Topic 4 - Enzymes - Biology 241 - University of Calgary
5.0(3)
Card Sorting
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:16 AM on 10/23/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
1
New cards
• Proteins that speed up metabolism or chemical reactions.
Enzymes
2
New cards
• Polypeptide folded into functional 3-D shape.
Proteins
3
New cards
• An organic compound containing a carboxyl group, amino group, and an R group.
• Building blocks of proteins.
• Building blocks of proteins.
Amino Acids (2)
4
New cards
• Portion of an amino acid that makes each amino acid different from each other.
• Decides polarity, size, structure, etc.
• Decides polarity, size, structure, etc.
R Group (2)
5
New cards
• Short chains of amino acids that can function as neurotransmitters or hormones.
Peptides
6
New cards
• A peptide with 10+ amino acids linked together by peptide bonds.
Polypeptide
7
New cards
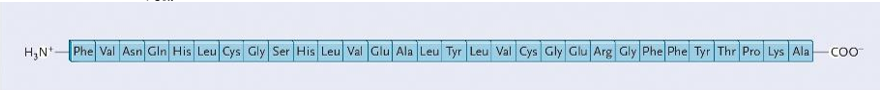
• Literal sequence of amino acids.
Primary Structure
8
New cards
• Formed by folding and twisting of the amino acid chain due to hydrogen bonding.
• Forms helices or sheets.
• Forms helices or sheets.
Secondary Structure
9
New cards
• Formed when the secondary structure folds again into a 3-D shape.
Tertiary Structure
10
New cards
• Group of tertiary structures consisting of more than one polypeptide chain bonded together.
Quaternary Structure
11
New cards
• End of a polypeptide or protein that has a free amino group.
N-terminus
12
New cards
• The end of a polypeptide or protein that has a free carboxyl group.
C-terminus
13
New cards
• A protein with all identical subunits.
Homomeric
14
New cards
• A protein with some subunits that are non-identical.
Heteromeric
15
New cards
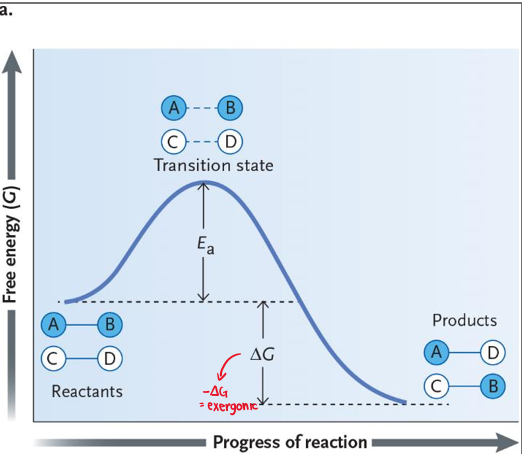
• Minimum amount of energy required to start a chemical reaction.
Activation Energy
16
New cards
• High-energy intermediate state of the reactants during a chemical reaction that must be achieved for the reaction to continue.
Transitional State (Summit)
17
New cards
• The difference between the reactants and transition states free energy.
Activation Barrier
18
New cards
• Increase the temperature.
• Increase the concentrations of the reactants so the reactants collide more often.
• Increase the surface area so that the reactants collide more often.
• Add a catalyst.
• Increase the concentrations of the reactants so the reactants collide more often.
• Increase the surface area so that the reactants collide more often.
• Add a catalyst.
What are some ways to speed up a chemical reaction? (4)
19
New cards
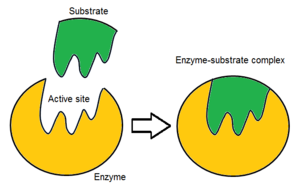
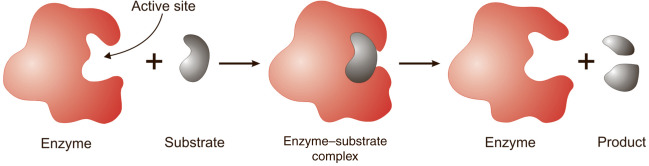
• A region that interacts with a substrate, causing the enzyme's shape to change.
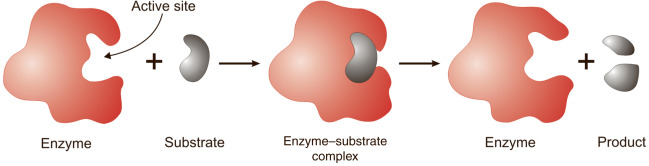
Active Site
20
New cards
• A temporary complex formed when an enzyme binds to its substrate molecule(s).
Enzyme-Substrate Complex
21
New cards
• The change in the shape of an active site so it binds better with the substrate, forcing it into a transition state. Once the reaction is complete, the enzyme releases the product and returns to its original shape.
Induced Fit
22
New cards
• Bringing reactants closer together.
• Exposing reactants to altered charge environment that promotes catalysis.
• Changing the shape of a substrate molecule.
• Exposing reactants to altered charge environment that promotes catalysis.
• Changing the shape of a substrate molecule.
What are some ways enzymes lower activation energy? (3)
23
New cards
• Use of energy released from exergonic reactions to drive endergonic reactions.
• Enzymes do this by becoming phosphorylated or reduced.
• Enzymes do this by becoming phosphorylated or reduced.
Energy Coupling Reactions (2)
24
New cards
• The concentration of the enzyme and the concentration of the substrate.
What factors effect the rate of an enzyme reaction? (2)
25
New cards
• Loss of protein structure due to heat, pH changes, or a non-competitive inhibitor.
Denaturation (3)
26
New cards
• Loss of protein activity from denaturation.
Inactivation of Proteins
27
New cards
• Is chemically like the substrate and binds noncovalently to the enzyme at the active site. However, it undergoes no reaction and prevents the substrate from entering the active site.
Reversible Competitive Inhibitor
28
New cards
• Not chemically like the substrate and binds noncovalently to the enzyme at the allosteric site. This changes the shape of the active site and reduces the enzyme's substrate affinity.
Reversible Noncompetitive Inhibitors
29
New cards
have both an active site for substrate binding and an allosteric site for binding of an allosteric effector (activator, inhibitor)
allosteric enzymes
30
New cards
• Binds to the enzyme which changes shape to a more active form.
Allosteric Activator
31
New cards
• Binds to the enzyme which changes shape to a less active form.
Allosteric Inhibitior
32
New cards
• A method of metabolic control in which the final product of a pathway that binds to the enzyme and inhibits it (turns it off).
Feedback Inhibition
33
New cards
• The acceleration of a chemical reaction by a catalyst.
Catalysis
34
New cards
• H-bonds.
• Ionic bonds.
• Van der Waals forces.
• Covalent bonds.
• Ionic bonds.
• Van der Waals forces.
• Covalent bonds.
Tertiary structures can form what types of bonds and forces? (4)
35
New cards
• Activation energy.
During glycolysis, the bonds in the reactants are stable, therefore, to destabilize the bonds what energy must be added to the reaction to get it going?
36
New cards
• Changing the concentration of inhibitors and activators.
How do cells control enzyme kinetics?
37
New cards
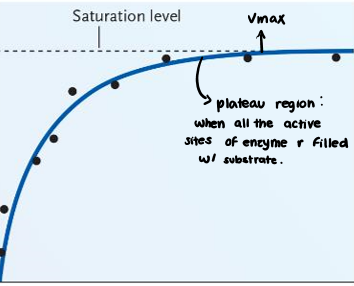
• When all the active sites of the enzyme are filled with substrate.
Plateau Region
38
New cards
• Highest.
The molecule with the ____________ concentration will outcompete the other.
39
New cards
• Vmax = the same.
• Km = increases.
• Km = increases.
When you have a competitive inhibitor, what happens to the Vmax and Km?
40
New cards
• Vmax = decreases.
• Km = very similar.
• Km = very similar.
When you have a non-competitive inhibitor, what happens to the Vmax and Km?
41
New cards
• High.
_____ concentrations of the substrate do not outcompete the inhibitor.