C35 - Principles of Ray Optics
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
ray approximation
modeling light waves as individual, uniform lines
photon energy
E = hf
Planck’s constant
6.63×10-34 J • s
Law of reflection
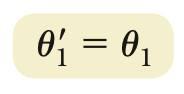
Law of refraction
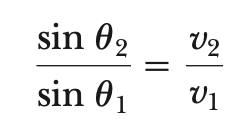
refractive index

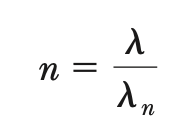
*As λ ↓, n ↑ (since v ∝ λ)
*λn = wavelength in medium with refractive index n
Snell’s Law
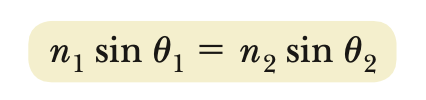
Huygens’s principle
All points on a wave front produce secondary waves (wavelets), which in tandem create an approximate wave front over time
dispersion
refractive index is a function of wavelength
big λ → small n (less bending)
small λ → big n (more bending)
total internal reflection
when nin medium > noutside medium (n1 > n2) & θ ≥ θc, the light gets reflected back into the medium
θc = critical angle
sin(θc) = n2/n1
n1 = nin medium
n2 = noutside medium
refractive indices
nair = 1
nwater = 1.333
nglass (crown/flint) = 1.52/1.66
ndiamond = 2.419