APHUG Exam
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
119 Terms
Space
The geometric surface of the earth
Activity Space
Space used for a human activity on a daily basis
Place
An area on earth’s surface that is bounded and of some human importance
Sequent Occupancy
Succession of groups and cultural influences over a place’s history; the idea that landscapes show evidence of all historical occupants
Relative Scale/Scale of Analysis
AKA level of aggregation; level at which you group things for examination
Culture Region Boundaries
Fuzzy, unclear borders
Political Region Boundaries
Finite, well defined
Environmental Region Boundaries
Transitional and measureable
Ecotone
Environmental transition zone between two bioregions
North and South Poles
At 90 degrees Latitude
Relative Location
Location relative to known place or geogrpahic feature
Linear Absolute Distance
Distance between two places measured in linear units (ex. kilometers, miles)
Distance Decay
The farther away things are, the less likely they are to interact
Tobler’s Law
All places are interrelated, but closer ones are more related than farther ones
Friction of Distance
Length of distance that becomes a factor inhibiting interaction between points
Space-Time Compresion
Decreased time and relative distance between places (ex. technological advancements making it easier to get from place to place)
Human-Environmental Transportation
The effect humans have on their environment, and vice versa
Central Place Theory
Developed in 1930s by Walter Christaller; holds that all market areas are focused on a central settlement that is a place of exchange and service provision
Agglomeration
Clustering occurs purposefully around a central point or economic growth pole
Sinuous pattern
Wavy lines
Rectilinear township and range
Surveys land based on lines of latitude and longitude
Long-lot
Grouping and surveying land in rectangular lots along a road or waterway
Spacial Analysis
Mathematical analysis of one or more quantitative geographic patterns
Topographic maps
Show natural landscape features (elevation, road, buildings, etc.)
Isoline maps
Lines drawn on a map connecting data pointsof the same value
Flow-line Maps
Use arrows to show flow of information; thicker = more
Cartograms
Use simplified shapes to represent real places; present information based on data rather than landscape
Linear map scale
Expresses distance on a map surface
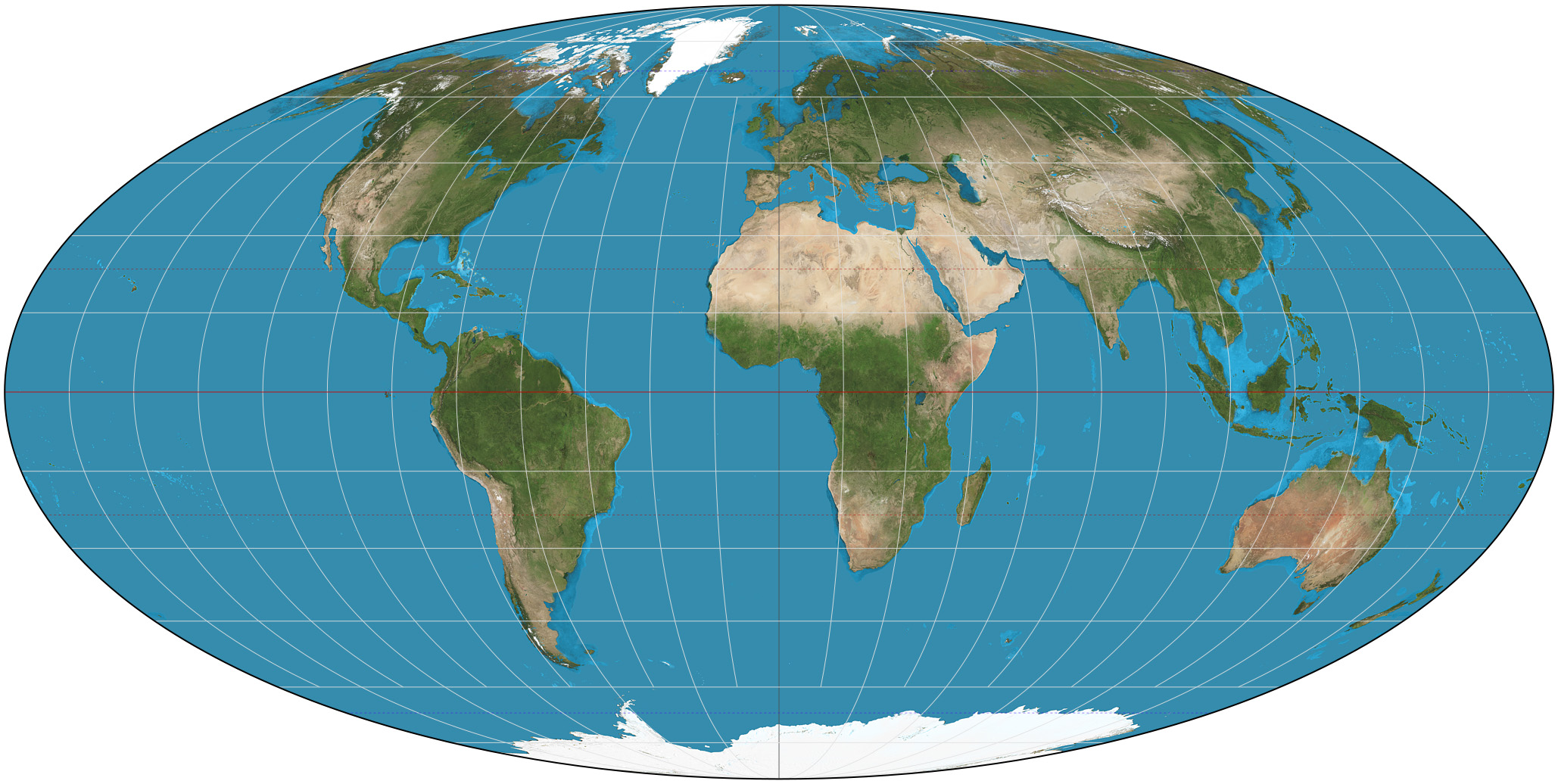
Equal-area Projections
Attempt to preserve relative distances and sizes, distort shapes
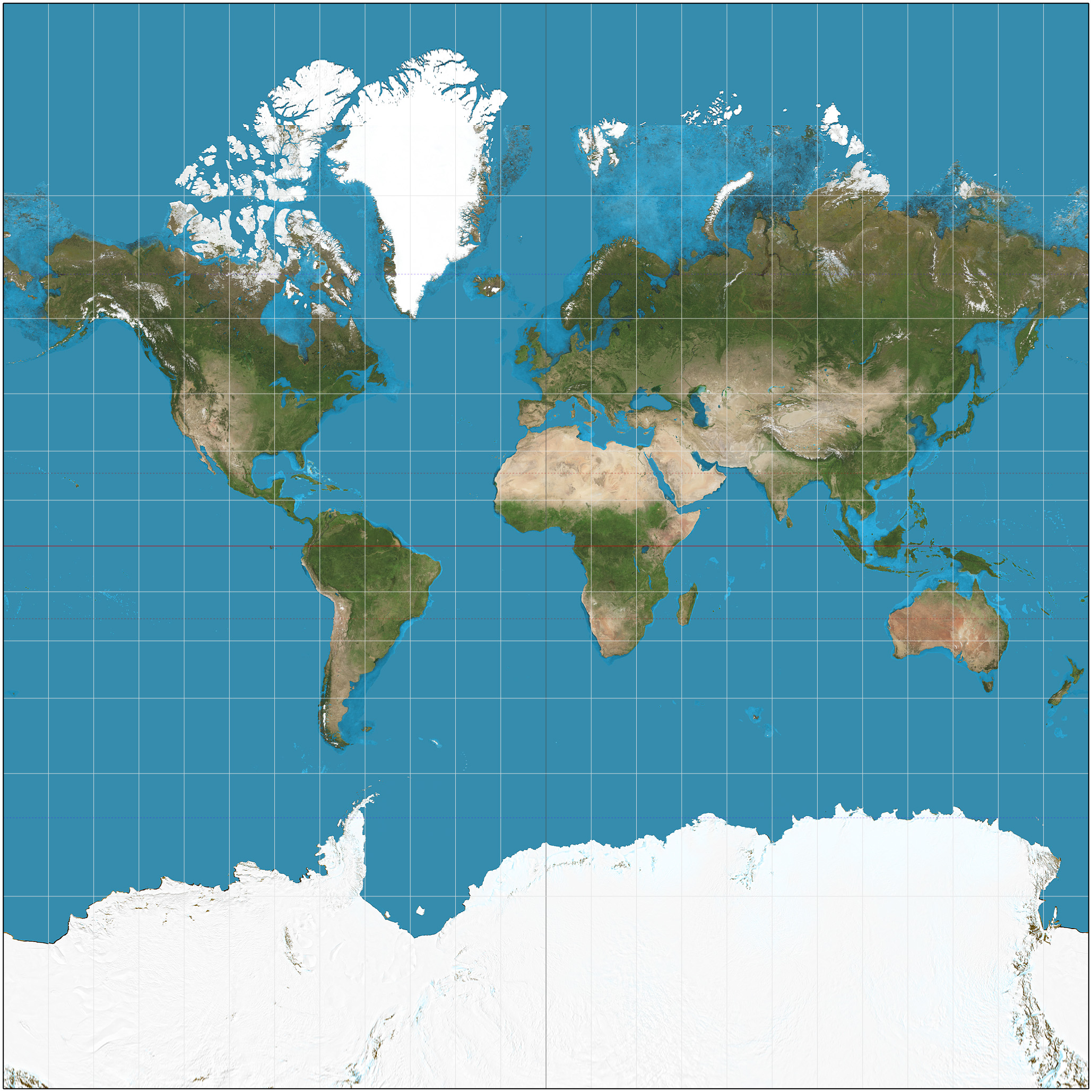
Conformal Projections
Attempt to preserve shape, distort relative distance and size (ex. Mercator Projection, preserves compass direction)
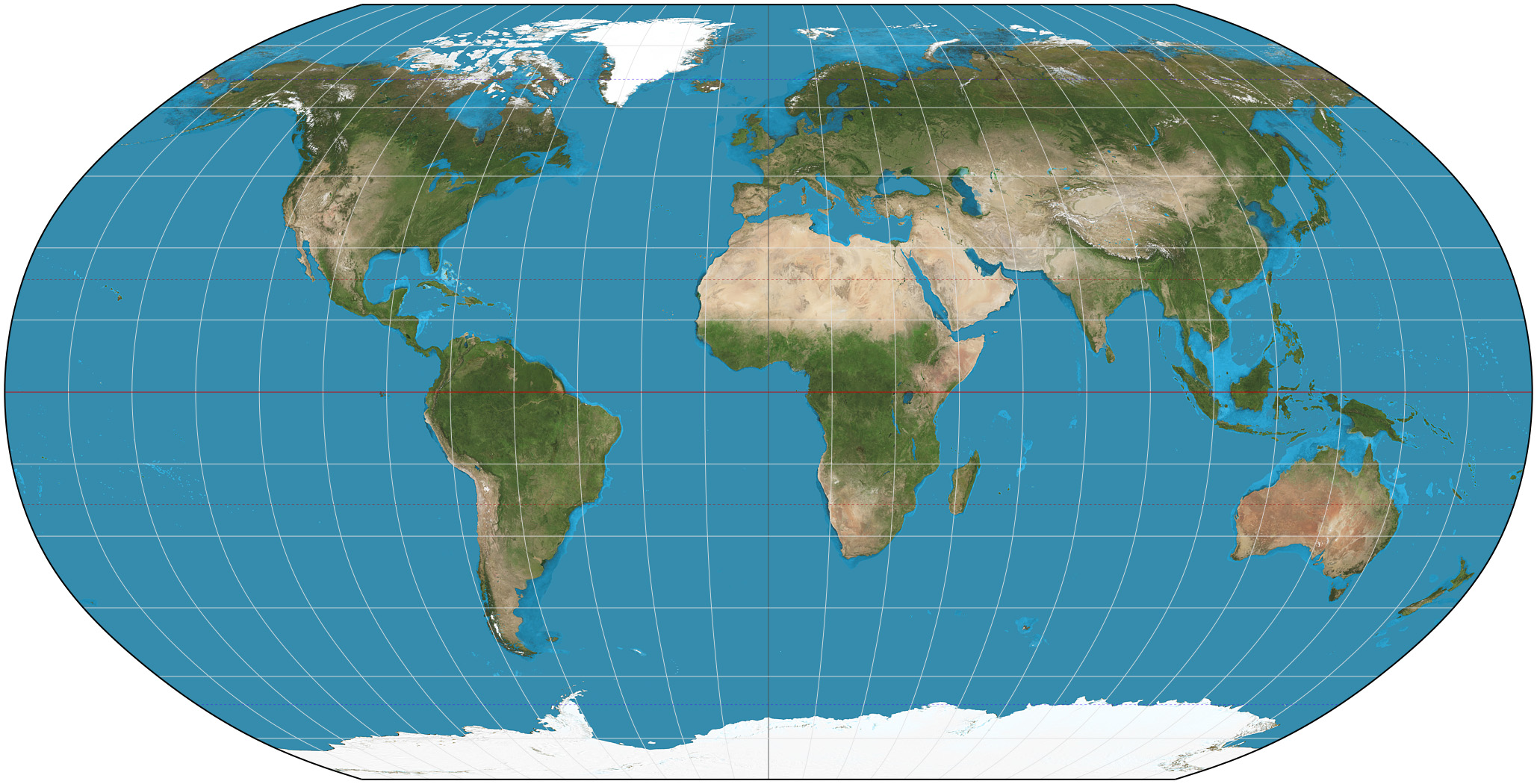
Robinson Projection
Round and simple
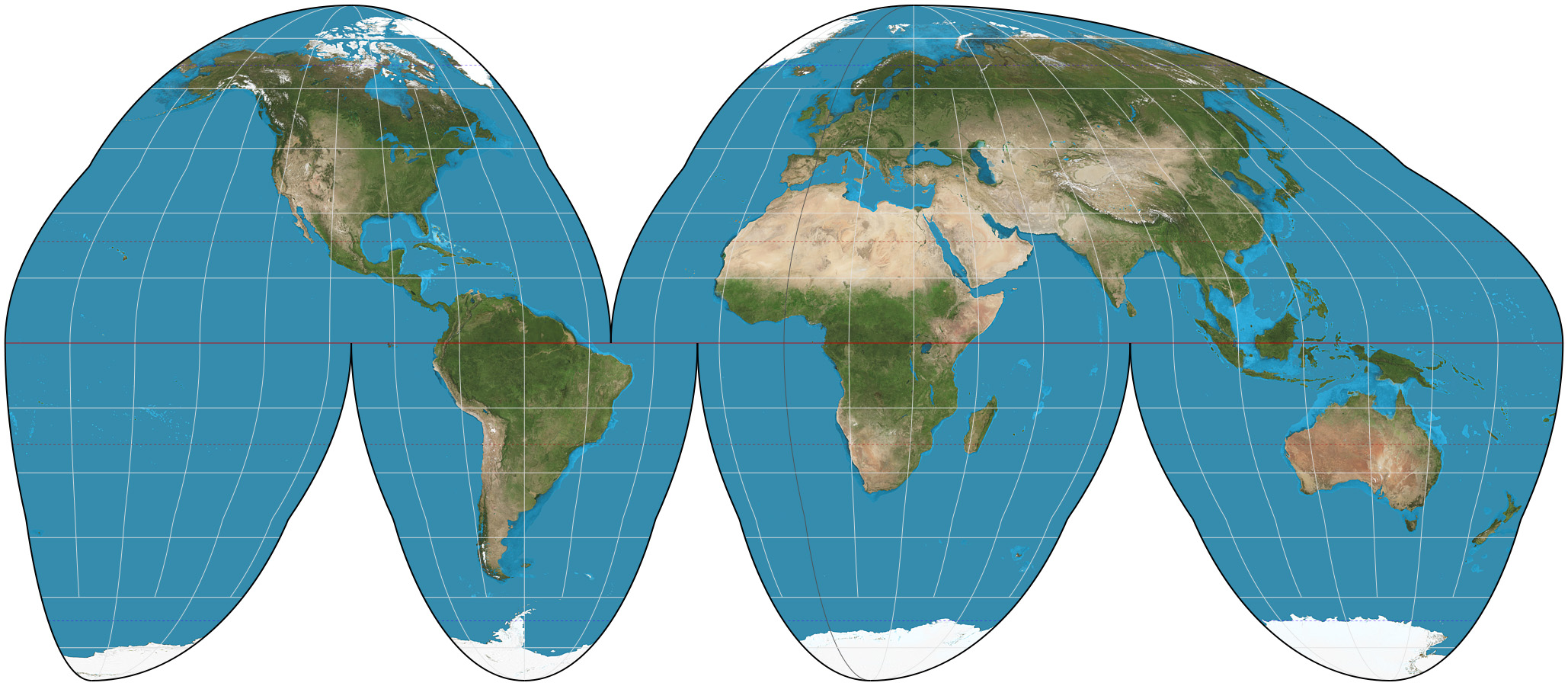
Goode Homolosine Projection
Balances area and form
Remote Sensing Satellites
Use computerized scanners to record data on earth’s surface
Population Doubling Time
70 / NIR
Level of Aggregation
Level at which you group things for examination
Human-Environment Relationships (Human Ecology)
Human interactions with nature (ex. farming, forestry, fisheries)
Conservation Agriculture
New sustainable farming system (ex. no-tillage, crop rotation, interplanting crops)
Sustainable Yield
Quantity of crops/animals that can be raised without endangering local resources
Linguistic Region
Everyone speaks the same language, but culture may vary (ex. US and Australia)
“Dixie Region” of the US
Fuzzy region, disagreed upon due to multiple imprecise factors
Topographic maps
maps that show contour lines of elevation and landscape features
Isoline maps
Lines drawn on a map connecting data points of different
Cyclic Migration
Movement that has a closed route and is repeated seasonally
Continental Cuisine
Food traditions emerging from 1800s Europe
Nouvelle Cuisine
Contemporary version of continental cuisine with healthier sauces (from France, Spain, and Italy)
Haute Cuisine
“High cooking” where a main meat course served with sauce and a side dish
Fusion Cuisine
More than one global cuisine combined into one dish
Modern/contemporary architecture
Buildings are simple and geometrical; quick and efficient to build
Traditional architecture
Reflects local lture’s history, eliefs, and values in the environment
Dialect
Pronunciation, grammar, and vocab variation in a language
Pidgin Language
A grammatically simplified version of a language that develops as a means of communication between speakers of different languages.
Creole Language
A language that is a mixture of two or more languages
Patois
Dialect that blends elements from different languages
Language family
Languages related through a common ancestral language
Language group
Languages within a branch that re an origin in the recent past
Language branch/subgroup
Collection of languages that are an origin from thousands of years ago
Anatolian Theory
Indo-European speakers ffused peacefully west with the Neolithic advance of farming
Kurgan Theory
Indo-European speakers ad west from Central Asia through conquering
Scripture
Sacred writing or books of a religion
Denomination
Subgroup within larger religious branch
Compromising religion
Religion with the ability to form or integrate other beliefs
Fundamentalism
Strict adherence to a group’s “principles” of religion
Proselytic Religion
A religion that is universalizing and seeking to convert people
Shaman
A spiritual leader or healer
Shamanism
When people commicate with spirits or the spiritual world
Caste System
Rigid inherited social class that one cannot change throughout life
Cosmology
The study of origin, properties, and evolution of the universe
Varna
4 social classes in India relating to the caste system
Theocracy
Government led by religious leaders
Secular
Not governing in a religious manner
5 Pillars of Islam
One: Five Daily Prayers
Two: Islamic Creed
Three: Alms to the poor
Four: Observance of Ramadan
Five: The Hajj (Pilgrimage to Mecca)
Ethnicity
A group of people that share common cultural traditions
Race
A group of people descended from a shared biological ancestor
Nation vs State
A nation is a large group of people united by shared culture, a state is a tically organized territory with a government
Mestizo
A person of mixed European and indigenous descent
Creole person
A person of mixed indigenous and African or European descent
Ethnocentrism
The belief in the superiority of one’s own cultural group
Xenophobia
Fear of foreigners
Cultural relativism
That cultures can only be understood their own context
Acculturation
The adoption of new culture while keeping one’s original culture
Assimilation
Immigrants fully integrate themselves into a new country’s culture
Native American Depopulation Model
Explains the decline in African American populations after European contact; by William Denevan
Confederation
A form of government where the national government gets its powers from the states
Republic
A form of government where citizens elect representatives
Expatriates
Individuals living in a foreign country
Perforated state
State surrounding another state
Prorupted state
An otherwise compact state with a large protruding extension
Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ)
Allows sole use of sea 200 miles from shore for commercial purposes
Territorial Sea
Area from shore out 12 nautical miles
Antecedent Boundaries
Boundaries that are drawn well before the area is populated
Relic Boundaries
Former boundary lines that still have cultural meaning
Subsequent Boundaries
Boundaries that result from a cultural divide or change
Boundary Defition
When borders are claimed, negotiated, or captured
Delimination
When border lines are drawn on a map
Demarcation
When markers are placed on the ground to show where borders lie
Geometric border
A border surveyed along lines of latitude and longitude
Definition Border Disputes
Disputes about where the border is
Locational border disputes
Disputes that arise when the border moves
Operational Border Disputes
Disputes that arise when passage across the border becomes a problem
Allocational Border Disputes
Disputes about shared resources are used