Physics I Lesson 3: Forces
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
CRB Compared to the Kinematics studied last lesson, this one will focus on Dynamics. Which of the following are included in Dynamics?
I. Free Body Diagrams
II. Translational Equilibrium
III. Rotational Equilibrium
(A) I only
(B) I and II only
(C) II and III only
(D) I, II and III
(D) I, II and III
Each of the following are key parts of dynamics.
I. Free Body Diagrams
II. Translational Equilibrium
III. Rotational Equilibrium
CRB Draw a Free body diagram of a box being pushed to the right on a flat surface. Label all forces acting on the box.
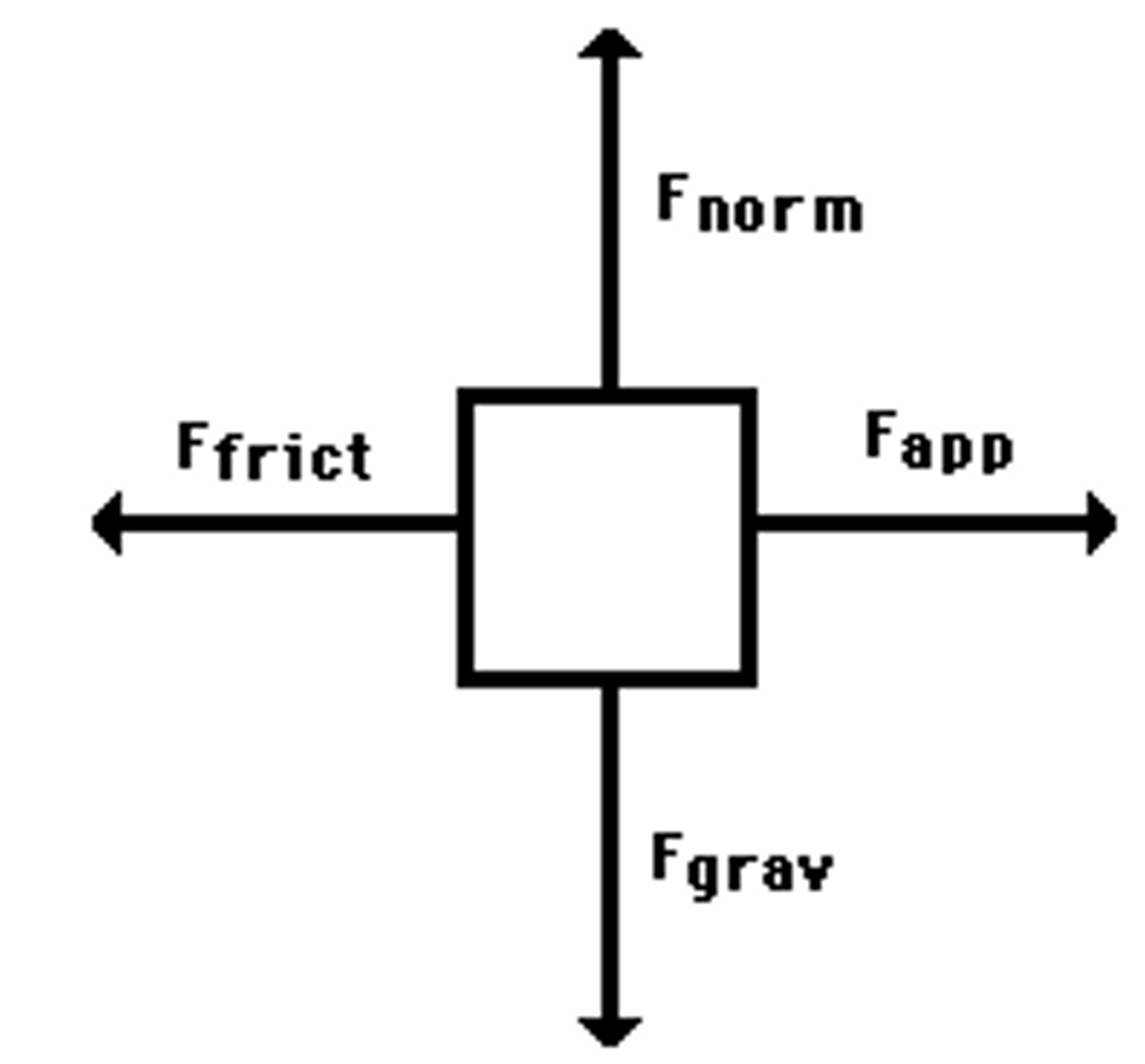
CRB That free body diagram has both vertical and horizontal forces. In which directions would it accelerate? If it would not accelerate in both directions, explain why.
The box will only accelerate horizontally if the force applied is greater than the force of friction. It will not accelerate vertically because the Normal Force and Gravity are equal forces in opposite directions, leaving 0 net force and no possible acceleration.
What is the equation for Torque?
Torque = Force x Distance
(distance is from fulcrum or center of gravity)
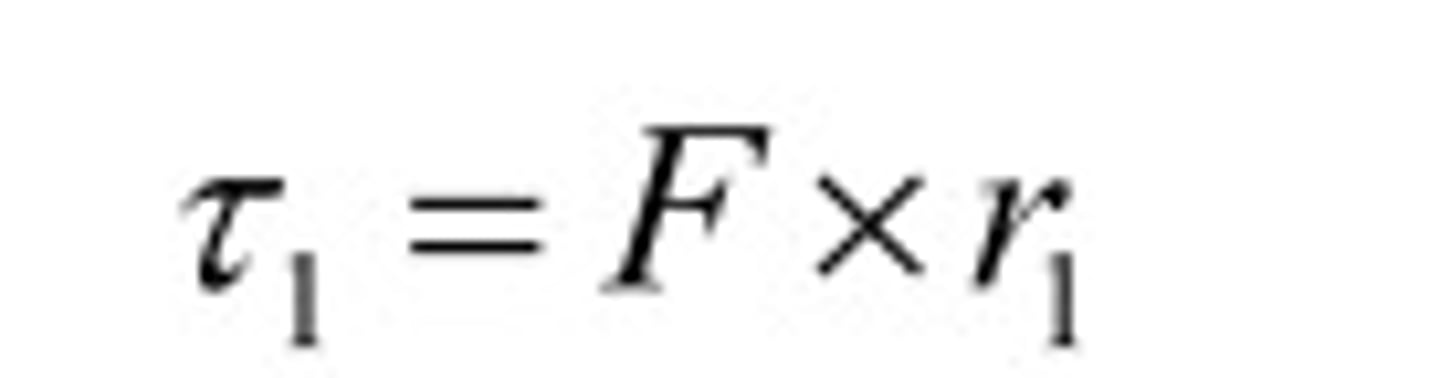
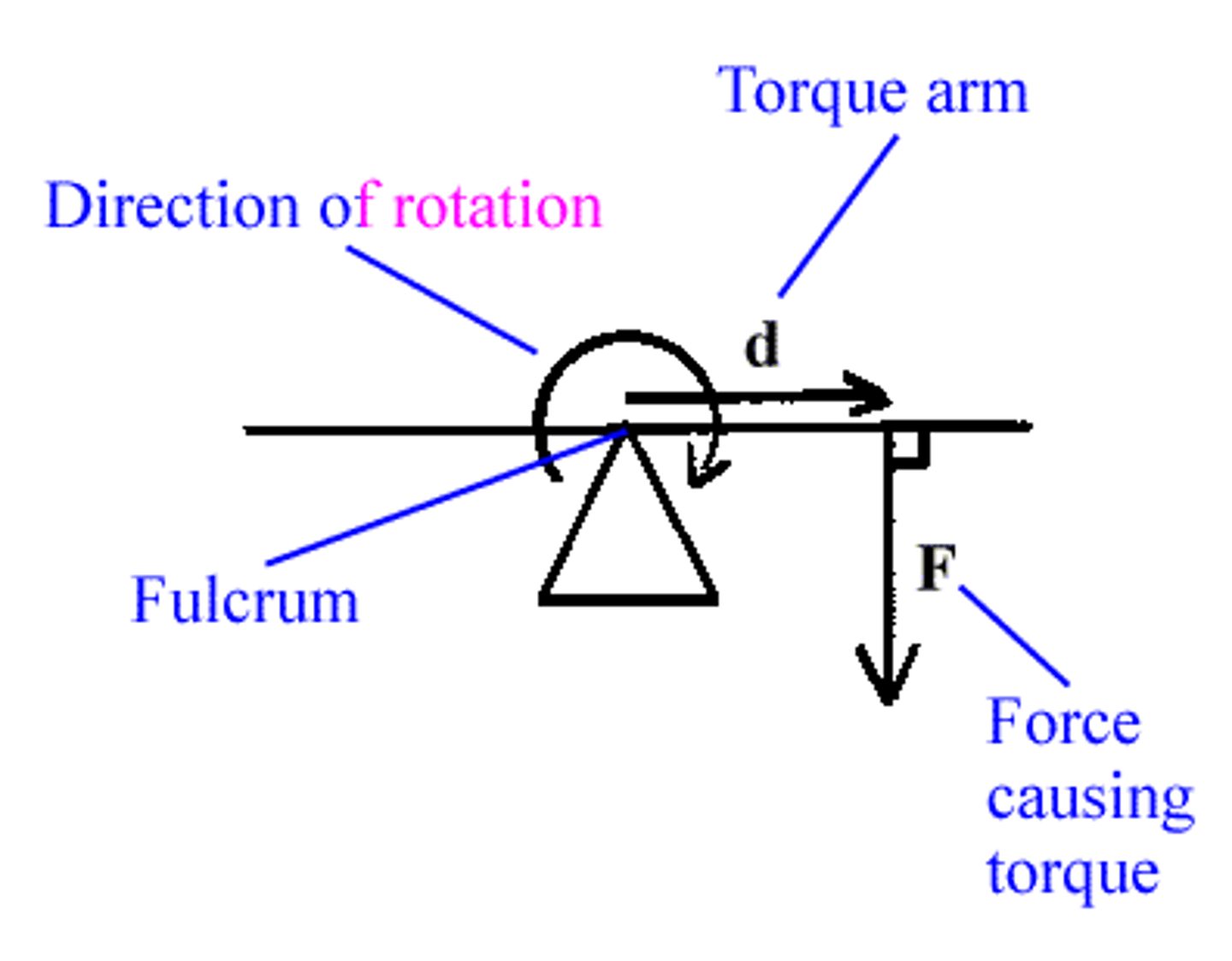
CRB Fill in the blanks: The _______________ is where the center of gravity of the object would be, and the ___________ is the distance from that center of gravity to where the force causing the torque is applied.
(A) Fulcrum, Torque Arm
(B) Fulcrum, Radius
(C) Lever Point, Torque Arm
(D) Lever Point, Radius
(A) Fulcrum, Torque Arm
The Fulcrum is where the center of gravity of the object would be, and the Torque Arm is the distance from that center of gravity to where the force causing the torque is applied.
CRB True or false? The Torque Arm can also be called the Lever Arm.
True. The Torque Arm can also be called the Lever Arm.
CRB Draw out a Free Body Diagram with a clearly labelled Fulcrum, Torque Arm, the force causing the torque, and the direction of rotation.
If a force of 11.32 N is applied at a distance of 6.78 meters from the fulcrum, what is the value of torque (in N·m)?
(A) 34.67
(B) 76.75
(C) 112.45
(D) 165.22
(B) 76.75
Torque = Force x Distance
Torque = 11.32 N x 6.78 m
Torque = approx. 70 N·m (actual: 76.75)
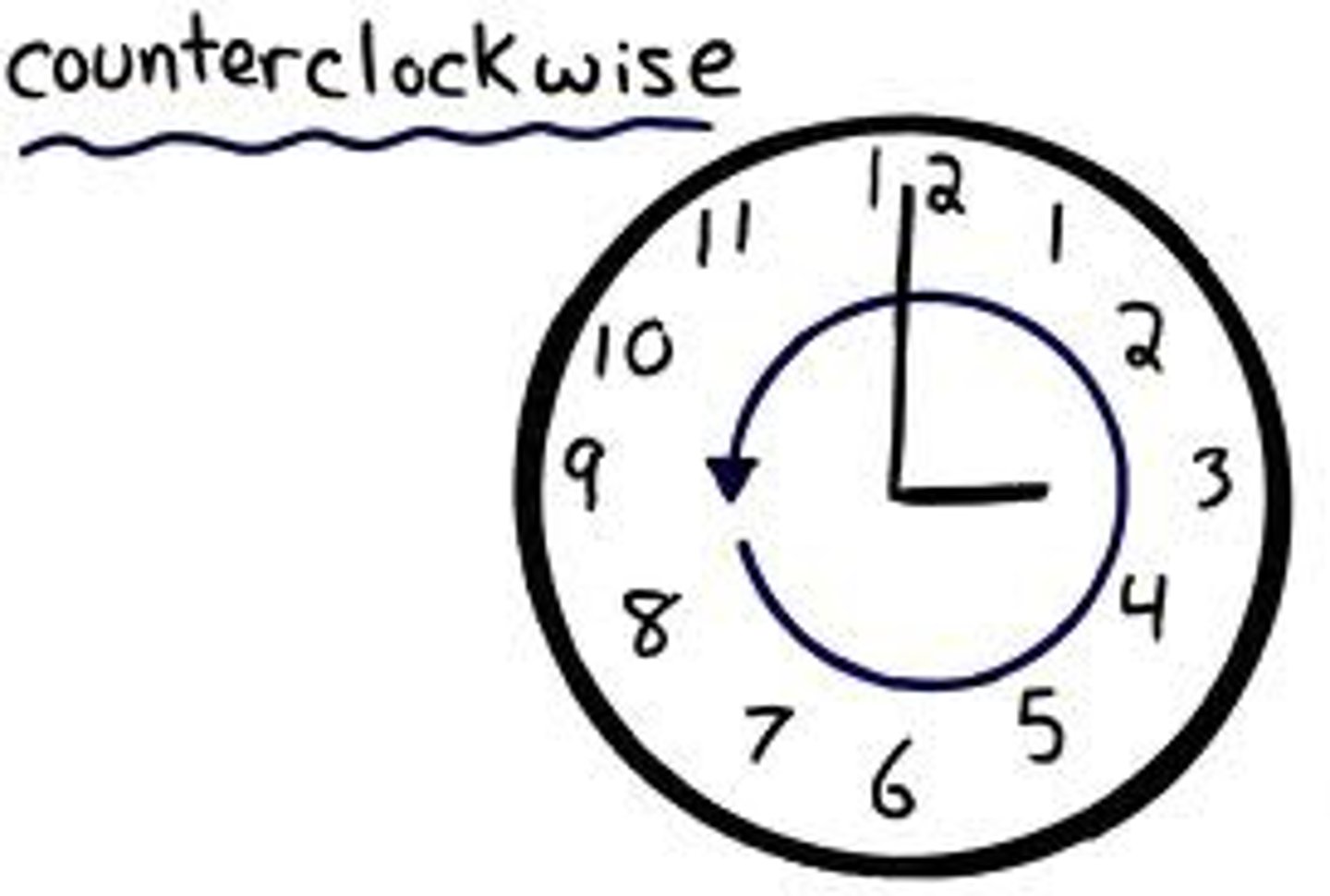
Which direction is positive with regards to torque?
Counter-clockwise
An object has two forces pushing on it in opposite directions. One force is 15.32 N and 5.44 m away from the fulcrum. The other force is 53.24 N. If net torque on the object is 0, what distance (in meters) is this second force from the fulcrum?
(A) .78
(B) 1.57
(C) 3.22
(D) 5.78
(B) 1.57
Torque 2 = Torque 1
Distance 2 x Force 2 = Distance 1 x Force 1
Distance 2 = Distance 1 x Force1 / Force 2
Distance 2 = 5.44 x 15.32 / 53.24
Distance 2 = approx. 1.5 m (actual 1.57 m)
CRB True or false? Because there is no net torques acting on that object in the previous problem, the object is in Translational Equilibrium.
False. Because there is no net torques acting on that object in the previous problem, the object is in Rotational Equilibrium.
CRB Compare Translational and Rotational Equilibria.
Translational Equilibrium occurs if and only if the net forces acting on an object are equal to zero. Rotational Equilibrium occurs if and only if the sum of all torques acting on an object are equal to zero.
CRB True or false? The further that the mass or force is from the axis of rotation, the easier it is to rotate.
True. The further that the mass or force is from the axis of rotation, the easier that it is to rotate.
To remember this, think of the equation for torque and having a longer lever arm.
CRB Fill in the blanks: The First Condition of Equilibrium requires ________________, whereas the Second Condition of Equilibrium requires __________. If both are met, then the object is in Dynamic Equilibrium.
(A) Positional Equilibrium, Rotational Equilibrium
(B) Translational Equilibrium, Rotational Equilibrium
(C) Rotational Equilibrium, Translational Equilibrium
(D) No net force, Translational Equilibrium
(B) Translational Equilibrium, Rotational Equilibrium
The First Condition of Equilibrium requires Translational Equilibrium, whereas the Second Condition of Equilibrium requires Rotational Equilibrium. If both are met, then the object is in Dynamic Equilibrium.
CRB Could an object be moving with a non-zero linear velocity and be in Dynamic Equilibrium? How about a non-zero angular velocity? Why or why not?
Yes, an object can be in Dynamic Equilibrium and still have a non-zero linear and/or angular velocity. The key is that there is no current net forces acting on the objects, so they must have no acceleration (be moving at a CONSTANT linear or angular velocity).
CRB If there is an object that is in Dynamic Equilibrium, which of Newton's Laws will best dictate how the object will move?
(A) Newton's First Law
(B) Newton's Second Law
(C) Newton's Third Law
(D) I will go study Newton's Laws again then come back to answer this!
(A) Newton's First Law
Newton's Law of Inertia states that an object in motion will stay in motion or that an object at rest will stay at rest until the object is no longer in Dynamic Equilibrium.
CRB Compare Static and Dynamic Equilibrium.
Dynamic Equilibrium allows for a constant velocity, only requiring that Translational and Rotational Equilibria are maintained. For Static Equilibrium, not only must Translational and Rotational Equilibria be maintained, but also the object's velocity must be equal to 0.
In which direction does normal force push an object?
(A) Straight up into the air.
(B) At a 90 degree angle to the earth.
(C) Perpendicular to the surface that the object is pushing against.
(D) Perpendicular to the center of mass that the object is pushing against.
(C) Perpendicular to the surface that the object is pushing against.
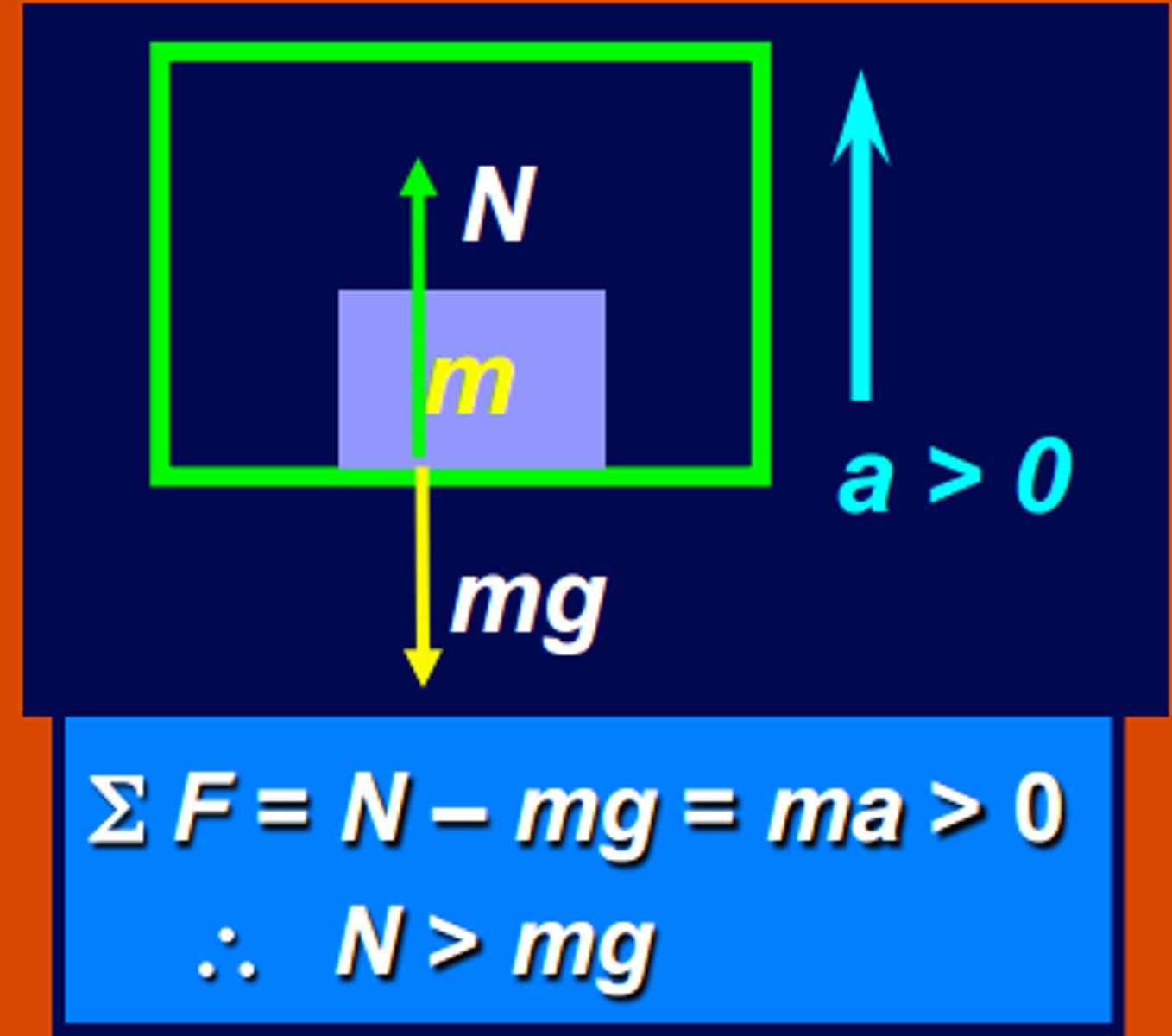
Johnny gets on the elevator. He has a mass of 103.54 kg (too many sweets, Johnny). The elevator starts accelerating upwards at 2.13 m/s^2. What is the Normal force acting on Johnny (in N)?
(A) 786.34
(B) 942.01
(C) 1235.23
(D) 1654.90
(C) 1235.23
Force of Gravity = 103.54 x -9.8 = -980 N (-1014.69)
Net Force = 103.54 kg x 2.13 m/s^2 = 200 N (actual: 220.54)
Force of Gravity + Normal force = Net Force
-1014.69 N + Normal Force = 220.54 N
Normal Force = 1180 N (actual: 1235.23)
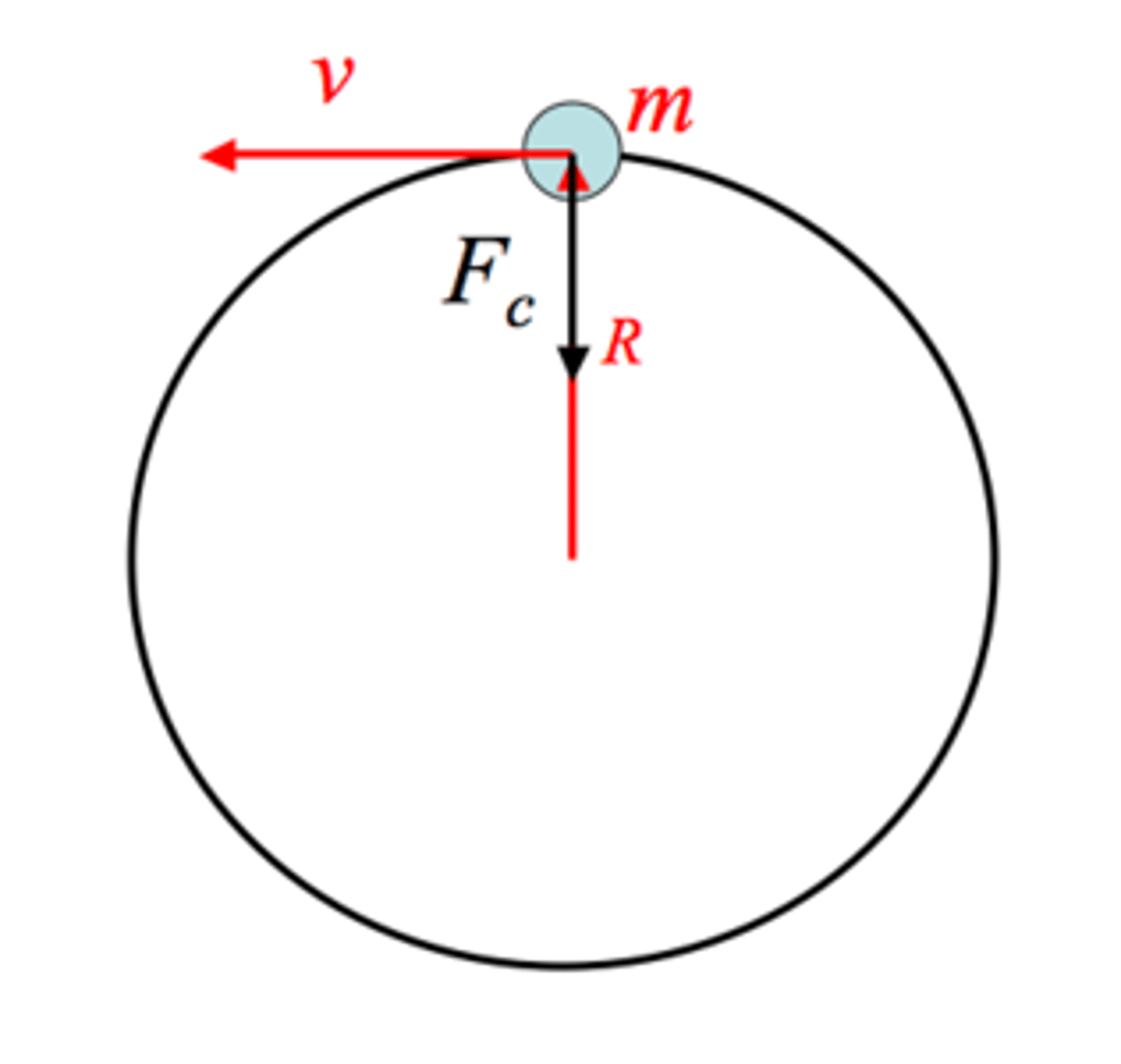
True or False: When travelling in a circular path at a constant speed, there are no net forces acting upon an object.
False. Even if the object’s speed is constant, it’s constantly changing direction (and velocity) as it moves in a circle. A change in velocity is acceleration (centripetal acceleration) which points radially inward. Newton’s 2nd law says that acceleration requires a net force, so there is a net force acting toward the center of the circle
Compare Force and Tension.
Force is something that causes a mass to accelerate.
Tension is the force of a string on an object.
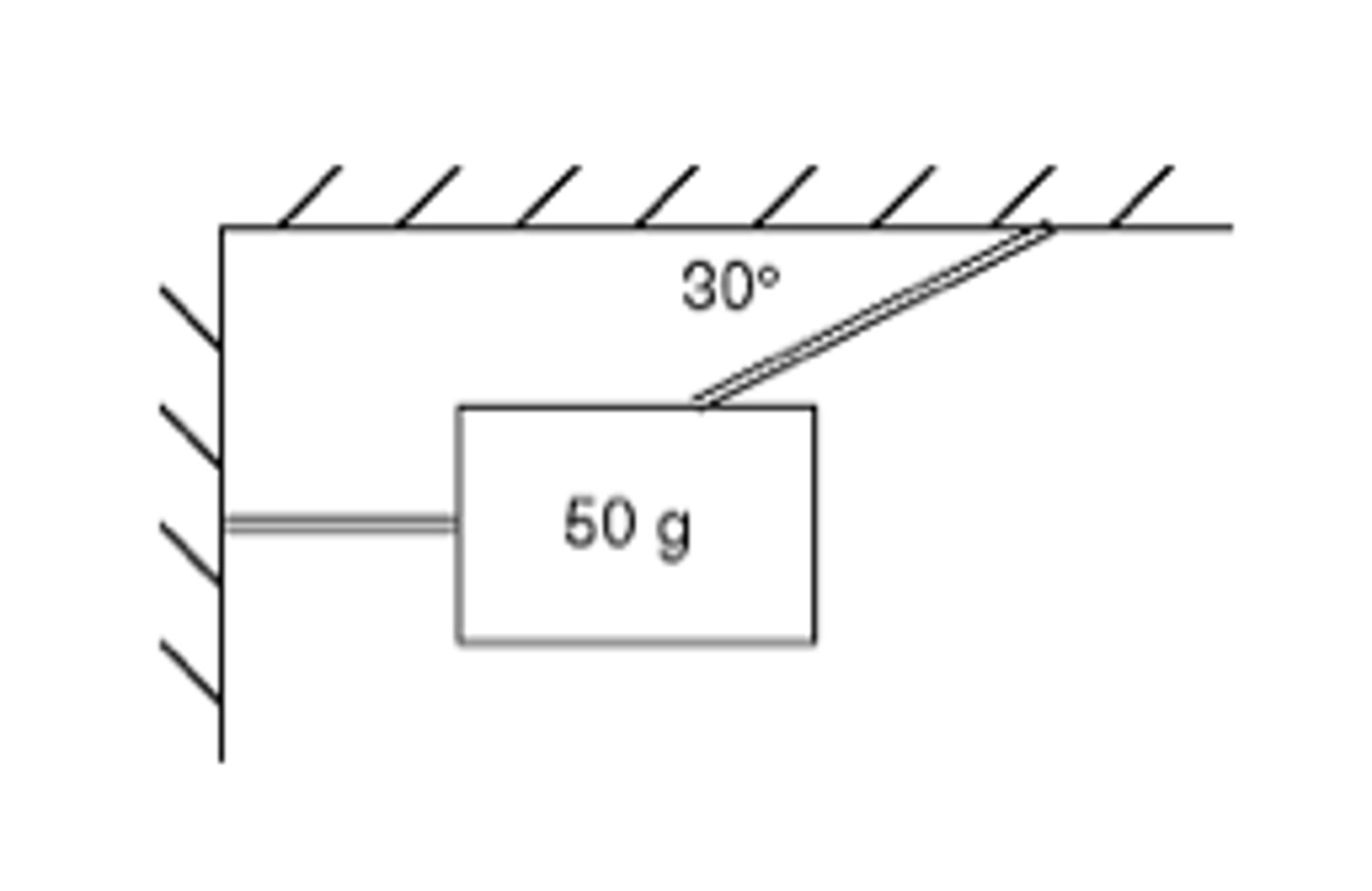
Johnny is hanging onto two wires. One of them connects to the ceiling forming a 30 degree angle with the ceiling. The other is connected to a wall and is parallel to the ceiling (see backside of notecard for a visual representation). Johnny weighs 750 N (he has been on a diet). What is the tension in the horizontal wire (in N)?
(A) 320
(B) 651
(C) 874
(D) 1299
(D) 1299
Angle = 30 degrees
Force downward = 750 N
y axis tension in wire 1 = 750N
tension in wire 1 = 750/sin(30) = 1500N
tension in wire 2 = x axis tension in wire 1 = 1500cos(30) = 1299N
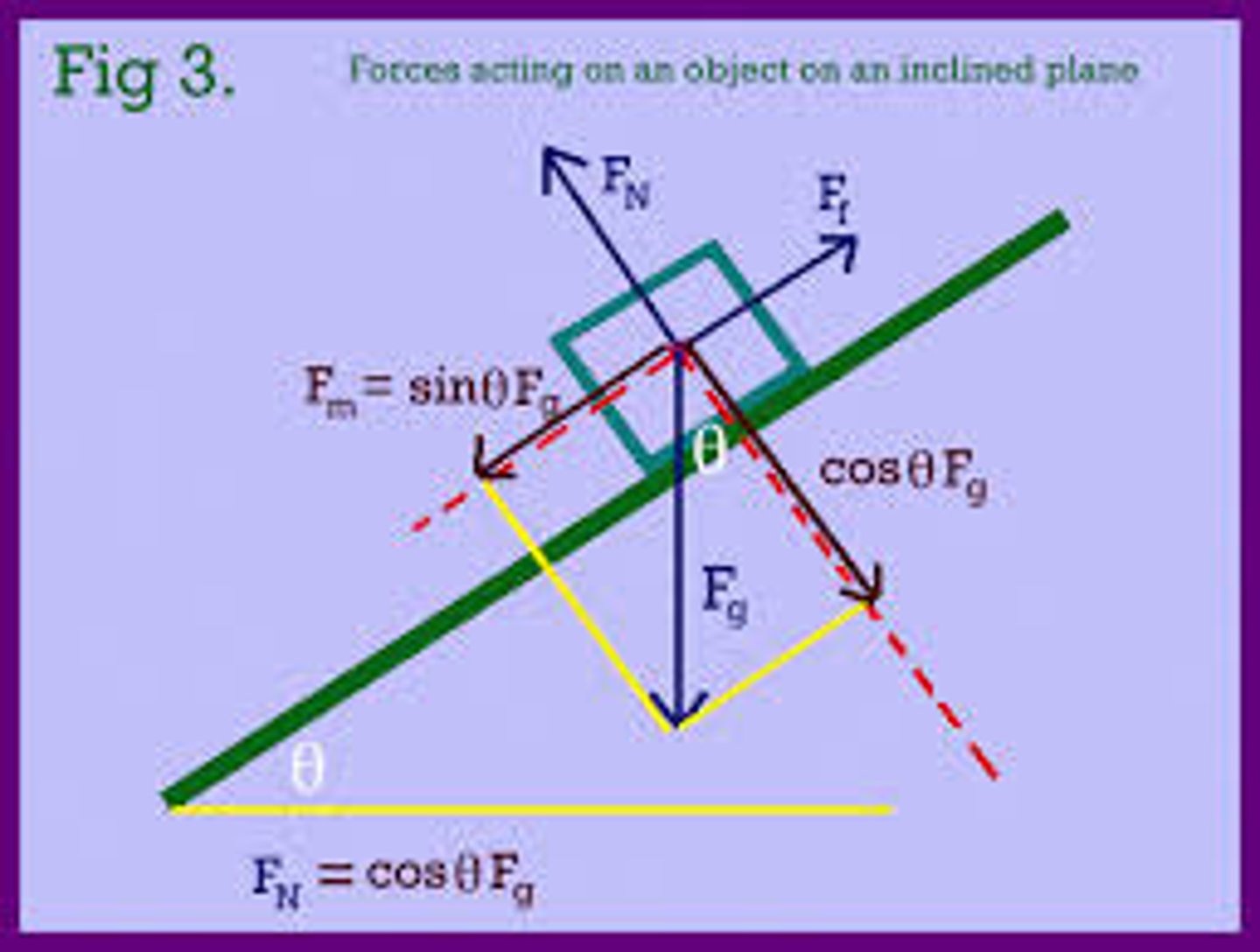
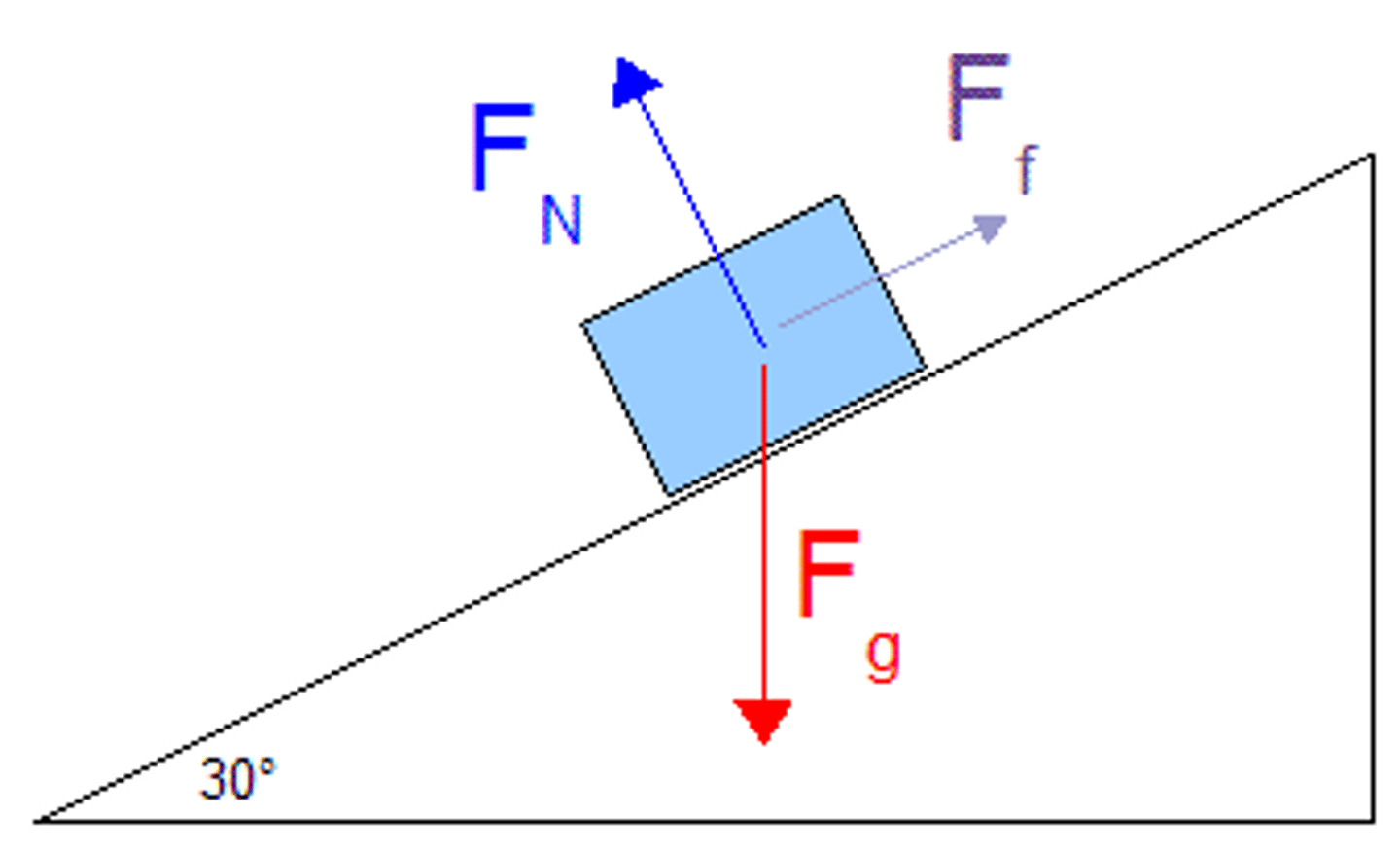
True or False: In an inclined plane system where the x-axis is the plane itself, gravity can have an x- as well as a y-component.
True. In an inclined plane system where the x-axis is the plane itself, gravity can have an x- as well as a y-component (see next card)
Draw a diagram showing all the forces acting on a box on an inclined plane. Break the force of gravity up into the components that are parallel and perpendicular to the surface, and define the size of these forces relative to the force of gravity, and the angle of the incline.