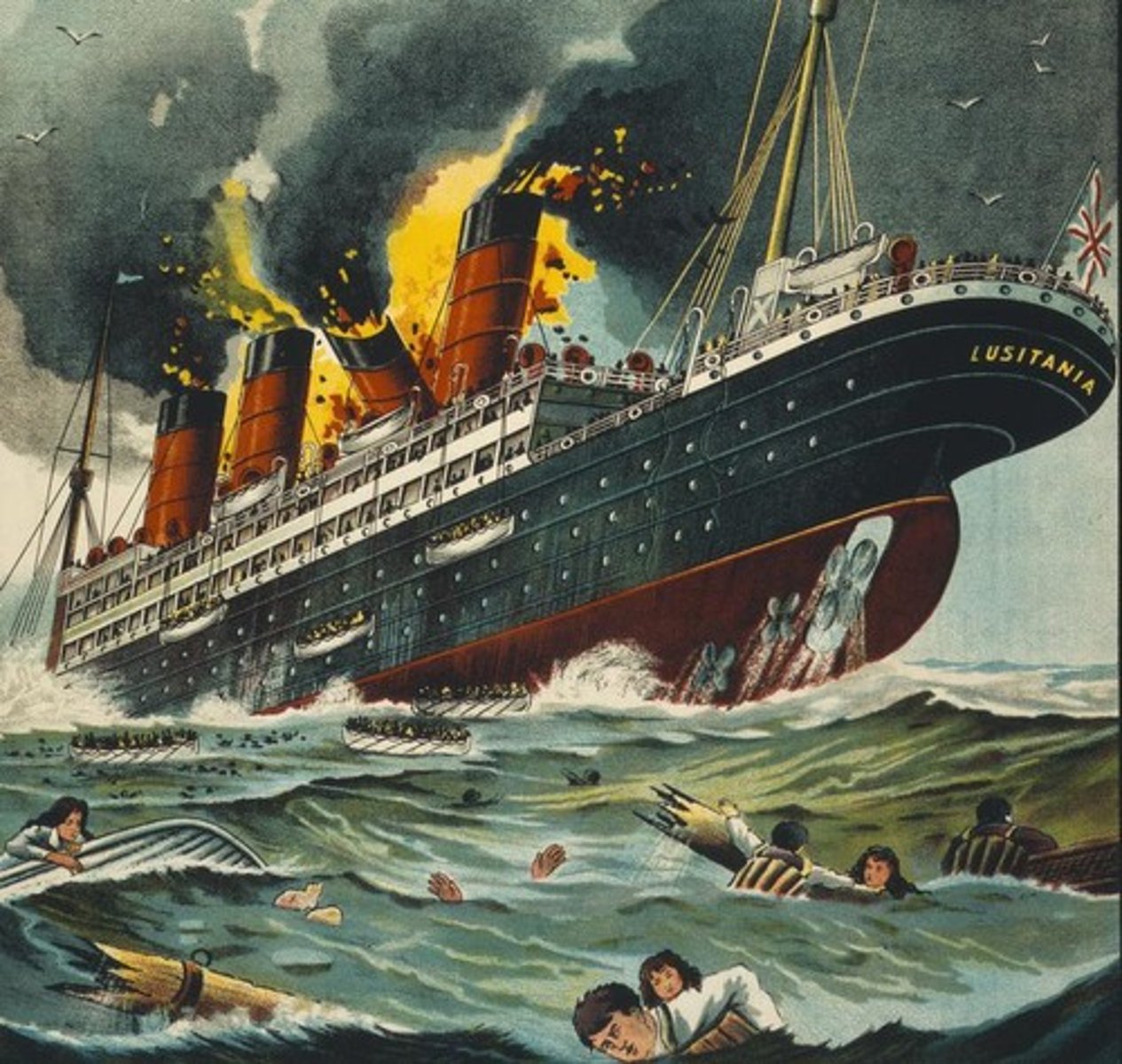
Sunk in 1915 by a German submarine. 139 American killed. Forced Germany to stop submarine warfare.
Lusitania (1915)

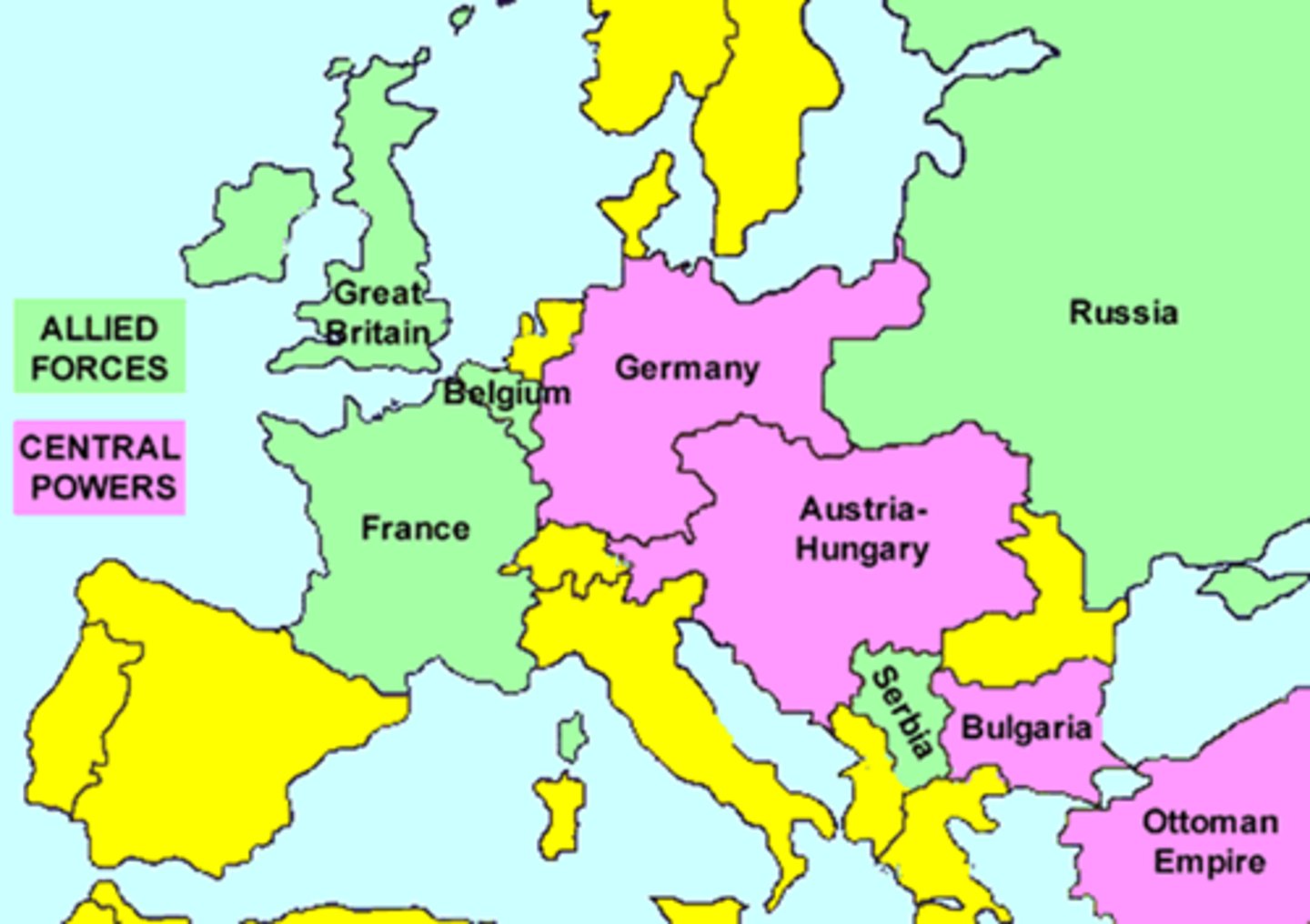
Great War (= World War 1)
A name originally given to the First World War (1914-1918).
Causes of the Great War
Militarism, Alliances, Imperialism, Nationalism
Causes of U.S. entry into war
1. Sinking of RMS Lusitania
2. The Zimmerman Telegraph (a german diplomat that tried to get Mexico to start a war with the US - offer Germany support- to ensure US will not enter the war.

Trench Warfare
A form of warfare in which opposing armies fight each other from trenches dug in the battlefield.

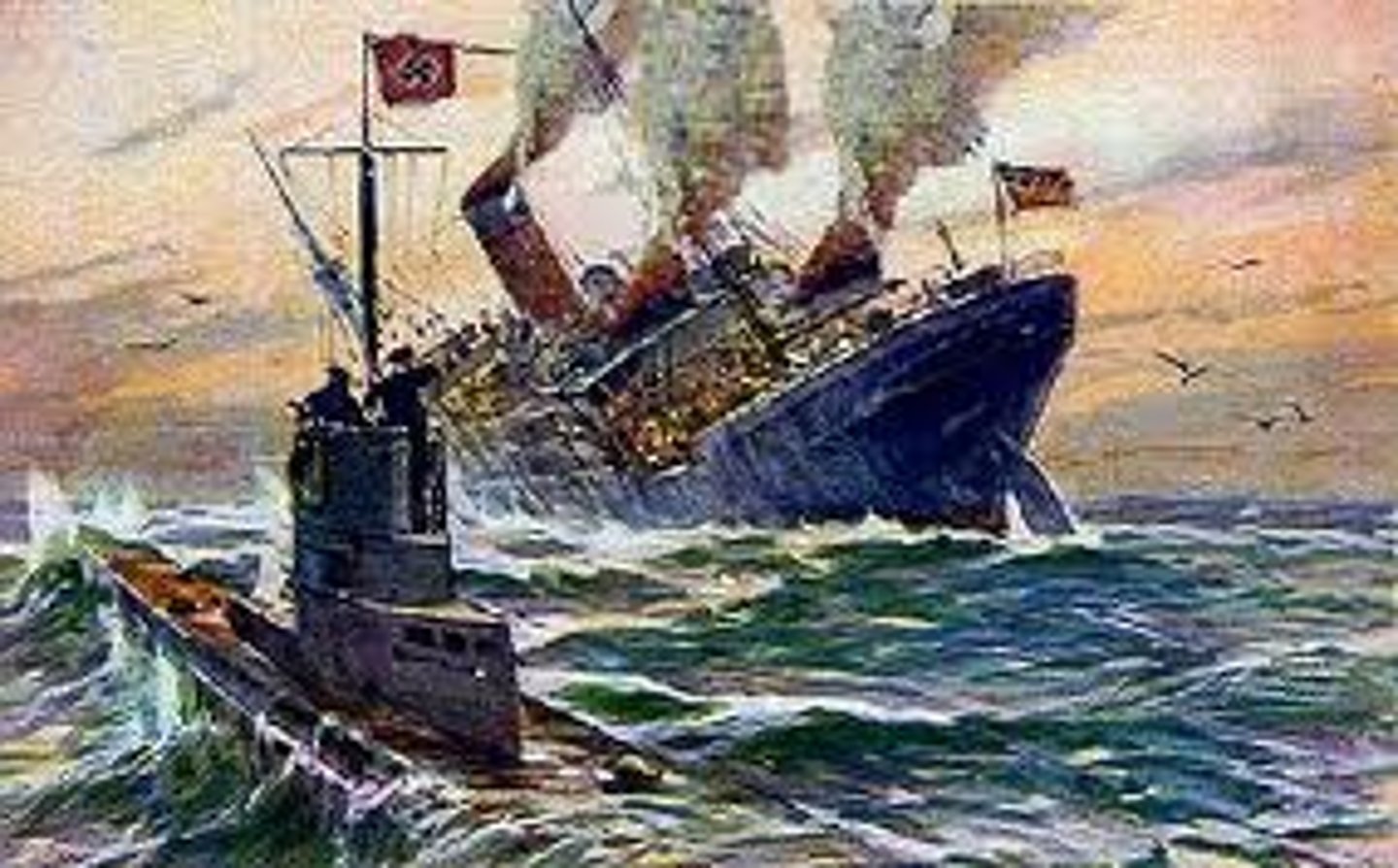
Submarine Warfare (U Boats)
Used during World War I mainly between German U-Boats and Atlantic supply convoys for Great Britain

Zimmerman Telegram/Note
A coded message sent by Germany to try to get Mexico to attack the US

Draft (Selective Service Act)
Required men to register with the government in order to be randomly selected for military service

Nativism ("hyphenated Americans")
Favoring the interests of native-born people over foreign-born people.

Committee on Public Information (CPI)
The government organization that produced propaganda to build support for the war

American Protective League
Made the "Hate the Hun" slogan, nativist groups would take out prejudices on "disloyal" minorities

Espionage and Sedition Acts
Two laws enacted to impose harsh penalties on anyone a) interfering with or b) speaking against U.S participation in WW1

War Bonds/Liberty Bonds
Certificates sold by the United States government to pay for the war.

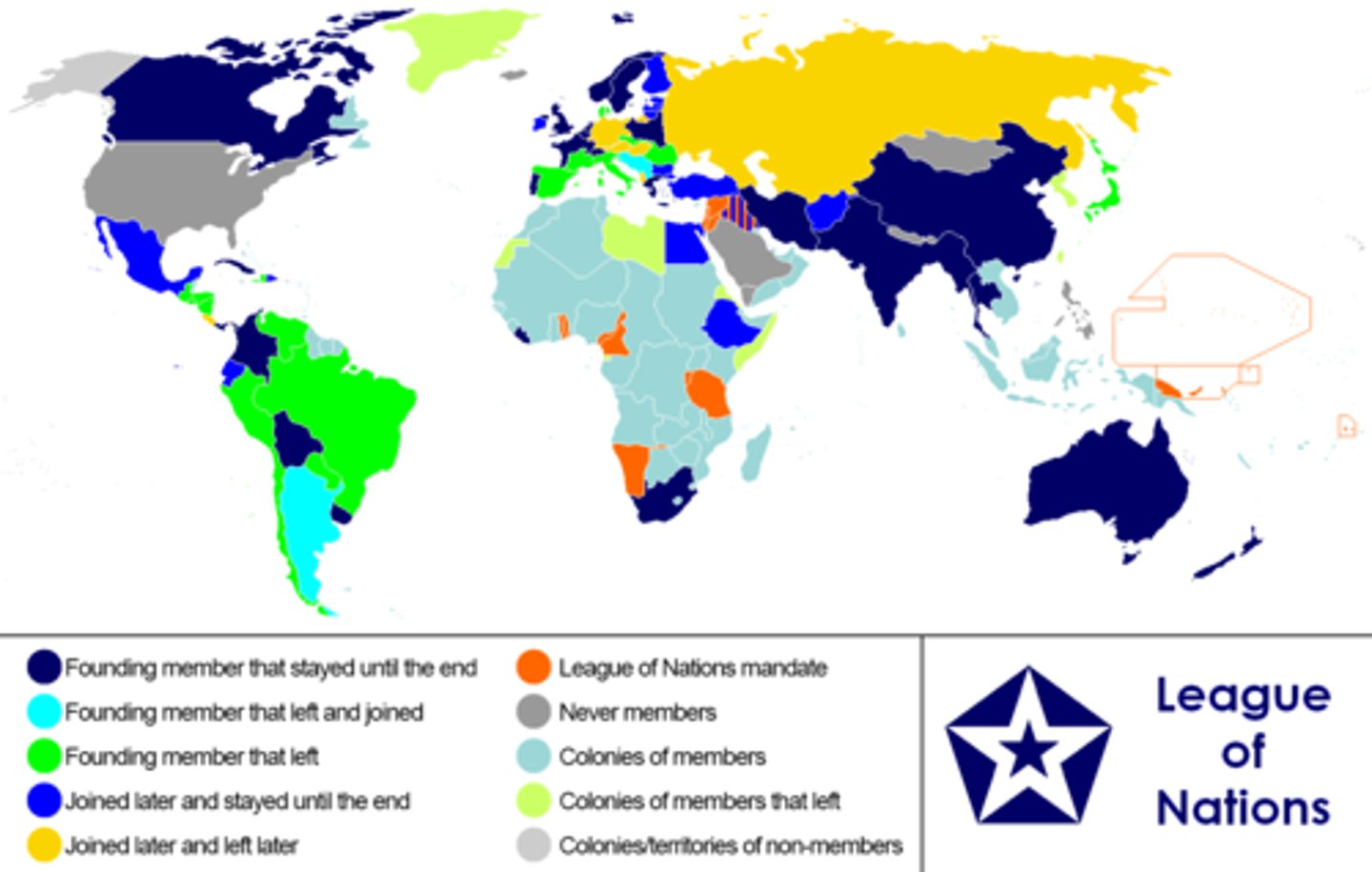
14 Points/League of Nations
President Woodrow Wilson's plan for organizing post World War I Europe and for avoiding future wars. Establish the League of Nations
It was an enlightened statement of war his and peace terms.

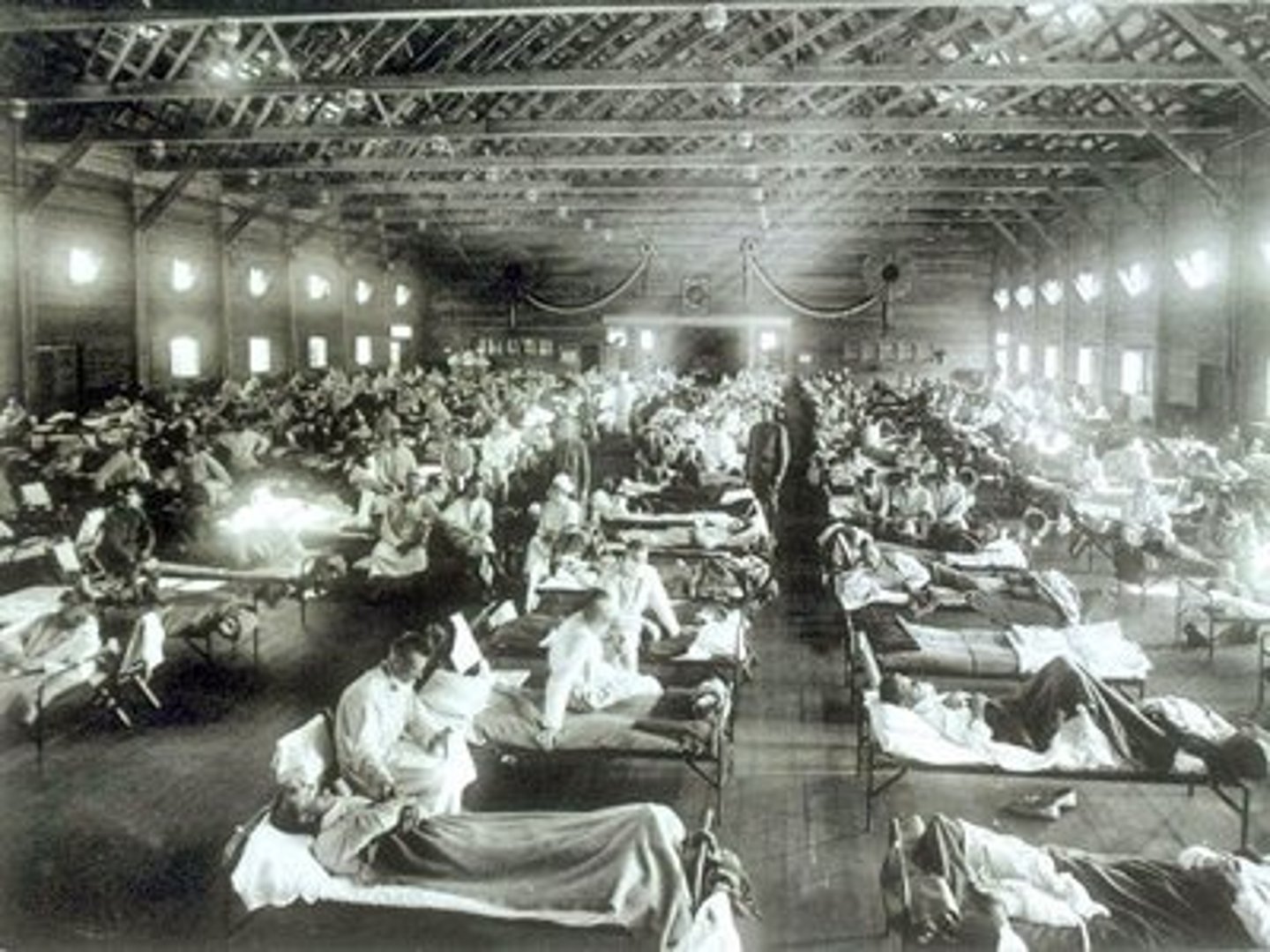
Influenza Pandemic of 1918-1919
Flu-like epidemic that killed more than 20 million people worldwide during 1918 and 1919
Treaty of Versailles
Treaty particularly known for its harsh reparations towards the Germans after World War I.

Red Scare (1919-1920)
A period of general fear of communists.
Fear that communists were working to destroy the American way of life.

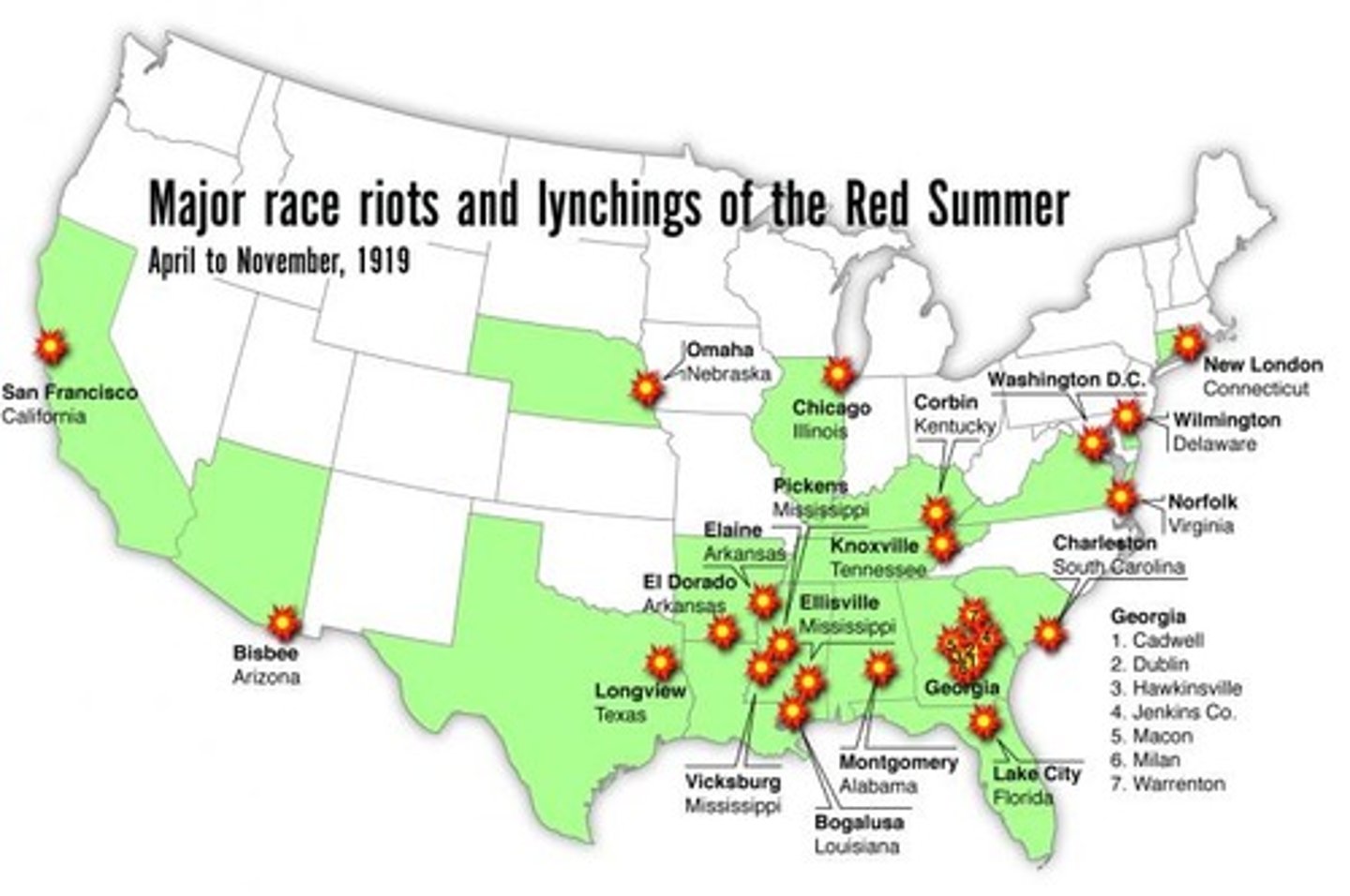
Red Summer of 1919
Racial tension in the post USA war resulted in violence broke down in at least 25 cities, including Chicago and Washington, D.C.
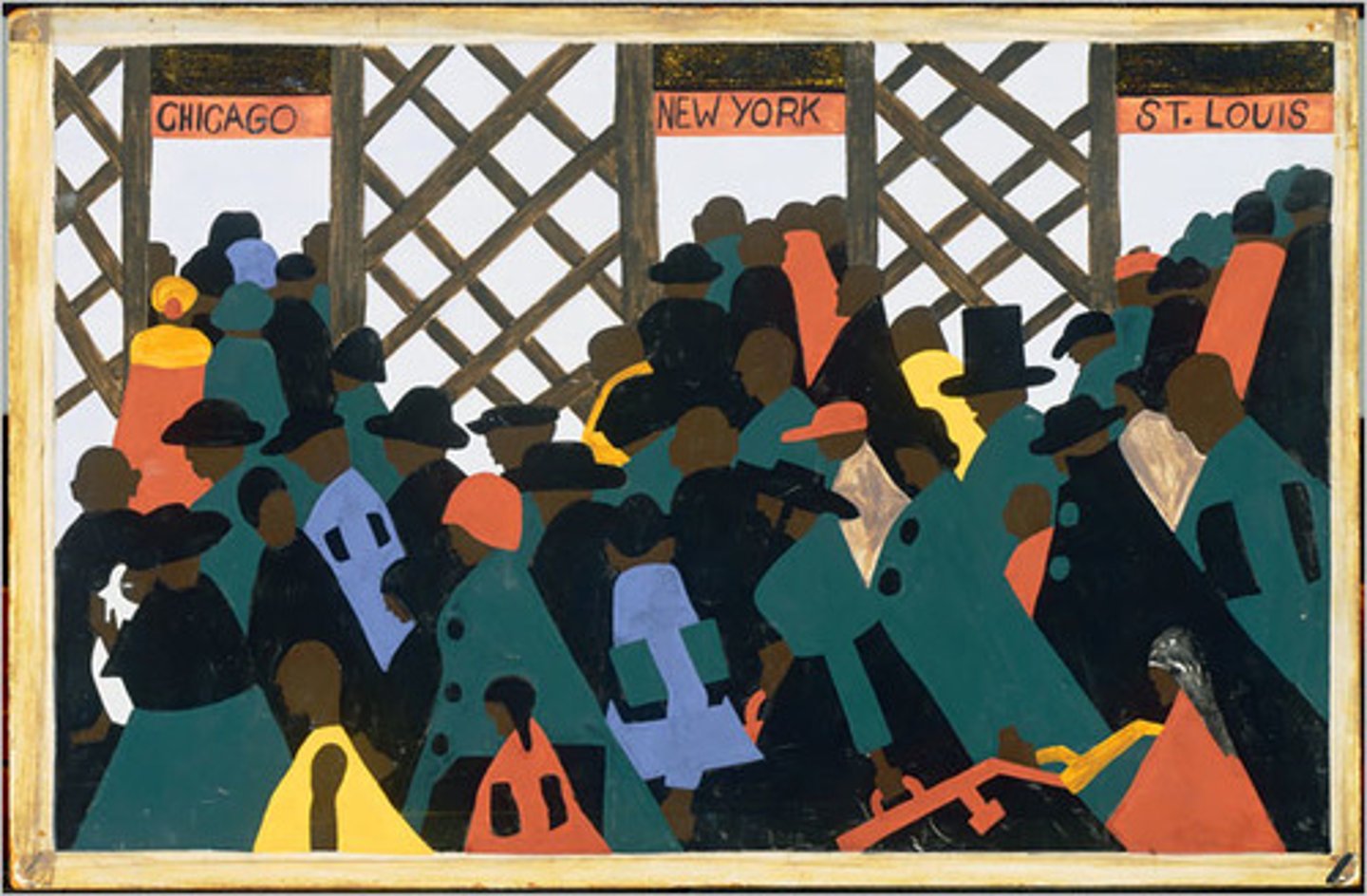
Great Migration
Movement of African Americans from the South to the North for jobs to escape Southern Poverty.

Strikes of 1919
women's walk out
Club women fought for women's rights to be in politics

Race Riots of 1919
Fueled by back Americans demands for equality and withe Americans desire to maintain the status quo (a world that did not include social, political or economic equality for black people).
It resulted in massive bloodshed with thousands of injuries, hundredth of deaths and a vast destruction of public and private property across the nation
Reasons for failure of the Kellogg-Briand Pact (1928)
There were no specific sanctions on nations that broke the pact. It was not possible to enforce the pact.
Woodrow Wilson's Economic Strategy in World War I
Centralized planning in industry. This means the US Government would direct manufacturers for the sake of producing wartime resources. This made a strong relationship with the US government and the US economy.
Kellogg-Briand Pact (1928)
1928 international agreement in which signatory states promised not to use war to resolve "disputes or conflicts of whatever nature or of whatever origin they may be, which may arise among them".
Sanction

Result of immigration laws after WWI
Mexican immigrants began to migrate to northern cities.
Palmer Raids
Raids targeted towards anarchists.

A major cause of United States' involvement in World War I
The sinking of the Lusitania

Indirect outcome of the US entering into WWI
Southern African Americans migrated to Northern Cities

Relationship change between US government and businesses during WWI
US government gave decreased taxes (called tax breaks) to American businesses that served US government programs.

Reason why the US did not economically suffer after WWI
The US had no major battles in it. The war was fought primarily in Europe. US cities were not bombed or burned.
economy
the wealth and resources of a country or region, especially in terms of the production and consumption of goods and services.

United Railway Administration
The government nationalized this railroad system during the war.
Nationalize
To change from private ownership to government ownership
The reason the US did not join the League of Nations
Joining the League of Nations would increase the United State's involvement in its European allies wars and politics.
League of Nations
An international organization formed in 1920 to promote cooperation and peace among nations