IPS1 -Medicinal Biochemistry p3
1/110
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
1. A five carbon sugar
2. A base that has a nitrogen (N) atom
3. An ion of phosphoric acid
Three Parts of Nucleotide
Adenine
Guanine
Cytosine
Thymine
Uracil
FIVE (5) NUCLEOTIDES
Adenine
if It is H(deoxyribose)
If it is OH (ribose)
[IDENTIFY THE PARTS]
Adenine
Guanine
Purine Bases [2]
Adenine
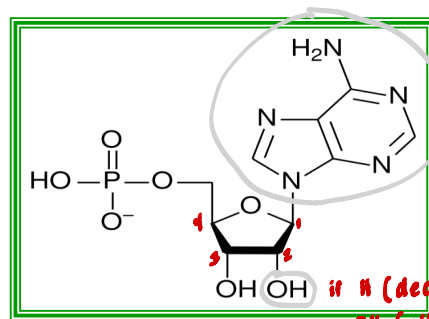
[IDENTIFY THE STRUCTURE OF 5 NUCLEOTIDE]
![<p>[IDENTIFY THE STRUCTURE OF 5 NUCLEOTIDE] </p><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/432d9402-b4b8-470d-afe8-891f00d822ee.png)
Guanine
[IDENTIFY THE STRUCTURE OF 5 NUCLEOTIDE]
![<p>[IDENTIFY THE STRUCTURE OF 5 NUCLEOTIDE] </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/16379e8e-f6c2-4cde-b3e6-bd69cb6438a0.png)
Uracil
[IDENTIFY THE STRUCTURE OF 5 NUCLEOTIDE]
![<p>[IDENTIFY THE STRUCTURE OF 5 NUCLEOTIDE]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/7e99f3ff-5e1c-4448-bc10-72008fdefdee.png)
Cytosine
[IDENTIFY THE STRUCTURE OF 5 NUCLEOTIDE]
![<p>[IDENTIFY THE STRUCTURE OF 5 NUCLEOTIDE]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/64e89375-add1-4a62-837f-498d3a80220a.png)
Thymine
[IDENTIFY THE STRUCTURE OF 5 NUCLEOTIDE]
![<p>[IDENTIFY THE STRUCTURE OF 5 NUCLEOTIDE]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/5e49ca5e-5e58-4411-9c26-a2feb59d07f7.png)
Purine
[TYPE OF BASE]
The structure consists of a 5-membered ring + 6-membered ring.
Pyrimidine
[TYPE OF BASE]
The structure consists of a 6-membered ring
Cytosine
Thymine
Pyrimidine Bases [2]
DNA
[DNA vs. RNA]
4 nitrogenous base A, T, C, G
RNA
[DNA vs. RNA]
4 nucleotides base A, U, C, G
DNA
[DNA vs. RNA]
Deoxyribose (sugar) + Phosphate group
RNA
[DNA vs. RNA]
Ribose (sugar) + Phosphate group
Proteins
____ - are made from combinations of 20 amino acids
polypeptide
Protein chains are called _____ ?
Protein
____- is a large molecule (macromolecule) with 4 level of structure
Primary
[PROTEIN LEVEL OF STRUCTURE]
_____- sequence of amino acids
Secondary
[PROTEIN LEVEL OF STRUCTURE]
_____- folding into shapes (like helices, sheets)
Tertiary
[PROTEIN LEVEL OF STRUCTURE]
_____- 3D shape of one chain
Quaternary
[PROTEIN LEVEL OF STRUCTURE]
_____- Arrangement of multiple polypeptide chains (subunits).
Health
According to WHO
____- is a state of “complete physical, mental and social well-being” and not merely the absence of disease and infirmity (physical or mental weakness)
Health
____- is a situation in which all thousands of intra- and extracellular reactions that occur in the body are proceeding at rates commensurate ( in proportion) with the organism’s survival in the physiologic state.
Health
_____- requires not only knowledge of biologic principles but also of physiologic & social principles
Maintenance of good health
optimal dietary intake
vitamins
amino acids
fatty acids
minerals
water
Biochemical Research Impact on Nutrition & Preventive Medicine [7]
Physical agent
Chemical agent
Biologic agent
Oxygen lack
Genetic disorders
Immunologic reactions
Nutritional inbalances
Endocrine imbalances
MAJOR CAUSES OF DISEASE [8]
mechanical trauma
extreme temperature
sudden changes in atmospheric pressure
radiation & electric shock
[MAJOR CAUSES OF DISEASE]
PHYSICAL AGENTS [4]
drugs
toxic compounds
[MAJOR CAUSES OF DISEASE]
CHEMICAL AGENTS [2]
viruses
bacteria
fungi
higher forms of parasites
[MAJOR CAUSES OF DISEASE]
BIOLOGICAL AGENTS [4]
loss of blood supply
depletion of oxygen carrying capacity of the blood
poisoning of the oxidative enzyme
[MAJOR CAUSES OF DISEASE]
OXYGEN LACK [3]
Inherited from birth
[MAJOR CAUSES OF DISEASE]
GENETIC DISORDERS [1]
Allergic reactions (anaphylaxis)
Autoimmune diseases (body attacks itself)
[MAJOR CAUSES OF DISEASE]
IMMUNOLOGIC REACTIONS [2]
Too little or too much of nutrients
[MAJOR CAUSES OF DISEASE]
NUTRITIONAL IMBALANCES/PROBLEM [1]
• Too little or too much hormone production
[MAJOR CAUSES OF DISEASE]
ENDOCRINE IMBALANCES/PROBLEM [1]
True
[T/F] Cystic fibrosis is caused by a genetic defect.
Cystic fibrosis
This disease causes the body to produce mucus that is thick, dry, and sticky.
phenylalanine
Diet low in ______ for treatment of phenylketonuria (PKU)
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
_____- is a genetic disorder inherited from both parents.
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
_____- is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder characterized by a deficiency in the enzyme Phenylalanine Hydroxylase (PAH).
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
It occurs when the body lacks the enzyme Phenylalanine Hydroxylase( PAH) which is needed to convert phenylalanine into tyrosine.
Phenylalanine Hydroxylase (PAH)
In Phenylketonuria (PKU)
_____- is the enzyme necessary to metabolize the amino acid phenylalanine to the amino acid tyrosine
phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH)
In Phenylketonuria (PKU)
Without this enzyme, phenylalanine builds up in the body and can cause brain damage
brain damage
In Phenylketonuria (PKU)
Without this enzyme, phenylalanine builds up in the body and can cause_____ damage
Avoid foods high in phenylalanine, such as meat, dairy, and nuts
What is the treatment for Phenylketonuria (PKU)?
A. High-protein diet including meat, dairy, and nuts
B. Avoid foods high in phenylalanine, such as meat, dairy, and nuts
C. High-phenylalanine supplements
D. No dietary restrictions needed
Phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH)
[BIOSYNTHESIS OF NEUROTRANSMITTERS FROM TYROSINE]
Phenylalanine is converted into Tyrosine by the enzyme_____ ?
Tyrosine Hydroxylase.
[BIOSYNTHESIS OF NEUROTRANSMITTERS FROM TYROSINE]
Tyrosine is changed into Dopa by the enzyme ______
Aromatic Amino Acid Decarboxylase
[BIOSYNTHESIS OF NEUROTRANSMITTERS FROM TYROSINE]
Dopa is changed into Dopamine by the enzyme______
Dopamine β-hydroxylase.
[BIOSYNTHESIS OF NEUROTRANSMITTERS FROM TYROSINE]
Dopamine is changed into Noradrenaline (also called Norepinephrine) by the enzyme_____
Phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase
[BIOSYNTHESIS OF NEUROTRANSMITTERS FROM TYROSINE]
Finally, Noradrenaline is changed into Adrenaline (also called Epinephrine) by the enzyme______
Norepinephrine
Noradrenaline is aka ____ ?
Epinephrine
Adrenaline is aka ____
Tryptophan Hydroxylase.
[BIOSYNTHESIS OF THE NEUROTRANSMITTER SEROTONIN]
Tryptophan is changed into 5-Hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP) by the enzyme _____
Aromatic Amino Acid Decarboxylase.
[BIOSYNTHESIS OF THE NEUROTRANSMITTER SEROTONIN]
5-Hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP) is changed into Serotonin (5-HT) by the enzyme _____
Histidine Decarboxylase.
[BIOSYNTHESIS OF HSITAMINE]
Histidine is changed into Histamine by the enzyme ______?
Adrenaline.
Noradrenaline is a neurotransmitter that is converted into _____ ?
catecholamine
Noradrenaline, Adrenaline and Dopamine are part of a group called ____ which work as a neurotransmitter
Creatine Kinase-MB (CK-MB)
The use of the enzyme______ in blood tests to diagnose a heart attack
Myocardial infarction
______- is a heart attack, happens when part of the heart muscle dies.
Myocardial infarction
This usually happens because a main heart artery is completely blocked.
myocardium
Heart muscle is aka ____ ?
heart attack (mycoardial infarction)
_________- happens when fatty buildup (atherosclerotic plaque) in a heart artery grows slowly and then suddenly breaks open. This blocks the artery completely and stops blood from reaching the heart muscle.
Measuring thyroxin or TSH levels in newborns.
_____- is use in neonatal diagnosis of congenital hypothyroidism
Measuring thyroxin or TSH levels in newborns.
The test is done to detect congenital hypothyroidism.
Congenital hypothyroidism (CHT)
____- is a condition of thyroid hormone deficiency present at birth
Congenital hypothyroidism (CHT)
_____- is a condition which baby is born with low thyroid hormone
Hyperthyroidism
Hypothyroidism
[Hypothyroidism vs. Hyperthyroidsim]
_______= increase metabolism
_______= decrease metabolism
Serum Glutamic Pyruvic Transaminase (SGPT)
Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT)
Use of the enzyme_______ [2] in blood tests to monitor infectious hepatitis.
infectious jaundice
Hepatitis A is also called as ____ ?
Hepatitis A
______- is caused by a virus called picornavirus.
Hepatitis A
_____- is transmitted by the orofecal route, such as through contaminated food.
orofecal route
Hepatitis A is transmitted by the _____ route , meaning people get infected by eating or drinking things contaminated with feces, like dirty food or water.
Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA)
Measurement of blood ______ levels in the blood of colon cancer patients after surgery.
Carcinoembryonic Antigen (CEA) measurement
____- is a marker that helps detect if the cancer comes back.
Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA)
_____ - is a protein that helps cells stick together.
fetal growth (baby growing in the womb)
birth
The body makes Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) during _____, but it stops being made before ______
True
[T/F] Healthy adults usually do not have Carcinoembryonic Antigen (CEA) in their blood.
True
[T/F] Heavy smokers may have higher Carcinoembryonic Antigen (CEA) levels
Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA)
_____-
is normally produced during fetal development, but production stops before birth
Not usually present in the blood of healthy adults
Raised levels can be found in heavy smokers
True
[T/F]
Treatment of colon cancer depends on the stage or extent , of disease.
Biochemical Thermodynamics
Bioenergetics is aka ____ ?
Bioenergetics (Biochemical Thermodynamics)
[TERMS]
_____- is the study of the energy changes accompanying biochemical reactions.
Isothermic
[TERMS]
____- uses chemical energy to power living processes (normal nutrition & metabolism)
Starvation
[TERMS]
Not enough energy in the body causing malnutrition and energy imbalance.
marasmus
[TERMS]
Severe lack of all nutrients (protein, carbs, fats)
Kwashiorkor
[TERMS]
Severe lack of protein, even if calories are enough
Thyroid Hormone
[Type of Hormone]
_____- control the rate of energy release (metabolic rate) and disease results when they malfunction
Thyroid Hormone
[Type of Hormone]
Control how fast the body uses energy (metabolic rate).
Problems happen if these hormones don’t work right.
Metabolic rate
[TERMS]
_____- is the rate of energy release
Obesity
[TERMS]
When the body stores too much extra energy as fat.
NAD & NADP+
[SUMMARY OF BIOLOGICAL CONCEPTS]
These are coenzymes made from the vitamin niacin.
NAD & NADP+
[SUMMARY OF BIOLOGICAL CONCEPTS]
They have a crucial role in oxidoreduction reactions.
NAD & NADP+
[SUMMARY OF BIOLOGICAL CONCEPTS]
They are essential electron carriers in processes like glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the respiratory chain.
Cytochrome Oxidase
[SUMMARY OF BIOLOGICAL CONCEPTS]
____-
This is a hemoprotein found in the respiratory chain inside mitochondria.
It transfers electrons from a substrate to oxygen.
Cytochrome Oxidase
[SUMMARY OF BIOLOGICAL CONCEPTS]
______-
This is the final step in cellular respiration
Is crucial for ATP production
Oxygenase
[SUMMARY OF BIOLOGICAL CONCEPTS]
_____-
This is a class of enzymes.
They catalyze reactions where oxygen is incorporated into a substrate.
Oxygenase
[SUMMARY OF BIOLOGICAL CONCEPTS]
The process has two steps:
first, oxygen binds to the enzyme's active site, and then
it is reduced or transferred to the substance
Cytochrome P450
[SUMMARY OF BIOLOGICAL CONCEPTS]
____-
This is a subgroup of monooxygenase enzymes.
They are important for detoxification and are found in tissues like the adrenal cortex, testes, and liver.
Cytochrome P450
[SUMMARY OF BIOLOGICAL CONCEPTS]
They are involved in making steroid hormones from cholesterol and in the metabolism of vitamin D.