Module 3: chapter 9 enthalpy changes
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What is enthalpy (H)
. Measure of heat in a chemical system, cannot be measured by an experiment
What is a system
The atoms, molecules o ions making up the chemicals
What is enthalpy change (Δ H)
The difference between the enthalpies of the reactants and the products measured and calculated through experiments
ΔH = H(products) - H(reactants)
What is conservation of energy
Energy cannot be created or destroyed only transferred between the system and the surroundings
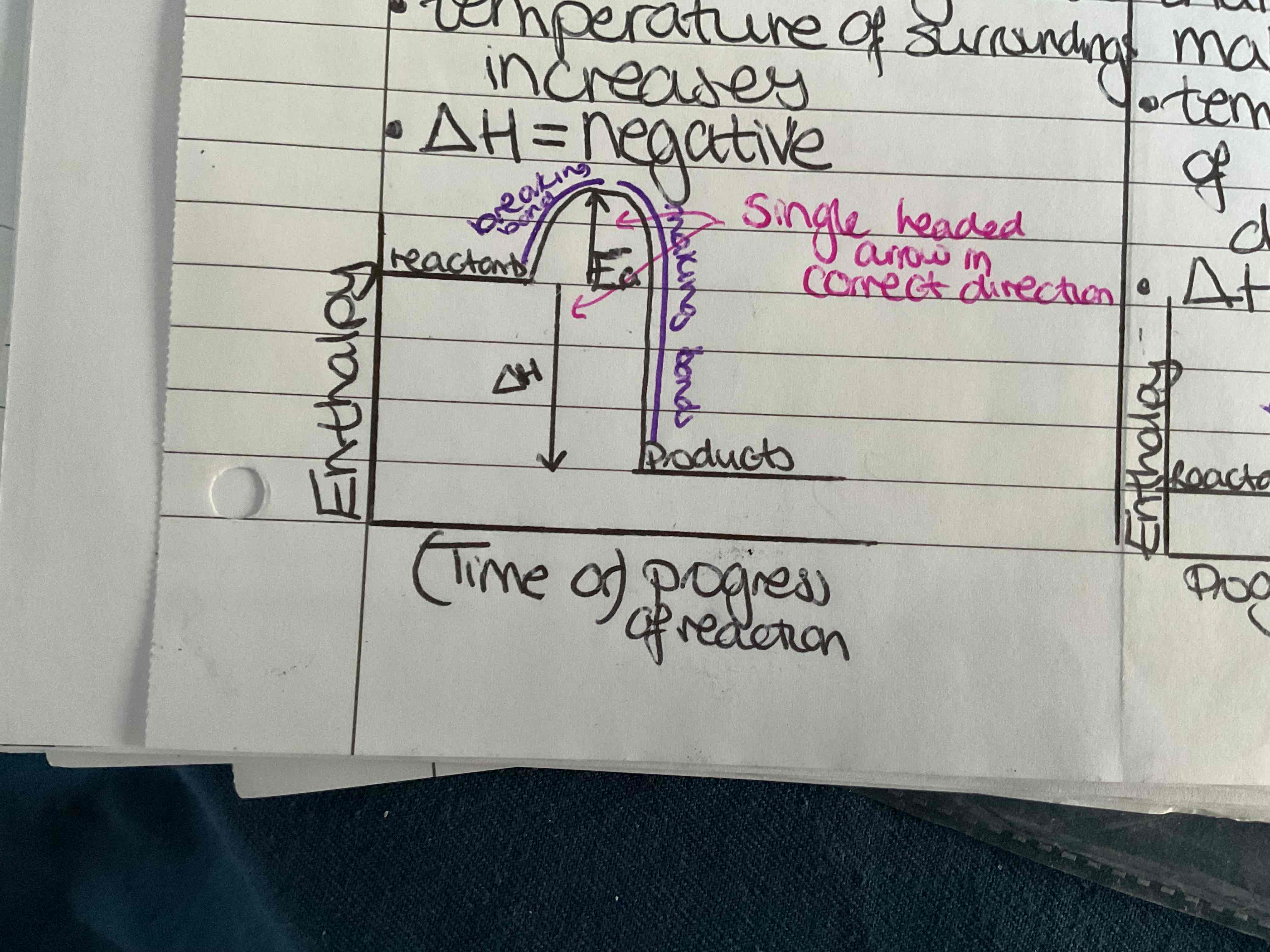
What is an exothermic change
More energy is given out making bonds than is taken in breaking bonds temperature of the surroundings increases ΔH= negative
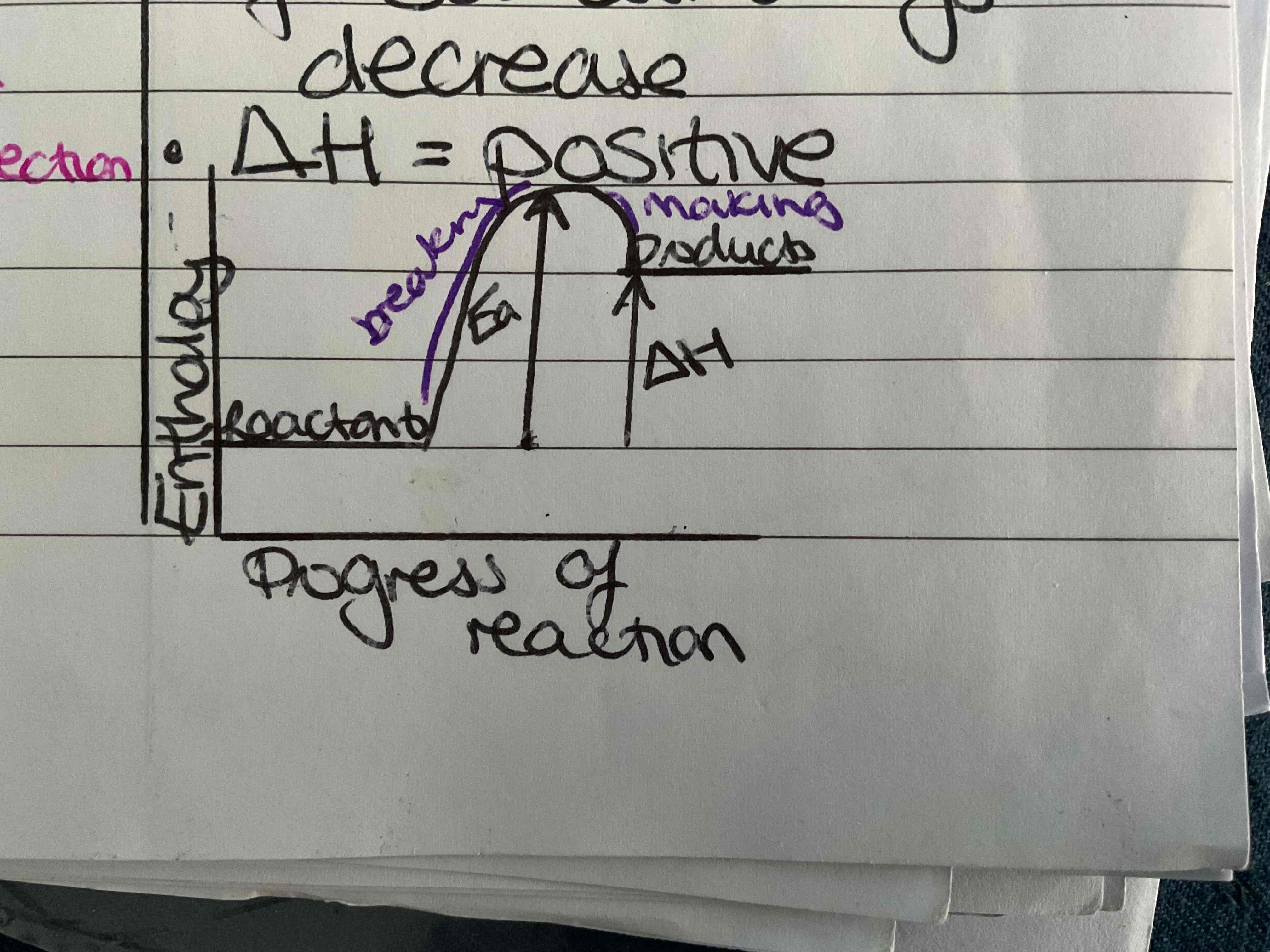
What is an endothermic change
More energy is taken in breaking bands than is given out making bonds temperature of surroundings decreases ΔH= positive
What is the activation energy (Ea)
The minimum amount of energy required to start a reaction
What is a standard enthalpy change
Enthalpy changes for a reaction vary depending on conditions used so use standard conditions for physical measurements such as enthalpy changes

What are the standard conditions
Pressure = 1atm or 100/101Kpa
Temperature = 298k
Concentration = 1moldm-3
State = state at standard conditions
What is enthalpy change of reaction (ΔrH⦵)
The enthalpy change that accompanies a reaction in the molar quantities shown in a chemical equation under standard conditions with all reactants+ products in their standard states
The standard enthalpy of combustion (ΔH⦵c)
Enthalpy change when 1 mole of a substance is completely burned in oxygen with all reactants and products in standard states under standard conditions
The standard enthalpy of formation (ΔH⦵f)
Enthalpy change when I more of a compound is formed from in elements under standard conditions with all reactants and products in standard states
Standard enthalpy of neutralisation ΔneutH⦵
Enthalpy change when I mole of water is formed in a reaction between an acid and an alkali under standard conditions at standard states
What are the two equations for calculating enthalpy change
Q = mcΔt
ΔH = q/mol

Now accurate is the experimental value
Heat lost too surroundings
Incomplete combustion
Evaporation of alcohol from the wick
Non stands conditions
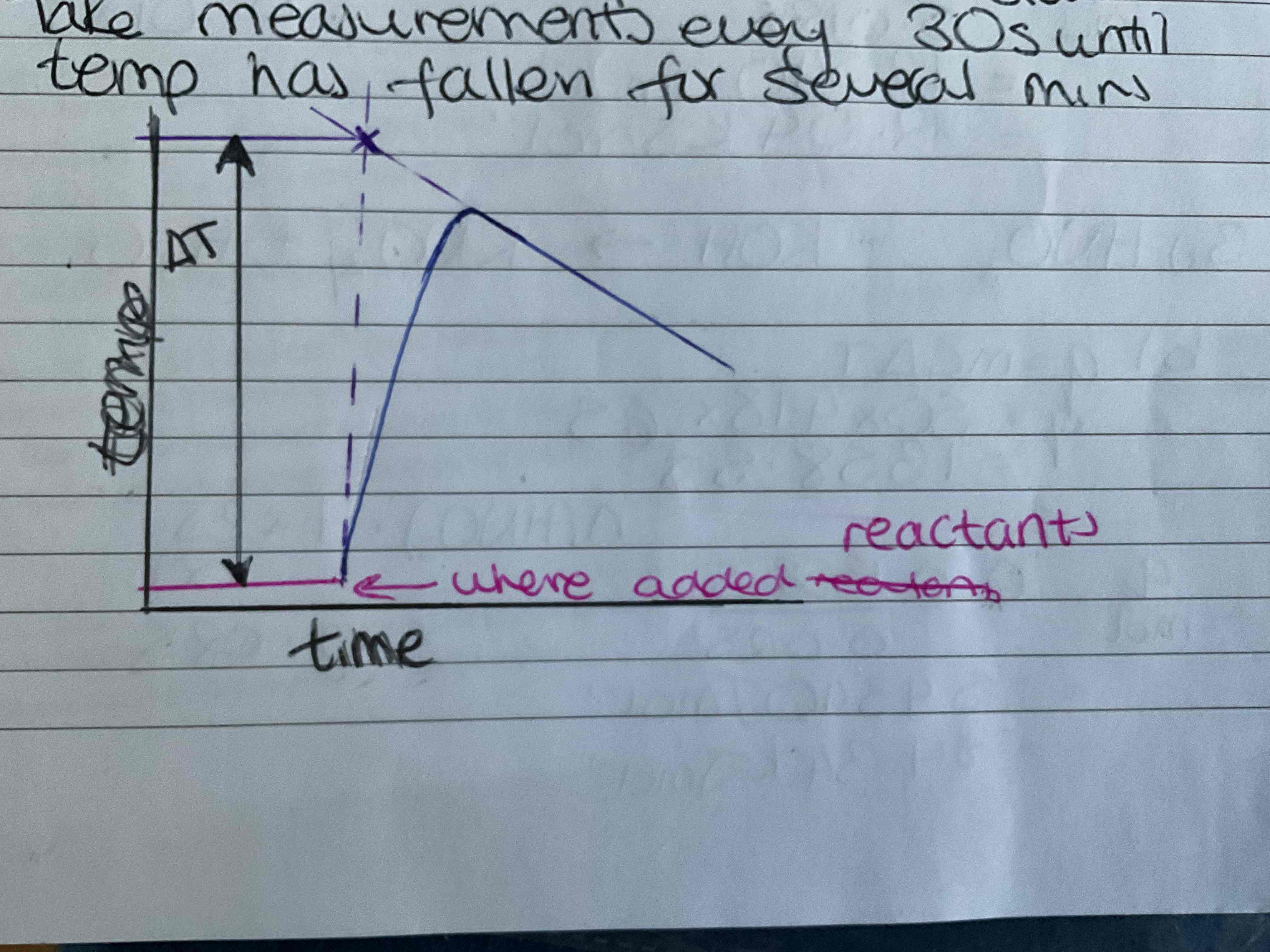
How can you improve experimental values
Use a cooling curve to correct for heat loss
Record start temp until constant take measurements every 30s until temp has fallen for several minutes
What is bond enthalpy
The energy required to break 1 mole of a specified type of bond in a gaseous molecule
Are bond enthalpies always exothemic or endothermic
Endothermic as energy is always required to break bonds so bond enthalpies always have a positive enthalpy value
What are the limitations of average bond enthalpies
The actual value can vary depending on the chemical environment of the bond. An average bond enthalpy is calculated from the actual bond enthalpy in different chemical conditions
How do you calculate bond energies
Bonds broken - bonds made = energy change
(Must put sign even if +)
What does Hess’ law allow us to do
Calculate enthalpy changes indirectly
What is Hess ‘ law
If a reaction can take place by two routes and the starting and finishing conditions are the same the total enthalpy change of each route is the same

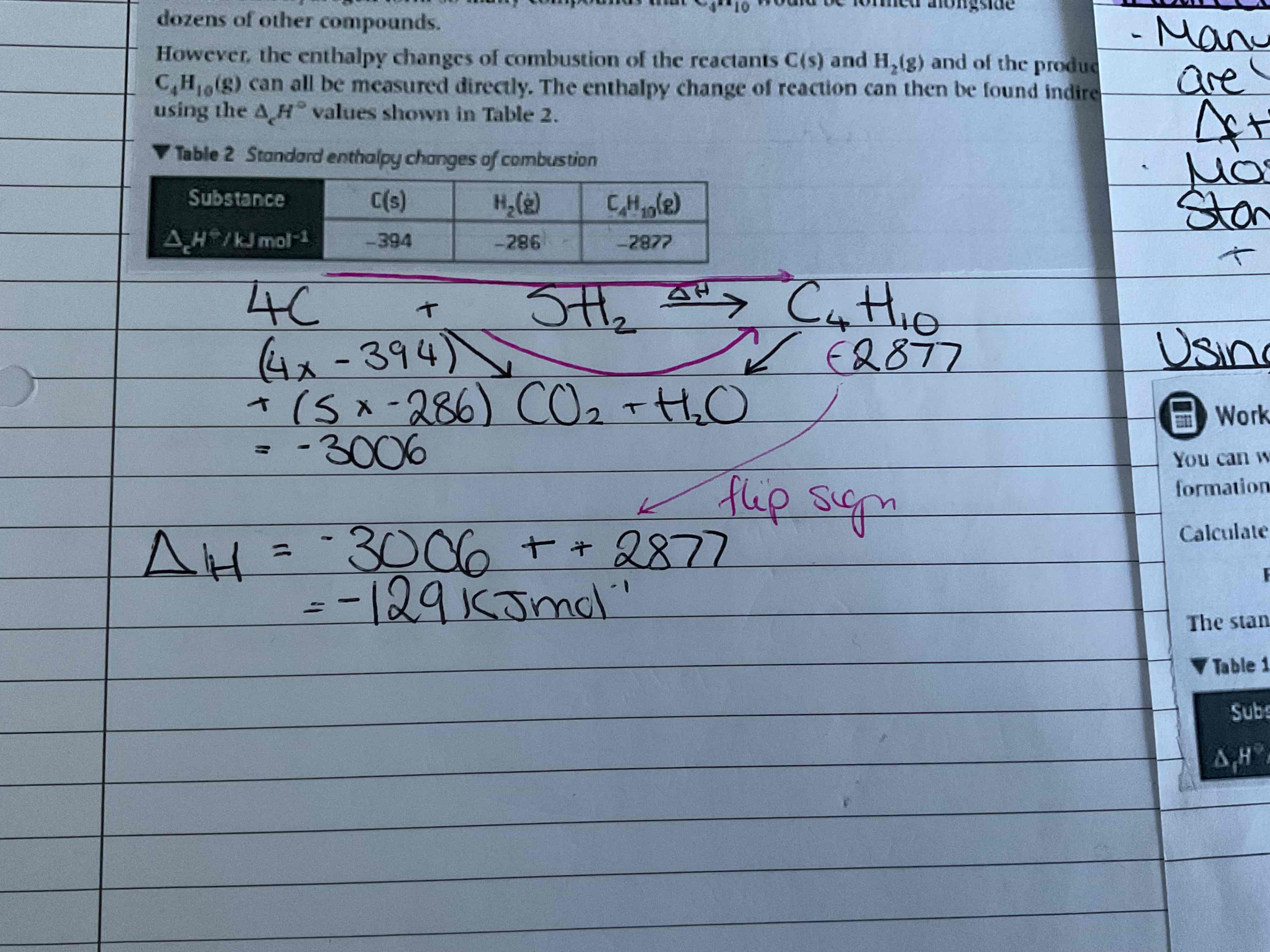
How do you find indirect determination of enthalpy changes
Many standard enthalpy changes are listed in data books, most useful are formation and combustion
Example of finding enthalpy changes from formation
Arrows go apart

Example of enthalpy changes from combuston
Arrows go together