Life Cycle of a Star - Worksheet
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Nebula
A large cloud of gas and dust in space where stars begin their life cycle.
Protostar
The earliest stage of a star’s life, formed from the contracting gas and dust of a nebula.
Nuclear Fusion
The process that occurs when a star becomes hot enough to fuse hydrogen atoms, marking the birth of a star.
Main Sequence Star
A star that has begun nuclear fusion and is in a stable phase of its life cycle.
Red Giant
A stage that occurs when a low or medium mass star runs out of hydrogen fuel and expands.
Red Super Giant
A stage for high mass stars similar to red giants but larger and more luminous.
Planetary Nebula
A cloud of gas formed when the outer parts of a low or medium mass star drift into space after becoming a red giant.
White Dwarf
The hot core left behind after a low or medium mass star has shed its outer layers.
Black Dwarf
The final stage of a white dwarf when it has cooled and no longer emits significant heat or light.
Supernova
The explosive death of a red super giant star, resulting in a massive release of energy and material.
Neutron Star
The dense core that remains after a high mass star undergoes a supernova explosion.
Black Hole
A region in space with a gravitational pull so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape from it, formed from the remnants of the most massive stars.

nebula
low-medium mass protostar
low-medium mass main sequence star
red giant
planetary nebula
white dwarf
black dwarf
life cycle of a low-medium mass star
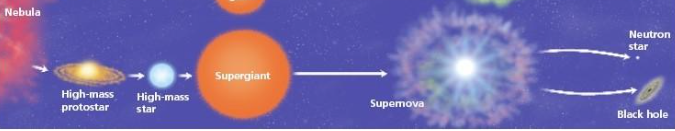
nebula
high mass protostar
high mass main sequence star
super red giant
supernova
a) neutron star b) black hole
life cycle of a high mass star
low-medium mass protostar
B
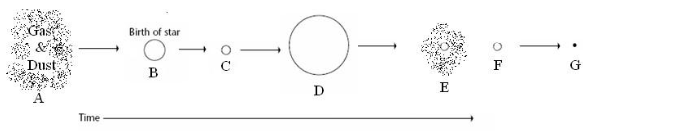
planetary nebula
E
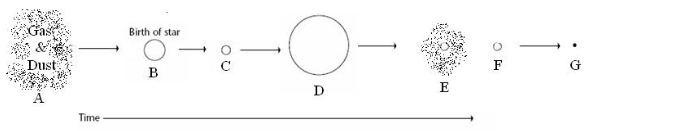
white dwarf
F
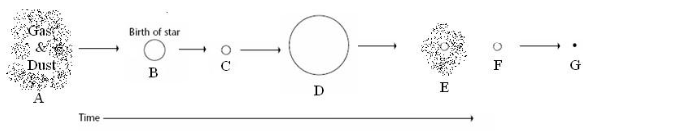
super red giant
D
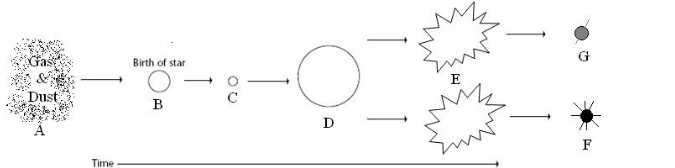
Supernova
E
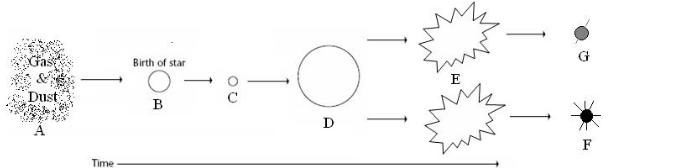
Black hole and neutron star
F and G
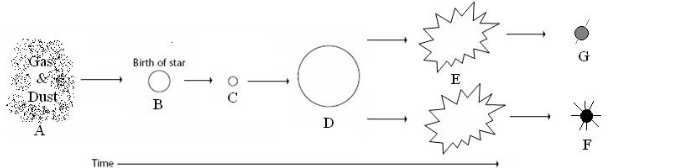
nebula, protostar, main sequence star
What life cycle stages to both high and low mass stars have in common?