Chapter 1 - Principles of Operating Systems
1/157
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
158 Terms
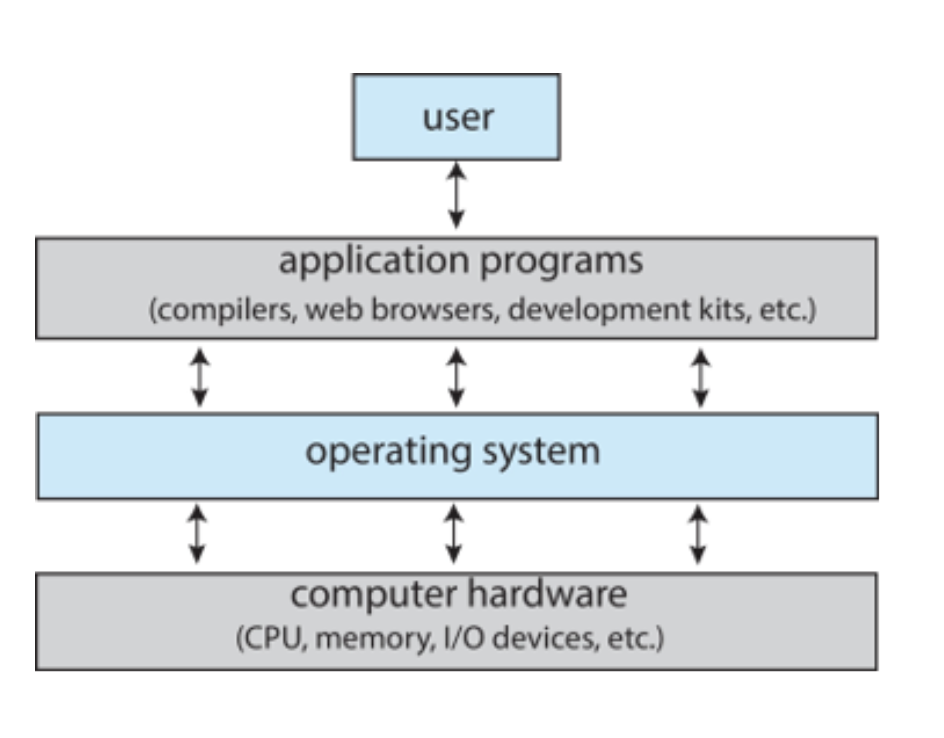
Operating System (OS)
acts as intermediary between user of a computer and the computer hardware
Operating system goals
Execute user programs and make solving user problems easier
Make the computer system convenient to use
Use the computer hardware in an efficient manner
Hardware
provides basic computing resources; CPU, memory, I/O devices
Operating System (OS)
controls and coordinates use of hardware among various applications and users
Application programs
ways in which the system resources are used to solve computing problems
word processors, compilers, web browsers, database systems, video games
Users
people, machines, other computers
Abstract view of component of computer
ease of use, good performance
Fill in the blanks:
Users want convenience, ______ and ____ ________
resource utilization
Fill in the blanks:
Users don’t care about _________.
mainframe or minicomputer
Fill in the blanks:
But shared computer such as ________ or ________ must keep all users happy
resource allocator, control program
Fill in the blanks:
Operating system is a ________ and ______ making efficient use of HW and managing execution of user programs.
Workstations
have dedicated resources but frequently use shared resources from servers
Mobile devices (e.g. smartphones and tablets)
are resource poor, optimized for usability and battery life
Mobile user interfaces
touch screens, voice recognition, etc.
Embedded computers
have little or no user interface; run without user intervention
Roles of Operating Systems
because of designs and uses of it
present in toasters through ships, spacecraft, game machines, TVs, and industrial control systems
born when fixed use computers for military became more general purpose and needed resource management and program control
True
True or False
An operating system has no universal accepted definition. “Everything a vendor ships when you order an operating system” is a good approximation, but it varies wildly.
Kernel
one program running at all times on the computer
System program
ships with the OS, but not part of the kernel
Application program
all programs not associated with the OS
Middleware
set of software frameworks that provide addition services to application developers, such as databases, multimedia, graphics, etc.
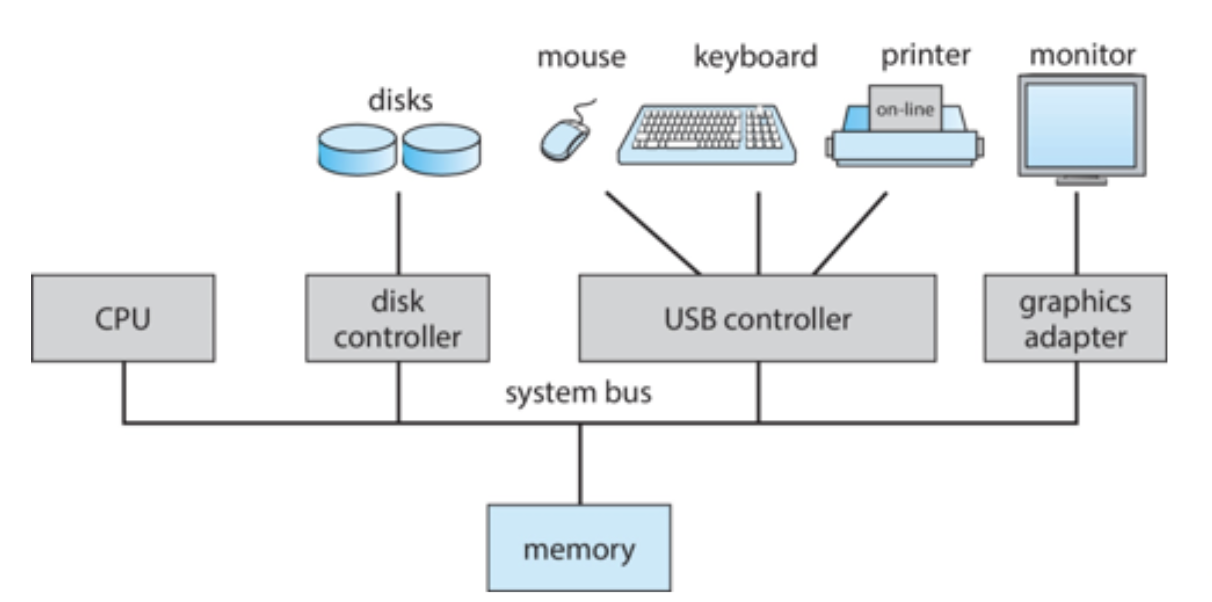
Bus
Connects one or more CPUs or device controllers to provide access to shared memory
Computer-system operation
Concurrent execution of CPUs and devices competing for memory cycles
One or more CPUs, device controllers connect through common bus providing access to shared memory
Computer System Organization (Overview of Computer System Structure
Concurrently
Fill in the blanks:
I/O devices and the CPU can execute ______.
Local buffer
Fill in the blank:
Each device controller has a ______ and is in charge of a particular device type
Device driver
Fill in the blank:
Each device controller type has an operating system _____ to mange it.
main memory, local buffers
Fill in the blanks:
CPU moves data from/to _______ to/from local buffers
I/O
is from the devices to local buffer of controller
Device controller
informs CPU that it has finished its operation by causing an interrupt
Interrupt
transfers control to the interrupt service routine
Interrupt Vector
contains the addresses of all the service routines
Interrupt architecture
must save the address of the interrupted instruction
Trap or exception
a software-generated interrupt caused either by error or a user request
interrupt driven
Fill in the blank:
An operating system is _____.
Interrupt Timeline
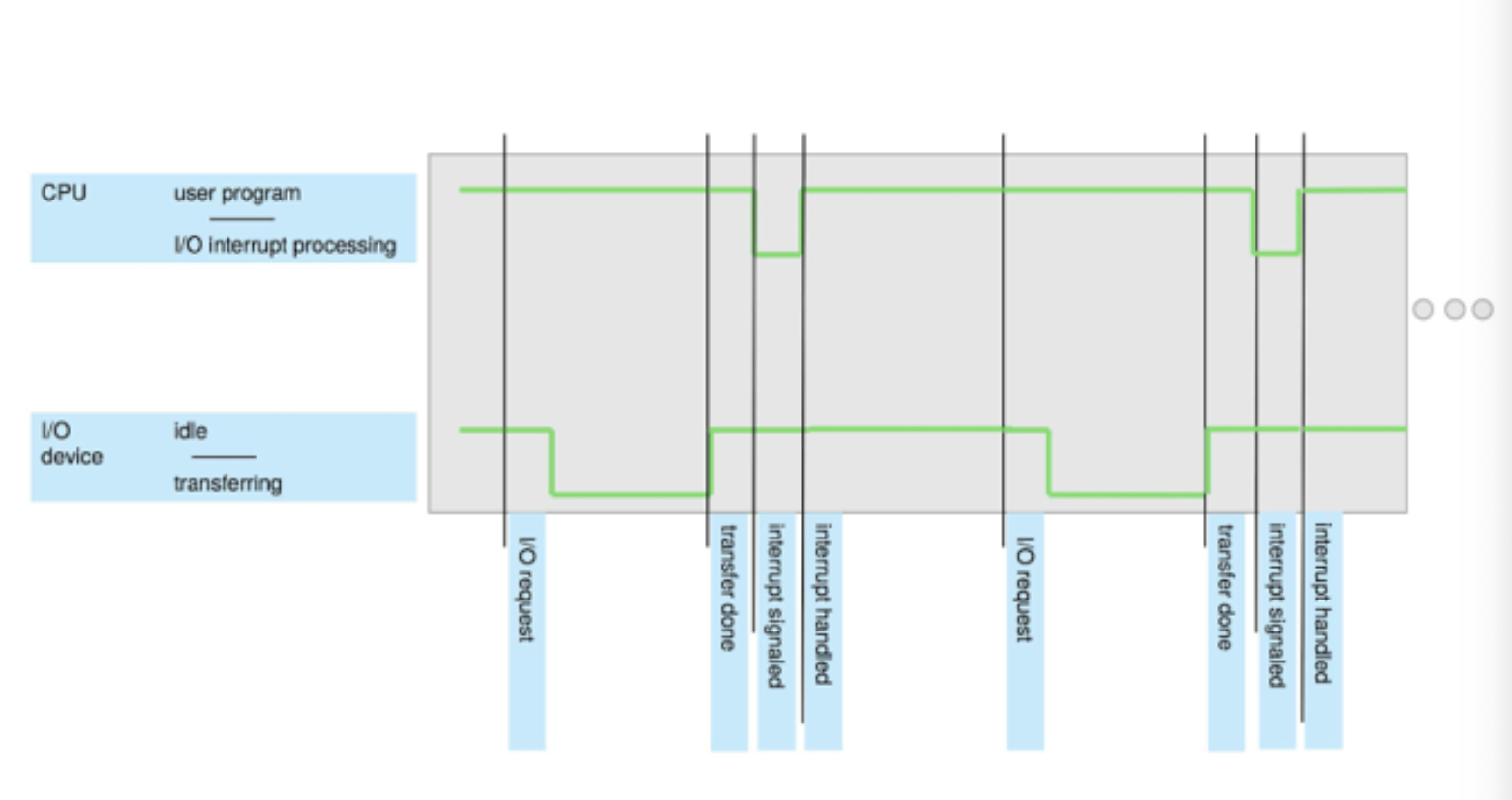
Interrupt handling
The OS preserves the state of the CPU by storing the registers and the program counter
Determines which type of interrupt has occurred
Separate segments of code determine what action should be taken for each type of interrupt
Interrupt-drive I/O Cycle
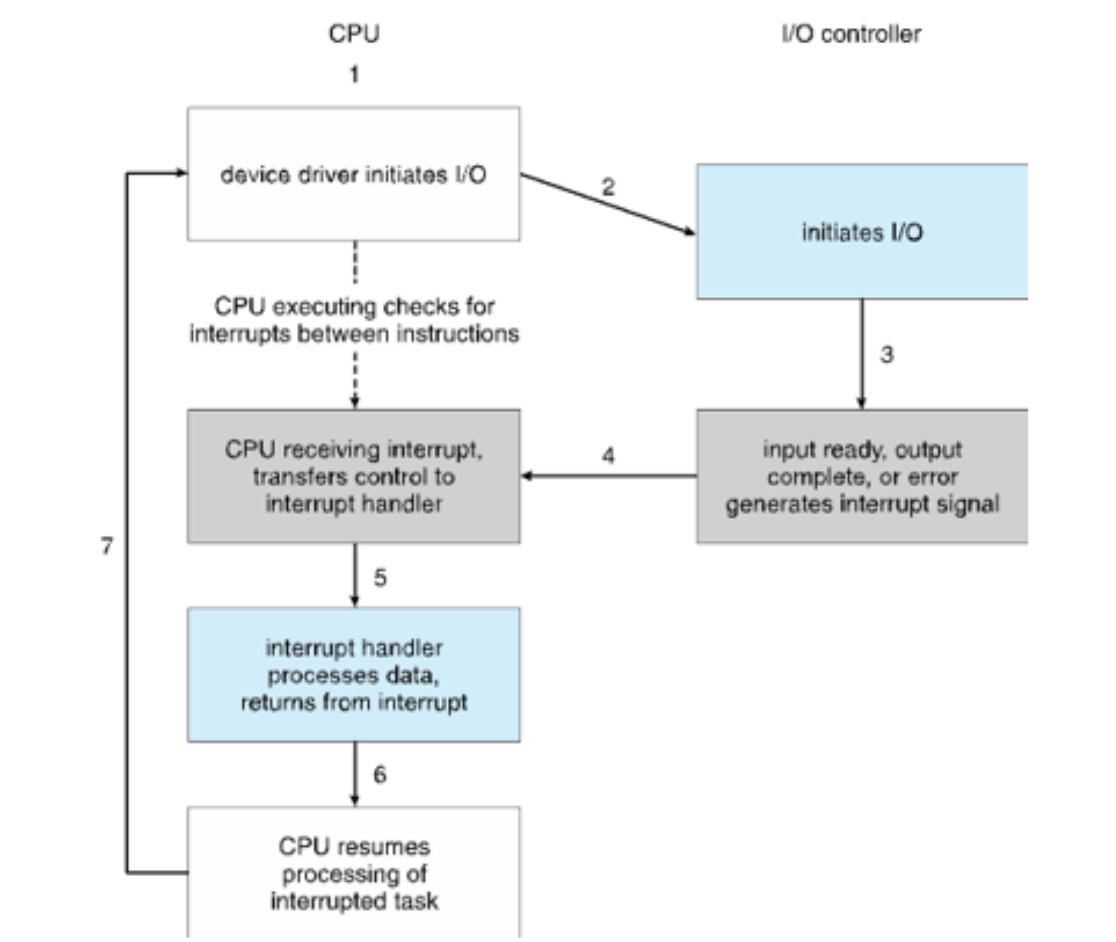
Two methods for handling I/O
After I/O starts, control return to user program only upon I/O completion
After I/O starts, control returns to user program without waiting for I/O completion
Only upon completion (after I/O starts; under I/O structure)
wait instruction idles the CPU until the next interrupt
wait loop (contention for memory access)
at most one I/O request is outstanding at a time, no simultaneous I/O processing
without waiting (after I/O starts; under I/O structure)
System call - request to the OS to allow user to wait for I/O completion
Device-status table contains entry for each I/O device indicating its type, address, and state
OS indexes into I/O device table to determine device status and to modify table entry to include interrupt
Wait loop
contention for memory access
System call
request to the OS to allow user to wait for I/O completion
Device-status table
contains entry for each I/O device indicating its type, address, and state
Main memory
only large storage media that the CPU can access directly
random access
volatile
dynamic random-access memory
Secondary storage
extension of main memory that provides large non-volatile storage capacity
Hard disk drives (HDD)
rigid metal or glass platters covered with magnetic recording material
tracks, sectors
Fill in the blanks:
Disk surface is logically divided into ____, which are subdivided into ____.
Disk controller
determines the logical interaction between the device and the computer
Non-volatile memory (NVM) devices
faster than hard disks, non-volatile. has various technologies. more popular as capacity and performance increases, price drops.
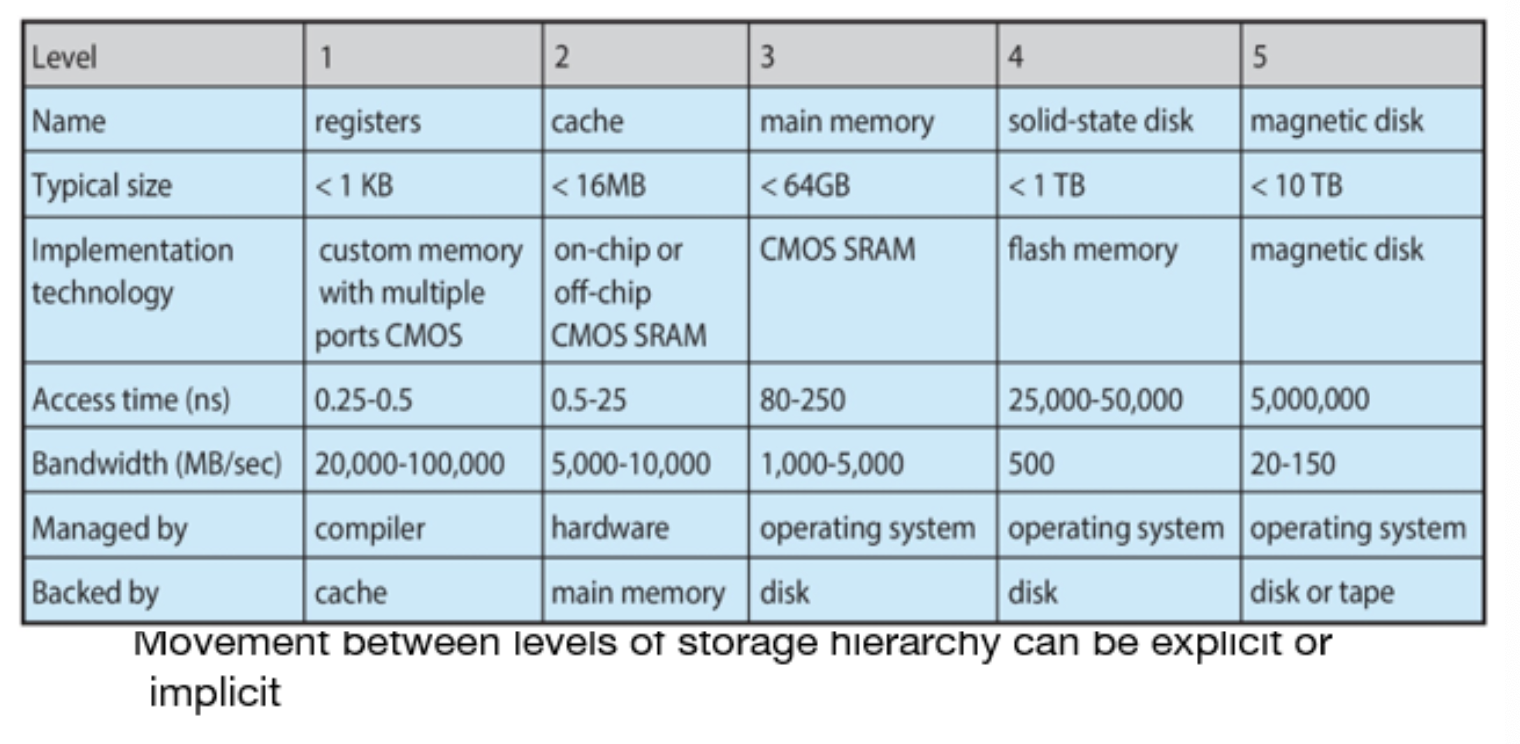
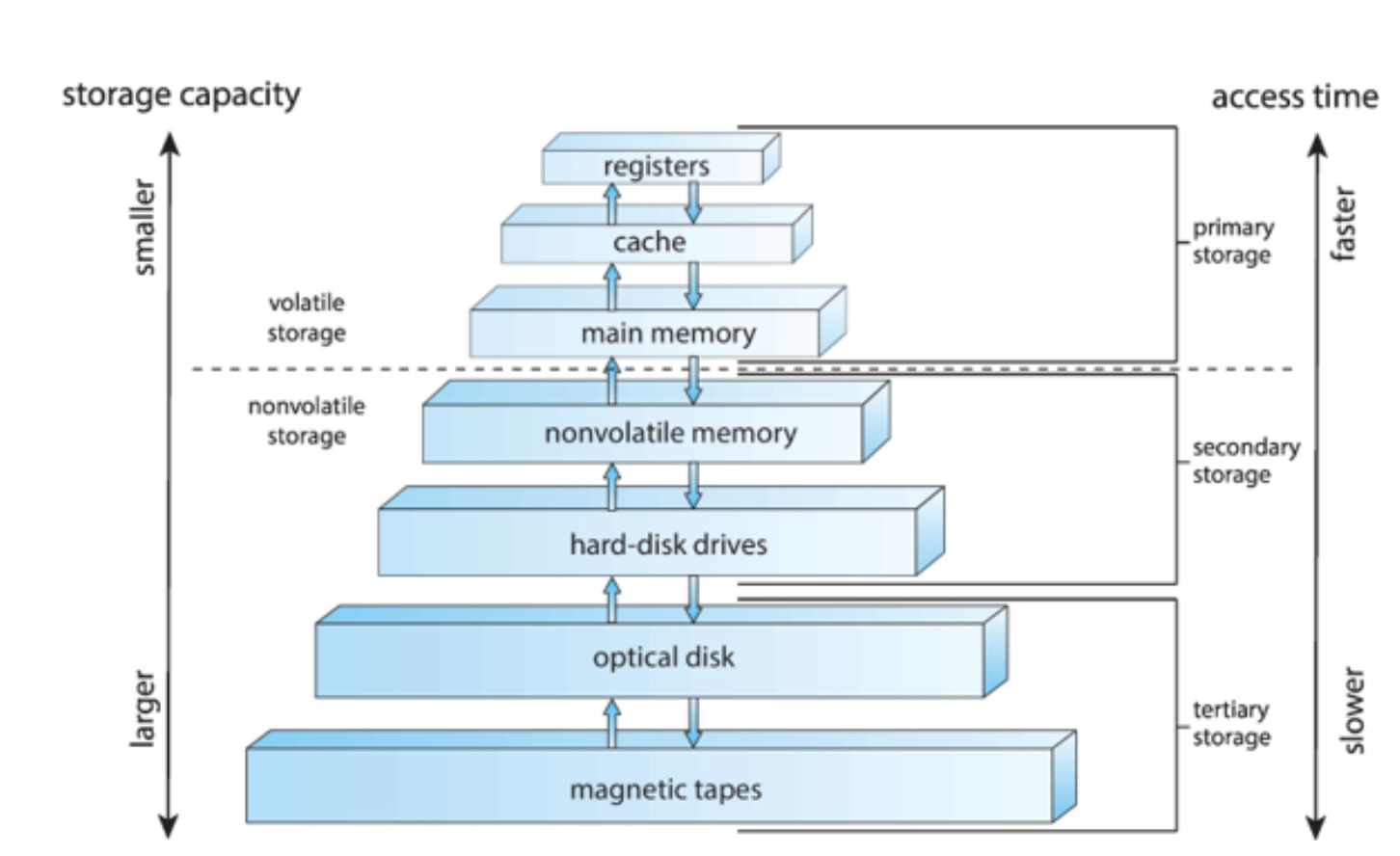
Storage hierarchy
Storage systems organized in hierarchy:
Speed
Cost
Volatility
Caching
copying information into faster storage system; main memory can be viewed as a cache for secondary storage
Device driver
provides uniform interface between controller and kernel; for each device controller to manage I/O
Storage-device hierarchy
von Neumann architecture
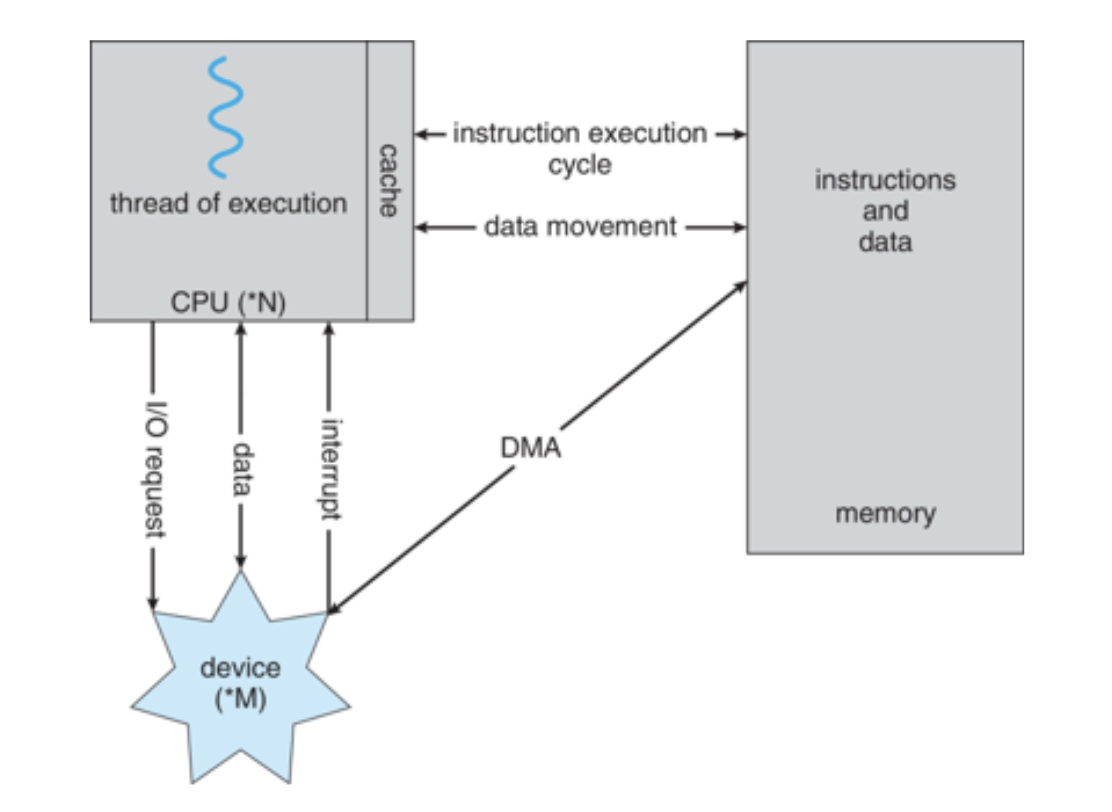
Direct Memory Access Structure
Used for high-speed I/O devices able to transmit information at close to memory speeds
Device controller transfers blocks of data from buffer storage directly to main memory without CPU intervention
Only one interrupt is generated per block, rather than the one interrupt per byte
Device controller
transfers block of data from buffer storage directly to main memory without CPU intervention
Bootstrap program
simple code to initialize the system, load the kernel
System daemons
services provided outside of the kernel
Kernel interrupt driven
hardware interrupt by one of the devices
software interrupt (exception or trap)
software error
request for operating system service — system call
other process problems include infinite loop, processes modifying each other or the operating system
System call
request for operating system service
Multiprogramming
organizes jobs (code and data) so CPU always has one to execute
Job scheduling
one job selected and run via ____
subset of total jobs
A ______ in system is kept in memory
switches to
When job has to wait, OS ___ another job
Multitasking
A logical extension of batch systems — the CPU switches jobs so frequently that users can interact with each job while it is running, creating interactive computing
less than a second (< 1 sec)
Response time should be _______
Process
each user has at least one program executing in memory
CPU scheduling
if several jobs ready to run at the same time
Swapping
If processes don’t fit in memory, _____ moves them in and out to run
Virtual memory
allows execution of processes not completely in memory
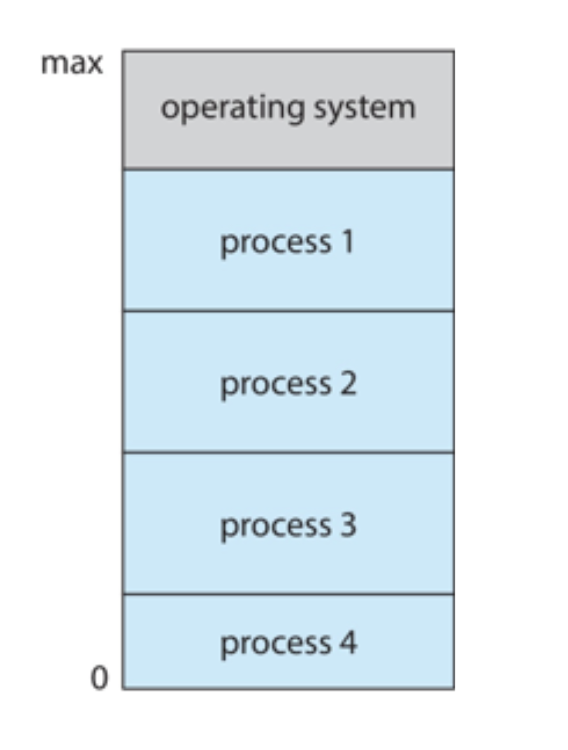
Memory Layout for Multiprogrammed System
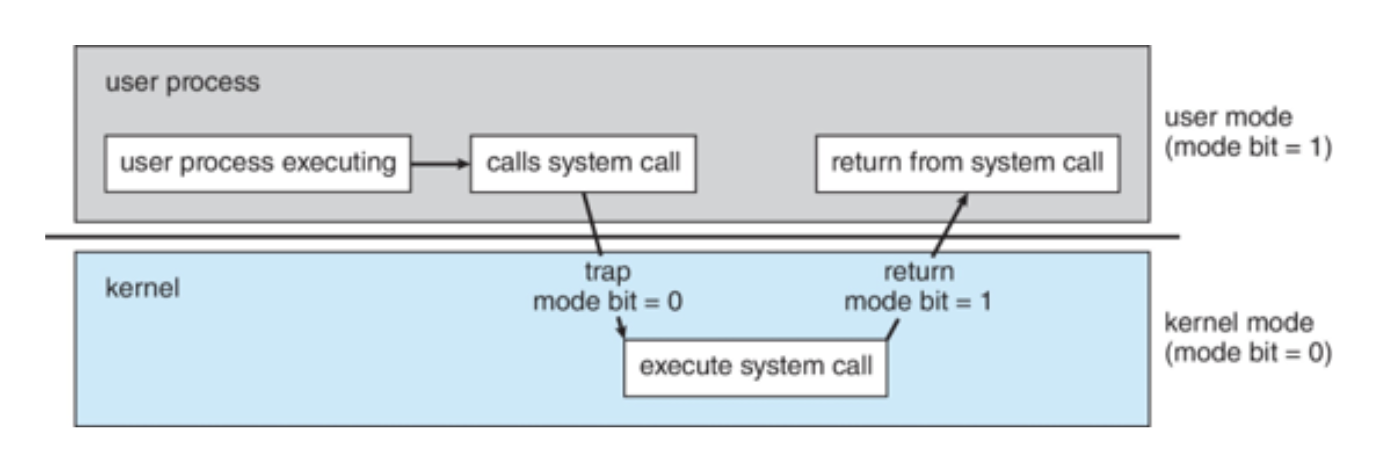
Dual-mode operation
allows OS to protect itself and other system components
User mode
Kernel mode
Mode bit
provides ability to distinguish when system is running user code or kernel code
Mode bit is user
When a user is running
Mode bit is kernel
When kernel code is executing
True
True or False
System call changes mode to kernel, return from call resets it to user, so it is guaranteed the user does not explicitly set the mode bit to kernel.
Privileged
only executable in kernel mode
Transition from user to kernel mode
Timer
prevents infinite loop or process hogging resources
Process
a program in execution
a unit of work within the system
active entity
needs resources to accomplish task
Program
a passive entity
Process termination
requires reclaim of any reusable resources
Single-threaded process
has one program counter, specifying location of next instruction to execute
Process
executes instructions sequentially (one at a time) until completion
Multi-threaded process
has one program counter per thread
Concurrency
Multiplexing the CPUs among the processes/threads
Process Managemenet Activities
Create & delete both user and system process
Suspend & resume processes
Provide mechanisms for:
process synchronization
process communication
deadlock handling
Memory management
determines what is in memory
To execute a program, all or part of the instructions must be in memory
Memory management activities
keep track of which parts of memory are currently used and by whom
decide which processes and data to move into and out of memory
allocate & deallocate memory space as needed
File
abstracts physical properties to logical storage unit
each medium is controlled by device (i.e., disk drive, tape drive).
varying properties include access speed, capacity, data-transfer rate, access method (sequential or random)
File-system management
files organized into directories
Access control
determine who can access what
OS activities (file-system management)
create & delete files/dirs
primitives to manipulate files/dirs
mapping files onto secondary storage
backup files onto stable (non-volatile) storage media
Mass-storage management
disks used to store data that does not fit in main memory or data must be kept for a long period of time
disk subsytem, algorithms
Entire speed of computer operation hinges on _____ and its ______.
OS activities (mass-storage management)
Mounting and unmounting
Free-space management
Storage allocation
Disk scheduling
Partitionning
Protection
Caching
performed at many levels in a computer
copied from slower to faster storage temporarily
faster storage checked first to determine if info is there
if yes, info used directly from the cache
if no, data copied to cache and used there
cache smaller than storage being cached
cache management important design problem
cache size and replacement policy
Characteristics of Various Types of Storage