ISP 205 Exam 4
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 15, 16, 17 and 18
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Which part of the galaxy contains the coldest gas?
The disk
Why do disk stars bob up and down as they orbit the galaxy?
because the gravity of other disk stars always pulls them toward the disk
Which part of the galaxy has gas with the hottest average temperature?
the halo
What is the typical percentage (by mass) of elements other than hydrogen and helium in stars that are forming right now in the vicinity of the Sun?
2%
Where would you be most likely to find an ionization nebula?
in the disk
Ionization nebula
a cloud of gas that glows because it is energized by a nearby hot star
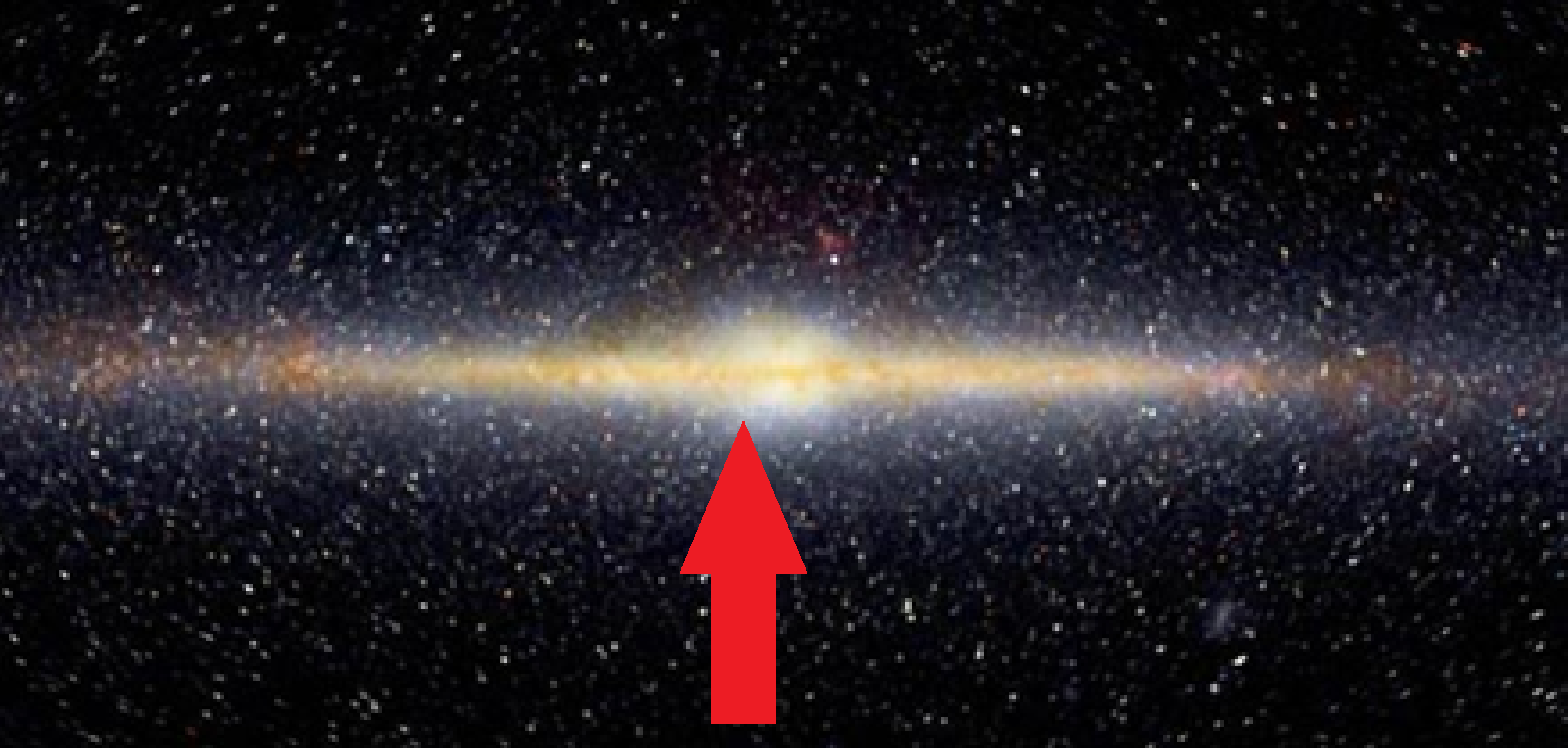

What part of the milky way is this?
Bulge
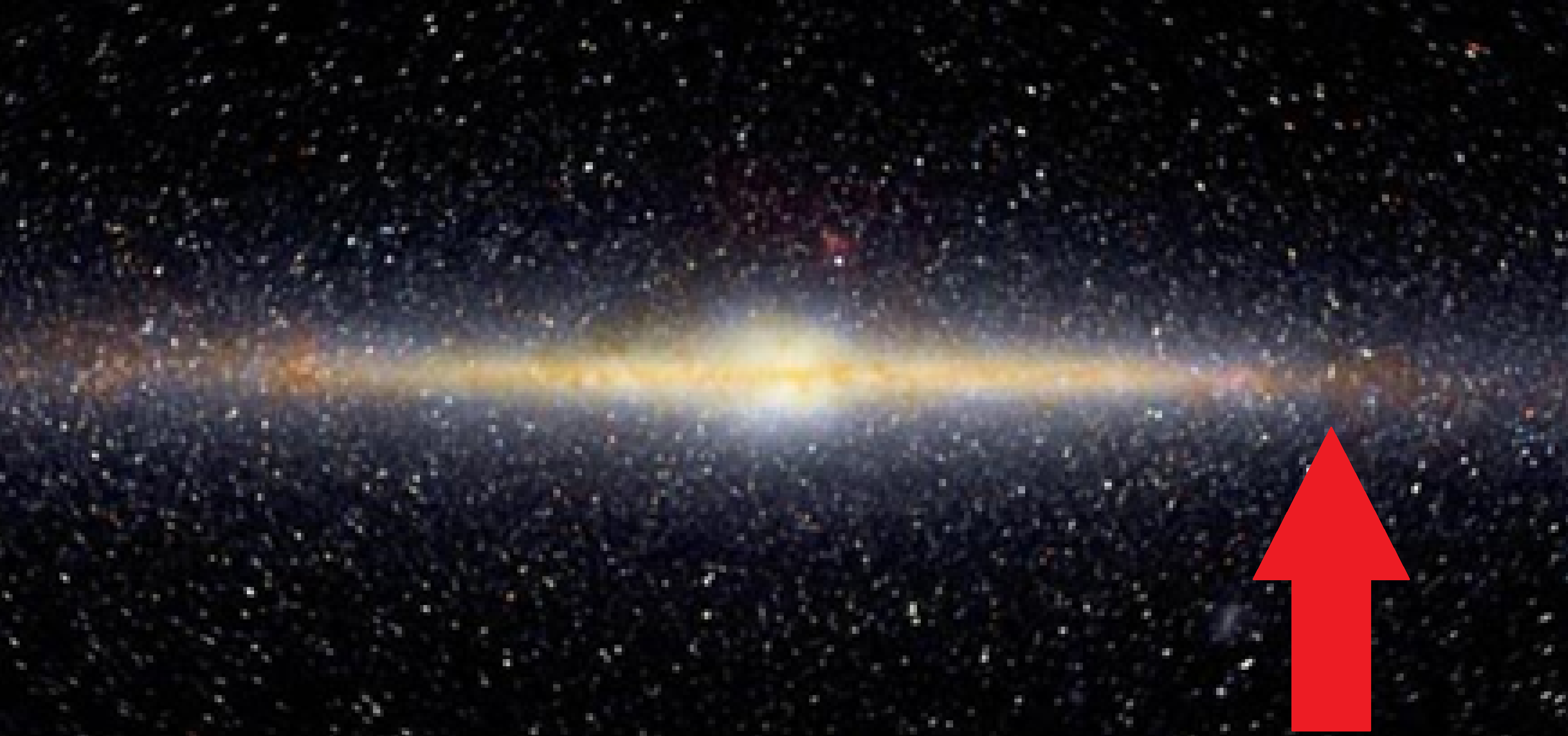

What part of the milky way is this?
Disc
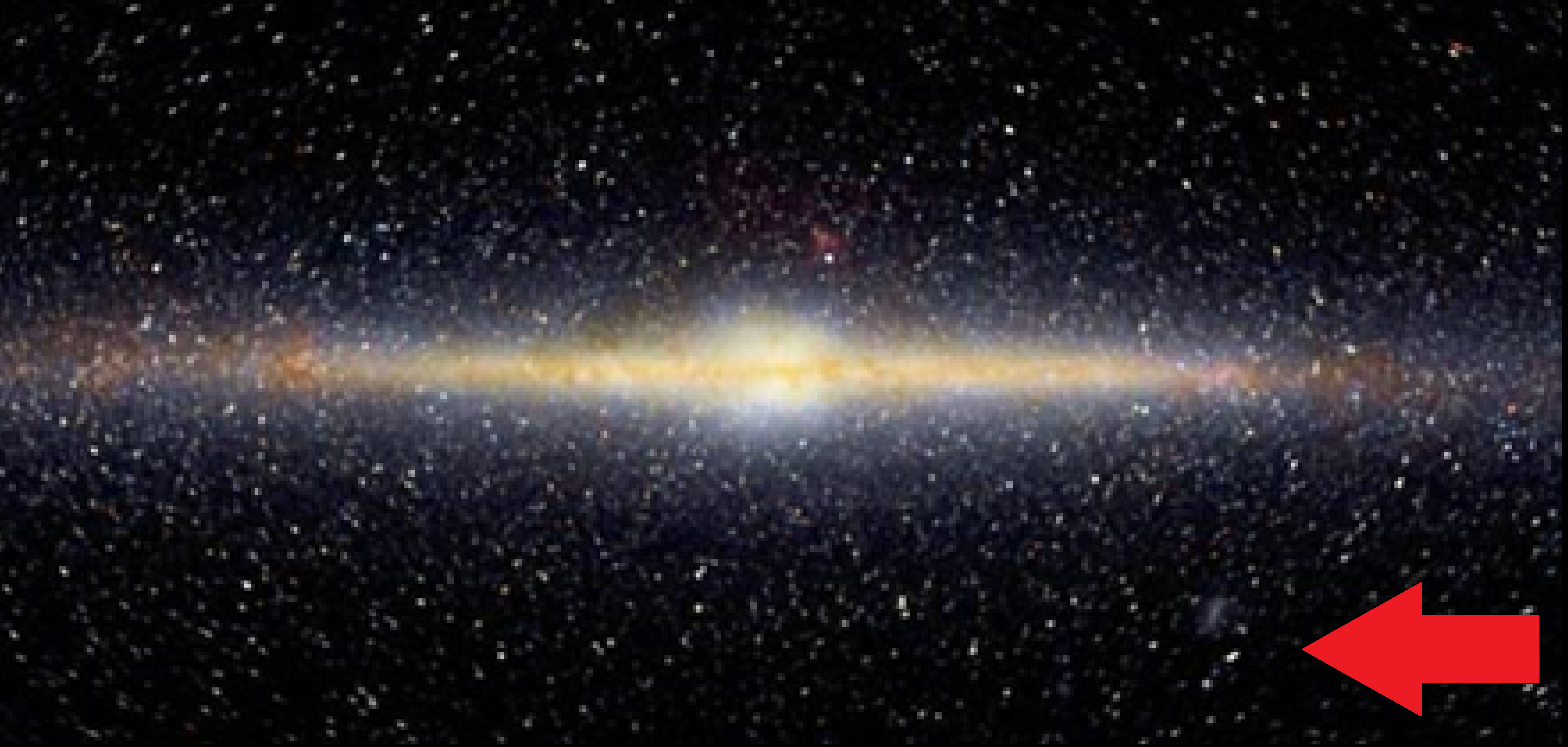

What part of the milky way is this?
Halo
The best measurements of the mass of the black hole at the galactic center come from
the orbits of stars in the galactic center.
Where are most of the Milky Way's globular clusters found?
in the halo
How do we determine the Milky Way's mass outside the Sun's orbit?
from the orbits of stars and gas clouds orbiting the galactic center at greater distances than the Sun
Where would you least expect to find an ionization nebula?
in the halo
Which kind of star is most likely to be part of the spheroidal population?
M star
Which of these galaxies would you most likely find at the center of a large cluster of galaxies?
a large elliptical galaxy
We determine the distance of a Cepheid by:
determining its luminosity from the period-luminosity relation and then applying the inverse square law for light
Which kind of object is the best standard candle for measuring distances to extremely distant galaxies?
a white dwarf supernova
Why do virtually all the galaxies in the universe appear to be moving away from our own?
Because expansion causes all galaxies to move away from nearly all others.
Which of these galaxies is most likely to be oldest?
a galaxy in the Local Group
When we observe a distant galaxy whose photons have traveled for 10 billion years before reaching Earth, we are seeing that galaxy as it was when the universe was
4 billion years old
Which of these items is a key assumption in our most successful models for galaxy formation?
Some regions of the universe were slightly denser than others.
Observations indicate that galaxies with more massive central black holes tend to also have
a greater mass of stars in their central bulges.
The luminosity of a quasar is generated in a region the size of
the solar system.
The primary source of a quasar's energy is
gravitational potential energy.
Quasar
Extremely bright core of a distant, active galaxy, powered by a supermassive black hole consuming gas and dust
The charge of an antiproton is
Negative
When a proton and an antiproton collide, they
convert into two photons.
The current temperature of the universe as a whole is
a few K.
When the universe was 380,000 years old, its thermal radiation spectrum consisted mostly of
visible and infrared photons.
Which of the following does NOT provide strong evidence for the Big Bang theory?
Observations of the amount of hydrogen in the universe
Which of the following does inflation help to explain?
the uniformity of the cosmic microwave background
Which of the following does inflation help to explain?
the origin of galaxies
Which of these pieces of evidence supports the idea that inflation really happened?
observations of the cosmic microwave background that indicate a flat geometry for the universe
Dark Matter
Matter that we infer to exist from its gravitational effects but from which we have not detected any light.
Dark Energy
Energy that could be causing the expansion of the universe to accelerate.
What is the earliest time in the universe that we can directly observe?
a few hundred thousand years after the Big Bang
Dark matter is inferred to exist because:
we can observe its gravitational influence on visible matter.
Dark energy has been hypothesized to exist in order to explain:
Observations suggesting that the expansion of the universe is accelerating.
Orbital speeds depend on distance from the center of our galaxy. This tells us that stars in the outskirts of the galaxy:
orbit the galactic center just as fast as stars closer to the center.
Strong evidence for the existence of dark matter comes from observations of:
clusters of galaxies.
A photograph of a cluster of galaxies shows distorted images of galaxies that lie behind it at greater distances. This is an example of what astronomers call:
a gravitational lens.
Based on the observational evidence, is it possible that dark matter doesn't really exist?
Yes, but only if there is something wrong with our current understanding of how gravity should work on large scales.
Based on current evidence, which of the following is considered a likely candidate for the majority of the dark matter in galaxies?
Subatomic particles that we have not yet detected
Which region of the early universe was most likely to become a galaxy?
a region whose matter density was higher than average
Based on current evidence, what is the overall inventory of the mass-energy content of the universe?
The actual density of the universe is about 32% of the critical density: 27% dark matter, 5% ordinary matter, including 0.5% from stars; Dark energy represents about 68% of the critical density.
What implications does the evidence for dark energy have for the fate of the universe?
The expansion would accelerate with time, causing galaxies to recede from one another with ever-increasing speed.
Which of the following possible types of universe would NOT expand forever?
a recollapsing universe
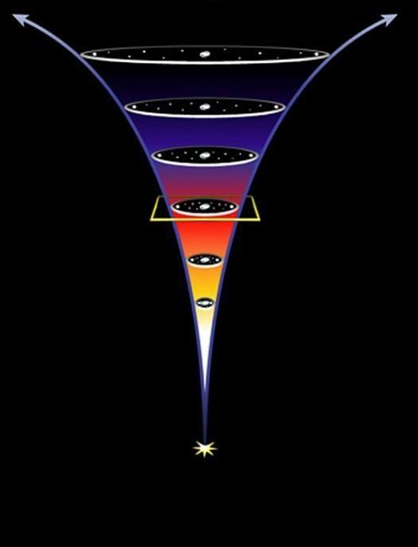
What possible type of universe is shown here?
Accelerating Universe
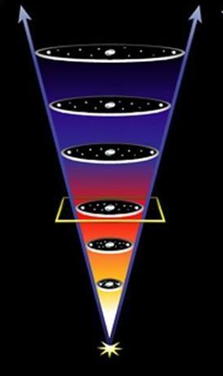
What possible type of universe is shown here?
Coasting Universe
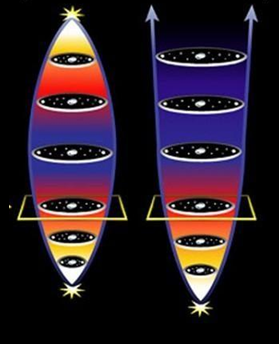
What possible type of universe is shown here?
Decelerating Universe
The major evidence for the idea that the expansion of the universe is accelerating comes from observations of:
white dwarf supernovae.