8 Microscopic UA Crystals
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
3 factors important in crystal formation
temperature (lower = more percip)
concentration (higher = more percip)
pH (crystal type)
Crystal ID (4 characteristics)
Morphology - shape, color, size
pH
Polarizing light
Solubility - heat/cold acid/alkaline
Amorphous crystal - Urate
Normal
acidic urine
form upon refrigeration
pink sediment, brown/yellow/pink granule microscopically
heat and sodium hydroxide (alkaline) soluble
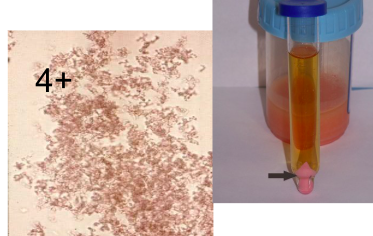
Amorphous crystal - Phosphate
Normal
Phosphates and calcium
white sediment
Soluble in acetic acid
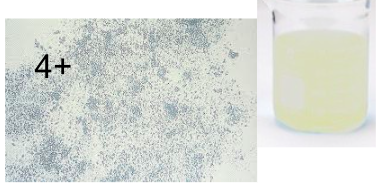
Sodium Urate Crystal
Normal
protein rich diet
usually not reported
seen in refrigerated specimens

Uric acid crystal
Normal in low amount
Acidic urine
Increased if purine and nucleic acid levels increase → can see high amounts in urine with
gout
acute febrile condition
chronic nephritis
lesch nyhan syndrome
Soluble in alkaline soln and heat
Polarized!!
Uric acid barrel shape

Uric acid rhombic shape

Uric acid rosette shape
nucleated crystal

Uric acid long hexagon shape
dont confuse with cystine

Distinguish uric acid crystal and cystine crystal
Polarized light (uric acid with polarize, cystine will not!)

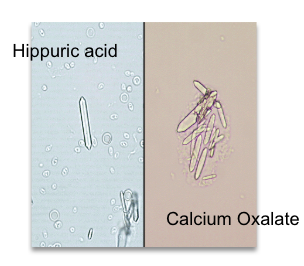
Calcium oxalate crystal
Normal in low amount
Acidic ~ neutral pH urine
Soluble in HCl but insoluble in acetic acid
Polarize!
Major component of kidney stone in high amount
Calcium oxalate dihydrate form
Most common form
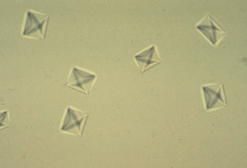
Calcium oxalate monohydrate form
dumbbell or oval shape, can be confused with RBC → use polarizer
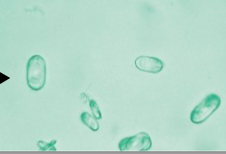
Pathologic conditions with elevated calcium oxalate
renal calculi (most common cause)
oxalic acid poisoning
liver disease
ethylene glycol poisoning (antifreeze breaks down into oxalic acid)
Hippuric acid crystal
Normal in low amount
acidic urine (can also be in neutral~alkaline)
soluble in alkaline, heat
No polarization
rare
seen in people with high fruit and veggie diet (high benzoic acid)
liver dysfunction
toluene exposure
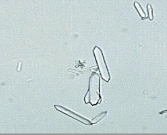
Distinguish hippuric acid with monohydrate calcium oxalate
polarization (calcium oxalate!)
solubility
Calcium oxalate: HCl
Hippuric acid: alkaline
Ammonium Biurate crystal
Normal
alkaline urine
soluble in acetic acid, heat
acetic acid turns crystals into uric acid crystal
Usually an artifact of old or improperly stored urine
If in fresh urine → clinically significant
Thorny apple, brown
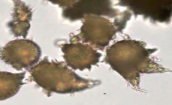
Ammonium biurate in acetic acid
Turns into uric acid crystal
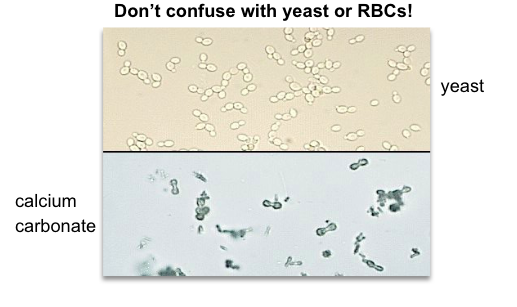
Calcium carbonte
Normal
alkaline urine
soluble: HCl and acetic acid will make it bubble (effervesce)
Can be confused with yeast, RBC
Calcium Phosphate
Normal
alkaline urine
Soluble in acetic acid
rosette can be confused with sulfonamide (sulfonamide wont dissolve in acid)
Sometimes in kidney stones
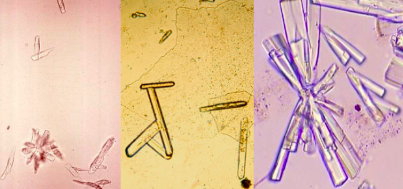
Triple phosphate
Normal
alkaline urine
soluble in acetic acid
Polarized!!
coffin shape

Dissolved triple phosphate shape
feathery
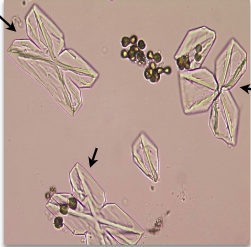
Abnormal crystals general info
Usually found in acidic urine
ID usually confirmed by other tests, patient history, and pathologist/technical specialist
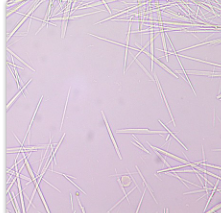
Cystine crystal
Abnormal
acid urine
Soluble in HCl, NaOH, NH4OH
No Polarization
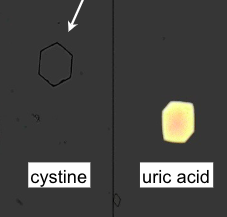
Cystine crystal cause
most common cause of kidney stone in kids
cystinuria
Cholesterol
Abnormal
Acidic urine
soluble in chloroform, ether
Polarization!!
flat plates
Rare - usually caused by refrigeration

Cholesterol crystal cause
excessive tissue breakdown - nephritis, nephrotic conditions
chyuria from lymph drainage obstruction

Tyrosine
Abnormal
Acidic urine
Soluble in HCl, NH4OH
SUPER RARE
Seen with positive bilirubin test, and leucine crystals
Tyrosine crystal cause
severe liver disorder
inherited disorders of amino acid metabolism
Tyrosine crystal seen with
positive bilirubin
positive urobilinogen (not always)
commonly seen with leucine crystal
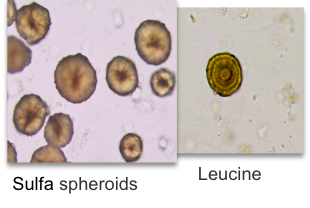
Leucine crystal
Abnormal
acidic urine
solube in NaOH, hot water
Biliruben and urobilinogen usually positive
Seen with tyrosine crystal
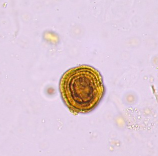
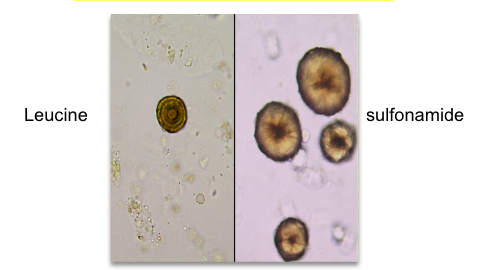
Leucine crystal cause
severe liver disorder
amino acid metabolism disorder
maple syrup disease
severe viral hepatits
Leucine crystal confused with
sulfonamide crystal
Bilirubin crystal
Abnormal
acidic urine
soluble in acetic acid, HCl, NaOH, acetone
Usually seen in refrigerated urine
bilirubin strip should be positive
Bilirubin pigement will stain WBC, RBC, etc
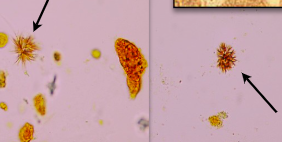
Bilirubin crystal cause
severe liver disorder
jaundice seen
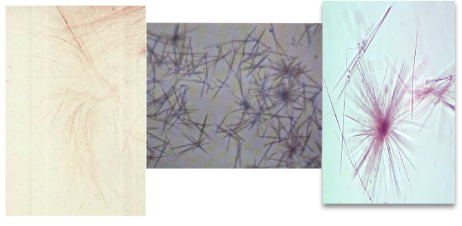
Radiographic dye crystal
check patient history
Specific gravity should be high >1.035
Polarizes!!!!
sheaves or flat needles
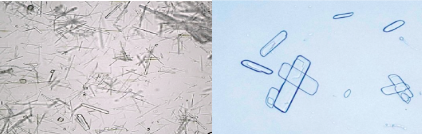
Radiographic dye crystal confused with
Cholesterol, tyrosine, sulfonamide crystal
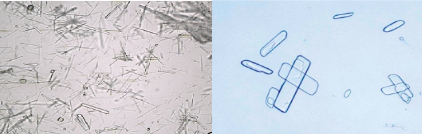
Sulfonamide crystal
acidic urine
soluble with acetone and alkaline
seen in patients taking sulfonamide antibiotics who are dehydrated → can cause tubular damage
shapes: flat needles, sheaves, small needles, spheroids, brown
Sulfonamide can be confused with
Leucine, tyrosine, radiographic dye crystals
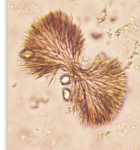
Acyclovir crystal
Neutral ~ slightly alkaline urine
From anti-viral medication for herpes
Acyclovir can be confused with
Tyrosine

Ampicillin
seen in patients with high dose and dehydrated
Shape: needles and bundles
increased with refrigeration
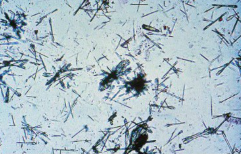
Talcum powder
Artifact
flat sheets
can be confused with cholesterol
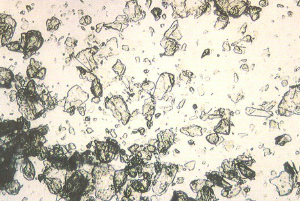
Starch
Artifact
dimpled
with polarize, for psuedo maltese cross
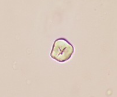
Schistosoma harmatobium
Parasite, lives in bladder
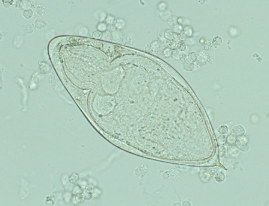
Trichomonas vaginalis
most frequently seen parasite in sediment
resembles WBCs or epithelial cell
STD so contaminant from genetilia
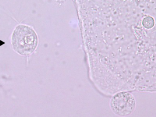
Enterobius vermicularis
Intestinal parasite, fecal contamination
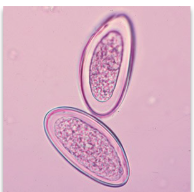
Giardia lambia
Intestinal parasite, fecal contamination
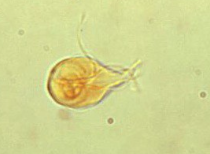
Mites
Skin parasite, contamination (dust mite)
