Bio 2040 - Exam 1
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
population
A group of individuals of the same species that occupy the same environment and can interbreed with one another.
gene pool
All of the alleles for every gene in a population.
microevolution
Changes in the gene pool of a population from generation to generation
diversifying selection
natural selection that favors the survival of two or more different genotypes that produce different phenotypes.
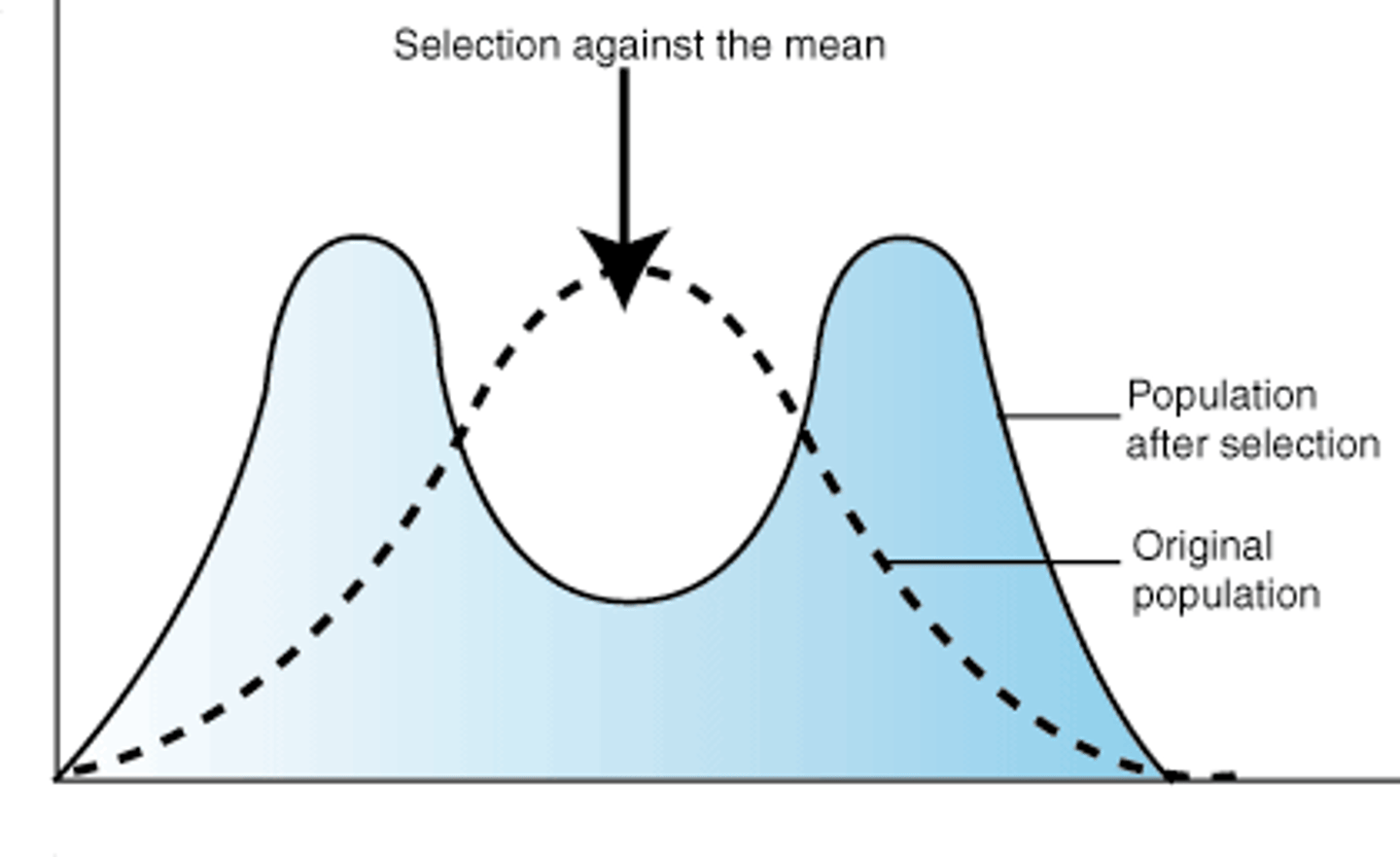
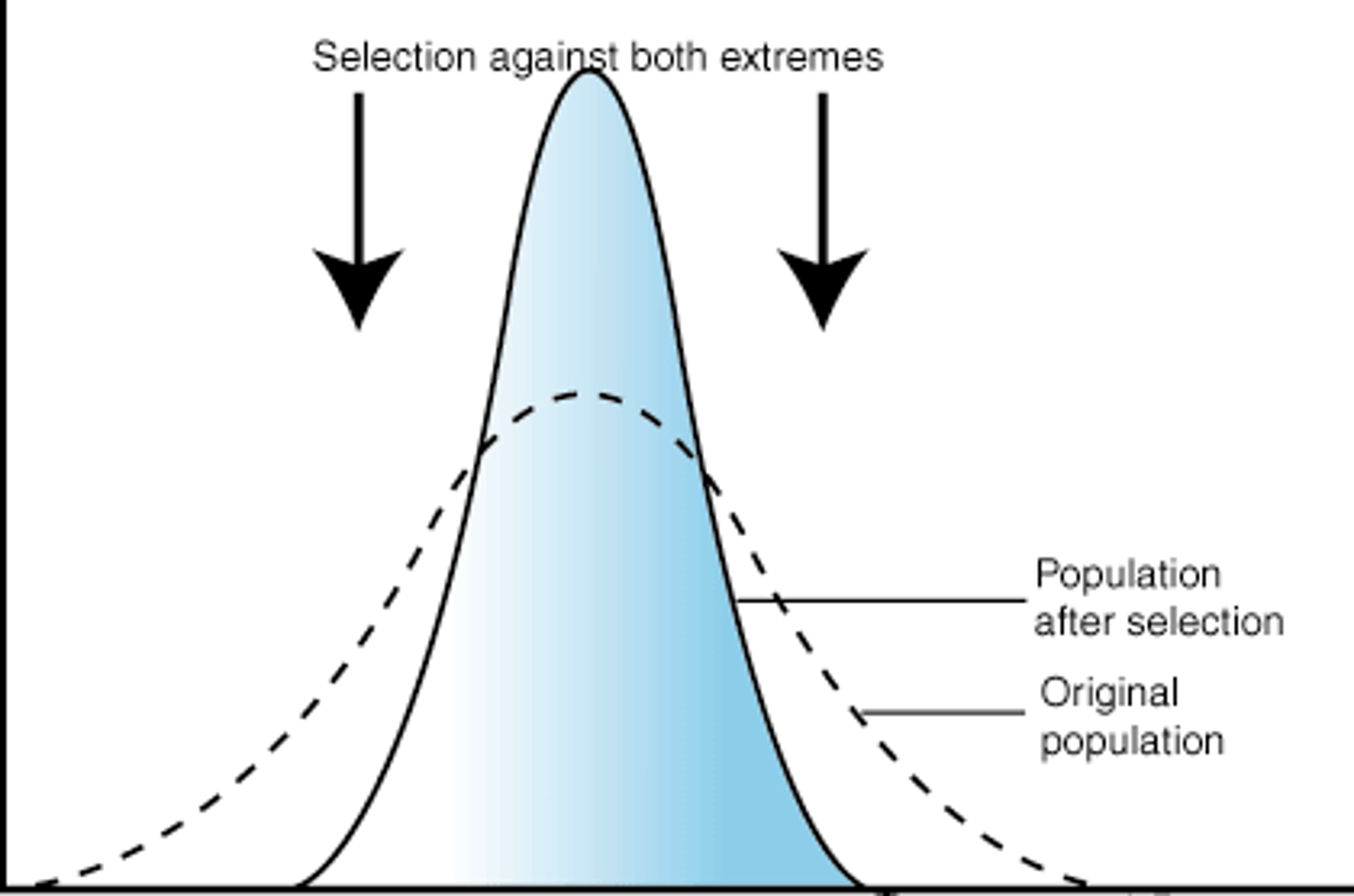
stabilizing selection
natural selection that favors the survival of individuals with intermediate phenotypes.
negative frequency-dependent selection (NFDS)
the fitness of a genotype decreases when its frequency becomes higher
trait
An identifiable characteristic; usually refers to a variant (different shape of seeds: circular or ovular)
true-breeding line
A strain that continues to exhibit the same trait after several generations of self-fertilization or inbreeding.
hybridization
The process in which two individuals of the same species with different characteristics are bred or crossed to each other
cross-fertilization
Fertilization that involves the union of a female gamete and a male gamete across individuals.
single-factor cross
A cross in which an experimenter follows the variants of only one character.
monohybrid
The F1 offspring, of true-breeding parents that differ with regard to a single character.
two-factor cross
A cross in which an experimenter simultaneously follows the inheritance of two different characters. (the 2 traits always show up together)
Mendel's law of independent assortment
The alleles of different genes assort independently of each other during the process that gives rise to gametes. (each pair of alleles segregates independently of each other)
Pedegree analysis/chart
An examination of human traits over several generations in a family as a way to deduce the pattern of inheritance.
sex-linked gene
A gene that is found on one sex chromosome but not on the other.
wild-type allele
A prevalent allele in a population. Dominant
mutant allele
An allele that has been altered by mutation.
incomplete dominance
The phenomenon in which a heterozygote that carries two different alleles exhibits a phenotype that is intermediate.
codominance
The phenomenon in which a single individual expresses two alleles.
gene interaction
1 character is controlled by 2 or more genes, and each gene has 2 or more alleles. (punnet squares)
epistasis
A gene interaction in which the alleles of one gene mask the expression of the alleles of another gene.
discrete trait
A trait with clearly defined phenotypic variants. (Red v.s White eyes)
quantitative trait
traits that show continuous variation over a range of phenotypes (can be affected by environment)
polygenic
Refers to a trait for which multiple genes contribute to the outcome.
endemic
Refers to species that are naturally found only in a particular place or region.
convergent evolution
evolution where 2 species from different lineages develop similar characteristics because they occupy similar environments.
analogous structure
features of different species that are similar in function that evolve due to similar environments and which do not derive from a common ancestral feature
transitional form
An organism that provides a link between earlier and later forms in evolution.
homologous structures
Structures that are similar to each other because they are derived from the same ancestral structure.
vestigial structure
An anatomical feature whose function is reduced or absent but resembles a structure of a presumed ancestor.
homologous genes
Genes derived from the same ancestral gene that have accumulated random mutations that make their sequences slightly different.
polymorphic gene
A gene that commonly exists as two or more alleles in a population.
polymorphism
The presence of two or more variations of a character within a population.
allele frequency
# of copies of an allele/total # of alleles in population

genotype frequency

Genetic drift
A change in genetic variation from generation to generation due to random chance. (Fitness has no effect).
Migration
can occur between two populations that have different allele frequencies.
adaptations
Changes in populations of living organisms that are the result of natural selection and that increase their ability to survive and reproduce in their environment.
reproductive success
The likelihood that an individual will contribute fertile offspring to the next generation.
directional selection
A pattern of natural selection that favors individuals at one extreme of a phenotypic distribution.
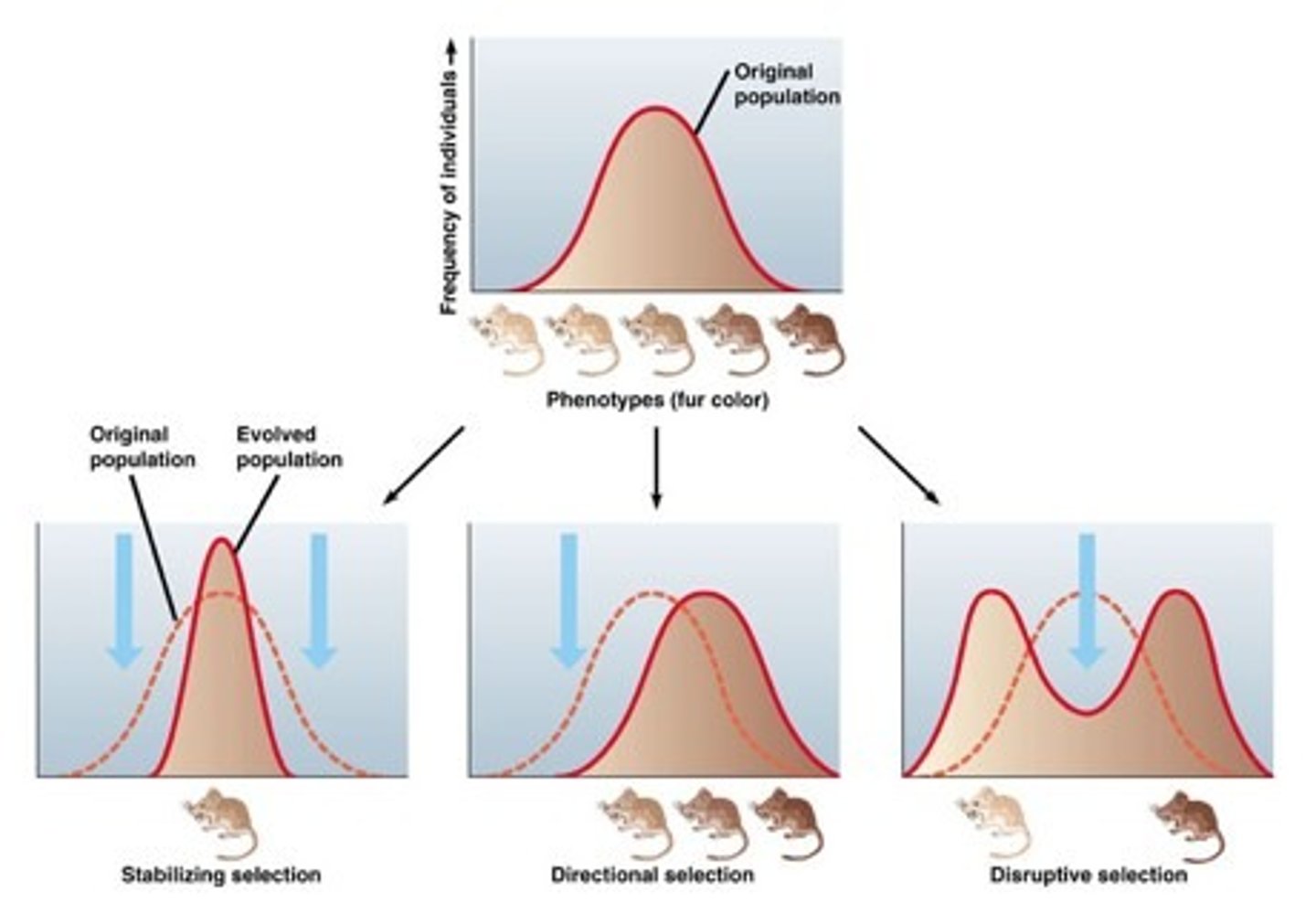
balancing selection
A pattern of natural selection that maintains genetic diversity in a population.
balanced polymorphism
The phenomenon in which two or more alleles are kept in balance and maintained in a population over the course of many generations.
heterozygote advantage
A phenomenon in which a heterozygote has a higher fitness than either corresponding homozygote.
fitness
The relative likelihood that a genotype will contribute to the gene pool of the next generation as compared with other genotypes.
sexual dimorphism
A pronounced difference in the morphologies of the two sexes within a species.
intrasexual selection
Sexual selection that occurs via competition between members of the same sex for the opportunity to mate with individuals of the opposite sex (Bucks with antlers fighting)
intersexual selection
Sexual selection between members of the opposite sex (Female chooses male with brightest feathers)
neutral variation
Changes in genes and proteins that result from genetic drift and do not have an effect on reproductive success.
bottleneck effect
A change in allele frequencies due to genetic drift in a population that has been dramatically reduced in size; this effect can reduce the genetic diversity of the population (natural disaster, hunting, habitat loss)
founder effect
Genetic drift that occurs when a small group of individuals separates from a larger population and establishes a colony in a new location.
nonrandom mating
The phenomenon that occurs when individuals choose their mates based on their genotypes or phenotypes.
gene flow
A transfer of alleles into or out of a population that occurs when fertile individuals migrate between populations having different allele frequencies.
inbreeding
Mating between genetically related individuals.
cryptic female choice
a preventative measure against successful inbreeding (the eggs can deny sperm with similar genetic makeup)
genotype
The genetic composition of an individual.
Evolution
heritable change in one or more characteristics in a population depends on 2 factors - genetic variation and natural selection
Discrete population
species divided by geography
natural selection
beneficial traits that are heritable become more successful through generations