BIO 1201 Final Exam (Cumulative Portion)
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
Atom Structure
protons (+) and neutrons are in the nucleus; electrons (-) form negative cloud around it
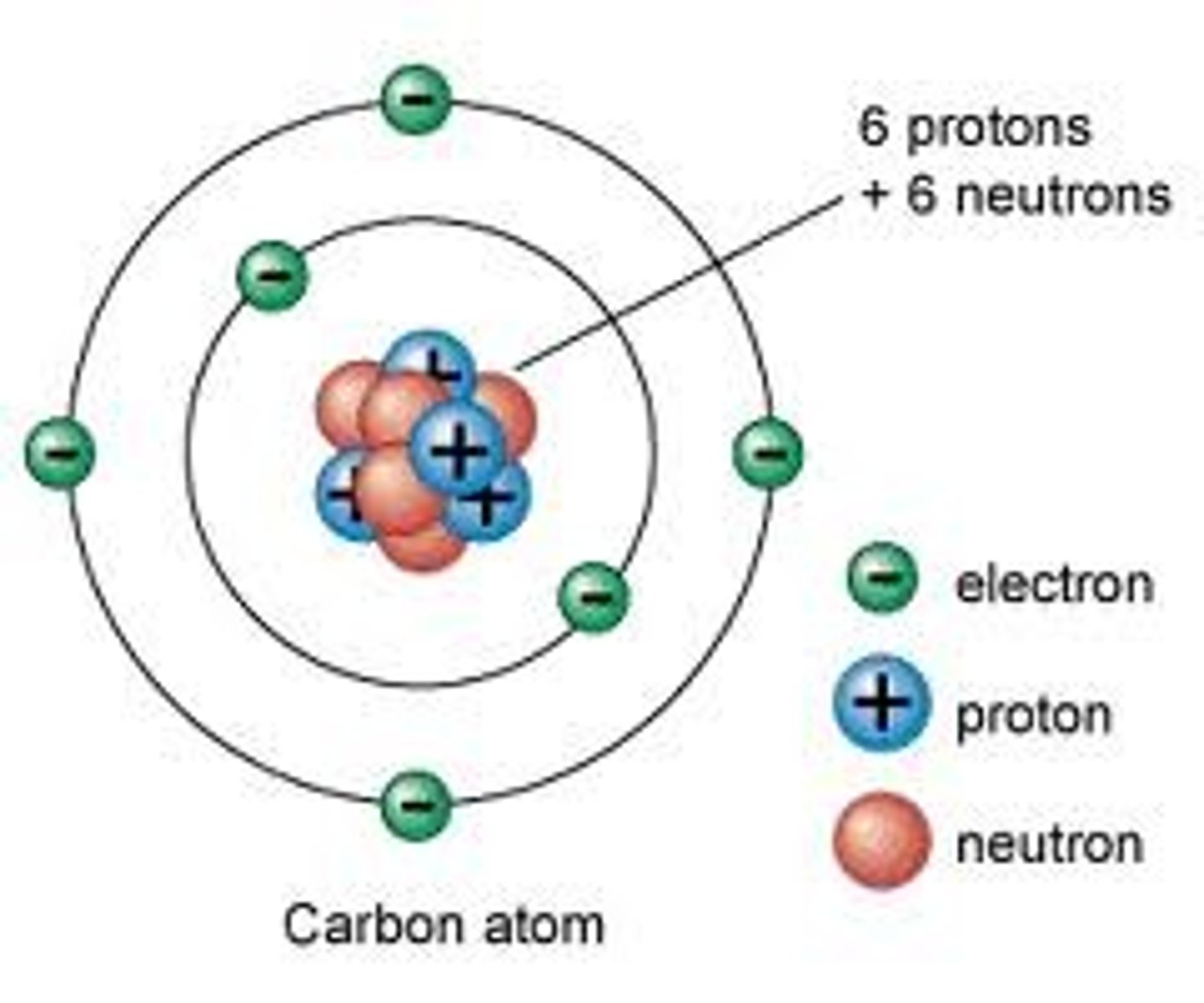
Atomic Number
number of protons; number of electrons; the same elements have the same number
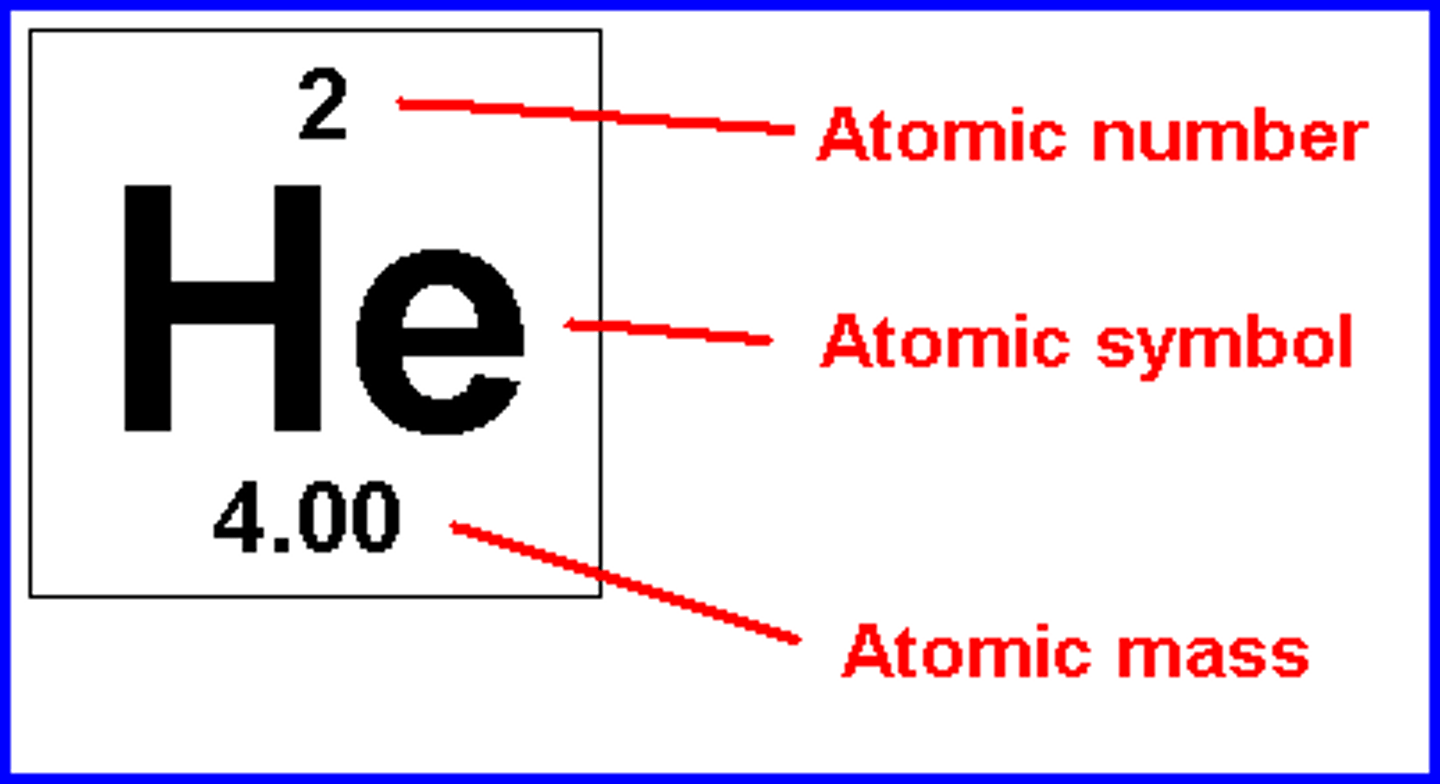
Atomic Mass
protons and neutrons combined
Hydroxide ion (OH-)
the basic end of pH scale (above 7)
Hydrogen ion (H+)
the acidic end of pH scale (under 7)
pH equation
pH = -log[H+]
Ex. pH problem: Beginning with a solution of pH 7 you decrease the [H+] by a factor of 100 what is the new pH of the solution?
9
(because you are taking away H+ so you are moving towards basic. You move 2 numbers because there are 2 zeros.)
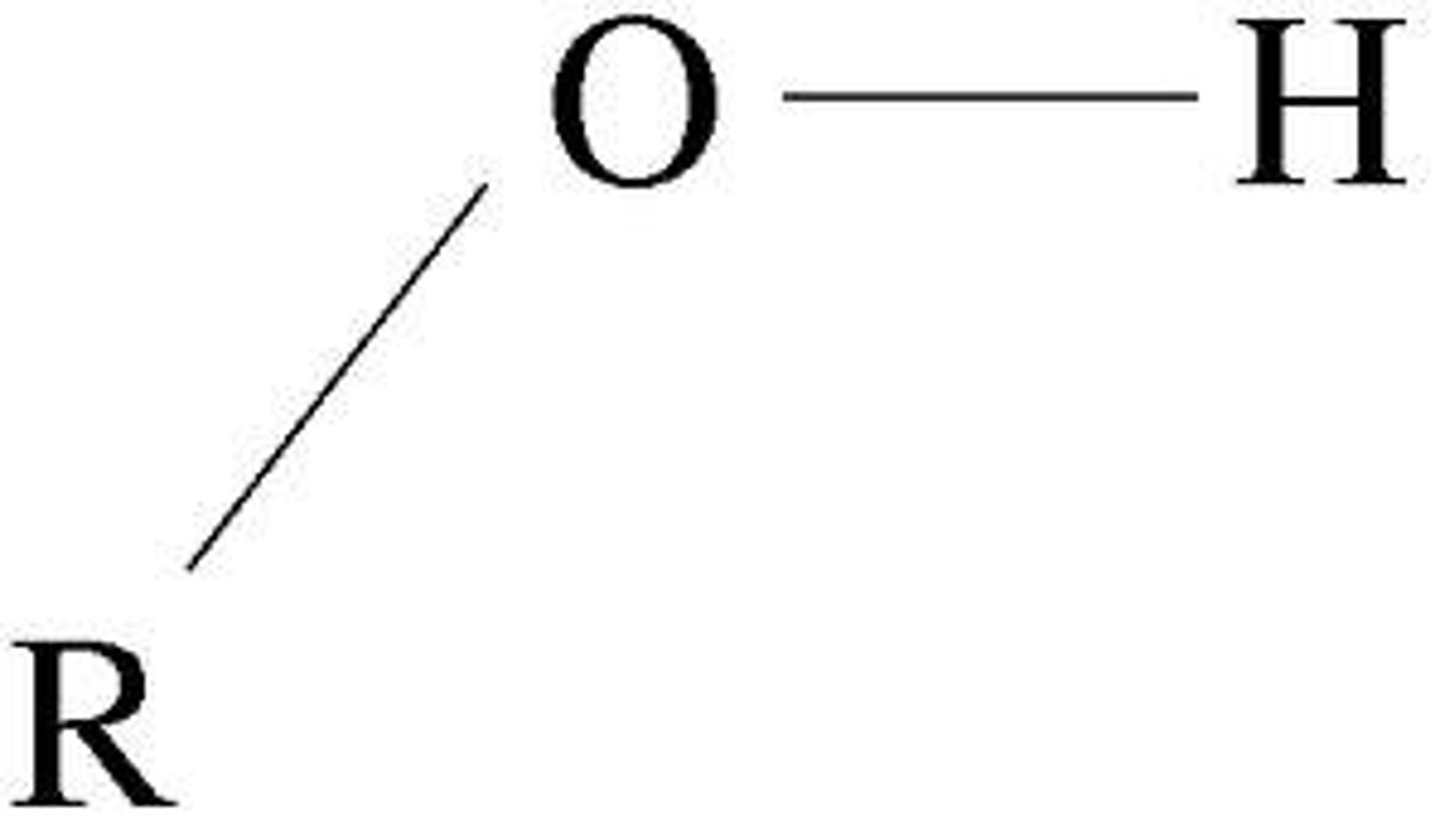
Hydroxyl group (OH)
oxygen (O) and hydrogen (H) bonded
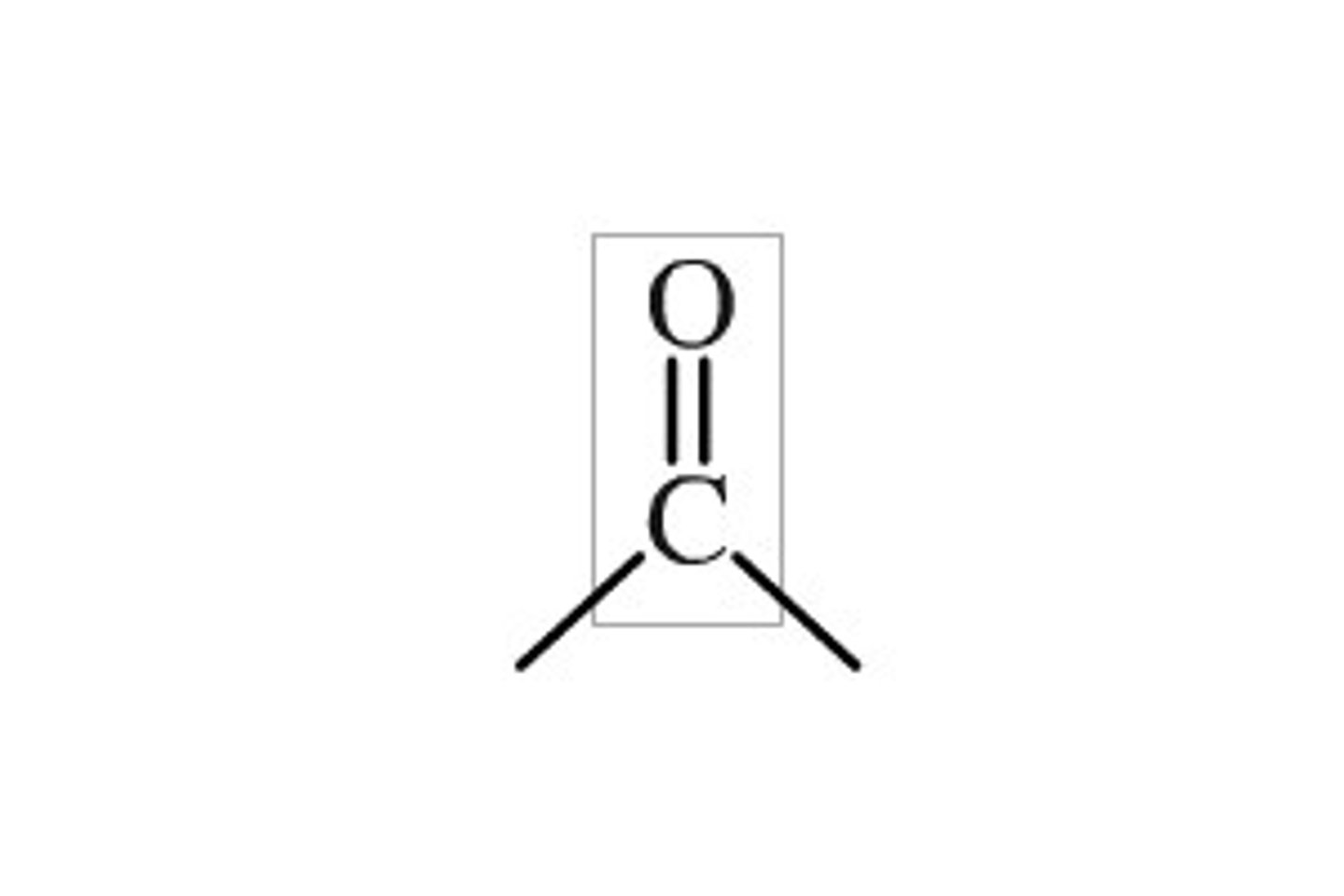
Carbonyl group (C=O)
carbon forms double bond with oxygen
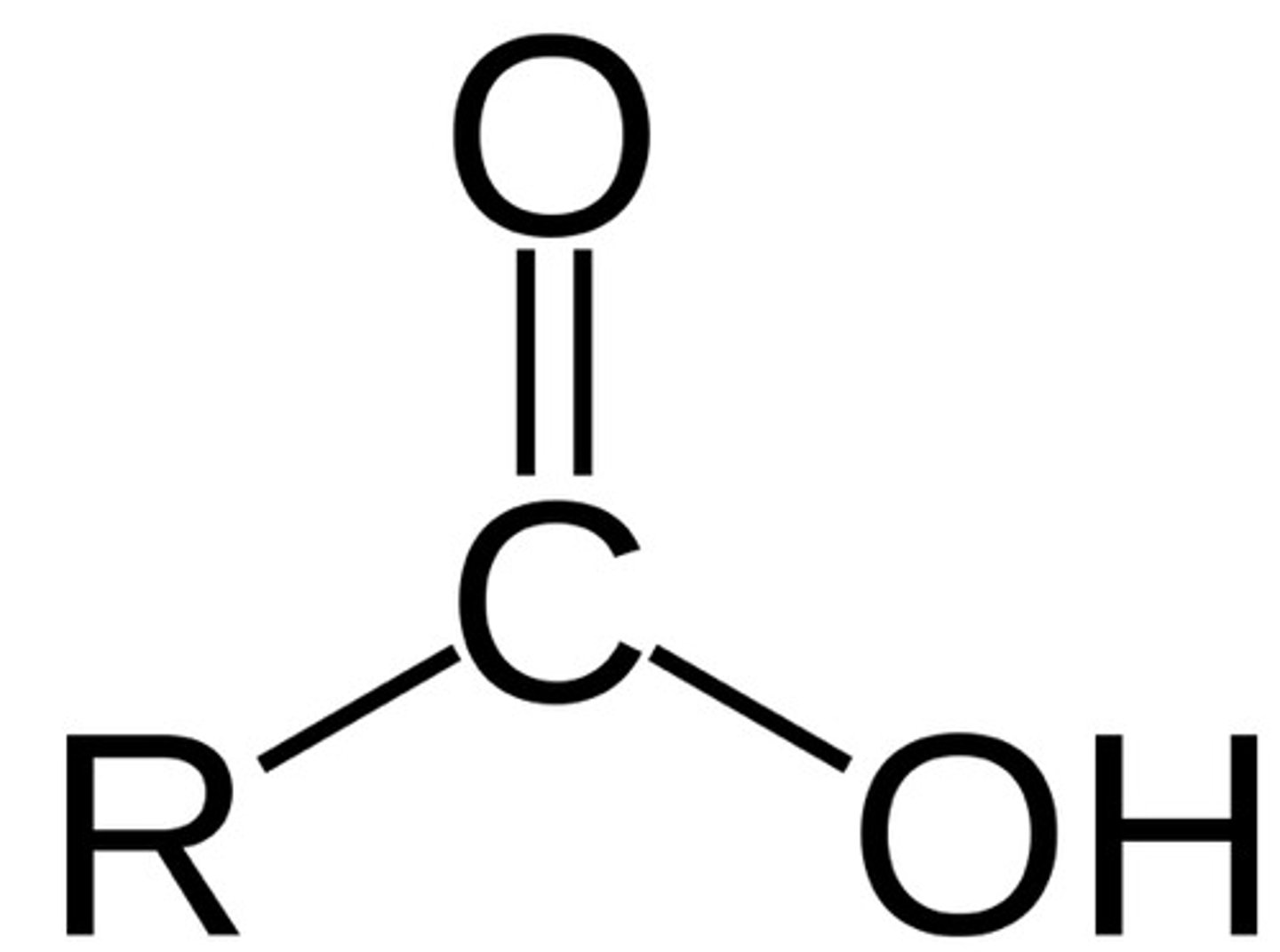
Carboxyl group (—COOH)
carbon bound to an oxygen and OH
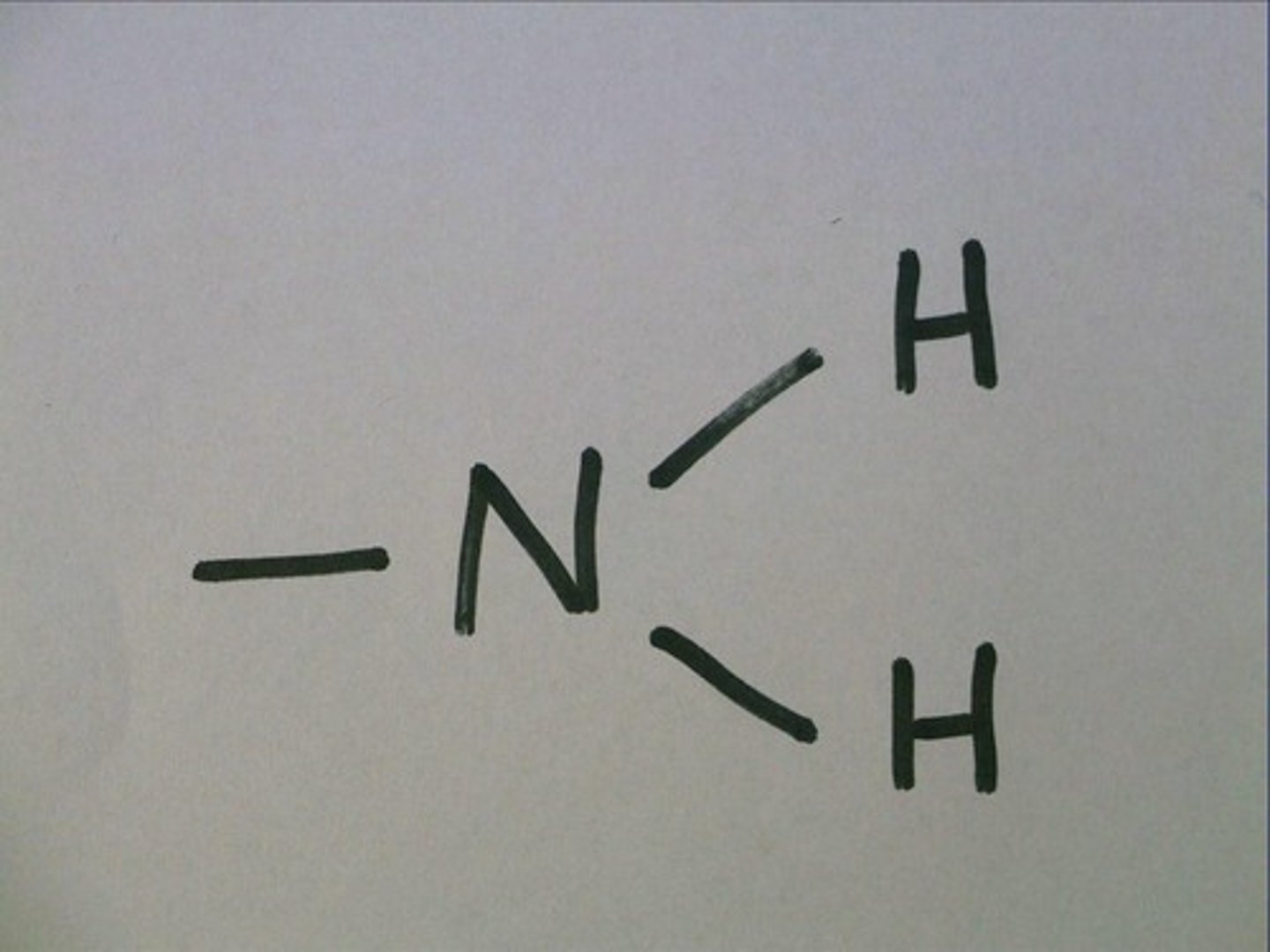
Amino group (—NH2)
nitrogen bound to 2 hydrogens (H)
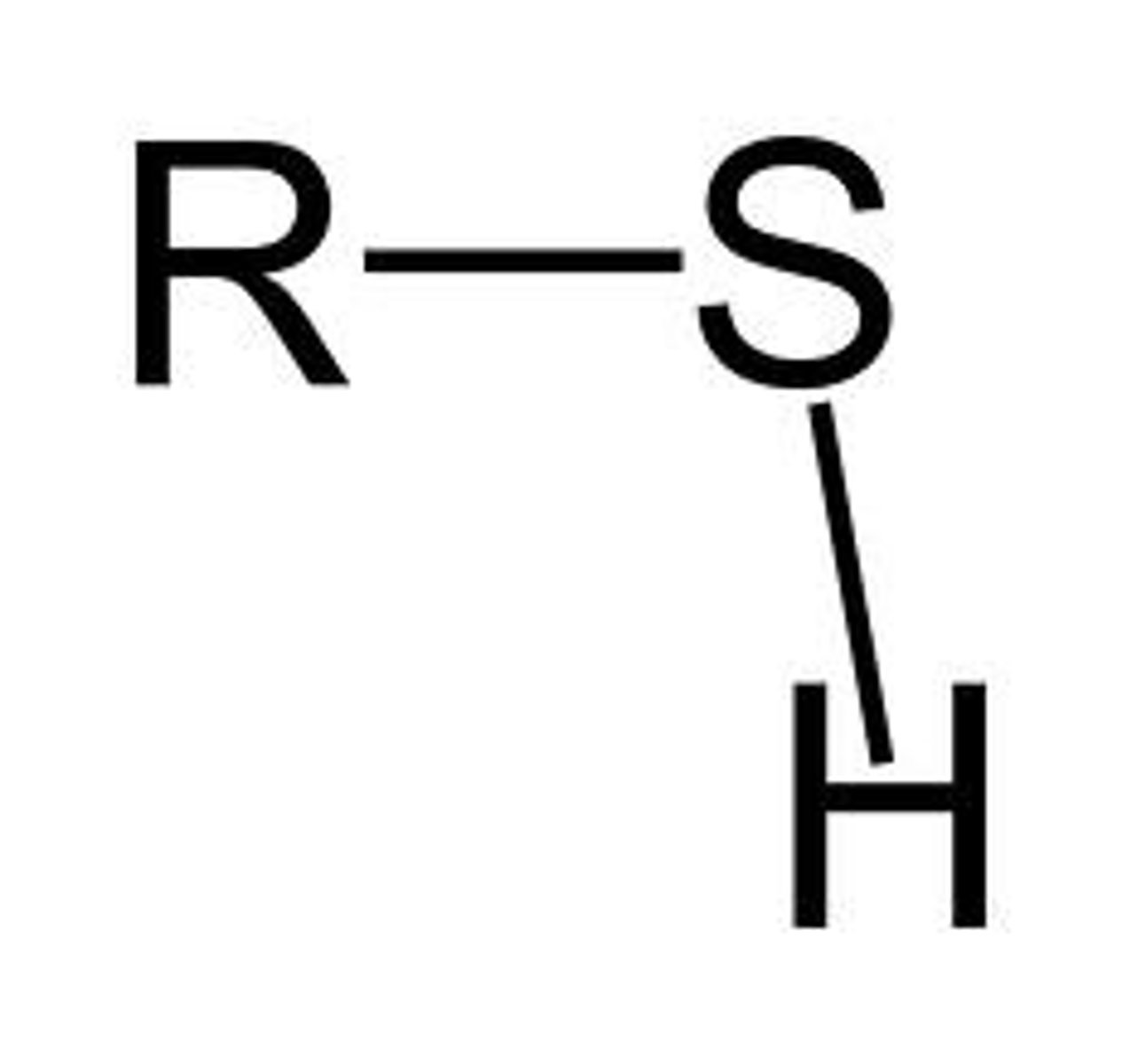
Sulfhydryl group (—SH)
Two —SH groups can react, forming a "cross-link" that helps stabilize protein structure
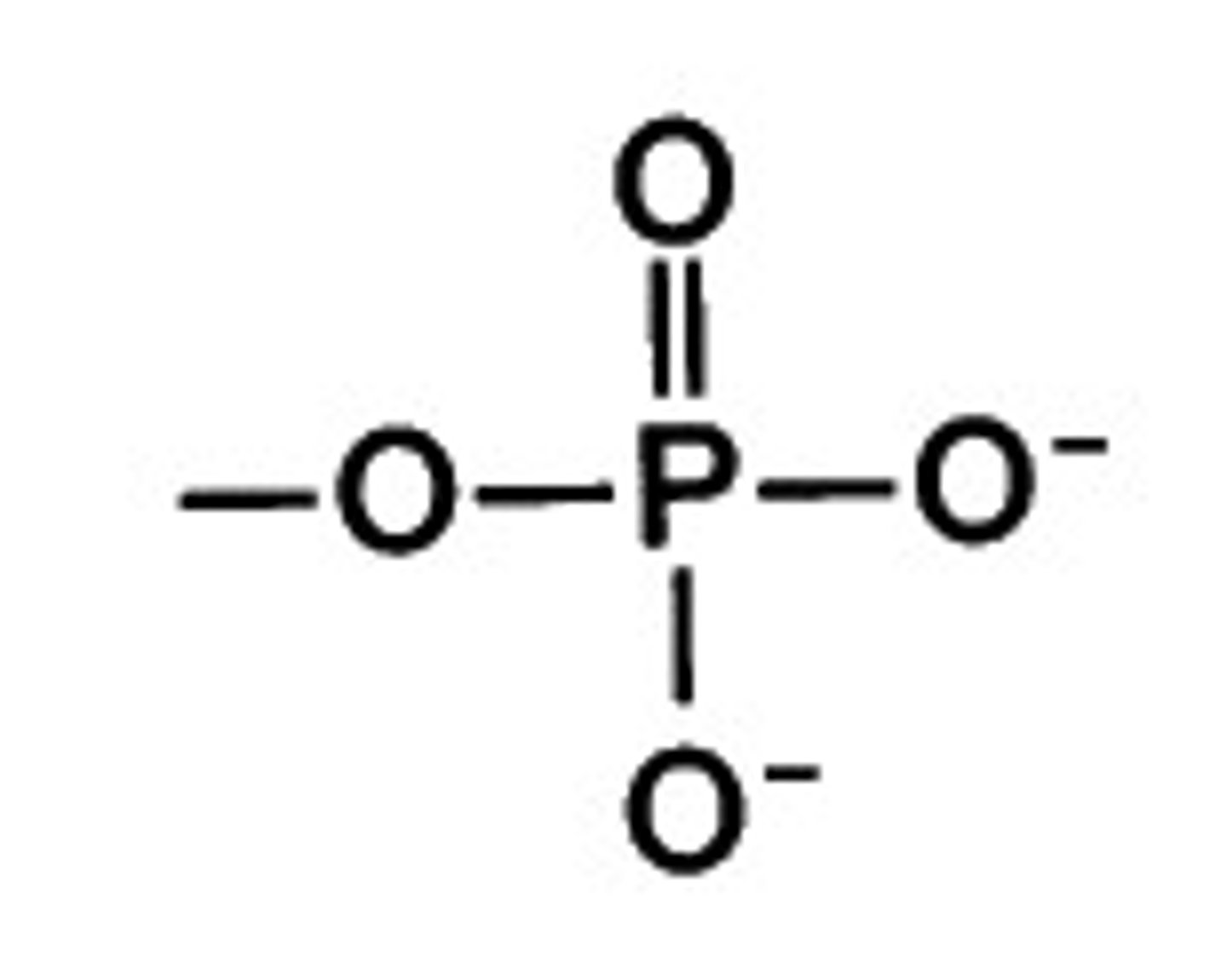
Phosphate group (—OPO32−)
Phosphorus bound to 4 oxygens
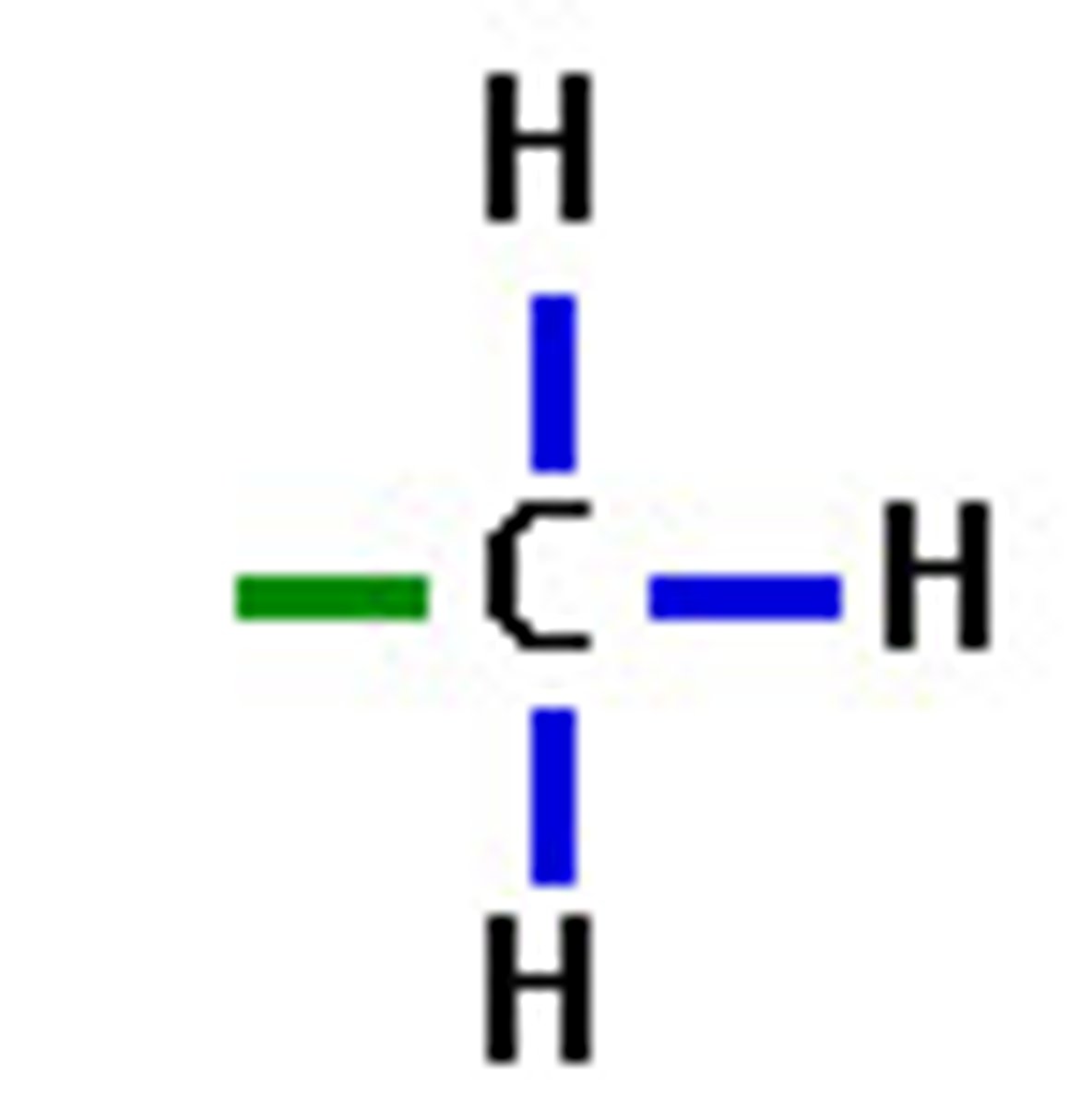
Methyl group (—CH3)
Carbon bound to 3 hydrogen
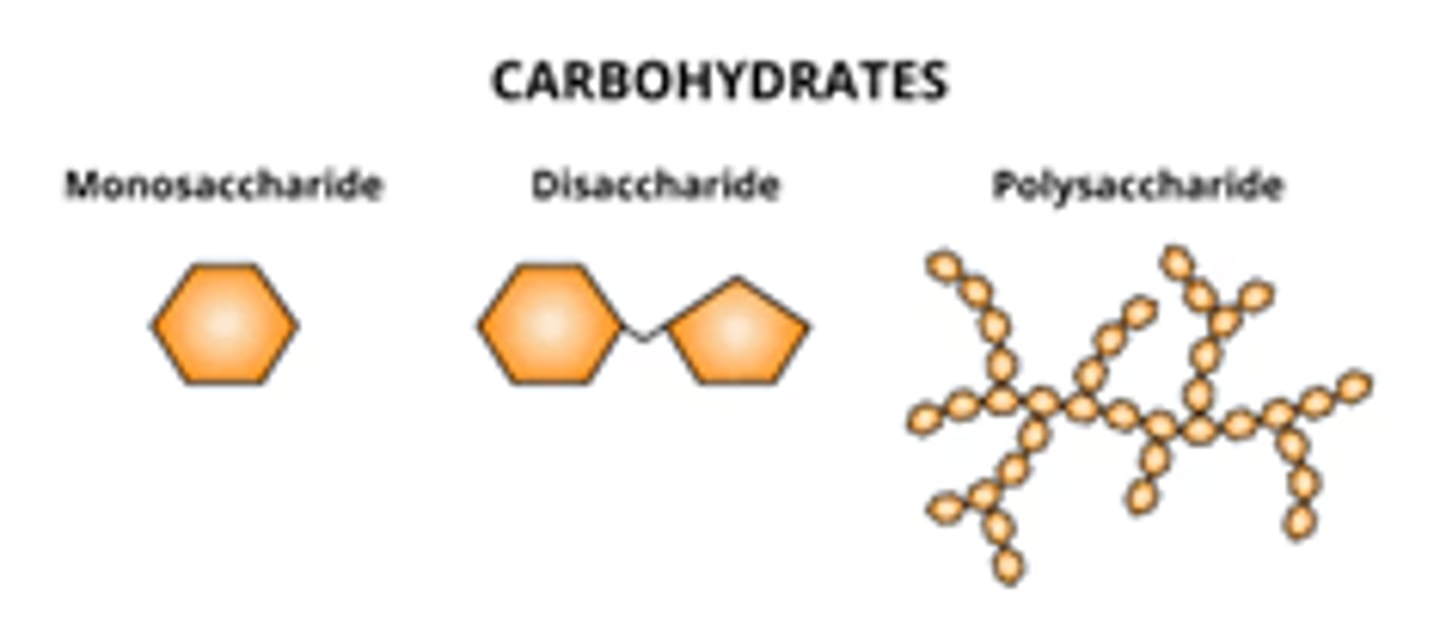
Carbohydrate
a macromolecule that is a polysaccharide; simplest carb is a monosaccharide; serve as fuel and building material ex. glucose and fructose
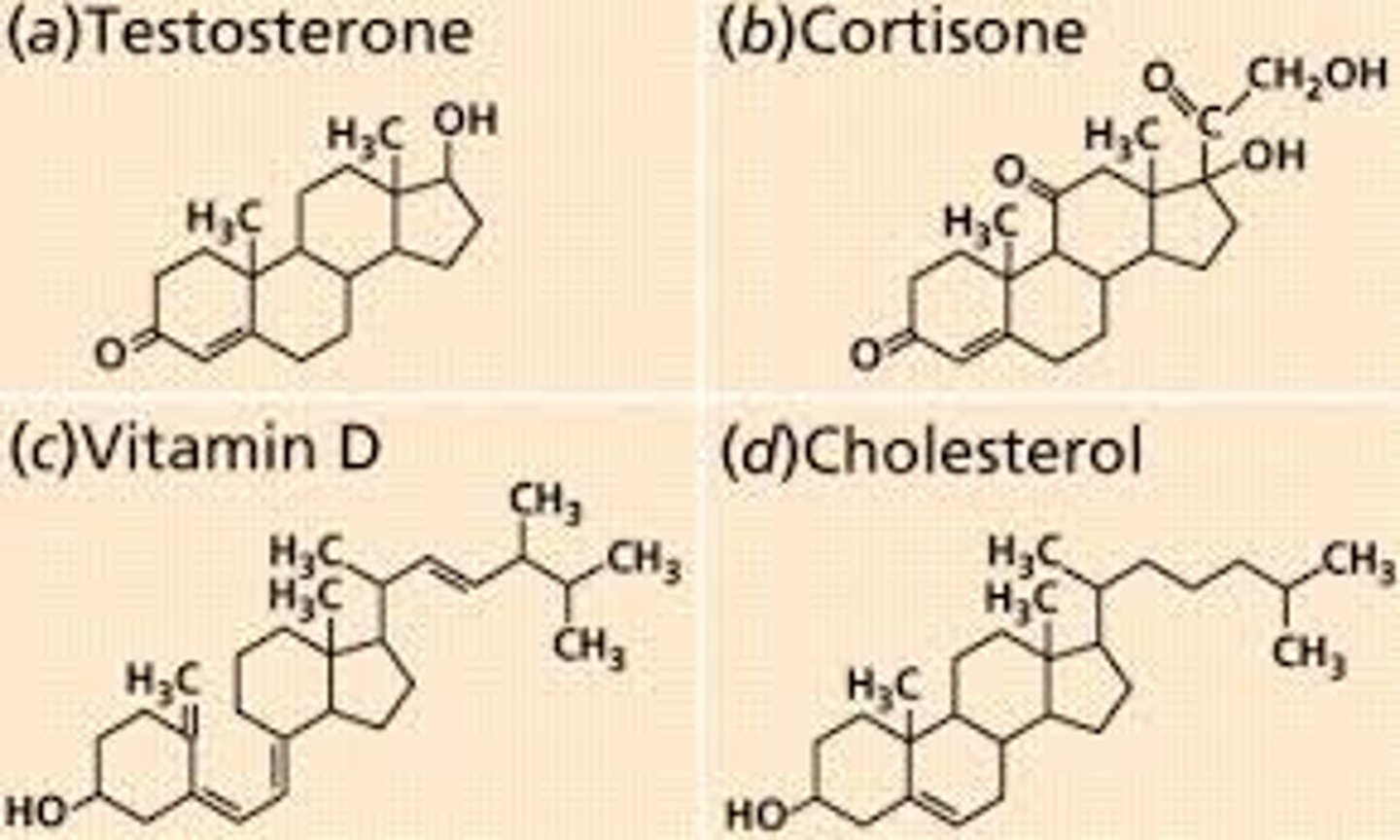
Lipids
diverse group of hydrophobic molecules; are not polymers ex. fats, steroids, and phospholipids
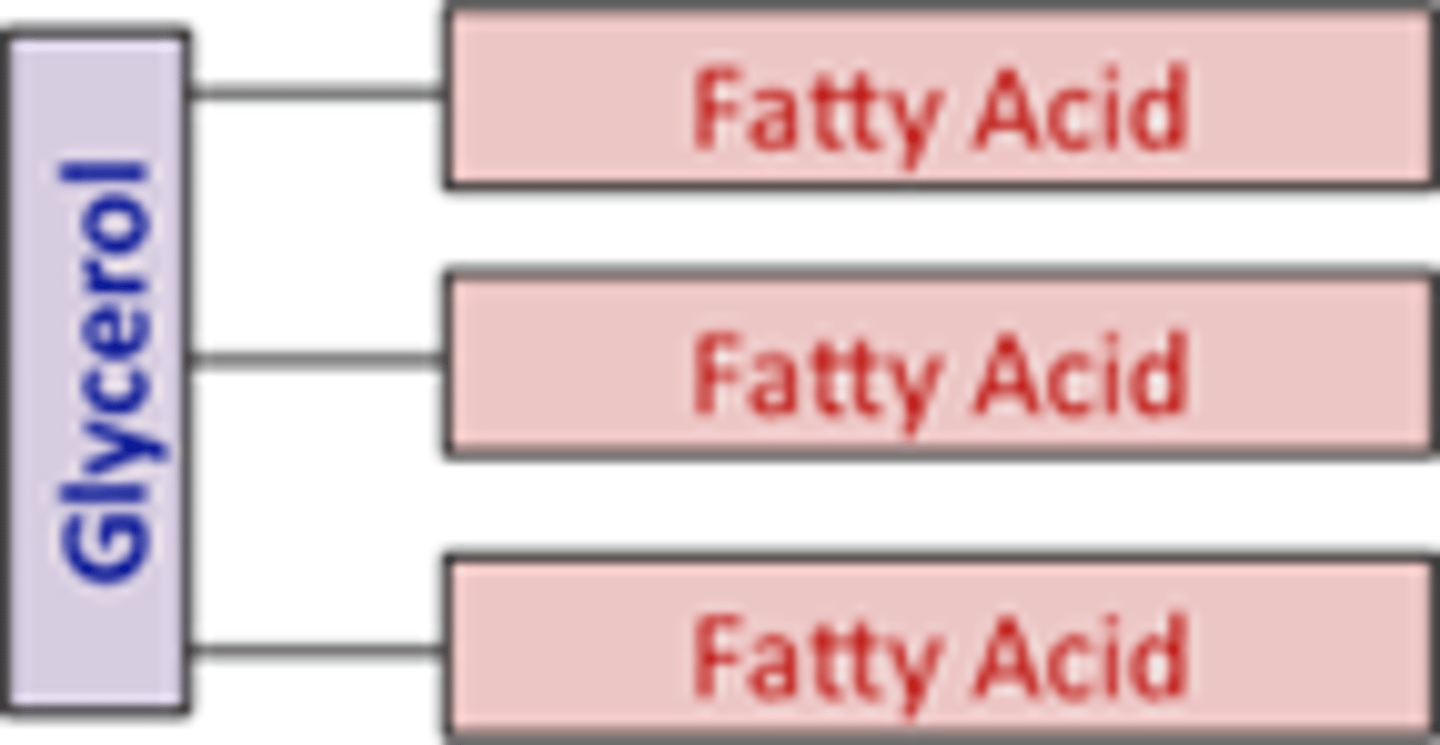
Fats
energy storage; consists of a glycerol and 3 fatty acids
- saturated: one double bond (animal fats)
- unsaturated: two double bonds (oils)
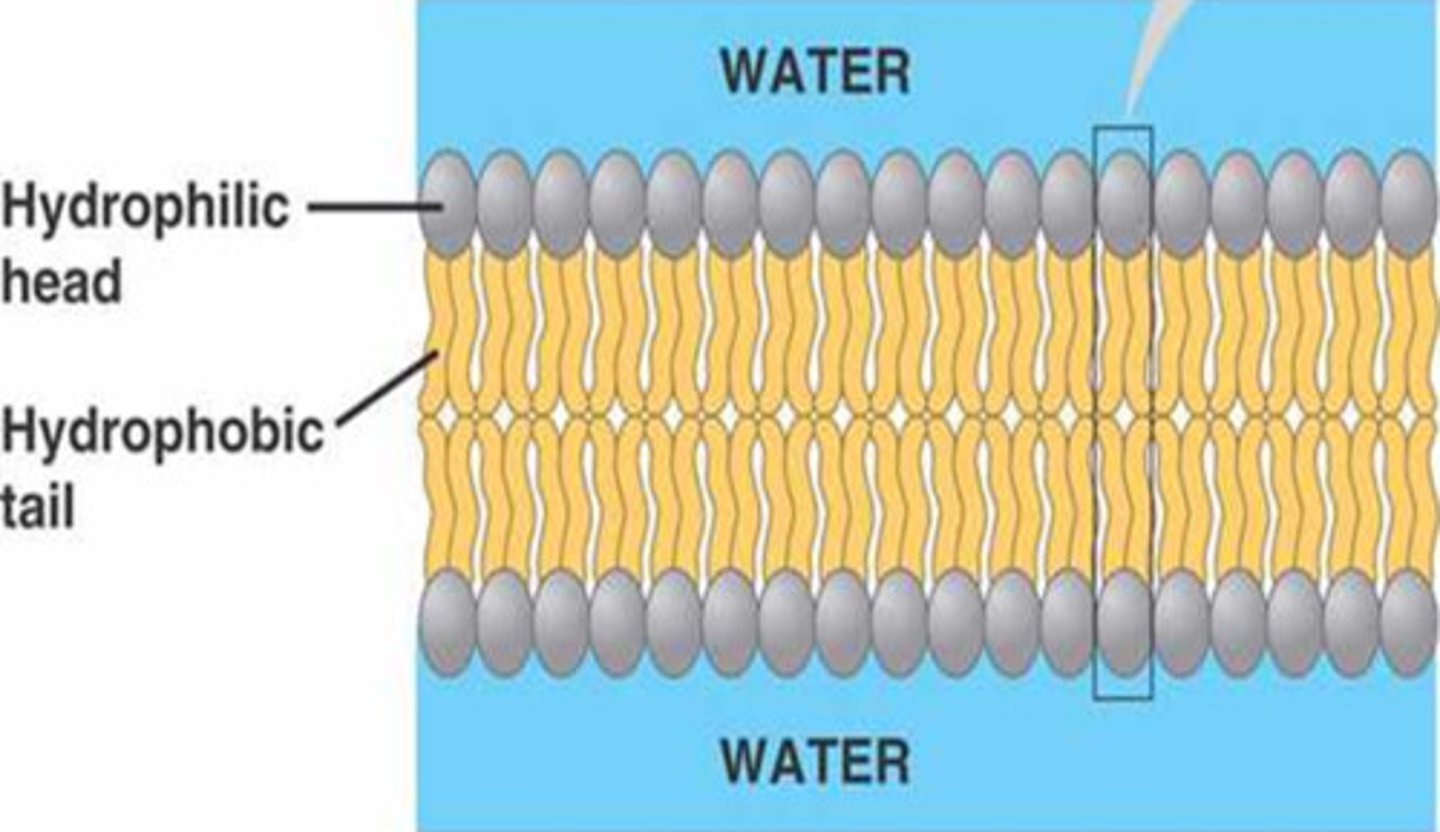
Phospholipids
2 fatty acid tails (hydrophobic) and phosphate heads (hydrophilic) ; when added into water it assembles a bilayer (2 layered sheets in cell membrane)
Steriods
lipids characterized by a carbon skeleton of 4 fused rings
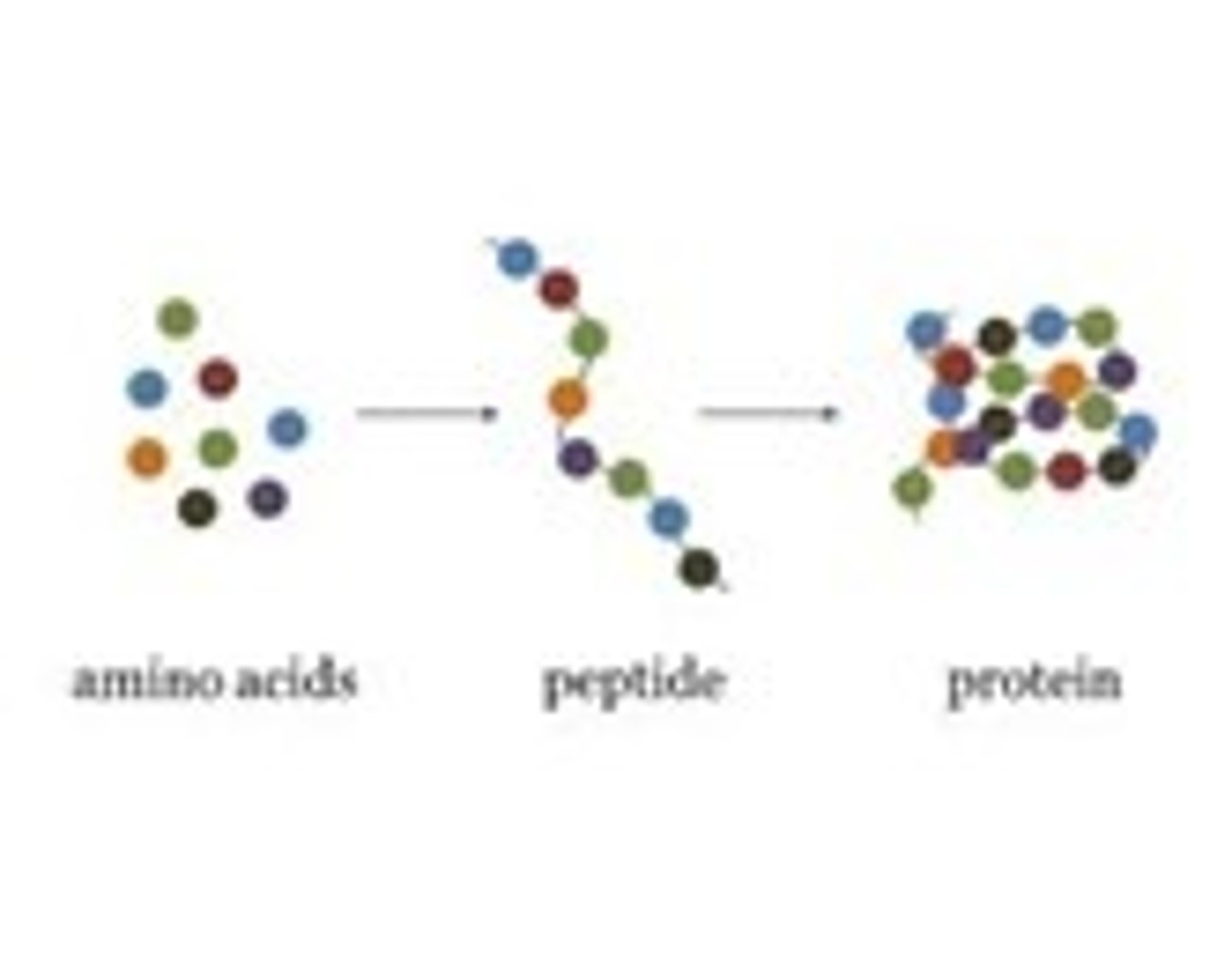
Proteins
biologically functional molecule that consists of one or more polypeptides made up of amino acids
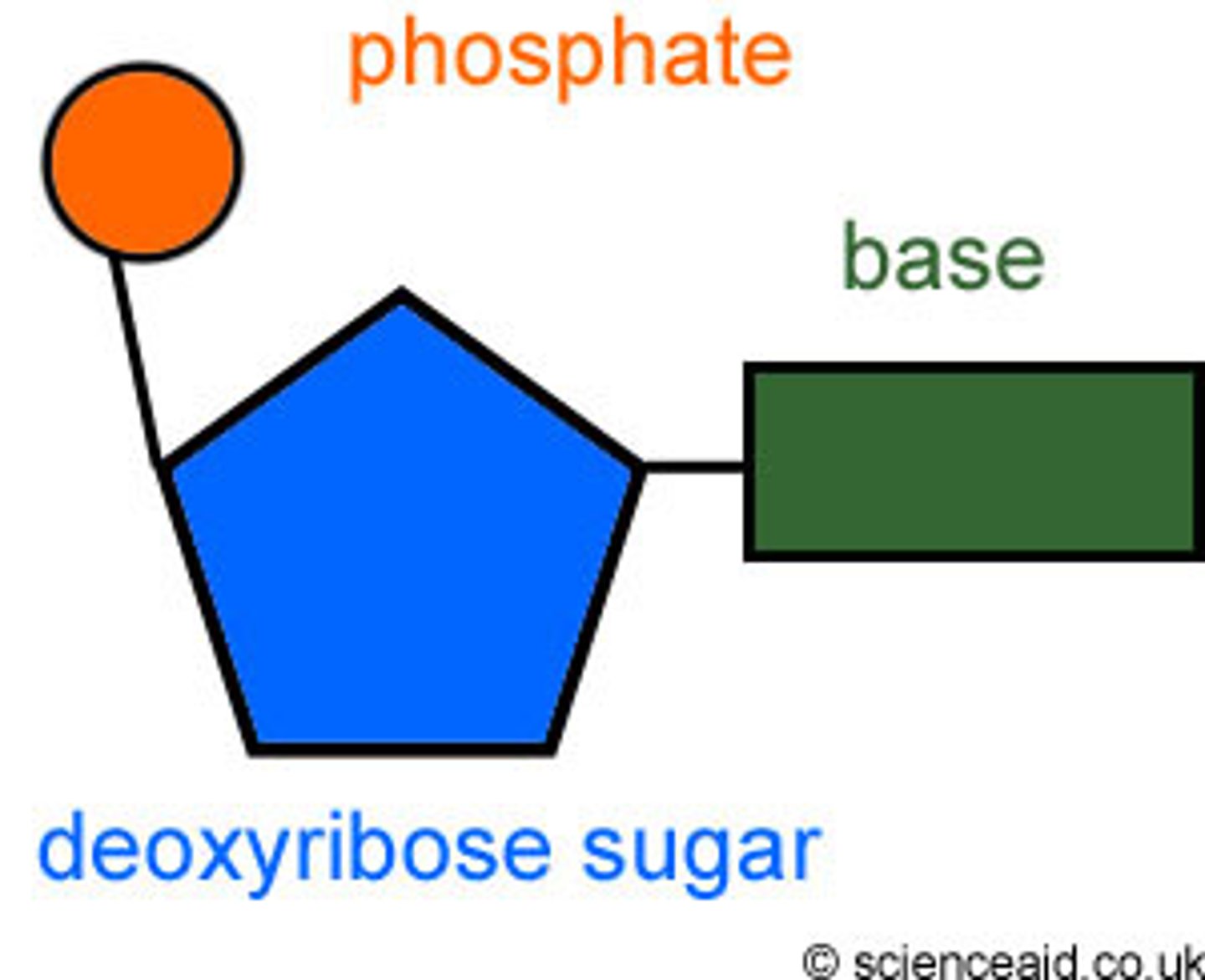
Nucleic Acids
store, transmit, and help express hereditary information; polymers called polynucleotides (DNA strands)
Plasma Membrane
selective permeable barrier that allows sufficient passage of oxygen, nutrients, and waste to service the volume of every cell; made of phospholipids; proteins in it help move material
Nuclear Envelope
encloses the nucleus, separating it from the cytoplasm; double membrane where each membrane consists of a lipid bilayer
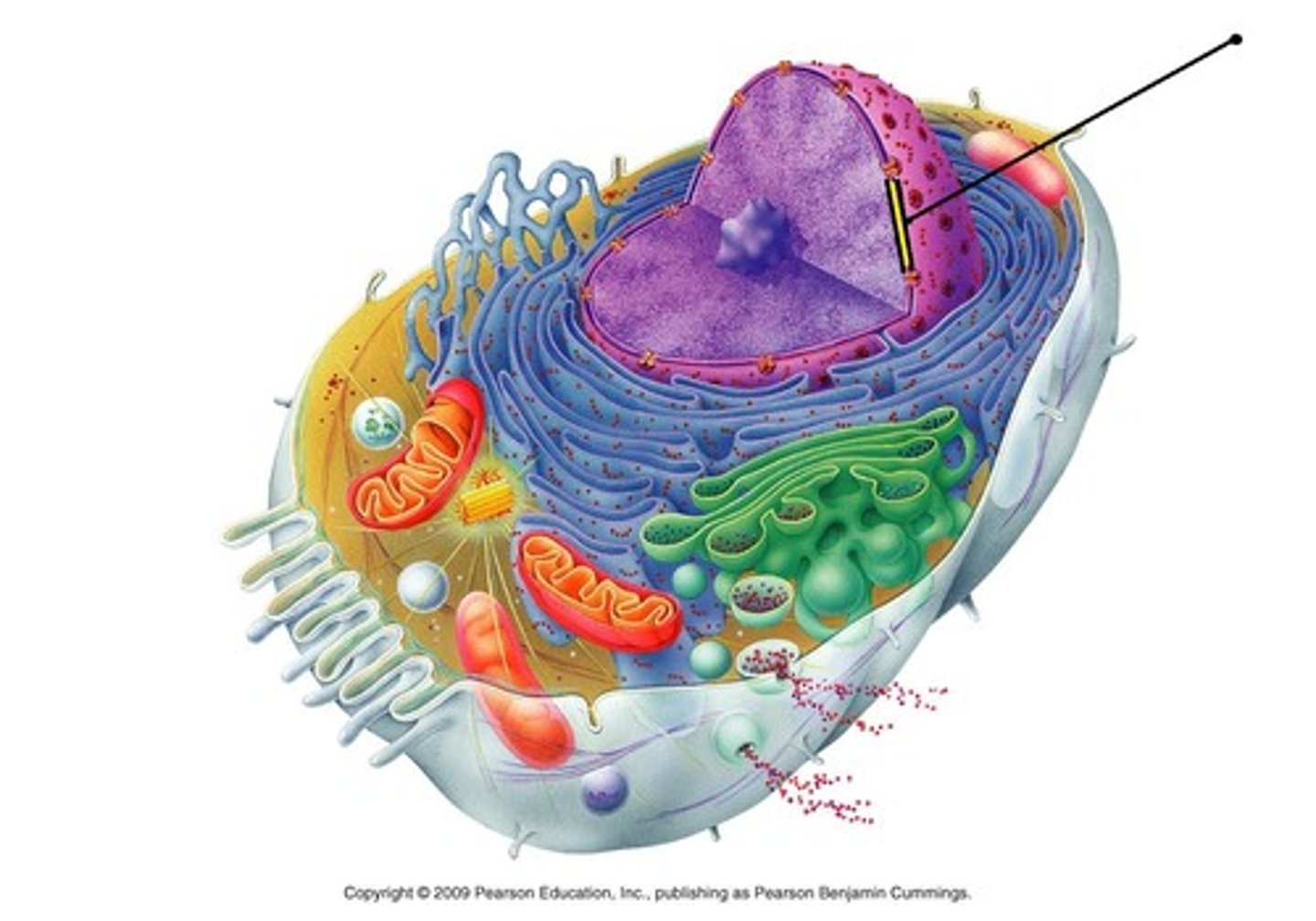
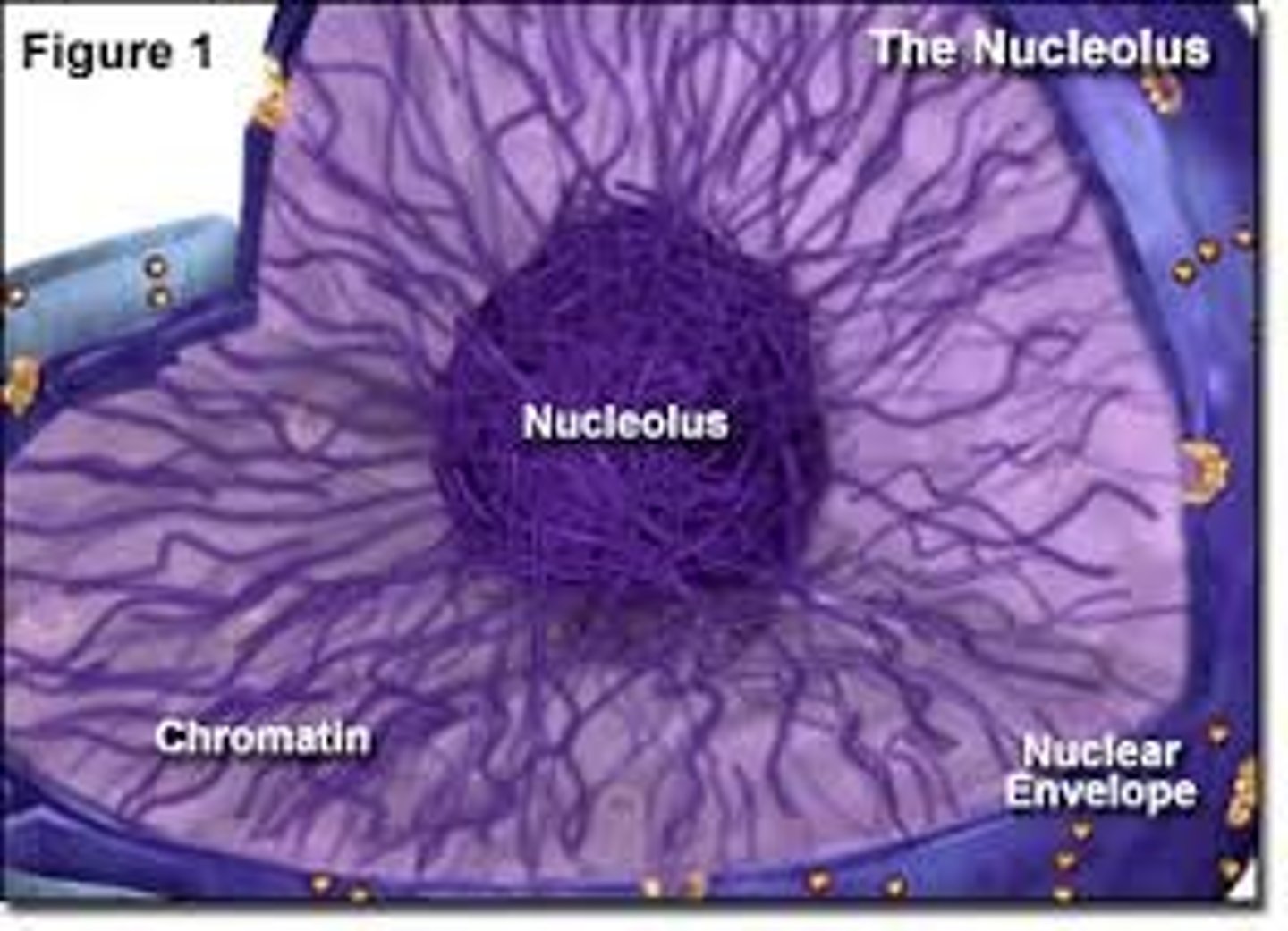
Nucleolus
located within the nucleus and is the site of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) production
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Biosynthetic Factory that consists of the smooth ER and rough ER
Smooth ER
lacks ribosomes
- Makes lipids (fats)
- Metabolizes carbohydrates
- Detoxifies drugs and poisons
- Stores calcium ions
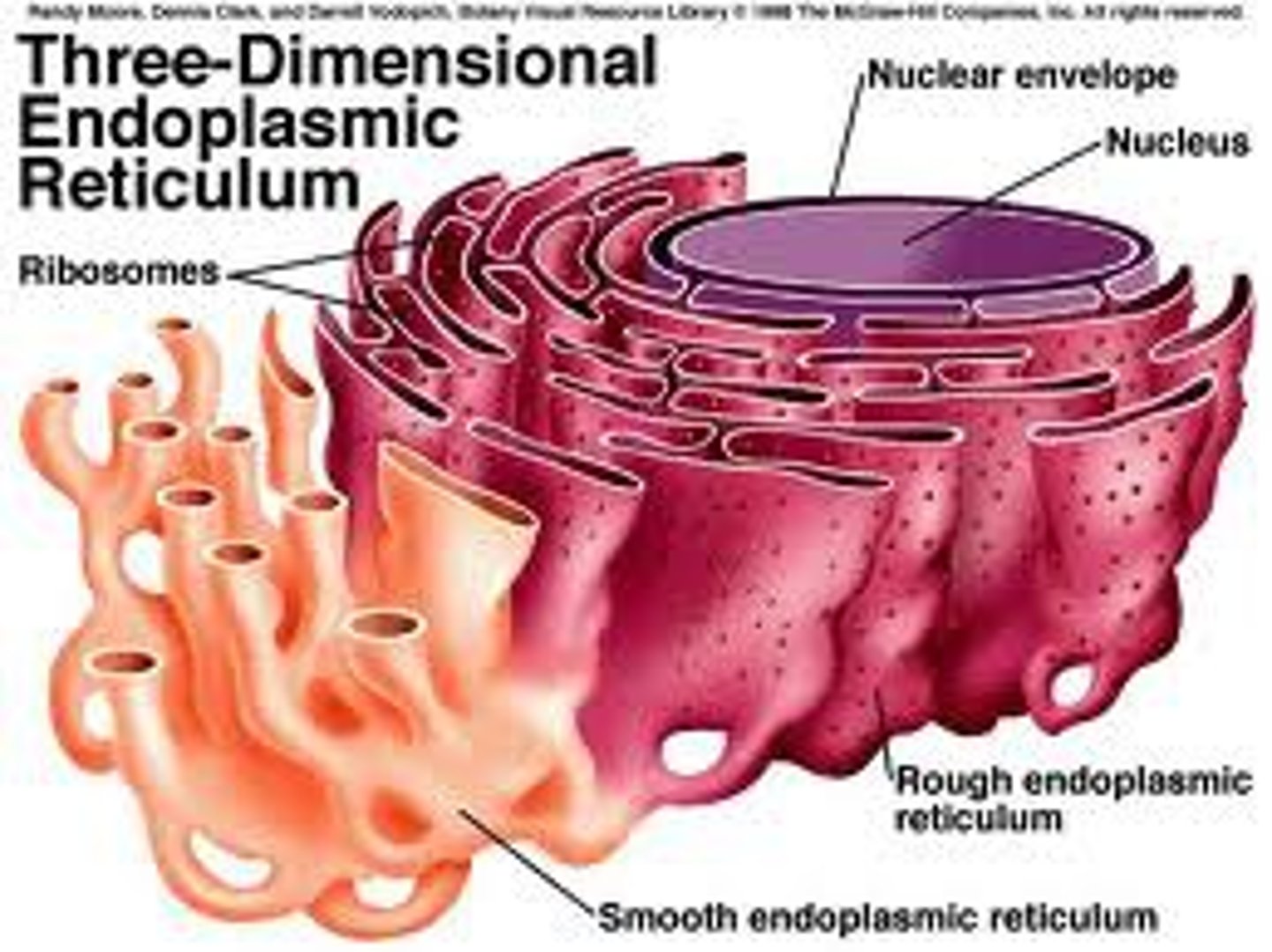
Rough ER
- Has bound ribosomes, which secrete glycoproteins (proteins covalently bonded to carbohydrates)
- Distributes transport vesicles (secretory proteins surrounded by membranes)
- Is a membrane factory for the cell
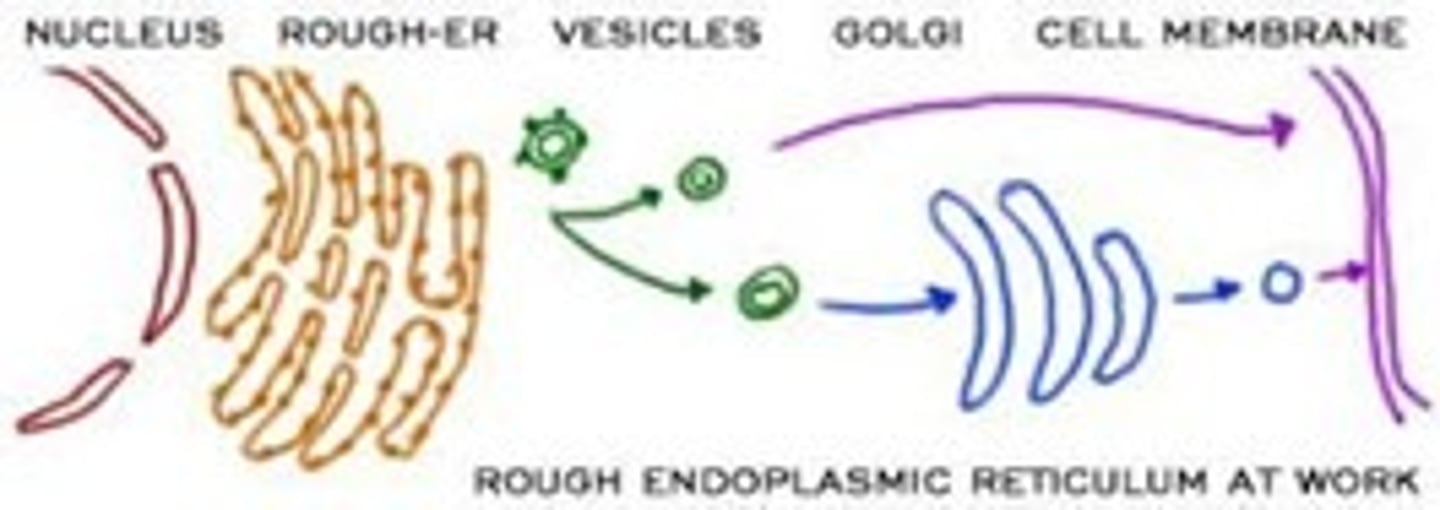
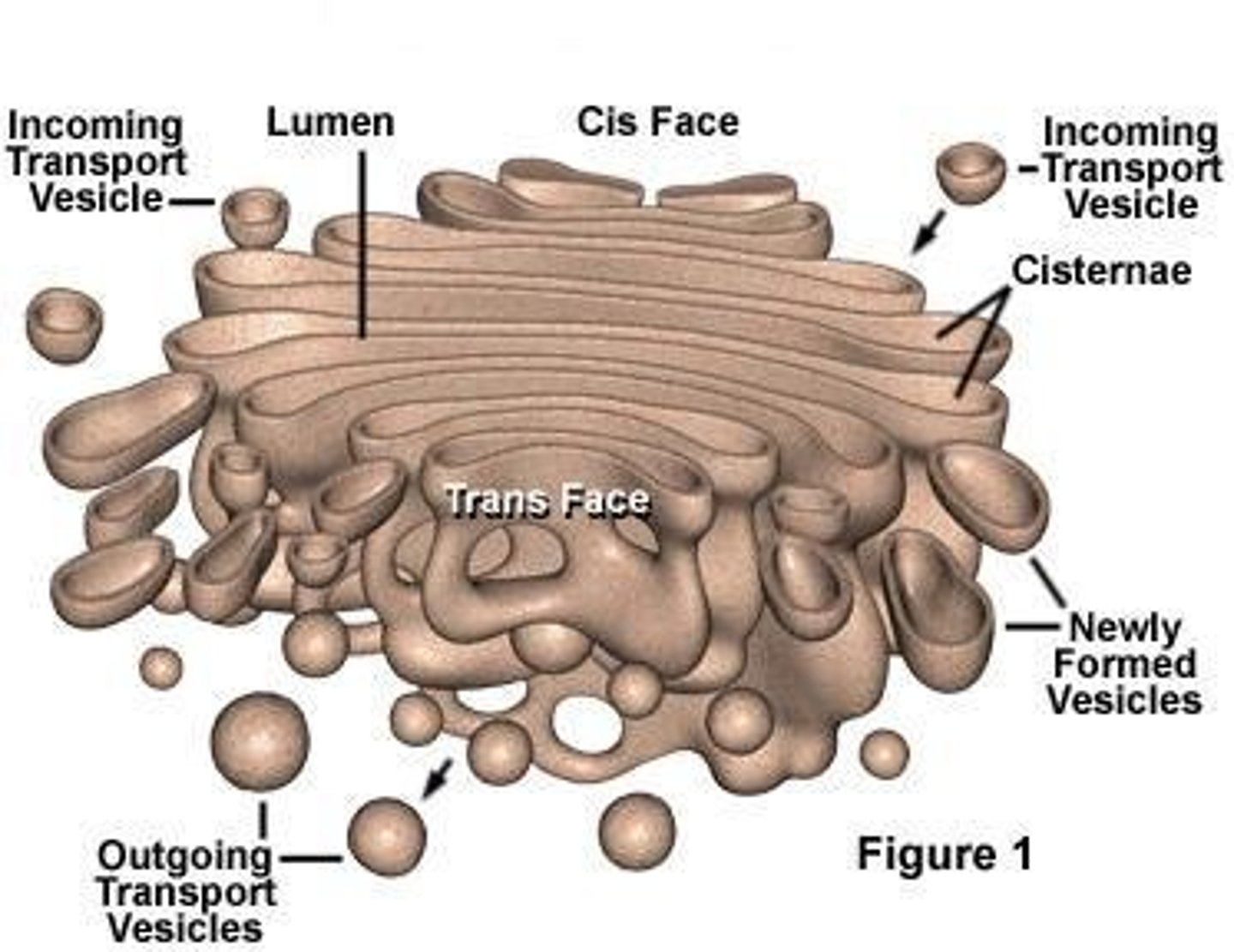
Golgi Apparatus
shipping and receiving center
- consists of flattened membranous sacs called cisternae
- Modifies products of the ER
- Manufactures certain macromolecules
- Sorts and packages materials into transport vesicles
Lysosome
membranous sac of hydrolytic enzymes that can DIGEST macromolecules; digests food or breaks down old material
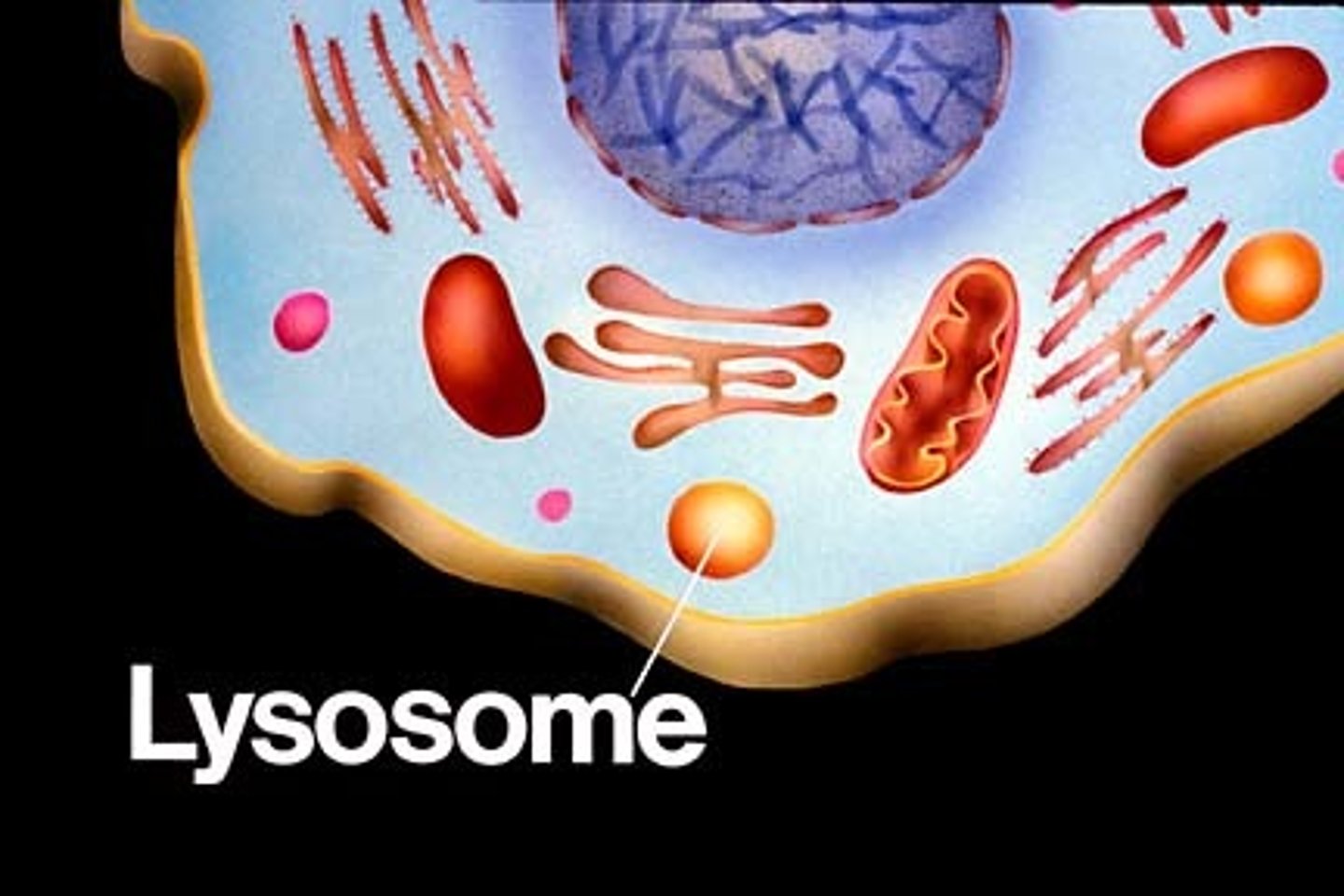
Vacuoles
storage compartment; large vesicles derived from the ER and Golgi apparatus
- Can store food
- Contractile Vacuole: contracts water out usually in aquatic cells
- Central Vacuoles: stores water in plants
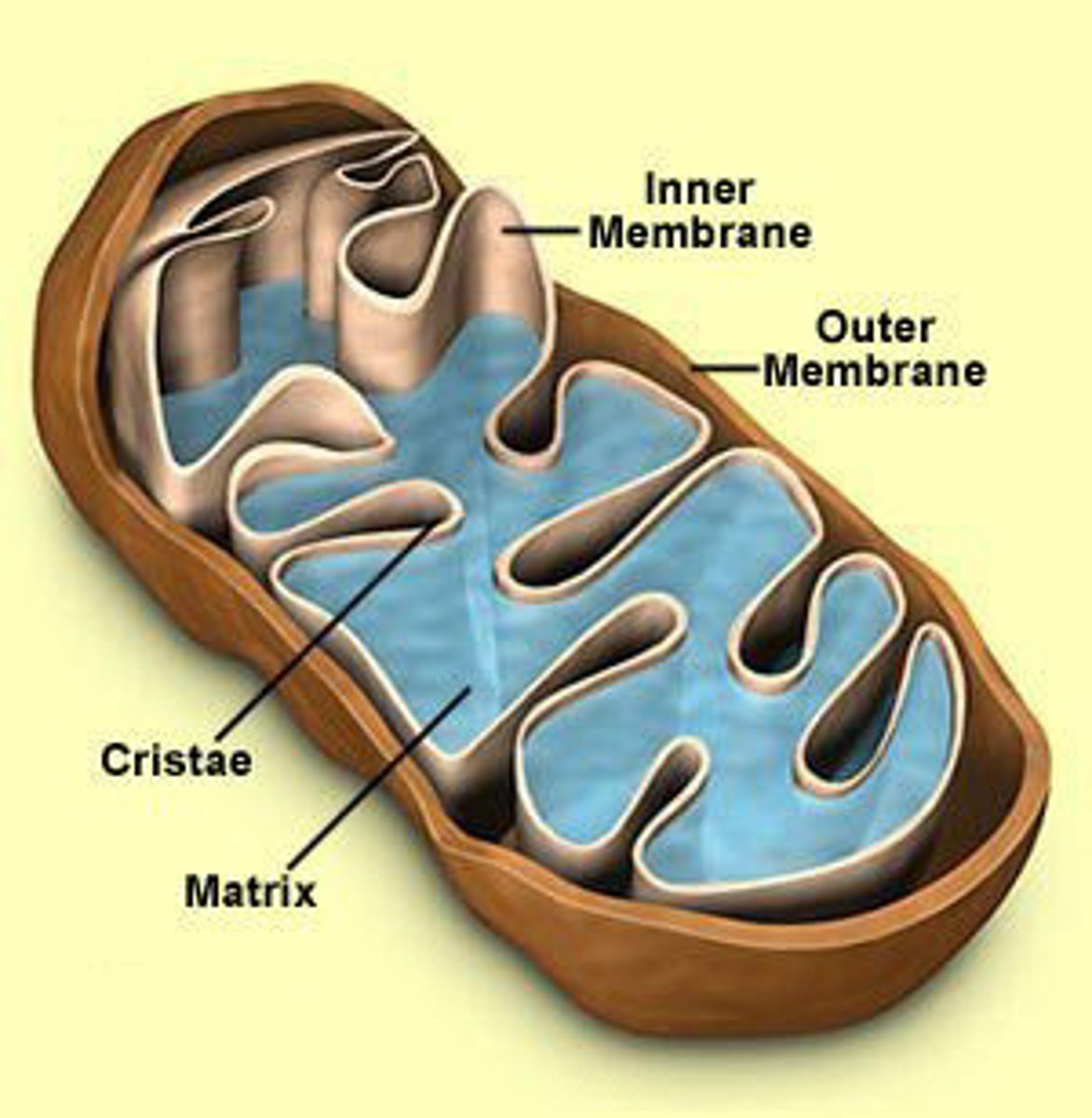
Mitochondria
site of cellular respiration; where a metabolic process happens that uses oxygen to generate ATP; chemical energy conversion
- Has outer and inner membranes
- Matrix: reactions happen here
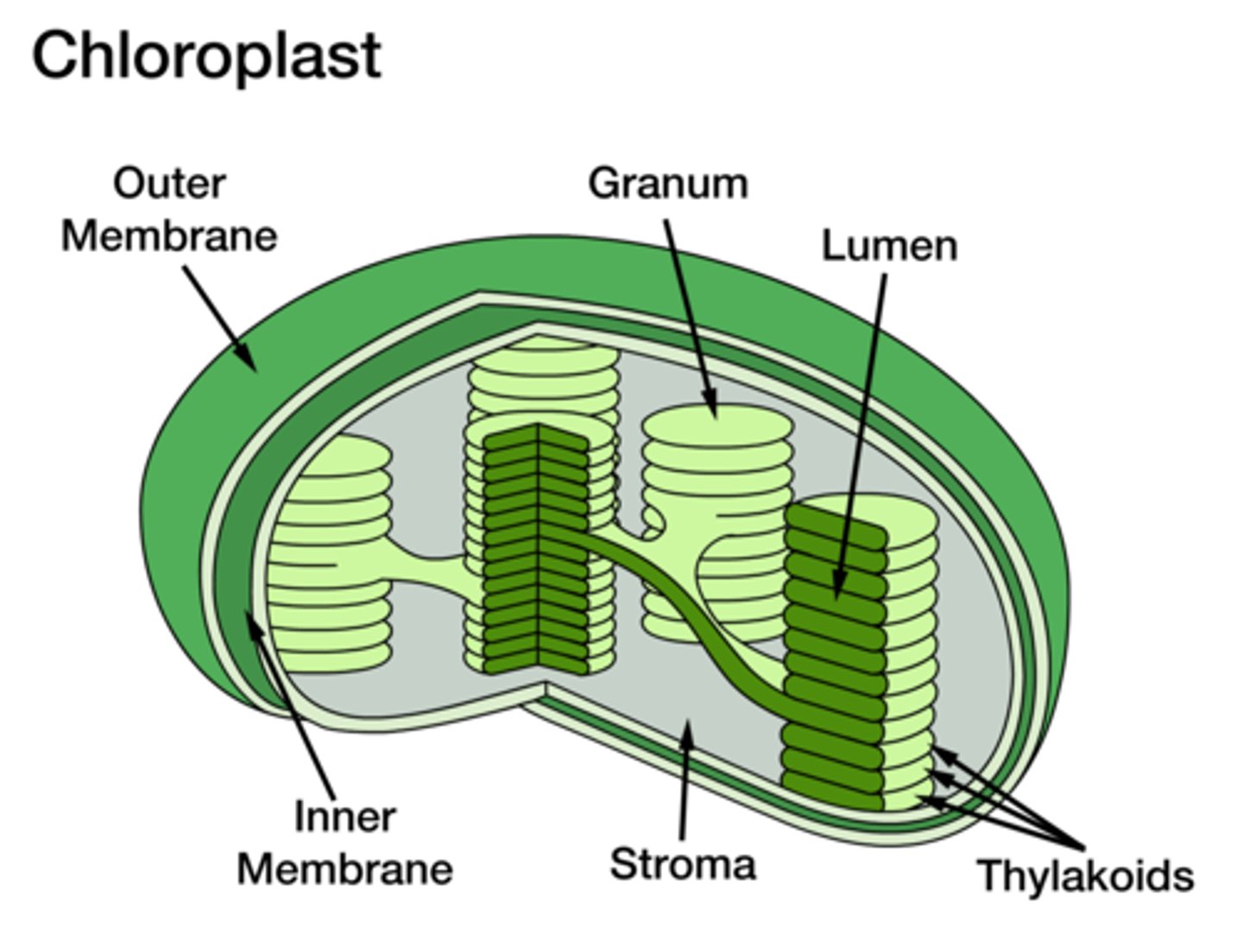
Chloroplast
site of photosynthesis in plants leaves and algae; contains the green pigment chlorophyll, as well as enzymes
- One of a group of plant organelles called Plastids
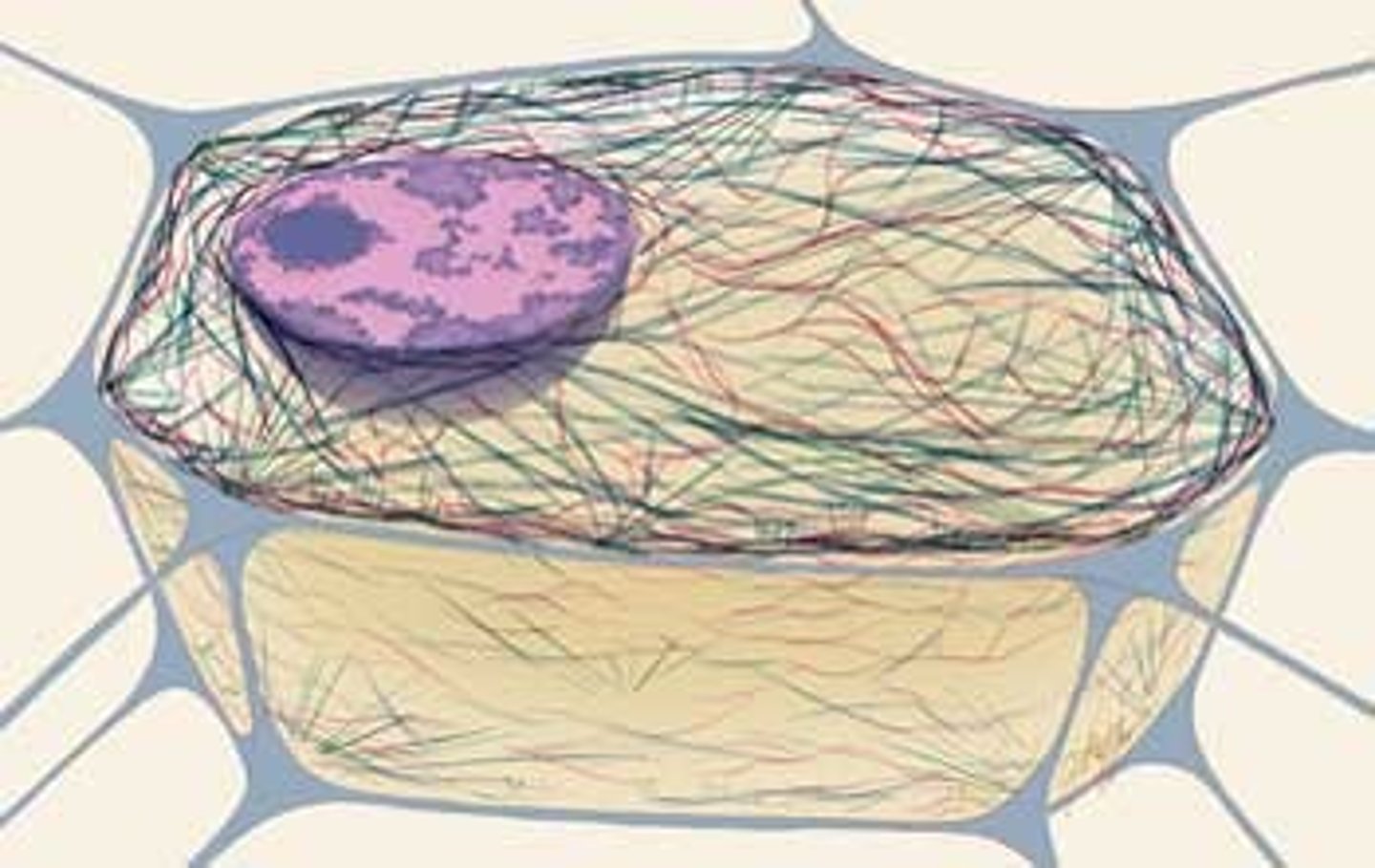
Cytoskeleton
network of fibers extending throughout the cytoplasm that organizes the cell’s structures and activities, anchoring many organelles; helps transport materials
- Helps support cell and maintain shape
- Interacts with motor proteins to produce cell motility
- vesicles move along its tracks
- microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments
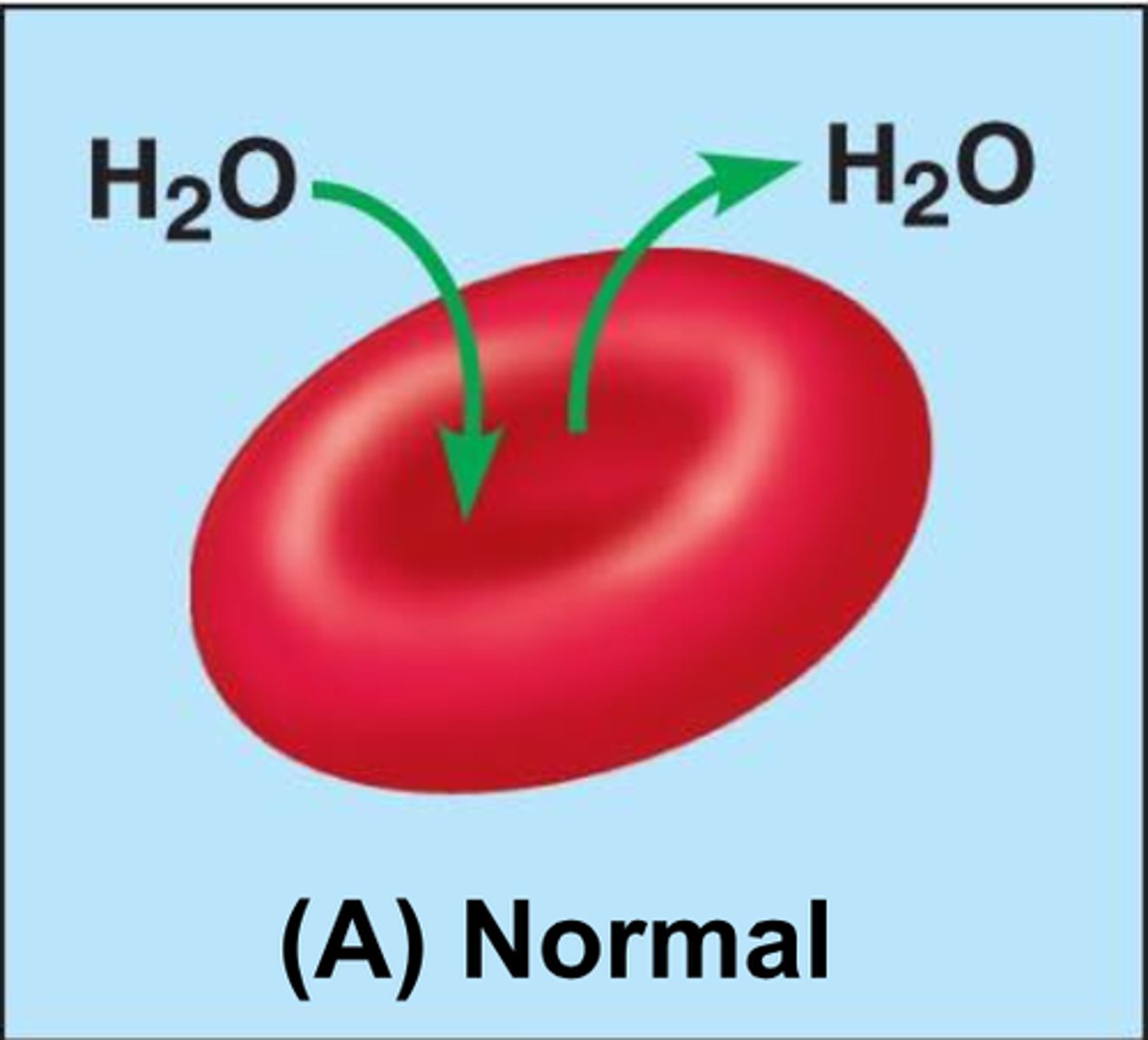
Osmosis
diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane from high water to low water concentration
Hypotonic
water filled; low solute
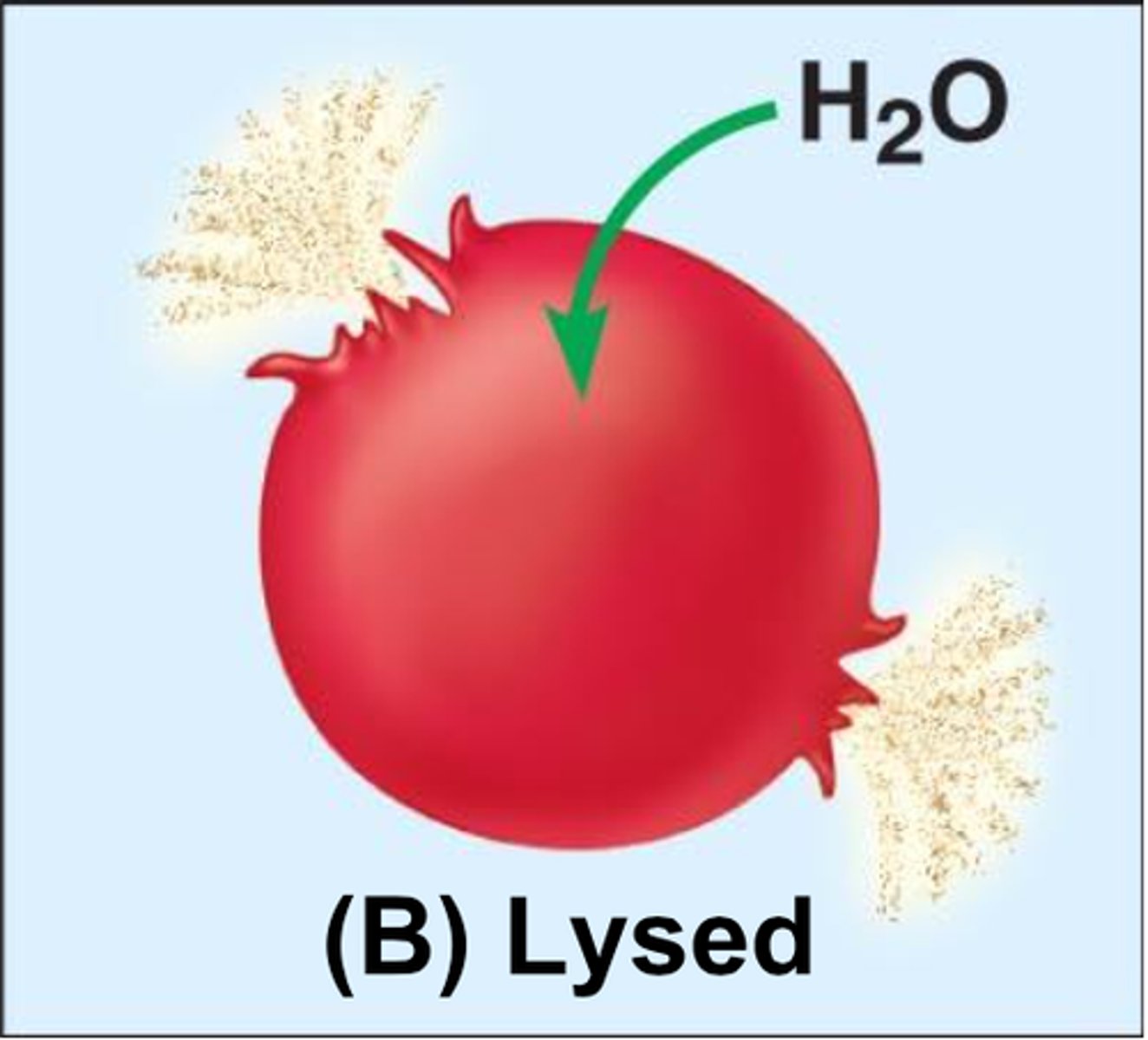
Hypertonic
high solute; low water
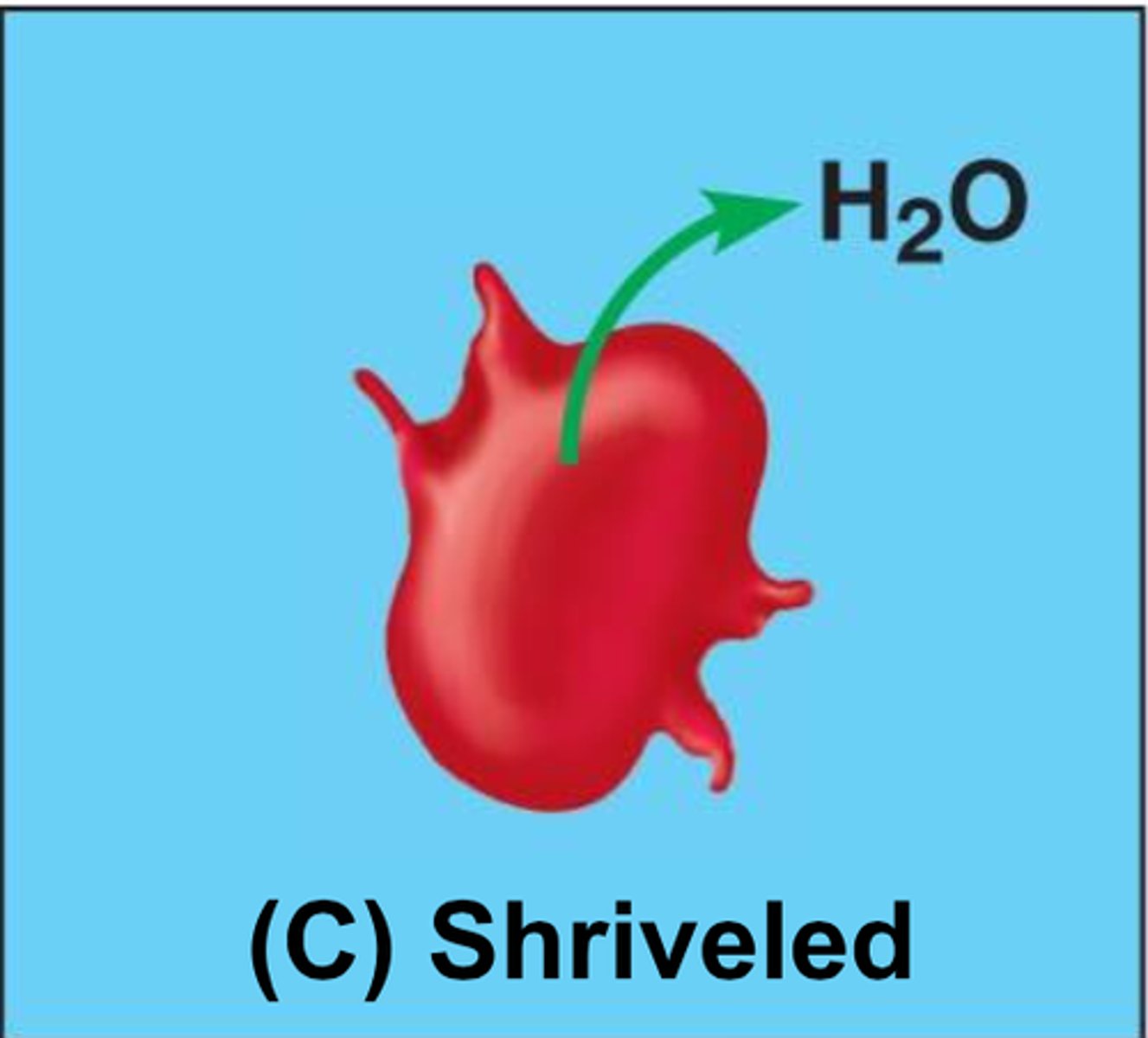
Isotonic
equal solute concentration
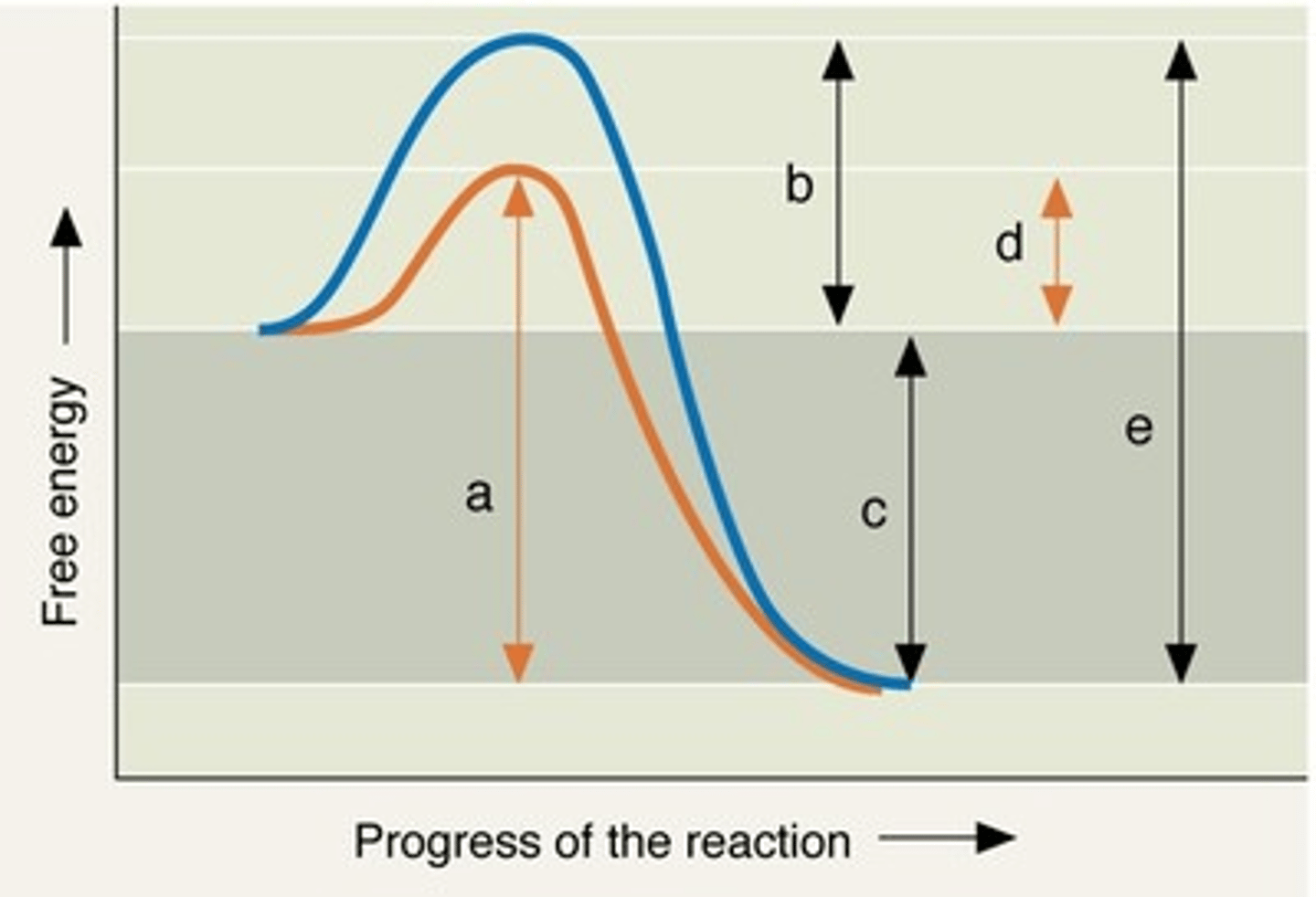
Enzyme Reaction Graph
A: catalyzed reaction
B: activation energy without catalyst
C: free energy (same in all reactions)
D: activation energy with catalyst
E: uncatalyzed reaction
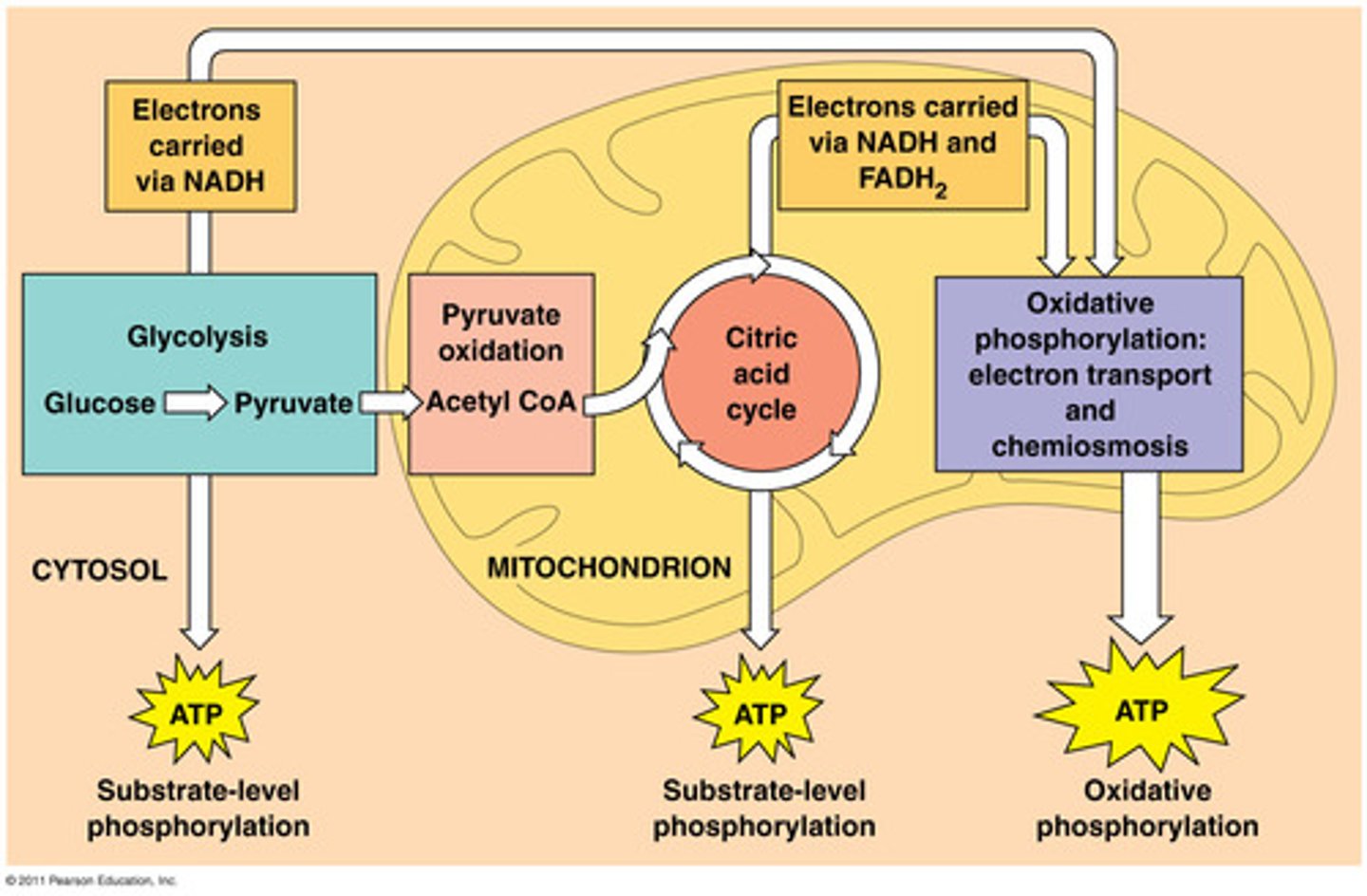
Cellular Respiration
Glucose + oxygen --> carbon dioxide, water, and energy
we eat and breathe in, then breathe out and have energy
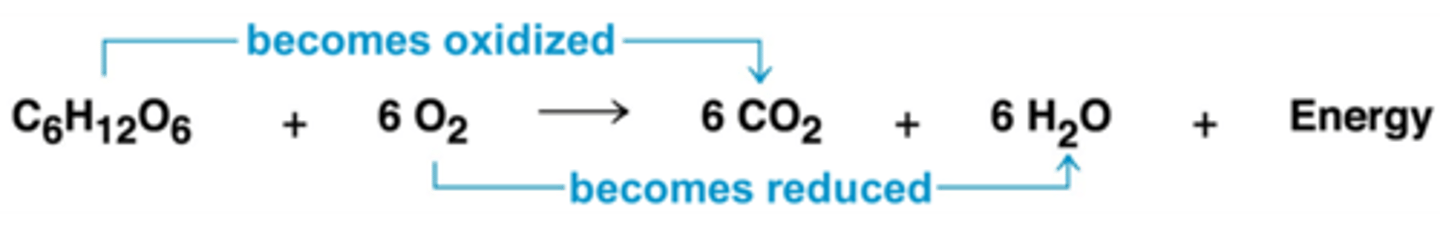
Redox Reaction in Cellular Respiration
glucose is oxidized (losing electrons)
oxygen is reduced (gaining electrons)
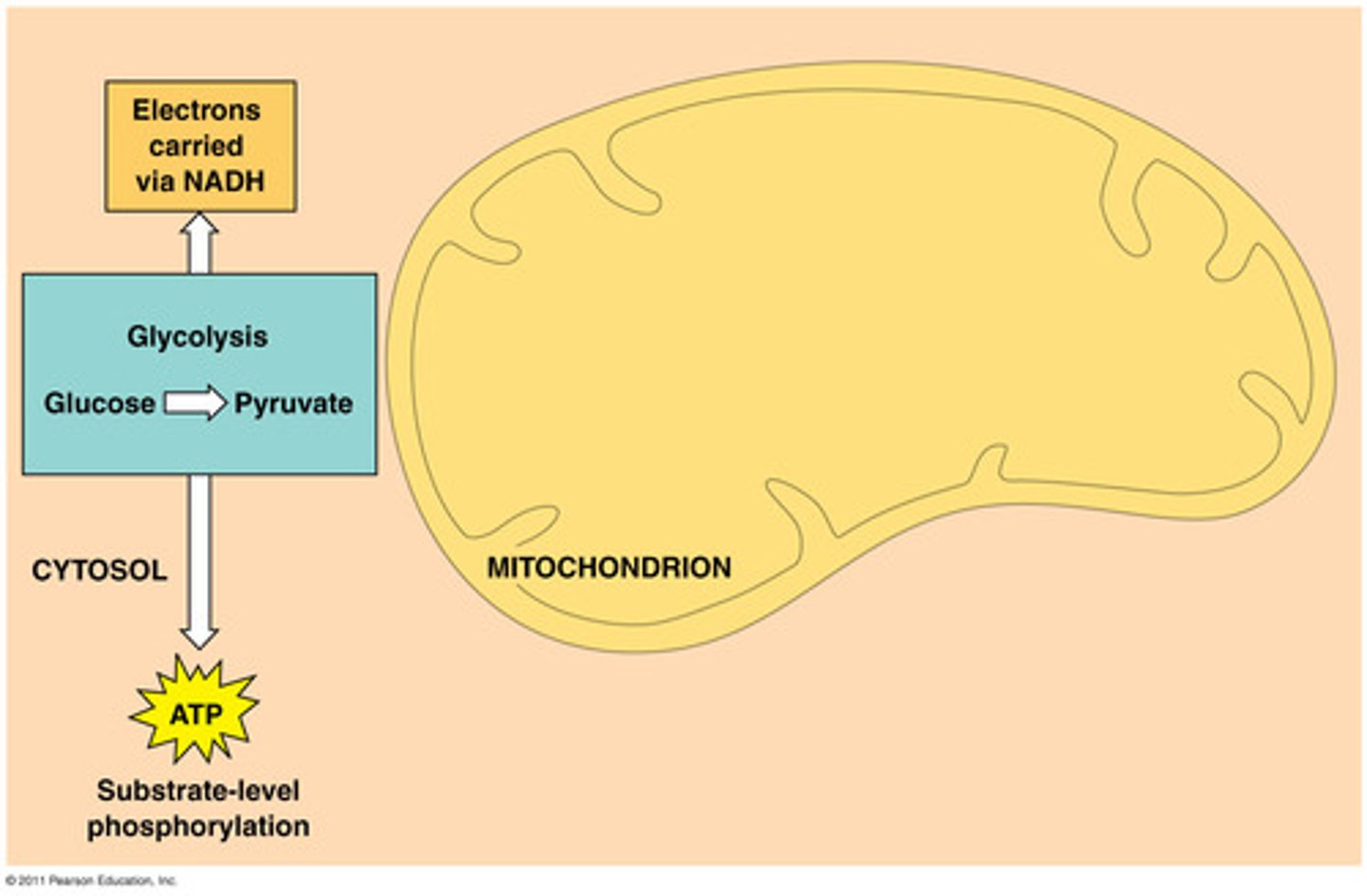
Glycolysis
glucose breaks down (oxidizes) into 2 Pyruvate in the cytoplasm; "sugar splitting"; Can occur with or without oxygen
- Input: glucose (and 2 ATP to get started)
- Output: 2 pyruvate, 2 ATP, 2 NADH
Pyruvate Oxidation
Pyruvate is converted into 2 Acetyl CoA in the matrix of mitochondrion
Citric Acid Cycle (Krebs Cycle)
completes the breakdown of Acetyl CoA to CO2 in the matrix in two turns
results:
- 2 ATP
- 6 NADH
- 2 FADH
Oxidative Phosphorylation
The process that generates almost 90% of the ATP; powered by redox reactions; in mitochondria inner membrane
- Consists of chemiosmosis and electron transport chain
Electron Transport Chain
in inner membrane (cristae) of mitochondria; the passing down of electrons in a chain through proteins to oxygen; at the end, oxygen combines with hydrogen to make water
- Generates no ATP directly
- Creates a H+ gradient with an accumulation of H+ in the intermembrane space
- Electrons lose energy through each pass
Chemiosmosis
it uses hydrogen gradient energy from electron transport for ATP synthesis (making of ATP)
- The energy released as electrons are passed down the electron transport chain is used to pump H+ from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space
- H+ then moves down its concentration gradient back across the membrane, passing through the protein complex ATP synthase
- Where most ATP is made (ADP combines with a P to make it)
Photosynthesis
Carbon dioxide + water + light = glucose and oxygen
plants take in carbon dioxide, water, and light, and make glucose and give off oxygen
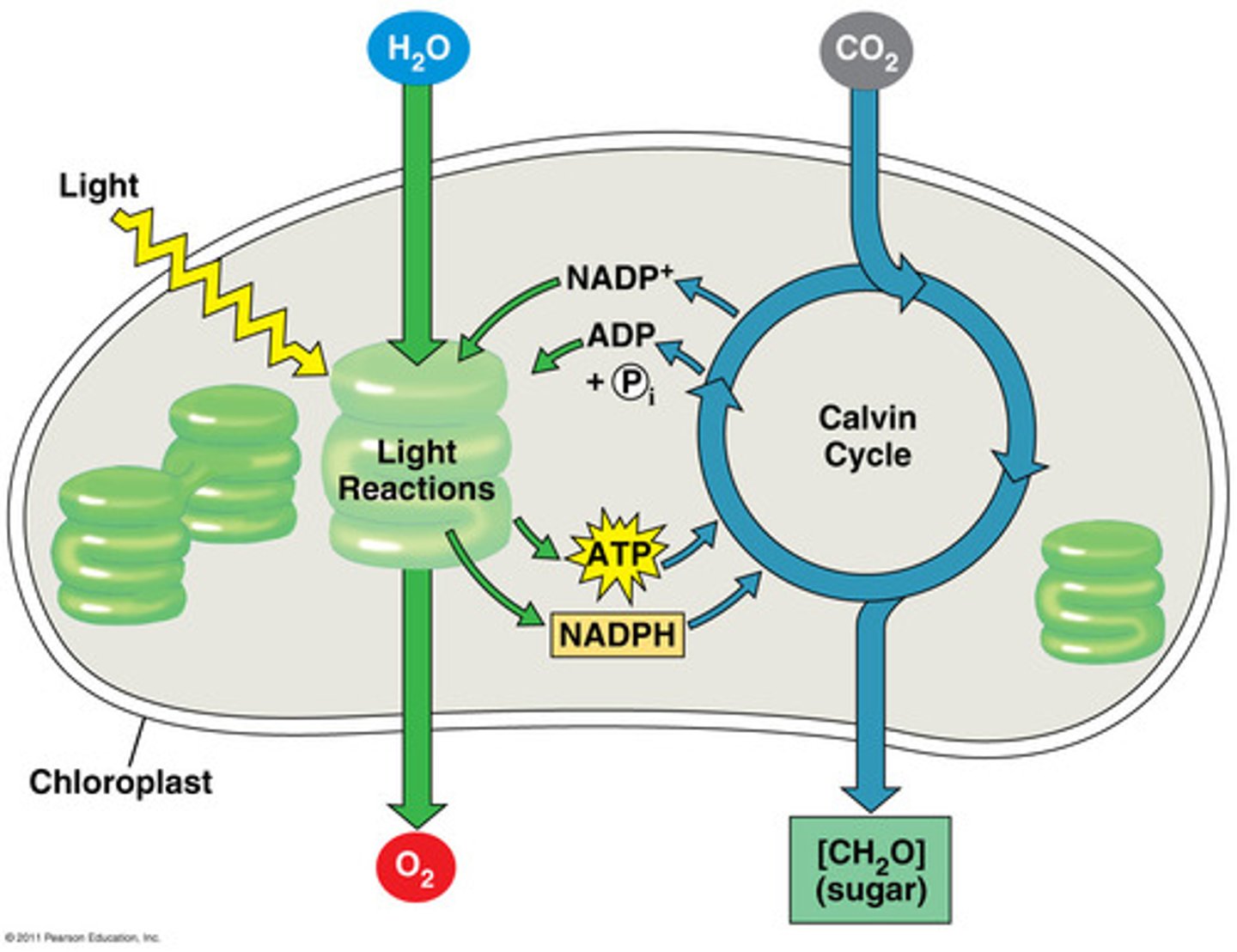
Redox Reaction in Photosynthesis
carbon dioxide reduced to glucose (gains electrons)
water oxidized to oxygen (loses electrons)
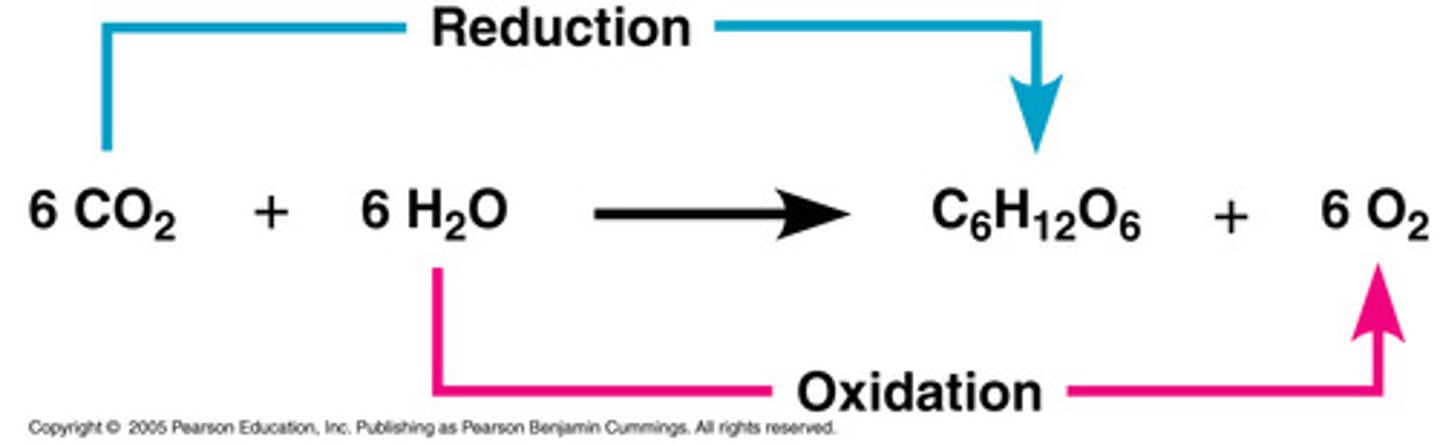
Chloroplast
an envelope of 2 membranes surrounding a dense fluid (stroma); consists of thylakoids and grana
Light Reactions (Light dependent reaction)
in thylakoids; convert solar energy into the chemical energy of ATP and NADPH through two photosystems
Photosytem II
light hits pigment molecules, electrons are lost and go to chlorophyll, carried by electron acceptor down electron transport chain
Photosystem I
light hits pigment molecules, electrons move up to electron acceptor; then down through electron transport chain, NADP+ is reduced to NADPH
Creation of water and ATP in photosynthesis
- water splits and makes oxygen
- hydrogens (from the electrons lost) move to ATP synthase in thylakoid and produce ATP
Calvin Cycle (light independent reaction)
uses the chemical energy of ATP and NADPH to reduce CO2 to sugar in the stroma
- carbon enters the cycle as carbon dioxide and leaves a sugar named glyceraldehyde 3-phospate (G3P)
1. Carbon fixation (catalyzed by rubisco to RuBP)
2. Reduction
3. Regeneration of the CO2 acceptor (RuBP)
Carbon Fixation
initial carbon input into cycle; carbon dioxide gets fixed onto Rubisco and becomes a 6 carbon molecule
Reduction
gets broken into 3 (G3P) through NADPH, some energy goes out to make glucose, what's remaining goes back into system
Regeneration
G3P is regenerated and converted back into Rubisco with the help of ATP
- Then at the end it returns ADP and NADP to light reactions
Mitosis
division of genetic material in nucleus, resulting in 2 identical daughter cells
- each with same chromosome number as parent cell
- chromosomes in unduplicated form
Mitosis Phases
- Prophase: spindle forms; chromosomes condense
- Prometaphase: microtubules of spindle pierce chromosomes
- Metaphase: chromosomes line up in the middle through spindle work
- Anaphase: chromosomes are pulled apart to opposite sides by spindle; sister chromatids separate; daughter chromosomes formed
- Telophase: cleavage furrow; nuclear envelopes and nucleolus forms in both cells as they separate
- Cytokinesis: division of cytoplasm
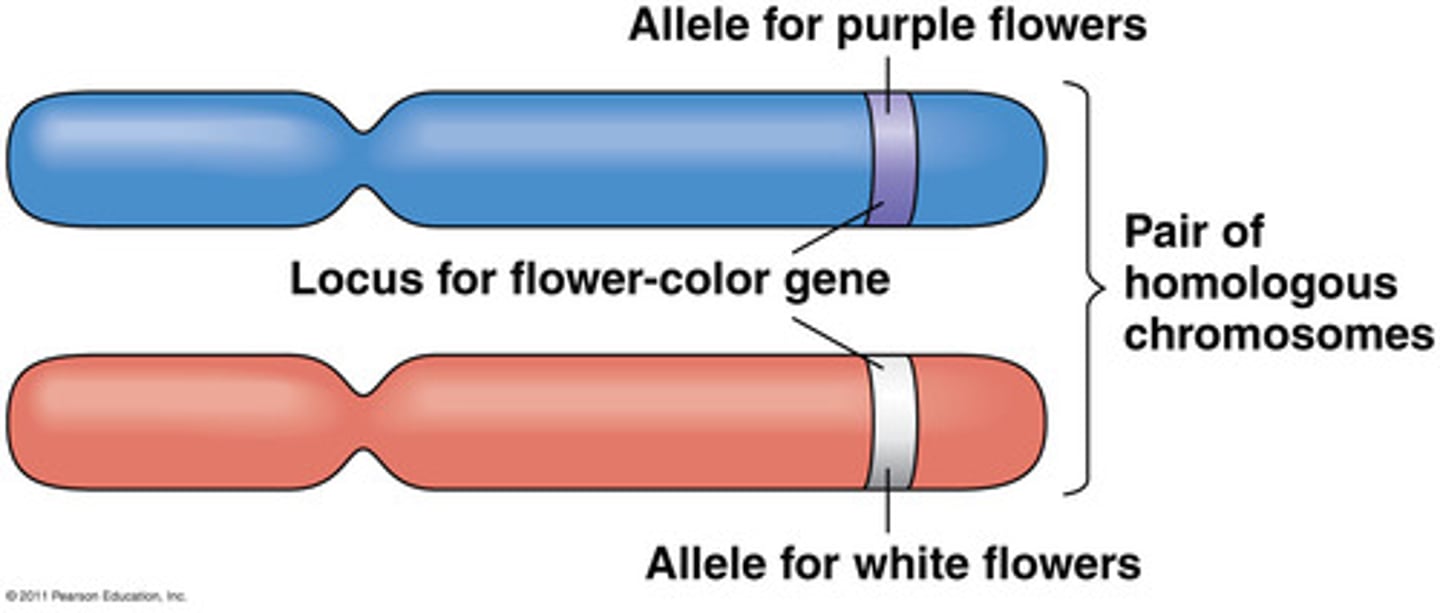
Homologous Chromosomes (homologs)
2 chromosomes in a pair where one comes from each parent; are the same length and shape and carry genes controlling the same inherited characters, but different types
- each parent has 2 sister-chromatids
Diploid Cell (2n)
2 sets of chromosomes ex. zygote
Haploid Cell (n)
1 set of chromosomes ex. gametes (egg and sperm)
- two haploid cells create a zygote that grows into a baby
Meiosis
single diploid cell makes 4 differing haploid cell gametes; consists of 2 divisions
Meiosis I
homologous chromosomes separate and result in 2 haploid cells with duplicated chromosomes
Prophase I: chiasmata forms from the pair of homologous chromosomes crossover, and form recombinant chromatids (total of 46 chromosomes)
- Metaphase I: line up in middle horizontally with spindle piercing them; homologous pairs orient randomly (independent assortment)
- Anaphase I: homologous chromosomes separate to opposite sides but sister chromatids remain attached
- Telophase I and Cytokinesis: cell breaks apart with cleavage furrow; has 23 duplicated chromosomes (two haploid cells)
Meiosis II
2 haploid cells make 4 haploid cells that all differ
- (similar to mitosis in that sister chromatids separate) and result in 4 haploid cells with unduplicated chromosomes
- Prophase II: 2 cells with crossed over chromosomes, spindle forms
- Metaphase II: crossed chromosomes line up in the middle in each cell
- Anaphase II: sister chromatids separate to opposite sides in each cell
- Telophase II and Cytokinesis: cleavage furrow of the two cells and 4 haploid daughter cells remain
Ex. A diploid cell contains 6 chromosomes. After meiosis I, each of the cells contains what?
A mixture of maternal and paternal chromosomes totaling 3. (After Meiosis I, the cells are halved (haploid) and total 3 now instead of 6. Theres a mixture of each parent's chromosomes from crossing over in prophase.)
Comparison of Mitosis and Meiosis
- meiosis reduces chromosome sets, while mitosis conserves them
- meiosis produces genetically different gametes, while mitosis produces identical ones
- in meiosis, crossing over of chromatids happen in prophase and they separate in anaphase, while in mitosis only sister chromatids separate
How much original DNA is left after mitosis and meiosis?
- mitosis: all because they are identical
- meiosis: half as many chromosomes as the parent cell
Character
A heritable feature that varies among individuals (such as flower color)
Trait
Each variant for a character (such as purple or white color for flowers)
True-Breeding Plants (Gregor)
plants that produce offspring of the same variety when they self-pollinate ex. purple flower producing purple
- P Generation: parents
- F1 Generation (1st cross): The hybrid offspring of the P generation
- F2 Generation (2nd cross): produced when F1 self-pollinate (cross pollinate) with other F1 hybrids
Gene
A segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific trait ex. chromosome can contain the same alleles for different ones
Alleles
different versions of a gene ex. brown or blue eyes
Homozygote
An organism with two identical alleles (PP or pp) for a character (flower color)
Heterozygote
An organism with two different alleles for a gene (Pp)
Phenotype
the visible and measurable physical characteristics of an organism (flower color)
Genotype
the particular pair of alleles present for a given gene
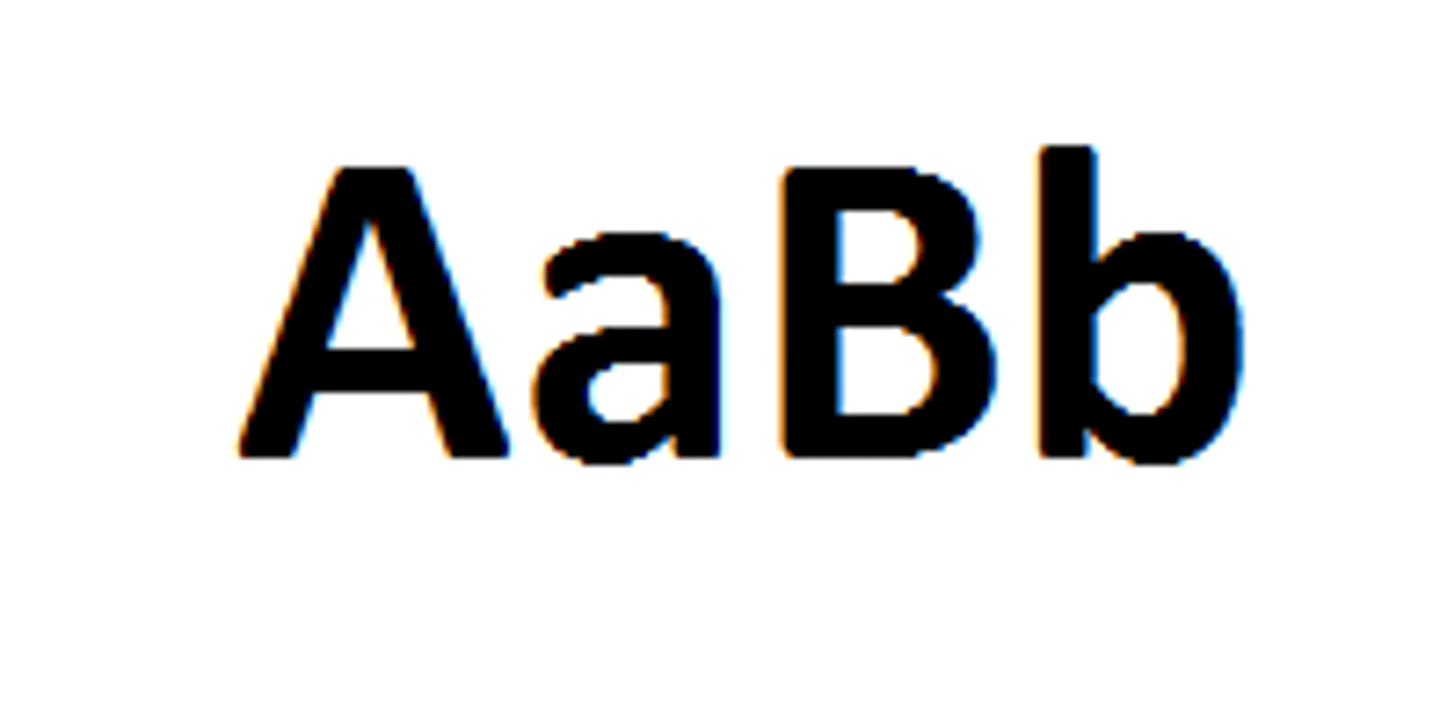
Combinations of Genotypes
- Homozygous dominant: PP
- Homozygous recessive: pp
- Heterozygous: Pp
Complete Dominance
occurs when phenotypes (flower color) of the heterozygote and dominant homozygote are identical (PP and Pp both make purple)
- Dominant allele masks the expression of the recessive

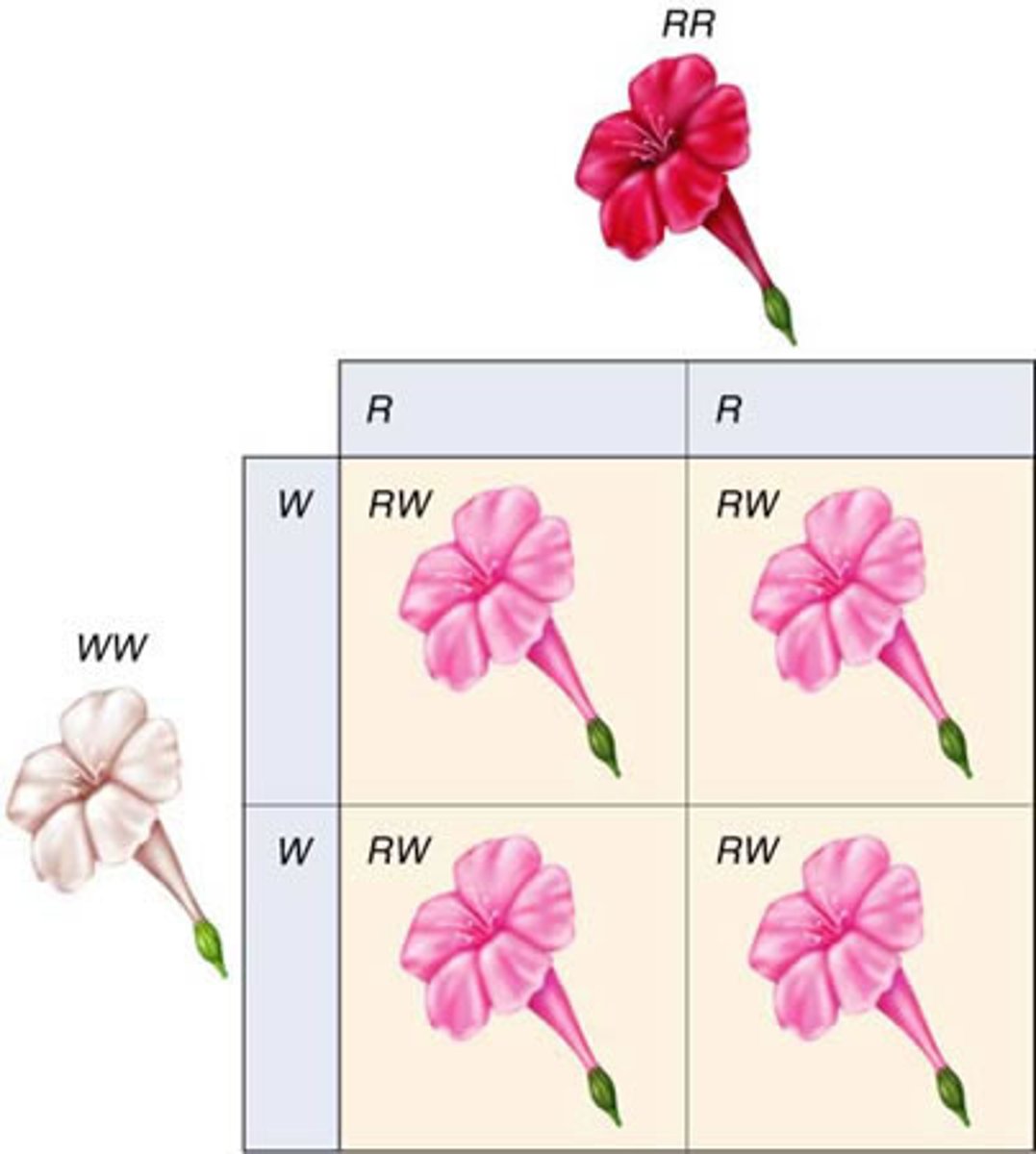
Incomplete Dominance
the phenotype (flower color) of F1 hybrids is somewhere between the phenotypes of the two parental varieties (red and white flower making pink offspring)
Codominance
two dominant alleles affect the phenotype (blood type) in separate, distinguishable ways (AB blood)
- A traits AND B traits are different
- AB: IA IB (codominant alleles)
Coat color of the Shorthorn breed of cattle represent an example of codominance. Red is determined by the genotype CRCR, roan by CRCW, and white by CWCW. When roan Shorthorns are crossed among themselves, what genotypic and phenotypic ratios are expected among their progeny?
In punnet square, cross CRCW with itself
- 1 red
- 1 white
- 2 roan
- 1:2:1 ratio
Multiple Alleles
Most genes exist in populations in more than two allelic forms ex. blood types
- the four phenotypes of the ABO blood group in humans are determined by three alleles for the enzyme that attaches A or B carbohydrates to red blood cells: IA, IB, and i
- The enzyme encoded by the IA allele adds the A carbohydrate to red blood cells
- the enzyme encoded by the IB allele adds the B carbohydrate to red blood cells
- the enzyme encoded by the i allele adds neither to red blood cells (recessive to A and B)
Possible Blood Type Combinations
A: IA IA Or IA i
B: IB IB Or IB i
AB: IA IB (codominant alleles)
O: ii
Blood typing is used as evidence in paternity cases. In one case the mother had blood type B and the child had blood type O. Which of the following blood types could the father not have?
AB because there is no ii allele to pass on to the child
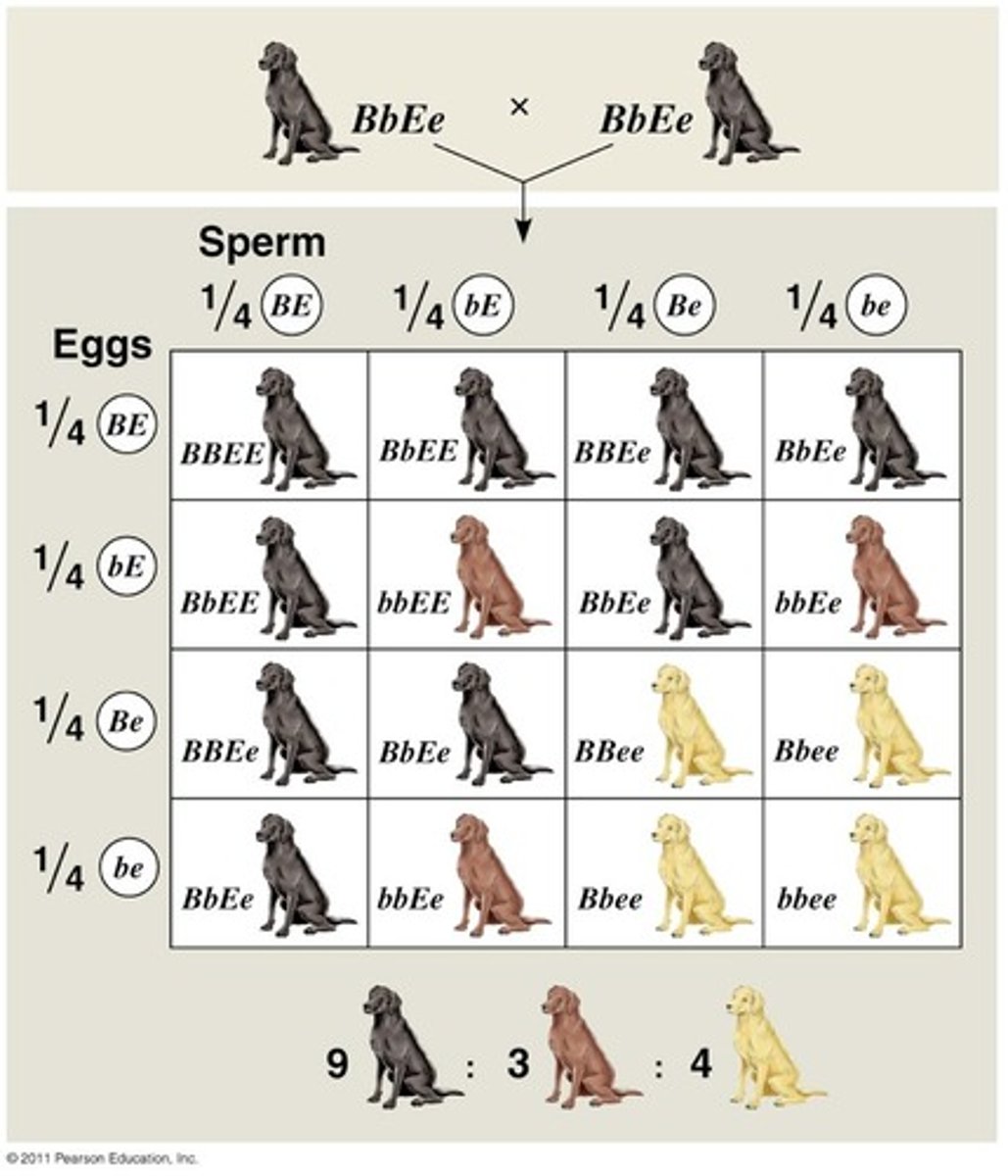
Epistasis
one character (hair color) is affected by multiple genes; expression of a gene at one locus (pigment) alters the phenotypic expression of a gene at a second locus (whether pigment will be shown)
- Ex. Labrador retrievers and many other mammals, coat color depends on two genes
- One gene determines the pigment color (with alleles B for black and b for brown)
- The other gene (with alleles E for color and e for no color) determines whether the pigment will be deposited in the hair
Polygenic Inheritance
a single phenotypic character (height) is affected by two or more genes (POLY-more than one gene to get)
- Quantitative Characters: those that vary in the population along a continuum ex. height 5’6 and 5’7, 5’8 and so on
- Quantitative variation usually indicates polygenic inheritance
- Ex. height (over 180 genes affect height)
Ex. individual with a genotype of AaBbCC is able to produce how many different types of gametes?
4 mixes: ABC, AbC, aBC, abC
- across both axis of punnett square gives 16 different phenotypes
Human Female's X Chromosome Disorders
caused by recessive alleles
- Color blindness (mostly X-linked)
- Duchenne muscular dystrophy
- Hemophilia
- Male pattern baldness
SONS INHERIT X CHROMOSOME TRAITS FROM MOTHER because they receive one X from her (XY) instead of two X like women (in women the other X masks the effect of the other)
Ex. A colorblind woman marries a man with normal color vision. Which is true of their children?
Woman: XcXc
Man: XnY
Mix these in Punnett square. Daughters will be normal but be carriers, sons will be colorblind since they inherit the mutated X from their mother
Linked Genes
genes that are located on the same chromosome and tend to be inherited together because they are located near each other on the chromosome
DNA structure
polymer of nucleotides, each consisting of a nitrogenous base, a sugar, and a phosphate group
- Nitrogenous bases include adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), or cytosine (C)
- Purines: G and A (have 2 linked rings of atoms)
- Pyrimidines: C, T, and U (have single ring)
- In RNA, uracil (U) binds with A (instead of T)
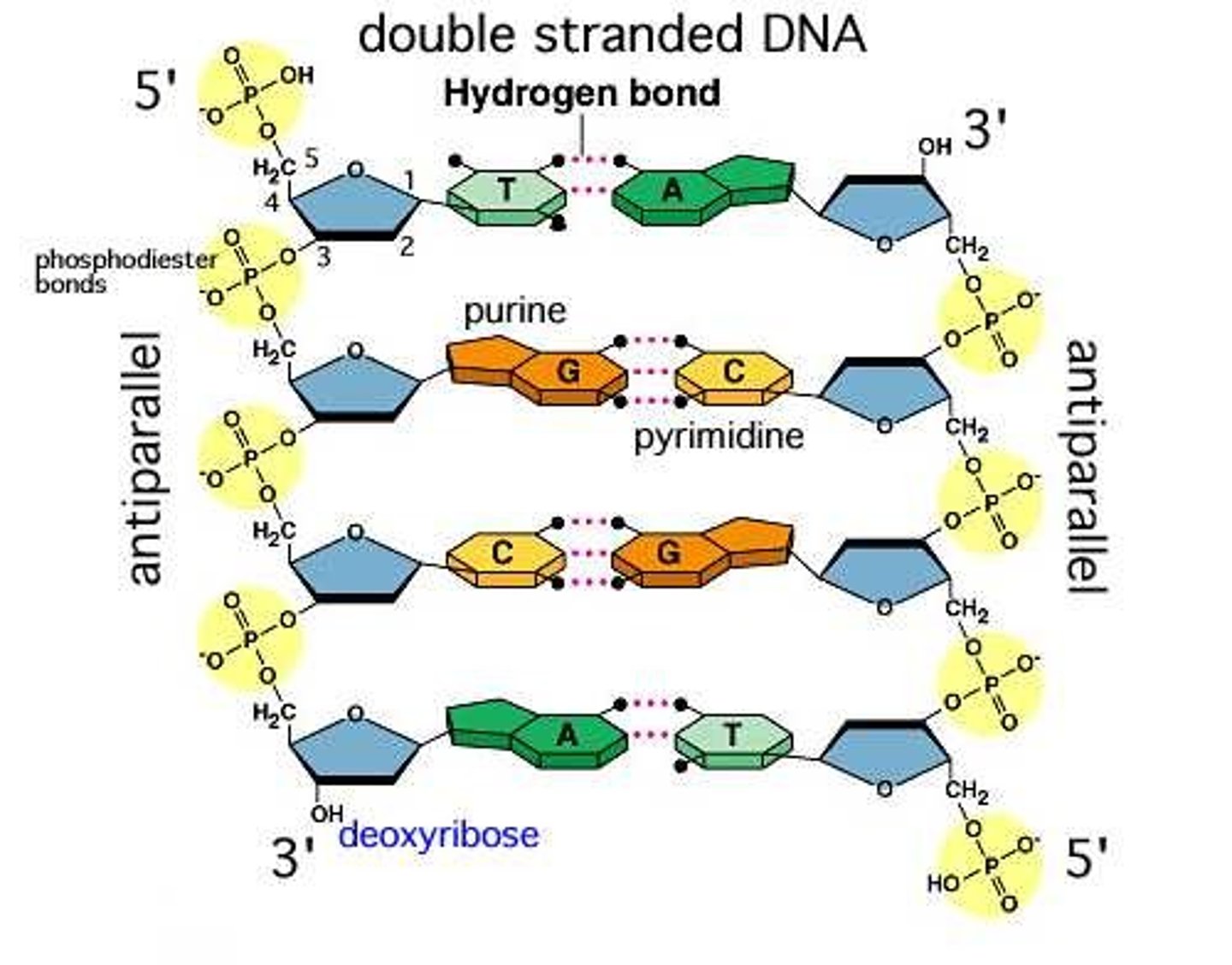
DNA backbones
- DNA is made up of 2 strands forming a double helix
- Phosphate-sugar backbones are antiparallel (the 3 and 5 run in opposite ways)
Gene Expression
DNA directs protein synthesis through transcription and translation
- DNA --> Pre-mRNA (RNA processing) --> mRNA -->Polypeptide
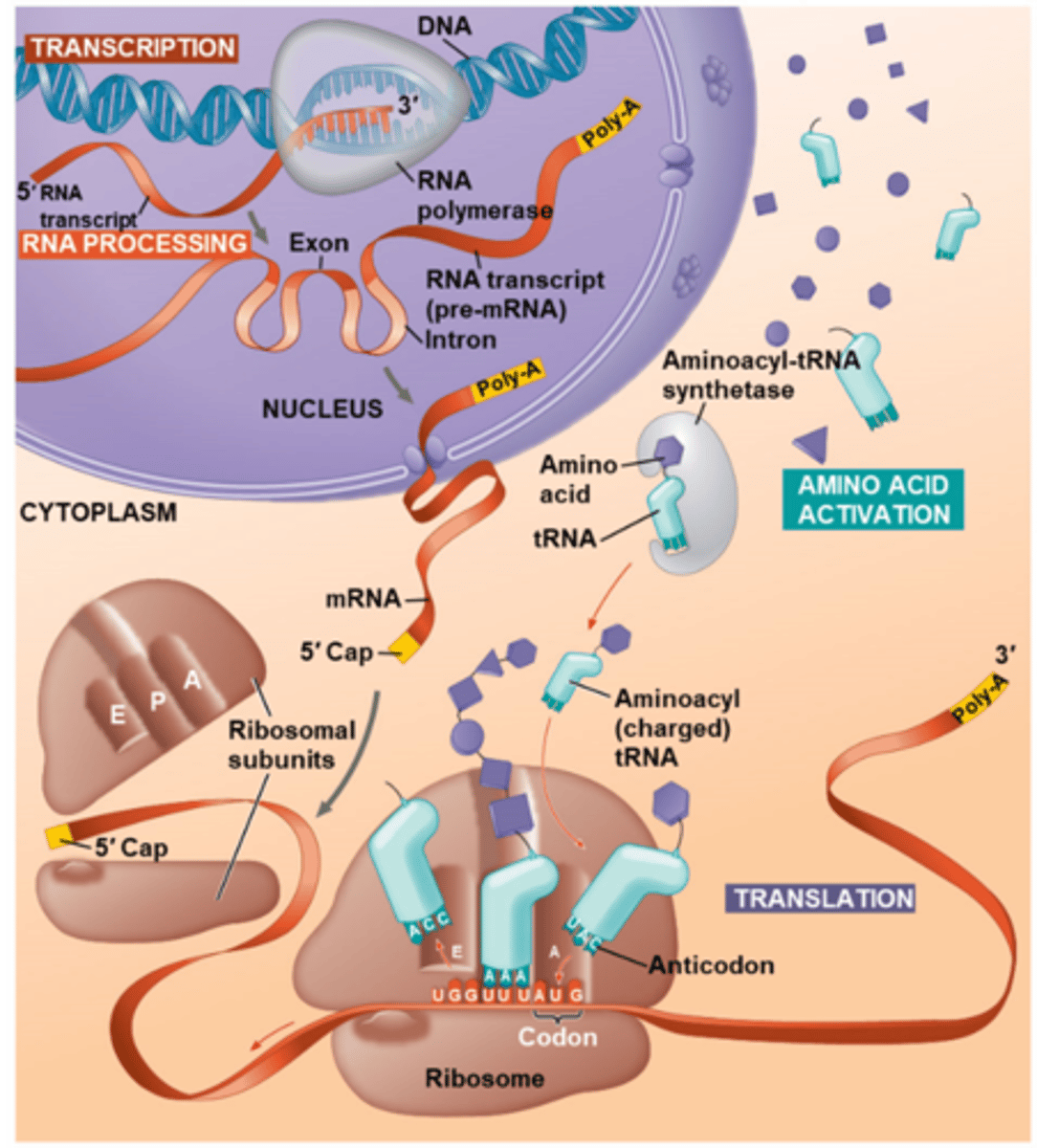
Transcription
synthesis of RNA using information in DNA; produces mRNA
- In nucleus
Translation
synthesis of a polypeptide using information in the mRNA
- Ribosomes in cytoplasm: sites of translation
If the DNA on the template strand was 3'-ATGCGT-5', the mRNA would be ___?
5'-UACGCA-3' (uracil instead of thymine when paring with A)
Initiation of Transcription
- On promoter region, there is a TATA region that signals transcription factors to bring RNA Polymerase to bind to DNA
- RNA polymerase sits on DNA strand’s starting point to unwind it in the 5’ to 3’ direction
- mRNA transcript fits into the unwound DNA bubble to begin its line on DNA template strand, pairing up nucleotide bases
Elongation of Transcription
DNA rewounds in its starting spot and RNA polymerase continues downstream unwinding and building RNA transcript along the way in 5' to 3' direction
Termination of Transcription
completed mRNA transcript and RNA polymerase stops
- In prokaryotes or bacteria, RNA polymerase stops transcription at the end of the terminator and the mRNA can be translated without further modification
- In eukaryotes, RNA polymerase II transcribes the tryadenylation signal sequence (a bunch of As); the RNA transcript is released 10-35 nucleotides past this sequence