C2.2 Neural signalling
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
C2.2.1 Neurons
Brain + spinal cord = Central Nervous System: receive sensory information from receptors, then interpret and process that sensory info. If response is needed, part of brain/spinal cord initiates the response.
Cells carrying info = neurons. Sensory: to CNS, Motor: to Muscles.
Together: peripheral nerves.
Neuron = individual cell carrying electrical impulse from 1→ 2, quickly.
Nerve = many neurons working tg
C2.2.1 Neuron structure
Dendrite (many short fibres) + cell body (nucleus) + axon(long fibre)
At end of axon = synaptic terminal buttons: release neurotransmitters → carry impulse to next neuron/muscle. Impulse carry from dendrite → axon → term.
Around axon = myelin sheath (Schwann cells), nodes of Ranvier (“holes”)
Impulse = action potential. electric (movement of + charged ions)
C2.2.2 Resting potential
Plasma memb restricts ion movement; so conc grad in vs out.
Neurons have membr pot of -70 mV, waiting for impulse transmission.
-70 bc. more Na out than K in so more + out then in
C2.2.3 Action potential
Electric signal = moving ion/electron
Nerve = + ions moving.
Nerve impulse is brief reversal of normal polarization (rest potential -70mV) of neuron membrane bc of facilitated Na+ K+ ion diffusion
Depolarization: Na+ channels open: Na+ into neuron; inside: +40mV
Repolarization: Right after: close Na+, open K+ , back to -70mV
Rebuilding gradients: after; Na+/K+-pump re-establish conc. grad
Propegation of nerve impulse: 1 action potential → another → another
C2.2.4 Variation in velocity of nerve impulses
Schwann cells = insulators → no “movement” of ions
Impulse goes from 1 node of ranvier to the next.
Myelin sheath prevent charge from leaking → faster and less E required
So: thicker + myelinated axons have faster moving impulse.
C2.2.5 Synapses
Synapse = junction between 2 cells in nervous system; signal only passed on 1 direction.
Transmitting neuron: pre-synaptic membrane: terminal (vesicles w neurtransm)
20-40 nm gap - synaptic cleft
Receiving neuron: post-synaptic membrane : dendrites
Chemical substance (neurotransm) transfers signal.
Response = carry signal to muscle or gland cell
C2.2.6 Neurotransmission
Sequence of event transferring impulse prom pre→post.
Action potential arrives at terminal button → depolarized of presyn/mem → take up calcium ions
Ca2+ = signalling chemical → pathway moving vesicles containing neurotrans through cell → vesicle ecocytosis (fuse w presyn membr)
Neurotransmitters released into synaptic cleft
Neurotrans bind w protein receptor on postsyn neuron mem
→ ion channel opening: Na+ diffuse through channel into cell
Initiate action potential to move down post-synapt (depolarized)
Any bound neurotransmitters are released back into cleft → broken down by enzymes
Ion channel in postsynaptic membr close to Na+ ions
Fragments of neurotransm diffuse back across clefs and reessembled (endocytosis) in presynaptic neuron
C2.2.4 Correlation coefficients
Correlation: 2 variables vary tg - interdependent
+ correlation: increase/decrease tg: /
- correlation: one increases while other decreases
correlation coefficient: R: how strong associated:close to ±1=strong correlation
coefficient of determination: R2 : same thing, just more spread
C2.2.7 Excitatory postsynaptic potential
Acetylcholine: neuromuscular junction neurotransmitter.
Acetylcholinesterase: enzyme that breaks down neurotrans in synaptic cleft into fragments that are retaken up by presyn-membrane. Broken down so the action potential only happens once.
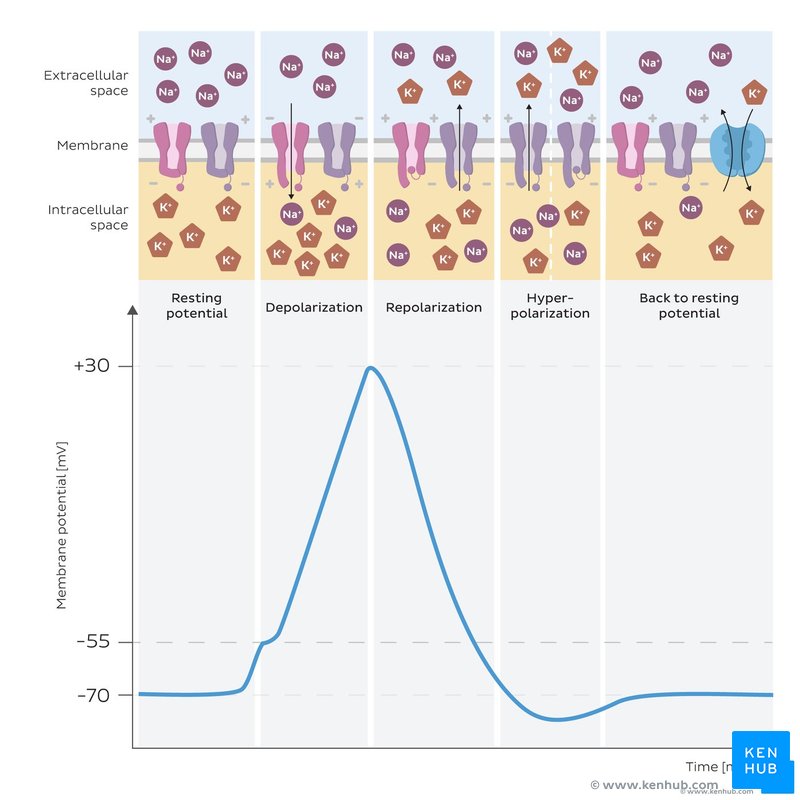
C2.2.8 Depol & Repol during action potential
Action potential is generated when stimulus causes increase in + charged Na+ ions into axon of neuron → depolarization of membr of neuron → action pot move through neuron in wave of depol/repol
Depolarization: voltage gate Na+channel open: 3Na+ into cell: -70mV→+40mV
Repolarization: Na close, K+ open: 2K+ out of cell: +40→-70mV
Hyperpolarization: too much K+ out of cell, -90 mV
Reestablish resting potential: Na+ out, K+ into cell. PUMP not channel:use ATP
In order for action potential to occur: threshold potential = reached: -50mV
C2.2.9 Propagation of action potential
Nerve impulse = action pot traveling from 1 end of axon to next.
Local current = movement of Na+ ions by diffusion between 1 depolarized part
Na+ : move from high conc to lower → local current to make potential less → depolarized area to polarized/repolarizde area
C2.2.10 Oscilloscope: show rest vs action pot
Electronic insturment displaying changes in voltage, see graph for c2.2.8.
C2.2.11 Saltatory conduction
action potentials only occur at nodes of Ranvier (gaps between schwan cells). → speeds up prop of nerve impulse. C
C2.2.12 Exogenous chemicals
Produced outside the body.can have effect on transmission of action.pot in syn
Eg. neonicotinoids + concaine
Neonicotinoid insecticides: similar to nic, receptor of neurot perm blocked; used for death of insects
Cocaine: increases neurotrans action (dopamin) → make happy; addictive
Brain becomes less sensitive to natural reinforces of dopamine.
C2.2.13 Excitatory vs inhibitory neurotransmitters
Excitatory: eg. acetylcholine: generate action pot by increase permeability of postsynaptic mem to + ions. Na+ diffuses into cell. Neuron depolarized → impulse carried forward: -70 → -50 or more
Inhibitory: hyperpolarization of neuron → inhibit action potential → inside of neuron more negative than normal (Cl- in or K+ out)→ inhibit impulse -70→-80
C2.2.14 Summation
Single neuron can form synapses w many other neurons. The more → the greater action potential so greater chance that it occurs cuz threshold overtook.
If both inhibatory and excitatory neurotransmitters → sum of them
C2.2.15 Perception of pain
Neuroreceptors notice change in T, pain(nocireceptor), EM, light, pressure, chemo etc…
Nocireceptors: notice pain: (actual or potential tissue damage). Eg. if you eat chili; they contain capsaicin → trigger opening of ion channel → allow calcium ions into neuron → interprets impulse as pain or heat.
C2.2.16 Consciousness
Conscious = aware. Not actively thinking persé.
Emergent property: different systems work tg.